Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Botany Study Material 11th Lesson Cell Cycle and Cell Division Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Botany Study Material 11th Lesson Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Between a Prokaryote and a eukaryote, which cell has a shorter cell division time?
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell.
Question 2.
Among Prokaryotes and eukaryotes, which one has a shorter duration of a cell cycle?
Answer:
Prokaryotic cell.
Question 3.
Which of the phases of the cell cycle is of the longest duration?
Answer:
Interphase.
Question 4.
Which tissue of animals and plants exhibits Meiosis?
Answer:
Meiosis occurs in diploid cells.
Question 5.
Given that the average duplication time of E.coli is 20 minutes. How much time will two E.coli cells take to become 32 cells?
Answer:
80 minutes.
Question 6.
Which part of the human body should one use to demonstrate stages in Mitosis?
Answer:
Cells lining the Gut and skin cells.
![]()
Question 7.
What attributes does a chromatid require to be classified as a chromosome?
Answer:
Each chromosome at Metaphase split and the two daughter chromatids now referred to as chromosoms.
Question 8.
Which of the four chromatids of a bivalent at prophase-I of Meiosis can involve in cross-over?
Answer:
Crossing over occurs between non-sisters chromatids of the homologous chromosomes.
Question 9.
If a tissue has at a given time 1024 cells. How many cycles of Mitosis had the original parental single cell undergone?
Answer:
10 Mitotic divisions.
Question 10.
An anther has 1200 pollen grains. How many pollen mother cells must have been there to produce them?
Answer:
300.
Question 11.
At what stage of cell cycle does DNA synthesis occur?
Answer:
‘S’ phase (synthesis phase).
Question 12.
It is said that one cycle of cell division in human cells, (Eukaryotic cells) take 24 hours. Which phase of the cycle, do you think occupies the maximum part of cell cycle?
Answer:
Interphase.
Question 13.
It is observed that heart cells do not exhibit cell-divisjon. Such cells do not divide further and exit phase to enter an inactive stage called of cell cycle. Fill in the blanks.
![]()
Question 14.
Identify the sub stages of Prophase n I in Meiosis in which synapse and desynapse are formed?
Answer:
Synthesis occurs in ‘zygotene’ a sub phase of Prophase I of Meiosis -I
Desynapse occurs in ‘diakinesis’ a sub phase of prophase I of Meiosis -I
G1 Phase. Quiescent stage (G0).
Question 15.
Name the stage of Meiosis in which actual reduction in chromosome number occurs.
Answer:
Anaphase – II
Question 16.
Mitochondria and plastids have their own DNA (genetic material). What is their fate during nuclear division like Mitosis?
Answer:
Mitochondria and plastids get distributed between the two daughter cells.
Question 17.
A cell has 32 chromosomes. It undergoes mitotic division. What will be the chromosome number during Metaphase? What would be the DNA content (c) during anaphase?
Answer:
32 chromosomes. The DNA content during anaphase gets doubled.
Question 18.
The following events occur during the various phases of the cell cycle. Fill the blanks with suitable answer against each.
a) Disintegration of Nuclear Membrane
b) Appearance of Nucleolus
c) Division of centromere
d) Replication of DNA
Answer:
a) Prophase
b) Telophase
c) Anaphase
d) S-Phase
Question 19.
While examining the Mitotic stage in a tissue, one finds some cells with 16 chromosomes and some with 32 chromosomes. What possible reasons could you give to this difference in chromosome number ? Do you think cells with 16 chromosomes could have arisen from cells with 32 chromosomes or vice versa?
Answer:
In cells with 16 chromosomes Mitosis is over, in cells with 32 chromosomes, Mitosis is not started. No. Cells with 16 chromosomes have not arisen from the cells with 32 chromosomes.
Question 20.
Two key events take place during S phase in animal cells. DNA replication and duplication of Centriole. In which parts of the cell do these events occur?
Answer:
Nucleus, Cytoplasam.
![]()
Question 21.
Name a cell that is found arrested in diplotene stage for months and years. Comment in two or three sentences how it complete cell cycle?
Answer:
Oocytes of some vertebrates.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
In which phase of meiosis are the following formed? Choose the answers from hint points given below,
a) synaptonermal complex
b) Recombination nodules
c) Appearance / activation of a Enzyme recombinase
d) Termination of chliasmata
e) Interkinesis
f) Formation of dyad of cells.
Hints :
1) Zygotene
2) Pachytene
3) Pachytene
4) Diakinesis
5) After Telophase I / before Meiosis II
6) /Telophase I / After Meiosis I
Answer:
a) Synaptonemal complex = Zygotene
b) Recombination nucleus = Pachytene
c) Appearance / activation of = Pachytene Enzyme recombinase
d) Termination of chaismata = Diakinesis
e) Interkinesis = The stage between the two meiotic divisions (After telophase I / before meiosis II)
f) Formation of dyad of cells = Telophase I / After meiosis I.
Question 2.
Mitosis results in producing two cells which are similar to each other. What would be the consequence if each of the following irregularities occurs during Mitosis?
a) Nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate
b) Duplication of DNA does not occurs.
c) Centromeres do not divide
d) Cytokinesis does not occur.
Answer:
a) Nuclear membrane fails to disintegrate : The nuclear divisions takes place.
b) Duplication of DNA does not occurs : Of two daughter cells, one cannot get DNA.
c) Centromers do not divide : Chromosomes are not distributed to daughter cells.
d) Cytokinesis does not occur : Multinucleate condition arises leading to the formation of syneytium (liquid endoplasm of coconut).
Question 2.
Describe the events of prophase – I
Answer:
Meiosis I is longer phase and consists of 5 sub phases namely Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene and Diakinesis.
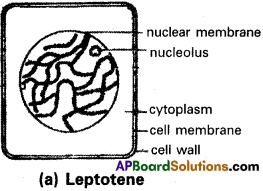
a) Leptotene :
The nucleus increases in size by absorbing water from the cytoplasm. The chromatin material organises into a constant number of chromosomes. The chromosomes are long, slender and show bead like structures called chromomeres.
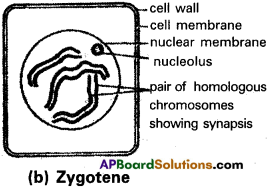
b) Zygotene :
The chromosomes become shorter and thicker. They approach each other and form pairs. This homologous pair is called bivalent and the process of pairing is called synapsis. It is accompanied by the formation of Synaptonemal complex. The synapsis occurs at proterminal point or procentric or random means.
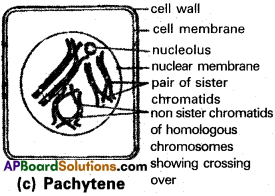
c) Pachytene :
Bivalent chromosomes now clearly appear as tetrads. This stage is characterised by the presence of recombination modules, the sites of which crossing over occurs between the non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes. Crossing – over is the exchange of genetic material between the two homologous chromosomes. It is also an enzyme mediated process by ‘recombinase’ crossing over leads to recombination of genetic material on the two chromosomes.
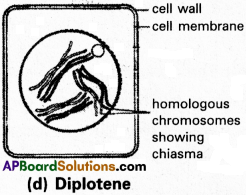
d) Diplotene :
The homologous chromosomes of a bivalent begin to separate from each other except at the sites of cross overs to dissolution of synaptonemal complex. The ‘X’ shaped structures are called chaismata.
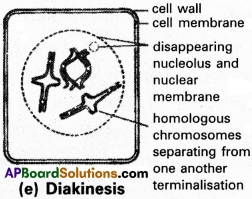
e) Diakinesis :
It is marked by terminalisation of chaismata. In this phase, the chromosomes are fully condensed and the meiotic spindle is assembled to prepare the homologous chromosomes for separation. By the end of this phase, the nuclear membrane breaks down the nucleolus disappears.
The chromatids undergo condensation, contraction and thickening.
Question 4.
Mention the significance of Meiosis.
Answer:
- It maintains the same chromosome number in the sexually reproducing organisms.
- It restricts the multiplication of chromosome number and maintains the stability of the species.
- Maternal and paternal genes get exchanged during crossing over. It results in variations among the offspring.
- All the four chromatids of homologous pair of chromosomes seggregate and go over separately to four different daughter cells this leads to variation in the daughter cells genetically.
- Variations play an important role in the process of evolution.
![]()
Question 5.
Which division is necessary to maintain constant chromosome number in all body cell of multicellular organism and why?
Answer:
Mitosis is necessary to maintain constant number of chromosomes in all body cells in multicellular organisms because mitosis results in the production of diploid daughter cells with genetic employment usually identical to that of the parent cell. The growth of multicellular organisms is due to mitosis. Cell growth results in distributing the ratio between the nucleus and cytoplasam.
It therefore essential for the cell division to restore the nucleo-cytoplasamic ratio. A very significant contribution of mitosis is cell repair. Mitotic divisions in the meristametic tissues, the apical and the lateral Meristems, results in a continuous growth of plants throughout their life.
Question 6.
Though redundantly described as a resting phase. Interphase does not really involve rest. Comment.
Answer:
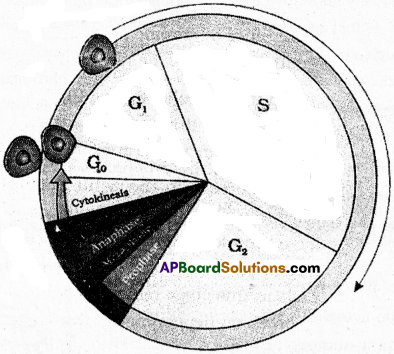
The interphase also called phase of non-apparent division through called the resting phase is the time during which the cell is preparing for division by involving both cell growth and DNA replication. The interphase is divided into three further phases. They are :
i) ‘G1‘ phase :
It corresponds to the internal between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication. In this the cell is metobolically active and continuously grows.
ii) ‘S’ phase :
Synthesis phase marks the period during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place. The amount of DNA per cell doubles. However, there is no increase in the number of chromosomes.
iii) ‘G2‘ phase :
Proteins are synthesized.
Question 7.
Comment on the statement – Meiosis enables the conservation of specific chromosome number of each species even though the process per se. results in reduction of chromosome number.
Answer:
Meiosis is the mechanism by which conservation of specific chromosome number in each species is achieved across generations in sexually reproducing organisms, even though the process per sec periodically results in the reproduction of chromosome number by half. It also increases the genetic variability in the population of organisms from one generation to the next. Variations are very important for the process of evolution.
Question 8.
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Answer:
In animal cells, cytokineis is achieved by the appearence of a furrow in the plasma membrane. The furrow gradually deepens and ultimately joins in the centre dividing the cell cytoplasam into two plant cells, are enclosed by a relatively inextensible cell wall. In plant cells, wall fromation starts in the centre of the cell and grows outward to meet the exiting lateral walls. The formation of the new cell wall begins with the formation of cell plate that represents the middle lamella between the walls of two adjacent cells.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Discuss on the statement – Telophase is reverse of prophase.
Answer:
Telophase is the final stage of Mitosis in which the chromosomes that have reached their respective poles decondenses and loose their individuality. Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements. Nuclear membrane assimilates around the chromosome clusters. Nucleolus, Golgi complex and endoplasmic reticulum reform where as in prophase, chromosomal material condenses and organises to form compact chromosomes. Nuclear membrane, Nucleolus, Golgi complexes. Endoplasmic reticulum disappears. Thats why Telophase is the reverse phase to prophase.
Question 2.
What are the various stages of meiotic prophase – I? Enumerate the chromosomal events during each stage?
Answer:
Meiosis I is longer phase and consists of 5 sub phases namely Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene and Diakinesis.

a) Leptotene :
The nucleus increases in size by absorbing water from the cytoplasm. The chromatin material organises into a constant number of chromosomes. The chromosomes are long, slender and show bead like structures called chromomeres.

b) Zygotene :
The chromosomes become shorter and thicker. They approach each other and form pairs. This homologous pair is called bivalent and the process of pairing is called synapsis. It is accompanied by the formation of Synaptonemal complex. The synapsis occurs at proterminal point or procentric or random means.

c) Pachytene :
Bivalent chromosomes now clearly appear as tetrads. This stage is characterised by the presence of recombination modules, the sites of which crossing over occurs between the non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes. Crossing – over is the exchange of genetic material between the two homologous chromosomes. It is also an enzyme mediated process by ‘recombinase’ crossing over leads to recombination of genetic material on the two chromosomes.

d) Diplotene :
The homologous chromosomes of a bivalent begin to separate from each other except at the sites of cross overs to dissolution of synaptonemal complex. The ‘X’ shaped structures are called chaismata. The chromatids undergo condensation, contraction and thickening.

e) Diakinesis :
It is marked by terminalisation of chaismata. In this phase, the chromosomes are fully condensed and the meiotic spindle is assembled to prepare the homologous chromosomes for separation. By the end of this phase, the nuclear membrane breaks down the nucleolus disappears.
Question 3.
Differentiate between the events of mitosis and meiosis.
Answer:
| Mitosis | Meiosis |
| 1. It occurs in both haploid and diploid organisms. | 1. It occurs only in diploid organisms. |
| 2. It occurs in somatic cells. | 2. It occurs in the reproductive cells. |
| 3. Nucleus divides once. | 3. Nucleus divides twice. |
| 4. Daughter cells are identical. | 4. Daughter cells are not identical. |
| 5. Two daughter cells are formed. | 5. Four daughter cells are formed. |
| 6. Prophase is simple. | 6. Prophase is complicated and shows five sub-stages. |
| 7. Pairing of chromosomes does not occur. | 7. Homologous chromosomes pair to form bivalents. |
| 8. Both chaismata and crossing over are absent. | 8. Crossing over occurs between non¬sister chromatids and chiasmata are formed. |
| 9. Centromeres undergo division in anaphase. | 9. Centromeres do not divide in anaphase-I, but divide in anaphase-II. |
| 10. Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite poles. | 10. Bivalents are separated. They move to opposite pies. |
| 11. The chromosome number of daughter nuclei is unchanged. | 11. The chromosome number of daughter nuclei is reduced to half. |
| 12. Duration of time is less. | 12. Duration of time is more. |
Question 4.
Write brief note on the following :
a) Synaptonemal complex b) Metaphase plate
Answer:
a) Synaptonemal complex :
The homologous chromosomes approach each other and form pairs called Bivalents and the process is called synapsis. The synapsis occurs at the both ends and progresses towards their centromeres called proterminal or the synapsis starts from their centromeres and the pairing progresses towards the end of the chromosomes called procentric or the pairing occurs at various points of homologous chromosomes called Randon synapsis. The paired homologous chromosomes are joined by a thick protein containing frame work called synaptonemal complex (Sc).Sc stabilizes the pairing of the homologous chromosomes and facilitates crossing over and recombination.
b) Metaphase plate :
Metaphase chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids’which were held together by the centromere. Small disc shaped structures at the surface of of the centromeres are called Kinetochores. These serve as the sites of attachment of spindle fibres to the chromosomes that are moved into centre of the cell. Hence all chromosomes lie at the equator with one chromatid of each chromosome connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibres from one pole and its sister chromatid connected by its kinetochore to spindle fibres from the opposite pole. It is called ‘Metaphase Plate’.
![]()
Question 5.
Write briefly the significance of mitosis and meiosis in multicellular organism.
Answer:
Significance of Mitosis :
- Growth in organisms is caused by Mitosis.
- The daughter cells formed by Mitosis are identical with the mother cell in characters. Hence it it important in conserving the genetic diversity of the organisms.
- In unicellular organisms, Mitosis help in reproduction.
- The old dead and decaying cells of body are replaced with the help of Mitosis.
- It is useful in regeneration of lost parts and for grafting in vegetative reproduction.
Significance of Meiosis :
- Meiosis helps in the maintenance of a constant chromosome number from one generation to the next.
- Due to crossing over, genetic recombinations are caused which help in the origin of new species and lead to evolution.
- It helps in the formation of gametes and is thus useful in sexual reproduction.
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Name a stain commonly used to colour chromosome.
Answer:
Giemsa strain is used.
Question 2.
Name the patholqgical condition when uncontrolled cell division occurs.
Answer:
Cancer.
Question 3.
An organism has two parts of chromosomes (i.e., chromosome number = 4) Diagra-matically represent the chromosomal arrangement during different phases of Meiosis II.
Answer:
An organism has two pairs of chromosomes (i.e., chromosome number = 4) Diagrammatically represent the chromosomal arrangement during phases of meiosis – II.
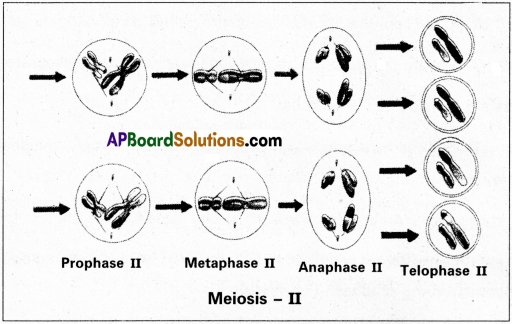
Question 4.
Meiosis has events that lead to both gene recombinations as well as mendelian recombinations. Discuss.
Answer:
An organism often many phenotypic fruits in its body; are determined by at least pair of alleles (or) gener During the events of meiosis – I (crossing over) recombination events occur to pass different combination of chromosomes and consequently different combination of characters in both daughter cells.
The random assortment of the genes is due not only to crossing over but also to the random distribution of the chromosomes in first and second division. How ever, since this separation is a random process, the resulting cells will contain different chromosomal combinations even in the abscence of crossing over.
![]()
Question 5.
Both unicellular and multicellular organisms undergo mitosis. What are the differences if any observed between the two processes?
Answer:
- In unicellulars it is referred as binary fission and in multicellulars it is referred as mitosis.
- Mitosis allows unicellular organisms to reproduce and create more (identical) organisms.
- In unicellular only one cell undergoes mitosis whereas in multicellular all cells undergo mitosis.