Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Civics Study Material 11th Lesson Constitutions Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Civics Study Material 11th Lesson Constitutions
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Constitution and explain its features of the Constitution.
Answer:
Introduction :
The age of Democracy led to political civilisation. Nowadays every civilised state possesses a constitution. A Constitution is a condition of modem state. The constitution is a living text of a political system. It represents the political character of the state and its constituents.
The term constitution implies a written document embodying the provisions relating to the powers and functions of the government organs, the rights and duties of the citizens.
Meaning:
The term constitution is an English word. It was derived from the Latin word “Constitution, which means to Establish”.
Definitions:
1) Aristotle :
“Constitution is the arrangement of offices in a state, especially the highest of all”.
2) Lord Bryce:
“Constitution is a set of established rules embodying and enacting the practice of Government”.
3) Stephen Leacock:
“Constitution is the form of Government”.
4) K.C. Wheare :
“Constitution is that body of rules which regulates the ends for which governmental power is exercised”.
Features of the Constitution:
1) Preamble :
Every Constitution will have a preamble. The preamble denotes the aims and aspirations of the Constitution. It is like the soul of the Constitution. Hence, preamble is considered as an important feature of the Constitution.
2) Clarity:
Clarity is another important feature of the Constitution. The Constitution clearly explains about the different policies and methods of governance. It is written in a simple and clear language.
3) Incorporation of Fundamental Rights :
Every Constitution includes some funda-mental rights. These fundamerital rights are meant for safeguarding the freedoms of the citizens. They enable the citizens to realise their personality in various spheres. They help the citizens for leading a happy and honourable life in the state.
4) Brevity :
Brevity is another feature of a Constitution. Brevity avoids confussion among the individuals in understanding and interpreting provisions. Unnecessary elements are not included in the Constitution. It should be precise. It must not contain large number of clauses.
5) Flexibility:
The Constitution must be flexible for adapting the wishes are aspirations of the people from time to time. There must be a scope of amending the provisions of the Constitution if necessary. Frequent changes in the Constitution tend to weaken the spirit of the Constitution. But, at the same time, the Constitution of a modem state should be adaptable to the progressive changes.
6) Permanence:
Permanence is one more feature of the Constitution. The Constitution must have everlasting values for the welfare of the whole nation. It represents the actual structure of the state and its political institutions. It obliges the customs of the people.
7) Mode of Amendment:
The Constitution specifies the mode of amendment. It will be relevant to the contemporary conditions of the state. It contains a special chapter on the constitutional amendment procedures. Usually the constitutional amendments are of three types, namely (i) Rigid (ii) Flexible and (iii) Half rigid and Half flexible. On the whole, the constitution of every state comprises both rigid and flexible elements.
8) Explanatory:
The Constitution is explanatory in nature. It denotes and discusses almost all elements relating to the People, Government and State. It contains separate provisions on the structure, powers and limitations of state activity.
![]()
Question 2.
Define Constitution and point out the differences between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions.
Answer:
Definition :
The age of Democracy led to political civilisation. Now-a-days every civilised state possess a Constitution. A constitution is a condition of modem state. The constitution is a living text of a political system. It represents the political character of the state and its constituents.
Flexible Constitution:
Flexible constitution is one whose provisions can be amended easily. It requires no special procedure for changing its provisions. It can be amended by the authorities by adopting the same procedure of ordinary laws. So we do not find differences between ordinary and constitutional laws. Flexible constitutions were prevalent in the ancient period. Ex : British constitution.
Rigid Constitution :
Rigid constitution is one whose provisions cannot be changed easily. In this system the constitutional amendment methods are different from those of ordinary laws. There will be a special procedure for amending the provisions of the rigid constitution. The rigid constitution will have firmness due to its special procedures of amendment. Ex : United States.
Differences between Flexible and Rigid Constitution
| Flexible Constitution | Rigid Constitution |
| 1. Constitutional matters are not clearly mentioned. | 1. Constitutional matters are clearly written. |
| 2. Not appropriate to a federal state. | 2. Appropriate for a federal state. |
| 3. Highly unstable. | 3. Highly stable. |
| 4. Constitution can be easily amended. | 4. Constitution cannot be easily amended. |
| 5. Provides no scope for judicial review. | 5. Provides scope for judicial review. |
| 6. Only one type of law is found. | 6. Two types of laws are found, constitutional and ordinary. Constitutional laws precede ordinary laws. |
| 7. Rights, freedoms and liberties of people may not be safeguarded by the Judiciary. | 7. Rights, freedoms and liberties of people will be better safeguarded by the Judiciary. |
| 8. No scope for revolutions. | 8. Scope for revolutions. |
| 9. Possibility of unlimited legislative power. | 9. Possibility of a limited legislative power. |
| 10. More suitable to the politically advanced states. | 10. More suitable to the developing nations. |
| 11. It makes no differentiation between constitutional and ordinary laws. | 11. It makes differentiation between constitutional and ordinary laws. |
| 12. Appropriate to small states. | 12. Appropriate to large states. |
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define Constitution. Explain its features. [A.P. 19]
Answer:
Features of the Constitution:
1) Preamble :
Every Constitution will have a preamble. The preamble denotes the aims and aspirations of the Constitution. It is like the soul of the Constitution. Hence, preamble is considered as an important feature of the Constitution.
2) Clarity:
Clarity is another important feature of the Constitution. The Constitution clearly explains about the different policies and methods of governance. It is written in a simple and clear language.
3) Incorporation of Fundamental Rights :
Every Constitution includes some fundamental rights. These fundamental rights are meant for safeguarding the freedoms of the citizens. They enable the citizens to realise their personality in various spheres. They help the citizens for leading a happy and honourable life in the state.
4) Brevity :
Brevity is another feature of a Constitution. Brevity avoids confession among the individuals in understanding and interpreting provisions. Unnecessary elements are not included inf he Constitution. It should be precise. It must not contain large number of clauses.
5) Flexibility:
The Constitution must be flexible for adapting the wishes are aspirations of the people from time to time. There must be a scope of amending the provisions of the Constitution if necessary. Frequent changes in the Constitution tend to weaken the spirit of the Constitution. But, at the same time, the Constitution of a modem state should be adaptable to the progressive changes.
6) Permanence:
Permanence is one more feature of the Constitution. The Constitution must have everlasting values for the welfare of the whole nation. It represents the actual structure of the state and its political institutions. It obliges the customs of the people.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the various bases of classifying constitutions.
Answer:
Political Scientists classified the constitutions into various types on the basis of (i) Evolution (ii) Nature (iii) Amendment. They are mentioned in the following table.
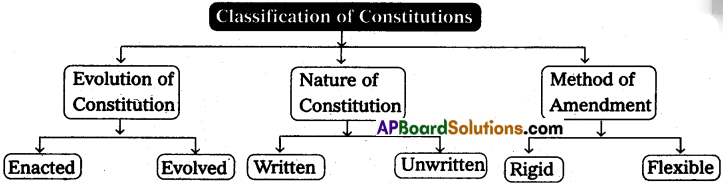
1) Evolution of Constitution:
On the basis of evolution, constitutions are divided into two types, namely (a) Evolved Constitution (b) Enacted Constitution.
a) Evolved Constitution :
Evolved Constitution is also called as Cumulative Constitution. It is the result of evolutionary changes. It may be the product of collected material. It acts as the basis to the political institutions of a country. It is not made as it grows with the roots in the past. Several customs, usages, traditions, principles and judicial decisions etc act as the sources of this consitution. E.g. Britain.
b) Enacted Constitution :
Enacted Constitution is also known as Conventional Constitution. It is consciously made. It is the outcome of the deliberations of the Constituent Assembly specially convened for that purpose. It is promulgated by the sovereign authority – King or Parliament. The provisions of this constitution are incorporated in a document or a series of documents. E.g. United States, India.
2) Nature of Constitution:
Constitutions are classified into two types on the basis of the incorporation of the various provisions. They are
a) Written Constitution and
b) Unwritten Constitution
Question 3.
What are the merits and demerits of a Written Constitution?
Answer:
Written Constitution :
A written constitution is formulated and adopted by a Constituent Assembly or a Convention. It comprises several principles and rules of the Government in a written form or document. The Constitution of India is an example of written constitution. The American Constitution is the first written constitution in the world.
Merits:
- A written constitution carries more simplicity. It gives no scope for confusion and ambiguity among the people in understanding the structure and organization of various institutions.
- It protects the fundamental rights of the people.
- It puts limitations on the powers of the Government.
- It renders political stability due to its rigid nature.
- It embodies the aspirations of the people. It cautions the Government about the importance of the accomplishment of popular needs.
- It maintains equilibrium between the centre and the states by allocating powers in a judicious manner.
- It safeguards the sanctity and spirit of a federation.
Demerits:
- A written constitution cannot provide a better Government as it impose some . stipulated conditions on the party in power.
- It makes the judiciary a predominant one.
- Its provisions cannot be changed according to the needs and wishes of the people. So, the progress of the nations lags behind.
- Its rigid nature is not helpful to the development of the state.
- It gives scope for conflicts among the governmental organs.
- It may not be conductive to the formation of a welfare state.
Question 4.
Explain the merits and demerits of Unwritten Constitution.
Answer:
Unwritten Constitution: Unwritten constitution is one whose provisions are not written in a single document. It includes several customs and traditions which are manifested in the form of the laws.
The Constitution of Britain is the best example of unwritten constitution.
Merits:
- An unwritten constitution paves the way for progressive legislation. It has development orientation.
- It always undergoes the process of evolution as it aims at ‘bettering the best’.
- It gives no scope for revolutions and such other agitations. It concedes to the popular demands.
- It can be amended according to the popular needs and aspirations.
- Its provisions are elastic in nature. So, changes in the constitution are easily made.
Demerits:
- An unwritten constitution may be changed frequently by the party in power for its political gains. This affects the political stability of the nation.
- It fails to protect the rights and freedoms of people.
- It is more informal in nature.
- It is also not suitable for federal states.
- An unwritten constitution is considered as a play tool of judges. This may lead to judicial manipulations.
- It is prone to frequent amendments.
- It is not suitable to democratic states.
![]()
Question 5.
Distinguish between Written and Unwritten Constitution.
Answer:
Written Constitution :
A written constitution is formulated and adopted by a Constituent Assembly or a Convention. It comprises several principles and rules of the Government in a written form or document. The Constitution of India is an example of written constitution. The American Constitution is the first written constitution in the world.
Unwritten Constitution:
Unwritten constitution is one whose provisions are not written in a single document. It includes several customs and traditions which are manifested in the form of the laws. The Constitution of Britain is the best example of unwritten constitution.
Differences between Written and Unwritten Constitutions
| Written Constitution | Unwritten Constitution |
| 1. Written constitution implies a document or few documents in which the rules regulating the main institutions of Government are written down. | 1. Unwritten constitution denotes a sum of customs, conventions and usages which have not been systematically documented. |
| 2. All the basic principles of the State are clearly written. | 2. All the basic principles of the State exist in the form of customs and traditions. |
| 3. Written constitution is framed by a special assembly convened at a particular point of time. | 3. Unwritten constitution contains some written elements also in the form of enactments of fundamental charters made from time to time. |
| 4. It is suitable to the educated and literate people. | 4. It is suitable to the uneducated and illiterate people. |
| 5. Courts of law protect the liberties of the citizens. | 5. Courts of law cannot provide much protection. |
| 6. It is formulated at a particular time. | 6. It is evolutionary in nature. |
| 7. It provides political stability. | 7. It could not ensure political stability. |
| 8. It cannot be easily amended. | 8. It can easily be amended. |
| 9. It is useful to federal states. | 9. It is advantageous to the unitary states. |
Question 6.
Explain the merits and demerits of a Rigid Constitution.
Answer:
Rigid Constitution :
Rigid constitution is one whose provisions cannot be changed easily. In this system the constitutional amendment methods are different from those of ordinary’ laws. There will be a special procedure for amending the provisions of the rigid constitution. The rigid constitution will have firmness due to its special procedures of amendment. The Constitution of the United States is the best example of a rigid constitution.
Merits:
- Rigid constitution secures political stability.
- It is a product of political experience.
- It avoids hasty and ill-considered legislation.
- It protects the fundamental rights of the citizens.
- It preserves and enhances the interests of the provinces in a federal state.
- It is suitable for all kinds of people.
Demerits :
- Rigid constitution cannot be easily amended to suit the changing needs.
- It may affect the nation’s progress and growth.
- It is not suitable for tackling the issues arising during emergencies.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by Constitution?
Answer:
The term constitution implies a written document embodying the provisions relating to the powers and functions of the Government organs, the rights and duties of the citizens.
![]()
Question 2.
What is an Evolved Constitution?
Answer:
Evolved constitution is also called Cumulative constitution. It is the result of evolutionary changes. It may be the product of collected material; It acts as the basis to the political institutions of a country. Several customs, usages, traditions, principles and judicial decisions are the major sources of this Constitution. Ex : British Constitution.
Question 3.
What is an Enacted Constitution?
Answer:
Enacted constitution is also known as Conventional constitution. It is consciously made. It is the outcome of the deliberations of the Constituent Assembly specially constituted for that purpose. It is promulgated by the Sovereign Authority i.e., king or queen or Parliament. Ex: The Constitutions of India and the U.S.A.
Question 4.
Write any three merits and demerits of Flexible Constitution.
Answer:
Merits of Flexible Constitution are :
- It is elastic and adaptable in nature. Its provisions can be easily amended from time to time.
- It is responsive and responsible to the popular wishes.
- It protects the people from the dangers of revolutions.
Demerits of the Flexible Constitution are :
- It is not suitable to the federal states, having rigid constitution.
- It is not suitable to democratic states.
- It is highly unstable.
![]()
Question 5.
Mention any two differences between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions.
Answer:
Differences between Flexible and Rigid Constitution
| Flexible Constitution | Rigid Constitution |
| 1. Constitutional matters are not clearly mentioned. | 1. Constitutional matters are clearly written. |
| 2. Constitution can be easily amended. | 2. Constitution cannot be easily amended. |