AP State Syllabus 7th Class Social Important Questions 2nd Lesson Rain and Rivers
Question 1.
Write two slogans about the topic “Protection of forests”.
Answer:
- Take care of the trees, they will take care of you.
- If you cut a tree, you kill a life.
Question 2.
Name the two rivers which joined into the Bay of Bengal?
Answer:
The Krishna, The Godavari, The Cauvery, The Penna, The Mahanadi, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
The Southwest Monsoon brings very little rain to Rayalaseema districts. Why?
Answer:
Southwest monsoon brings very little rain as most of the moisture in the clouds fall down in rain in the Western Ghats and only dry clouds and winds reach Rayalaseema.
Question 4.
“Many times river and well water is polluted. Unless we take preventive steps, most of the weli or river water might soon become unsafe for drinking or even bathing.” Write any two causes of pollution of river and well water? Suggest two measures to control water pollution.
Answer:
Causes of pollution of river and well water.
- Mining of minerals.
- Chemicals released by factories.
- Overuse of chemical pesticides and fertilizers.
Preventive measures.
- Controlling of chemical waste from factories being let out into water bodies.
- Reduce the use of chemical fertilizers
- Waste material from mining should be disposed off properly etc.
Question 5.
A graph showing the seasonal rainfall across Andhra Pradesh in 2017 is given below. Study the graph and answer the following questions.
Seasonal Rainfall across Andhra Pradesh in 2017 (in millimetres)
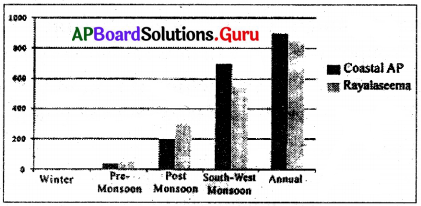
i) In the year 2017, the maximum rainfall in Andhra Pradesh was received from …………..
Answer:
South-West monsoon.
ii) Which region of Andhra Pradesh received more annual rainfall?
Answer:
Coastal Andhra Pradesh.
![]()
Question 6.
List four ways water gets stored as it passes through the water cycle.
Answer:
Water gets stored in rivers, canals, tanks, well, ocean, aquifers, underground water, clouds etc.
Question 7.
Study the map given below and answer the following questions.
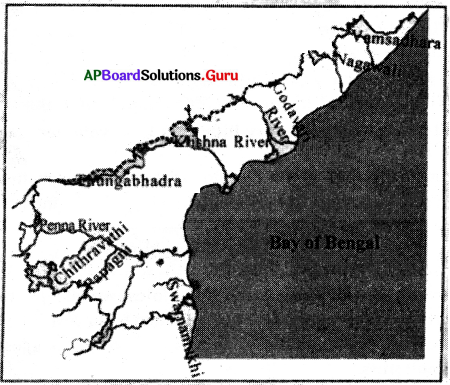
a) The Chitravathi river is a tributary of which major river systems of Andhra Pradesh?
Answer:
Chitravathi River is a tributary of the river Penna river system of Andhra Pradesh.
b) Name two major river systems of Andhra Pradesh.
Answer:
Krishna, Godavari are the two major rivers of Andhra Pradesh.
Question 8.
Explain the process of evaporation. How does evaporation help in the formation of rain?
Answer:
- Water bodies are heated up by the Sun’s rays.
- Then the water becomes vapour.
- This water vapour rises with hot air and reaches high up in the sky and it gets cooled.
- With the cooling, water vapour is transformed into tiny water droplets. These droplets gather around minute dust or smoke particles in the air and gradually increase in size.
- These small water droplets gather to form the clouds.
- The clouds continue to rise upwards, it gets cooler and more droplets are formed.
- As they get heavier, it gets more and more difficult for them to remain in the air and they began to fall like raindrops.
![]()
Question 9.
Read the table and answer the following questions.
| Sl. No. | Name of the River | Origin | Name of Tributary | Which sea does it meet |
| 1 | Godavari | Nashik | Manjeera | Bay of Bengal |
| 2 | Krishna | Mahabaleswar | Tungabadra | Bay of Bengal |
| 3 | Kaveri | Brahmagiri | Hemavathi | Bay of Bengal |
| 4 | Penna | Nandi Durga | Papagni | Bay of Bengal |
| 5 | Ganges | Gangothri | Yamuna | Bay of Bengal |
a) The Tungabadra river is a tributary of which river system?
Answer:
Krishna River system.
b) Among the above river systems, which one belongs to North India?
Answer:
The Ganges.
c) Which river originates from the Himalayas?
Answer:
The Ganges.
d) Which river is called the Southern Ganga?
Answer:
The Godavari river is called as Southern Ganga.
Question 10.
Observe the given below table and answer the following questions.
| S.No, | River | Birth Place | Which sea does it meet |
| 1. | Godavari | Nasik | Biiy of Bengal |
| 2. | Krishna | Mahakaleswar | Bay of Bengal |
| 3. | Penna | Nandi Durga Hills | Bay of Bengal |
| 4. | Narmada | Amantak | Arabian Sea |
| 5. | Tapti | Multa | Arabian Sea |
Questions:
1) What is the largest river in South India?
Answer:
The Godavari is the largest river in South India.
2) Which river flows in a Westward direction?
Answer:
Narmada & Tapti rivers are flowing in a Westward direction.
3) Which rivers meet the Bay of Bengal?
Answer:
Godavari, Krishna, Penna are the rivers that meet the Bay of Bengal.
4) Which rivers are not flown in Andhra Pradesh?
Answer:
Narmada & Tapti rivers are not flowing through Andhra Pradesh.
![]()
Question 11.
In which season do you think there would be more evaporation in summer or winter?
Answer:
I think in summer there would be more evaporation. There are several water bodies on the earth’s surface – oceans, rivers, lakes, etc. There is constant evaporation of water from these water bodies. In fact, wherever there is moisture, like on a wet cloth, there is evaporation. In summer there would be more evaporation.
Question 12.
When will the evaporation be more, during the day or night?
Answer:
The evaporation will be more during the day.
Question 13.
From which direction does the wind blow during the rainy season?
Answer:
The winds come all the way from the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal and they transport the rainy clouds. They are called ‘Monsoon winds’. They are also called ‘South-West Monsoon winds’ as they blow from that direction. These winds blow only in the summer.
There are two arms of the monsoon winds: one blows from the Arabian Sea and the other from the Bay of Bengal, The direction of the winds reverse in the months after October as the winds begin to blow from the Bay of Bengal South-Westwards. This causes heavy rains in October – December months in coastal Andhra Pradesh and moderate rains in Rayalaseema and Telangana districts.
Question 14.
Define Precipitation and Humidity.
Answer:
Precipitation: Different forms of condensation of water vapour is known as precipitation. This may take place in the form of dew, fog, rain, snow, and hail, etc.
Humidity: The amount of invisible water vapour present in the atmosphere is known as humidity. When temperature and humidity are high, we feel uncomfortable. We perspire and the sweat does not evaporate quickly. We feel sticky and such weather is called sultry.
![]()
Question 15.
How are floods beneficial to agricultural fields?
Answer:
Flood water carries nutrients and sediments, which are deposited on flood plains, enriching the soil. Rice, paddies are flooded deliberately to take advantage of this natural fertilization process. Floods recharge water sources also.
Question 16.
In what way have the floods affected the villages, agricultural fields and trees?
Answer:
Floods have become a major problem in our country in recent years. Some part of the country or the other is flooded every year during the rainy season.
- This causes severe damage to people, crops and livestock.
- Floods affect the poorest most. It is therefore the responsibility of the government to build safe housing for all people.
- Usually immediately after the floodwaters recede, all sources of water are polluted and become unsafe for drinking. But people especially the poor are forced to use the polluted water and face the risk of several diseases like cholera, dysentery, jaundice, etc.
- Only those with resources are able to arrange for safe bottled water to drink. Since roads are damaged and it rains heavily, bringing in relief to the worst affected areas is not easy. Here people are forced to rely on their own resources to save themselves.
- While the immediate damage of the floods is also heavy – like loss of lives, Crops, houses, etc. But more importantly, they also cause long term damages.
- For example, the life savings of most of the poor stored in the houses in the form of food, tools, cattle, small shops, vehicles, boats, nets, etc., are destroyed.
- To go back to their work they need to buy all these again. Many families also lose their working members.
- Daily wage workers face loss*of work for several weeks till normally returns and therefore loss of livelihood. Farmers too not only face loss of crops but also permanent damage to their lands.
Question 17.
How can people meet the challenge of disasters like cyclones and floods? (or)
Explain how people can be prepared to meet the challenges of disasters like cyclones and floods. (or)
Read the following paragraph and answer the question.
The immediate damage of the cyclones is also heavy like loss of lives, crops, houses etc, more importantly, they also cause long term damages. For example, the life savings of most of the poor stored in the houses in the form of food, tools, cattle, small shops, vehicles, boats, nets, etc., are destroyed, Many families may lose their working members. Farmers too not only face loss of crops but also permanent damage to their lands.
Q. Interpretation of the devices, suggestions that you can give during cyclone times to the Government.
Answer:
This can be done through long term planning by governments and close cooperation between the people and government agencies. Today, with the installation of early warning systems by the government, it is possible to predict the possibilities of natural disasters like cyclones and floods. Governments thus put in place these systems and inform people about the possibility of disasters.
Governments are also responsible for providing for the long-term security of all people by building strong roads which are not easily destroyed, safe pucca houses for those living in vulnerable areas like sea coast or along the rivers or in low lands. Food, water and medical emergency teams should be kept ready whenever there is a forecast of cyclones.
![]()
Question 18.
Can forest and vegetation help in reducing droughts?
Answer:
Yes. The vegetation and forest can help the rainwater to percolate into the soil. By using this percolated water, they can give us some food during droughts. These also reduce soil erosion and its fertility. This helps the cattle during droughts.
Question 19.
What do you think is the direction of slope in Andhra Pradesh – from North to South or East to West or West to East?
Answer:
West to East.
Question 20.
Have you ever observed dew? Where is it formed?
Answer:
Yes, I have observed dew during mornings and evenings on car roofs, grass leaves, and railings etc.
Question 21.
In which part of the day will you find fog?
Answer:
In morning.
Question 22.
In which season do you have more foggy days?
Answer:
In winter.
Question 23.
Have you ever seen snowfall? How is it different from rainfall?
Answer:
Yes. Rainfall is a liquid state of matter whereas snowfall is a fall of snow.
Question 24.
Have you ever experienced a hail storm?
Answer:
Yes. I have experienced the hail storm.
![]()
Question 25.
Study the following figure and answer the questions.
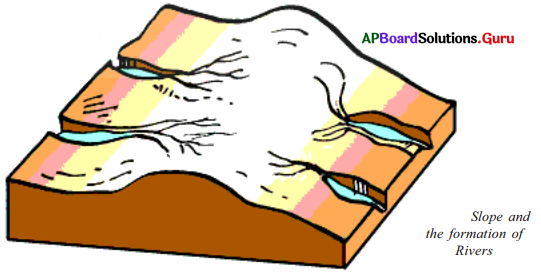
a. Mark the flow of the river with arrows.
Answer:
(Marked on the figure.)
b. Mark the slope of the land with – arrows.
Answer:
(Marked on the figure.)
c. Does the river flow in the same direction as that of the slope of the land?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 26.
Observe the following figures and answer the following questions.
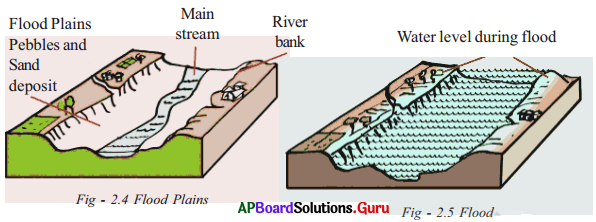
a. Has the river water covered the entire flood – plain or is it confined to the tiny stream that was flowing in the dry season?
Answer:
The river water is confined to the tiny stream in the dry season.
b. Is the water confined to the flood plain or has it overflown the banks of the river?
Answer:
The water is confined to the flood plain only.
c. In what way have the floods affected the villages, agricultural fields and trees?
Answer:
Refer Q.No. 6 under the section ‘Conceptual Understanding’.
d. How are floods beneficial to agricultural fields?
Answer:
Floods are beneficial to agricultural fields if they are harvested in air wells, dew ponds, canals, tanks and check dams, etc.
![]()
Question 27.
Observe the following diagrams.
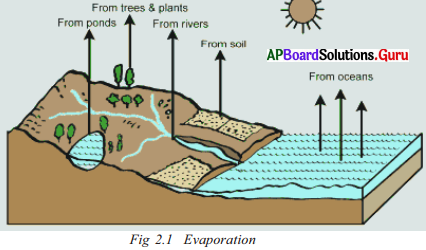
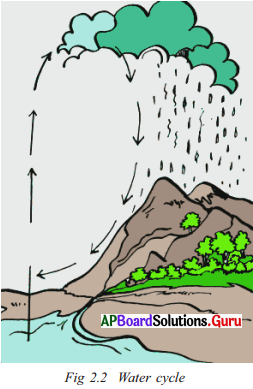
Answer the following questions.
Define the water cycle.
Answer:
The cycle of water evaporating from the seas, becoming clouds in the sky, coming down as rain and flowing down the slope on the land in the form of rivers and finally joining the sea again is called the water cycle.
b. Name some water bodies.
Answer:
There are several water bodies on the earth’s surface – oceans, rivers, lakes, etc.
c. Where do you think maximum evaporation would take place-from plants, rivers, oceans or soils?
Answer:
From oceans.
d. When do you think there is more evaporation during the day or night?
Answer:
The more evaporation is during the day.
e. Can you say what is the first stage of the water cycle?
Answer:
The cycle of water evaporating from the seas becoming clouds in the sky.
f. Look at the diagram and make a list of all places from which evaporation takes place.
Answer:
Ponds, trees, rivers, soil and oceans.
![]()
Question 28.
Can forests and vegetation help in reducing droughts?
Answer:
- Vegetation cover on the land (trees, plants, grass, etc.) obstructs the runoff of rainwater and slows down the speed of its flow. This slowing down helps the rainwater to percolate into the soil.
- Floods are often caused by a sudden increase in the volume of water reaching a river. Vegetation allows the water to flow slowly into the river, thus preventing sudden flooding.
- It also helps to increase the amount of water, which goes into the soil.
- Vegetation also helps to prevent floods in another way.
- It reduces the erosion of soil by rainwater.
- If the surface of the land is covered with vegetation, soil erosion is greatly reduced.
- In recent years there has been a large scale felling of trees and hence the forest cover in the Himalayas has been reduced considerably.
- As a result, every time there is heavy rainfall, the rainwater rapidly flows down the slopes of the mountains and fills up the flood plain of the river. This results in frequent floods, which cause heavy damage to life and property along the river.
Question 29.
Explain about the flood – plain of the river.
Answer:
- A river does not contain the same amount of water all year round. While the river is full during the rainy season, it usually shrinks during the dry season. We can see that the river trough is very wide and it has high banks.
- This valley is filled with sand and gravel. The river flows as a small stream amidst them.
- We will notice that there are no trees here.
- This is because every year when it rains heavily, this valley is filled with water allowing no permanent trees or plants to grow here.
- This treeless bed is called the flood – plain of the river. All major rivers have their flood plains.
Question 30.
What were the destructive cyclones mentioned in the lesson? Explain them.
Answer:
Our state has a long coastline and is frequently faced with very destructive cyclones. When heavy winds blow from the sea, heavy rains lash the lands, and high waves make the sea very unsafe. These usually occur between June and December. The worst cyclone hit the state in November 1977, perhaps, the worst cyclonic storm to hit the Indian shores. Six-metre high tidal waves swept across villages in coastal Andhra Pradesh, killing 9941 people. At least 100 villages were washed away by the cyclonic storms and the ensuing floods. Seen from the air, it seemed like a sheet of water drawn over the affected areas floating in the swirling waters. About 100 people who left their homes to seek shelter in a building in Bapatla town died when the building collapsed. Most lives were lost in Diviseema, Krishna District. Recently in 2014 “Hud Hud” cyclone created huge destruction in Vishakapatnam.
Question 31.
Why do you think it is necessary for the clouds to rise in -order to cause rain?
Answer:
As the clouds continue to rise upwards, it gets cooler and more droplets are formed. The droplets get together to form bigger drops. As they get heavier it gets more and more difficult for them to remain in the air and so they begin to fall as raindrops. So it is necessary for the clouds to rise in order to cause rain.
![]()
Question 32.
Locate the following on the map of Andhra Pradesh.
- Godavari
- Krishna River
- Tungabhadra
- Penna River
- Bay of Bengal
- Vamsadhara
- Nagavali
- Chitravathi
- Papagni
Answer:
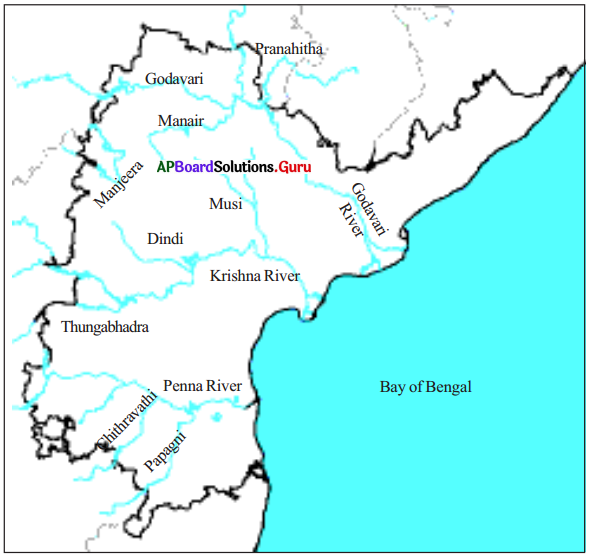
Question 33.
Look at the map given below showing rainfall received in different parts of Andhra Pradesh.
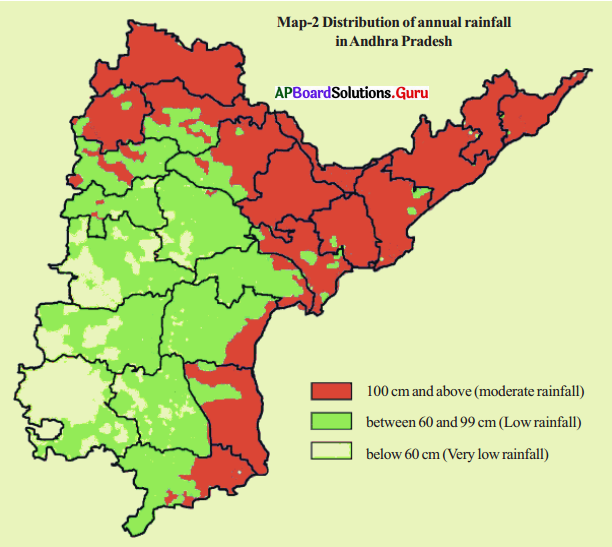
i) Does your district receive high rainfall or moderate rainfall or low rainfall?
Answer:
Our district is It is and receives rainfall. (Self exercise)
ii) Which town has the least/highest rainfall – Ongole, Anantapur, Machilipatnam?
Answer:
Highest – Machilipatnam, Least – Anantapur
iii) Make some more questions and ask each other.
a. Does Chittoor district receive high rainfall?
Answer:
No, it receives low rainfall (between 60 cms to 99 cms. )
b. Name two districts that receive moderate rainfall.
Answer:
Srikakulam, Vizianagaram and Visakhapatnam receive moderate rainfall.
c. Which district receives very low rainfall?
Answer:
Ananthapur district. It receives very low rainfall, (below 60 cm)
d. Name two districts that receive low rainfall.
Answer:
Guntur and Prakasam.
![]()
Question 34.
a) Look at the physical map of India in your Atlas and identify the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats. Fill in the blanks in the following sentences.
i) the Western Ghats are spread across the following states …………………
ii) the Eastern Ghats are spread across the following states …………………
Answer:
i. Karnataka, Kerala, Goa, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra
ii. Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu
b) In which region do Western and Eastern Ghats intersect?
Answer:
The western and eastern ghats intersect in the region of Nilgiris (Tamilnadu).
c) First, create rough outlines of India in a notebook; then draw the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats; After that, roughly mark the areas that are in Rayalaseema and Kostha; Finally, label them with months in which it rains.
Answer:
Student’s activity.
Question 35.
Make a diagram to explain how vapour is transformed into clouds. Label your diagram with these terms – earth, sky, rising vapour, cloud, dust particles, water droplets, clouds…
Answer:
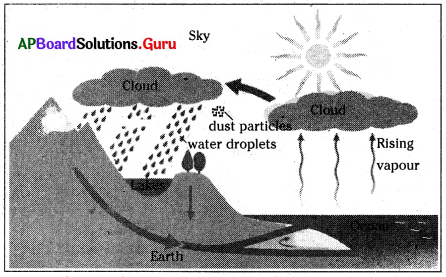
Student’s activity.
Question 36.
Observe the following map and answer the questions.
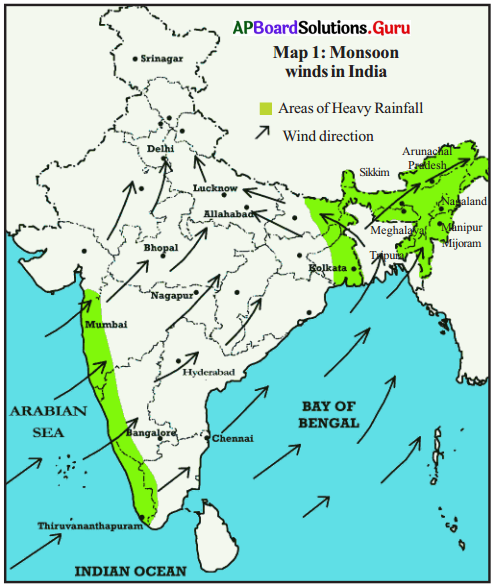
1. Towards which parts of the country will the winds take the clouds on the Bay of Bengal?
Answer:
North-East parts.
2. Towards which parts of the country will the winds take the clouds on the Arabian Sea?
Answer:
South/West/East/North.
3. From which direction will the winds blow to bring monsoon rains to West Bengal, Lucknow and Delhi?
Answer:
North-East.
4. From which direction will the winds blow to bring monsoon rains to Mumbai, Hyderabad, Bangalore?
Answer:
South-West.
5. From which direction does the wind blow during the rainy season?
Answer:
The wind blows from South-West to North-East during the rainy season.
![]()
Question 37.
Look at the map and answer the questions.
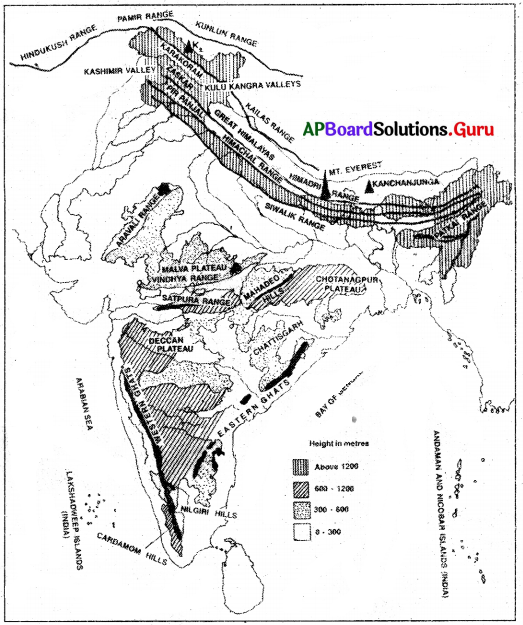
a. Look at the given physical map of India and identify Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats.
Answer:
Self Exercise.
b. In which direction of Andhra Pradesh are the Western Ghats?
Answer:
Westside.
c. Now create rough outlines of India in a notebook – then draw imaginary hills, along ‘The Western Ghats’, Eastern Ghats. Roughly mark the areas that are in Rayalaseema and Telangana. And label them with months in which it rains.
Answer:
Self exercise.
Question 36.
Look at the map and prepare a list of rivers that rise from/flow through.
Answer:
| Western Ghats | Rayalaseema | Eastern Ghats |
| Krishna | Tungabhadra | Krishna |
| Godavari | Penna | Godavari |
| Penna | Penna |
Question 37.
Can you explain the causes of devastating floods? In what way is it a natural occurrence and in what way is it man-made?
Answer:
Climate change has contributed to a rise in extreme weather events. This is a natural occurrence. Deforestation is also the cause of devastating floods. Thus this is the man-made way.
![]()
Question 38.
In which months of the year does it rain most in your place? List three rainiest months.
Answer:
June, July and Aug.
Question 39.
Name three driest months.
Answer:
October, November and December.
Question 40.
Do you have ‘normal’ rainfall every year in your place or does it vary every year?
Answer:
It varies every year.
Question 41.
Have you ever experienced drought years in which it rained very little?
Answer:
Yes, I have experienced drought years in which it rained very little.
Question 42.
Have you ever experienced flood years in which it rained too much?
Answer:
Yes, I have experienced flood years in which it rained too much.
![]()
Question 43.
Define water cycle and evaporation.
Answer:
a) Water cycle: The process of water evaporating from the seas, forming clouds in the sky, coming down as rain and flowing down the slopes on land in the form of rivers and finally joining the sea is called the water cycle.
b) Evaporation: The change of water into vapour is known as evaporation. The process in which water vapour changes into water is called condensation. Clouds are tiny droplets of water hanging in the air above.