Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Accountancy Study Material 4th Lesson Not-for-Profit Organizations Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Accountancy Study Material 4th Lesson Not-for-Profit Organizations
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
State the meaning of Not-for-profit organisations. Give suitable examples.
Answer:
There are certain organizations like schools, colleges, libraries, athletic clubs, hospitals, charitable trusts, welfare societies, co-operative societies, clubs, etc. were established for providing service to its members or to the public. The main objective of this type of organisations is to do service rather than earn profits. This organization calls not-for-profit organisations.
Question 2.
Write the characteristics of not-for-profit organisations.
Answer:
The following are the characteristics of not-for-profit organisations:
- Working without profit motive: Not-for-Profit organisations are formed for providing services to a specific group or public at large such as education, recreation, health, and so on.
- Its sole aim is to provide service either free or cost or at nominal cost and not to earn profits.
- Organised bodies: These are organised as charitable trusts, and societies and subscribers to such organisations are called members.
- Source of income: The main source of income of such organisations is donations, legacies, grant-in-aid, subscriptions, income from investments, etc.
- Elected management: The organisation is managed by a managing committee or executive committee elected by members.
- No diffusion of surplus: The surplus generated in the form of income over expenditure is not distributed amongst the members. It is added to the capital fund.
- Reputation: Not-for-profit organisations earn their reputation by their contribution to the welfare of society.
- Accounting information: The account information provided by such organisations is meant for present and potential contributors and meets the statutory requirements.
![]()
Question 3.
Distinguish between profitable organisations and not-for-profitable organisations.
Answer:
Differences between profitable and not-for-profit organisations.
| Baste of distinction | Profitable organization | Not-for-profit organization |
| 1. Motive | The main motive is to earn profit. | The main motive is to render service to the members and society. |
| 2. Funds | Funds are represented by capital contributed by proprietors. | Funds are represented by capital funds comprising the form of surplus, legacies, and life membership fees. etc. |
| 3. Financial statements | These include the manufacturing account, trading and profit, loss account, and balance sheet. | They include receipts and payment accounts, income and expenditure accounts, and balance sheets. |
| 4. Surplus/Profit | The balance of profit and loss account is either net profit or a net loss. | The balance in the income and expenditure account is either surplus or deficit. |
Question 4.
List out the accounts prepared by not-for-profit organisations.
Answer:
Not-for-profit organisations prepare the following accounts.
- Receipts and Payment Account
- Income and Expenditure Account
- Balance Sheet
Question 5.
What are the final accounts prepared by not-for-profit organisations?
Answer:
Not-for-profit organisations prepare at the end of the financial period receipts and payments account, an Income and expenditure account, and a Balance Sheet in order to ascertain cash in hand or at the bank, surplus or deficit, and various assets and liabilities and capital funds respectively. So the final accounts in not-for-profit organisations consist of the following.
- Receipts and Payments Account
- Income and Expenditure Account
- Balance Sheet
Question 6.
What do you mean by Receipts and Payment Accounts?
Answer:
The receipts and payments account is a mere summary of the cash book for a year. It is maintained and prepared by not-for-profit organisations in lieu of a cash book. Like cash books, receipts of cash are written on the debit side and payments on the credit side. All receipts and payments whether they are relating to the current, preceding, or succeeding period, or all the receipts and payments of capital and revenue nature and written in this account. The closing balance of this account shows the cash in hand/at the bank at the end of the accounting period.
Question 7.
What are the characteristics of receipts and payments accounts?
Answer:
Features of Receipts and Payment Account:
- It is a summary of the cash book.
- All the amounts of receipts and payments irrespective of the period are recorded.
- Irrespective of capital or revenue nature all the receipts and payments are recorded.
- Noncash items like depreciation and outstanding expenses are not shown in this account.
- It begins with an opening balance of cash in hand and cash at a bank or bank overdraft and closes with the year-end balance of cash in hand/cash at a bank or bank overdraft.
Question 8.
In what way do receipts and payment accounts differ from cash books?
Answer:
The distinction between receipts and payment account and cash book.
| Basis of Distinction | Receipts and Payment Accounts | Cashbook |
| 1. Cash transactions | It is a summary of the cash book and all transactions are recorded. | All cash transactions are recorded. |
| 2. Period | It is prepared at the end of the accounting year. | It is written daily. |
| 3. Chronological order | The transactions are written date-wise. | Transactions are written in chronological order. |
Question 9.
What is an income and expenditure account?
Answer:
The income and expenditure account is prepared in non-profit concerns in the lien of profit and loss account. The income and expenditure account is credited with all incomes, both realized and unrealized, and debit with all expenses, both paid and unpaid. There is no opening balance but the closing balance will show either surplus i.e. excess of income over expenditure or deficit i.e. excess of expenditure over income only revenue items are taken into consideration. It consists of income and expenditure relating to the current year and those incomes and expenditures relating to preceding and succeeding periods are excluded. This account is prepared on the accrual basis of accountancy and all adjustments relating to prepaid, outstanding expenses and incomes, provision for depreciation, or doubtful debts will be made.
![]()
Question 10.
Explain the basic features of the income and expenditure accounts.
Answer:
The following are the features of income and expenditure.
- It is a nominal account.
- It is similar to a profit and loss account.
- Expenditure and losses are recorded on the debit side and incomes are recorded on the credit side.
- Only revenue incomes and expenditures are recorded.
- Expenses and incomes relating to the current year are only taken into consideration.
- Adjustments for prepaid, and outstanding, provisions are made in this account.
- Differences between the two sides will show either surplus or deficit and it is transferred to the capital fund on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 11.
Differences between receipts and payments account and income and expenditure.
Answer:
Differences between Receipts and Payment Account and Income and Expenditure Account.
| Basis of distinction | Receipts and Payment Account | Income and Expenditure Account |
| 1. Type of account | Real account. | Nominal account. |
| 2. In lieu of | It is prepared in lieu of a cash book. | It is prepared in lieu of a profit and loss account. |
| 3. Sides | Debit side receipts and credit side payments. | Debit side payments and Credit side receipts. |
| 4. Opening balance | There can be an opening balance which represents cash in hand/cash at the bank. | No opening balance. |
| 5. Closing balance | This shows cash in hand/cash at the bank at the end of the accounting period. | There is no closing balance but the difference represents either surplus or deficit. |
| 6. Capital and Revenue | All items are taken irrespective of capital and revenue. | Only revenue items are taken. Capital items are excluded. |
| 7. Period | All receipts and payments whether relating to current succeeding or preceding periods are taken into consideration. | Only current period incomes and expenditures are taken into consideration. Preceding and Succeeding period items are excluded. |
| 8. Balance sheet | It is not necessary to prepare a Balance sheet along with this account. | The balance sheet must be prepared along with this account. |
| 9. Adjustments | No adjustments are required to be made at the end of the year. | All adjustments are made at the end of the year. |
| 10. Non-cash items | It does not record noncash items such as depreciation etc. | It records non-cash items. |
| 11. Basis of accountancy | It is prepared on a cash basis. | It is prepared on an accrual basis. |
Question 12.
In what way income expenditure account differs from the profit and loss account?
Answer:
| Basis of distinction | Income and Expenditure A/c | Profit and Loss A/c |
| 1. Object | The object of this account is to find a surplus or deficit. | The object of this account is to find net profit or loss. |
| 2. Concerns | This account is prepared by non-trading concerns. | This account is prepared by trading concerns. |
| 3. Basis of preparation | This account is prepared on the basis of receipts and payment account and additional information. | This account is prepared on the basis of trial balance and additional information. |
| 4. Balance | The balance of this account is termed as surplus or deficit. | The balance of this account is called net profit or a net loss. |
Question 13.
What do you mean by Revenue expenditure? Give examples.
Answer:
Any amount spent to earn revenue or profits is called revenue expenditure. These expenses are recurring in nature. Its useful life also would be less than one year.
e.g. salaries, rent, wages, insurance, etc.
Question 14.
What do mean by capital expenditure? Give examples.
Answer:
Capital expenditure is that expenditure that is generally incurred for the acquisition of assets and to increase the earning capacity of the business. The expenditure gives benefits for a number of years.
e.g. purchase of tangible and intangible assets like plant and machinery, furniture, buildings, patents, trademarks, goodwill, etc.
Question 15.
How do you prepare receipts and payment accounts?
Answer:
The following procedure is adopted for preparing receipts and payment accounts.
- Take the opening balances of cash in hand and cash at the bank and enter them on the debit side. In case of bank overdraft at the beginning of the year enter the same on the credit side of the account.
- Show all items of receipts on the debit side and payments on the credit side irrespective of nature, whether capital or revenue, and whether pertaining to past, current and future periods.
- Neither the receivable income nor payable income is considered.
- Find the difference between the debit side and the credit side of the account. If the total on the debit side is more, show the difference on the credit side and vice-versa and close the account.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the procedure to convert receipts and payments account into income and expenditure accounts.
Answer:
Conversion of receipts and payment account into income and expenditure account.
- Opening and closing balance of cash and bank given in receipts and payments accounts should be excluded.
- Consider only revenue items of income and expenditure and exclude the items of capital receipts and payments.
- Make all adjustments regarding outstanding, prepaid incomes and expenses, depreciation, and provision for bad debts.
- Take only items for the current year and exclude all items from preceding and succeeding years.
- Consider the following items not appearing in receipts and payments accounts and need to be taken for determination of surplus or deficit.
- Depreciation on fixed assets.
- Provision for doubtful debts.
- Profit or Loss on the sale of fixed assets.
Question 17.
What is capital income? Give two examples.
Answer:
Any amount received as investment by owners or raised by way of loans and sale of fixed assets is known as capital receipts. These amounts lie in huge amounts. These are non-recurring in nature. All the items of capital receipts are to be shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 18.
What is revenue income? Give two examples.
Answer:
Any amount received in the normal course of the business is called revenue receipts, which are recurring in nature.
e.g. sales, interest, discounts, commission, rent received, etc.
Question 19.
Distinguish between capital income and revenue income.
Answer:
Any amount received as investment by owners or raised by way of loans and sale of fixed assets are capital receipts that are non-recurring in nature.
Any amount received in the normal course of the business is called revenue receipts, which are recurring in nature.
Question 20.
Distinguish between revenue expenditure and capital expenditure.
Answer:
Capital expenditure is that expenditure that is generally incurred in the acquisition of assets and to increase the earning capacity of the business. This expenditure gives benefits for a number of years. Any expenditure spent to earn revenue or profits is called revenue expenditure. It is useful for less than one year.
Question 21.
What is a subscription?
Answer:
Subscriptions are a major recurring source of income for non-profit entities that are paid by members periodically. Subscriptions relating to the current year are shown as income.
Question 22.
What is the capital fund?
Answer:
Excess of assets over liabilities is called capital or (General) fund and it is made up of a surplus of income over expenditure and certain items which are capitalized like life membership fees, donations, legacies, entrance fees, etc.
Question 23.
What is a legacy?
Answer:
It is the amount that a not-for-profit concern will receive as per the will of a deceased person. It should be capitalised being an item of non-recurring nature and should be shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 24.
What differs from revenue expenditure? Give examples.
Answer:
It is in the nature of revenue expenditure. But when the huge amount is paid, the benefit of which may be for more than one year, a portion will be debited to P & L A/c, and the balance is shown as an asset on the balance sheet.
e.g. for differed revenue expenditure is the huge amount spent on advertisement.
![]()
Question 25.
What is the Entrance fee?
Answer:
Entrance fees or admission fees are received from the members. When they were admitted into the concern. In the absence of specific instructions, this amount should be treated as revenue income.
Question 26.
What is meant by life membership?
Answer:
It is paid to a member once in a lifetime. So it should be capitalised and shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 27.
What are donations? Explain different types.
Answer:
Donations are the amounts that are given to the organisation as gifts by the public. These are two types.
- General donations: When they do lay down any specific conditions for their use, it is called general donations and treated as revenue and shown on the credit side of the income and expenditure account. If the amount is huge, then it should be capitalised.
- Specific donations: If the donation is for a specific purpose, then they are called a specific donation.
e.g. Building Fund. This is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Textual Exercises
Question 1.
From the following particulars, prepare Receipts and Payments A/c

Solution:
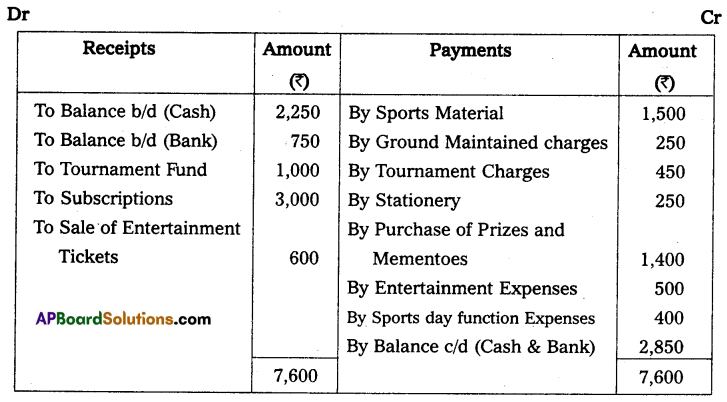
Question 2.
Prepare Receipts and Payments Accounts.

Solution:
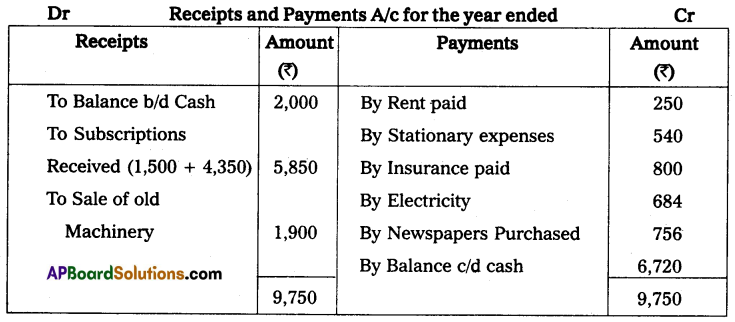
Question 3.
From the following details prepare receipts and payments A/c
Solution:
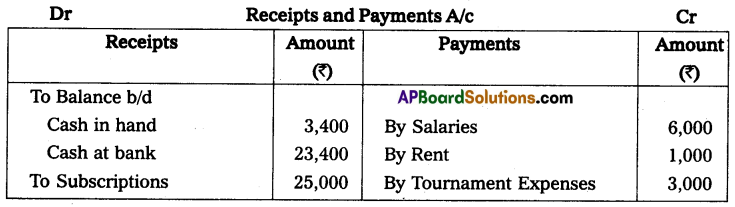
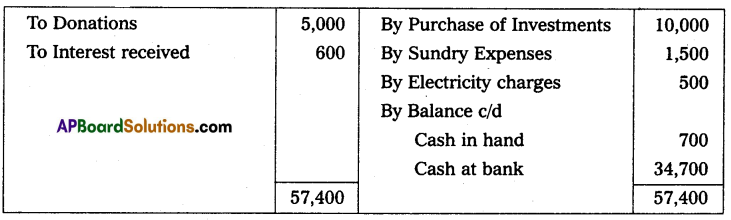
![]()
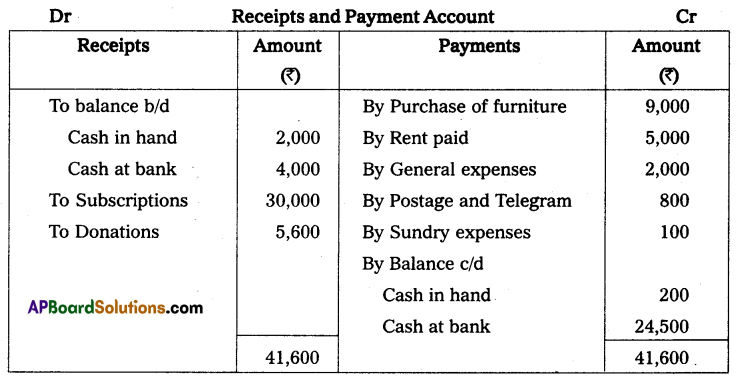
Question 4.
From the following particulars Prepare Receipts and Payments A/c.
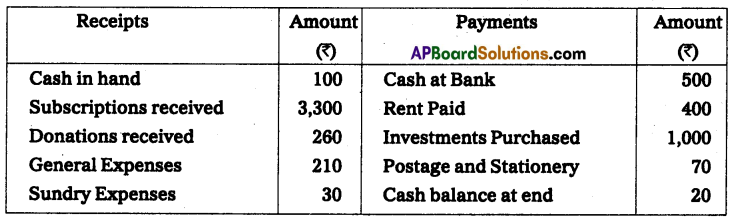
Solution:
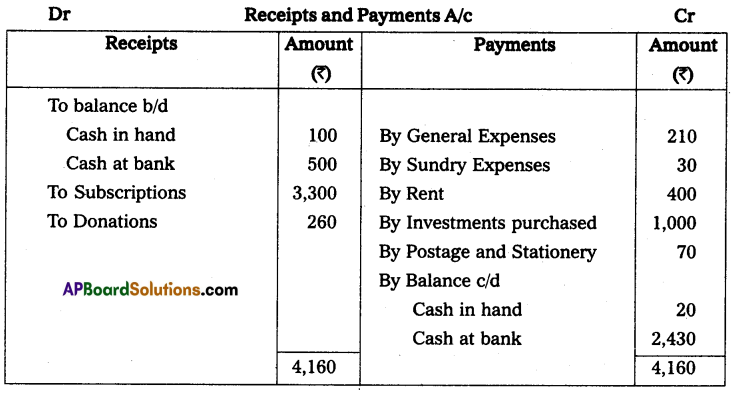
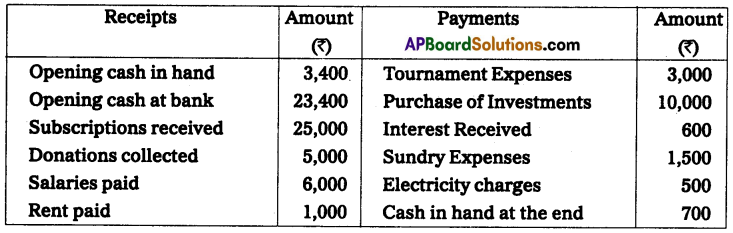
Question 5.
Following is the receipts and payments A/c of Gandhi cultural club for the year ended 31-Dec-2014.
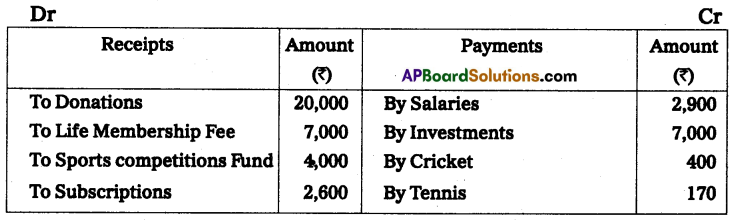
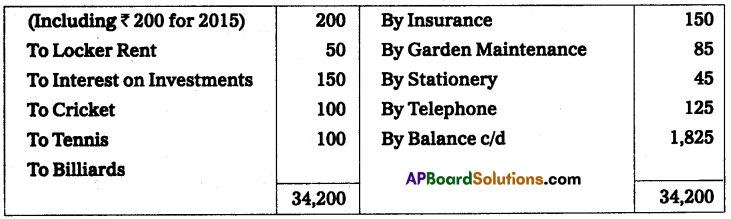
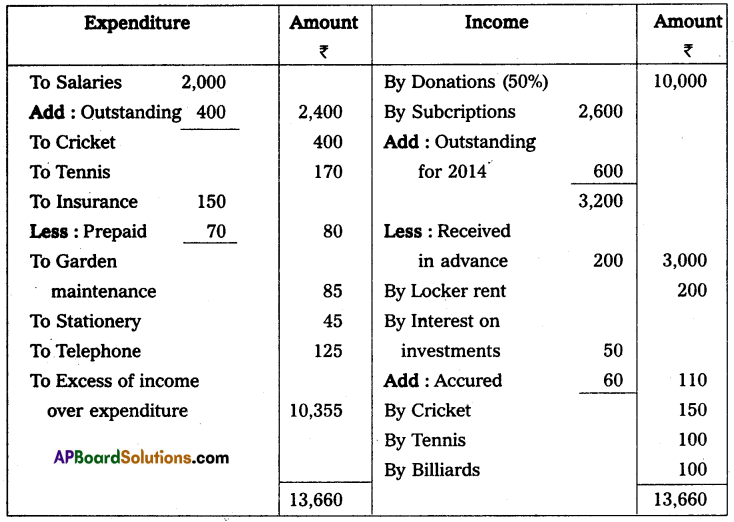
Subscriptions are receivable for the year 2014 ₹ 600.
Outstanding Salaries ₹ 400.
Half of the Donations are to be capitalized, with accrued interest of ₹ 60.
Prepaid Insurance ₹ 70.
Prepare income and Expenditure A/c for the year ended 31-Dec-2014.
Solution:
Income and expenditure account of Gandhi Cultural club for the year ended 31st Dec. 2014
Question 6.
Prepare income and expenditure A/c of Tirupathi Club from the following receipts and payments A/c, for the year ending 31-Dec-2014.
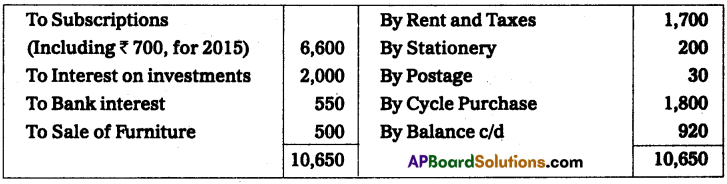
Adjustments:
(a) Rent paid included ₹ 200 for December 2013
(b) Salaries Payable ₹ 900.
(c) Subscriptions received included ₹ 600 for the year 2013.
(d) Subscriptions Due for the year 2014, ₹ 400.
(e) Cost of furniture sold ₹ 800.
Solution:
Income and expenditure account of Tirupathi club for the year ending 31st Dec. 2014.
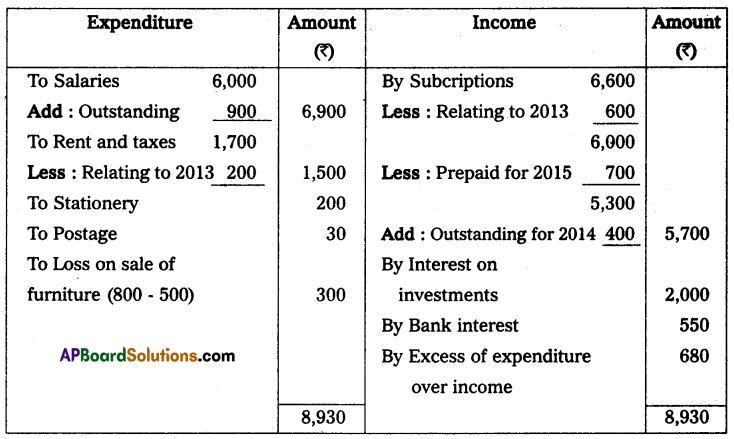
Question 7.
From the following receipts and payments a/c of the Venkateswara Society for the year ended 31-Dec-2014. Prepare income and expenditure a/c for the year ended 31 -Dec-2014.
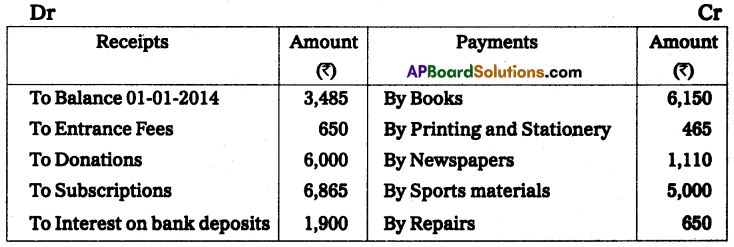
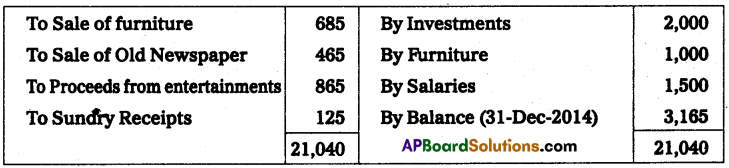
The entrance fees and donations are to be capitalized. Sports materials value ₹ 4,000 as of 31-Dec-2014.
Solution:
Income and expenditure of Venkateswara society for the year ending 31st December 2014.
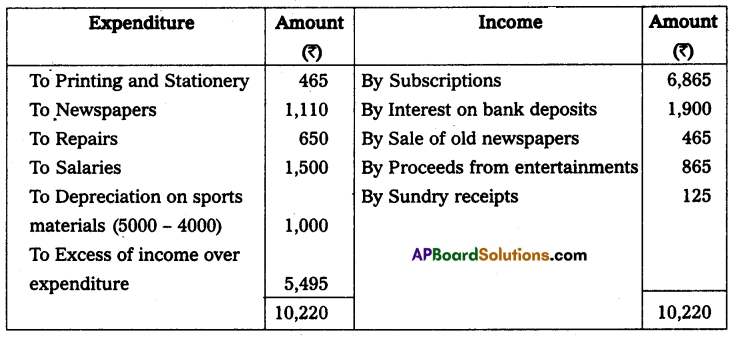
![]()
Question 8.
Visakha Sports Association extracts the following receipts and payments A/c for the year ended 31-Dec-2014. From the particulars given, prepare income and expenditure a/c.
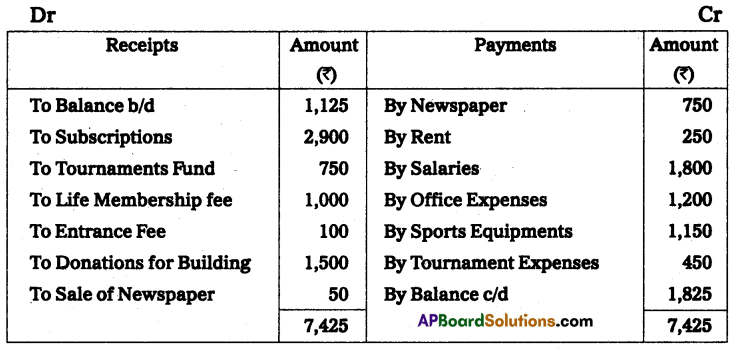
Adjustments:
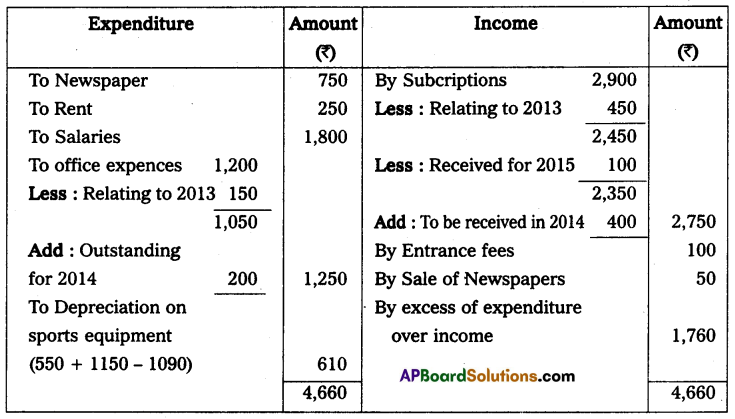
(a) Subscriptions are outstanding on 31-Dec-2013, ₹ 450, and on 31-Dec-2014, ₹ 400. Subscriptions received include ₹ 100 on account of the year 2015.
(b) Sports equipments was valued on 31-Dec-2013, @ ₹ 550, and on 31-Dec-2014, @ ₹ 1090.
(c) Office expenses include ₹ 150, for the year 2013 whereas ₹ 200 is still payable on this account for 2014.
Solution:
Income and expenditure of Visakha sports association for the year ended 31st Dec. 2014
Question 9.
From the following, Prepare income and expenditure A/c of Tirupathi Sportsmen Club for the year ended 31-Dec-2010.
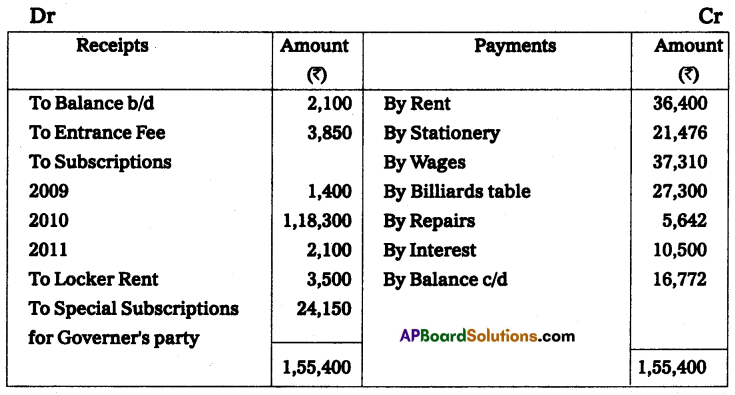
Adjustments:
Locker rent ₹ 420 pertaining to 2009 and ₹ 630 is still owing. Rent ₹ 9,100 Pertaining to 2009 and ₹ 9,100 is still due. Stationary expenses ₹ 2,184 relating to 2009 and ₹ 2,548 is still owing, Subscriptions receivable for the year 2010, ₹ 3,276.
Solution:
Income and expenditure a/c of Tirupathi sportsmen club for the year ended 31st Dec. 2010.
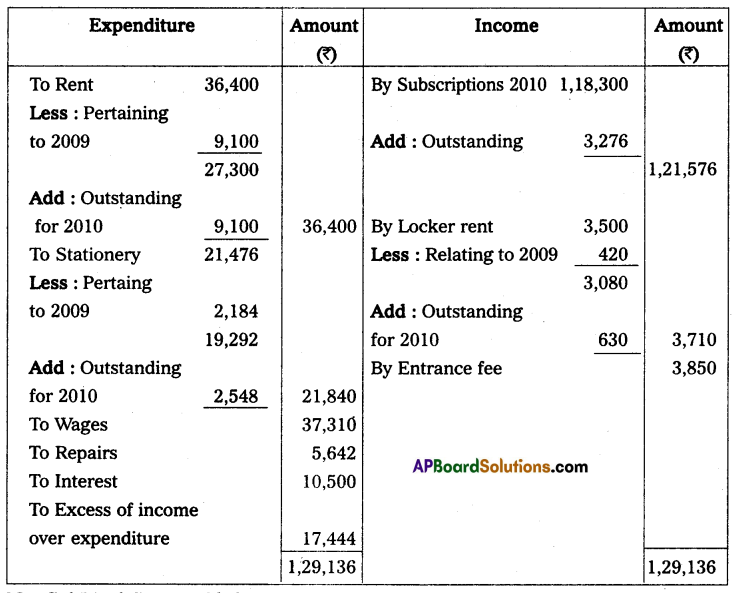
Question 10.
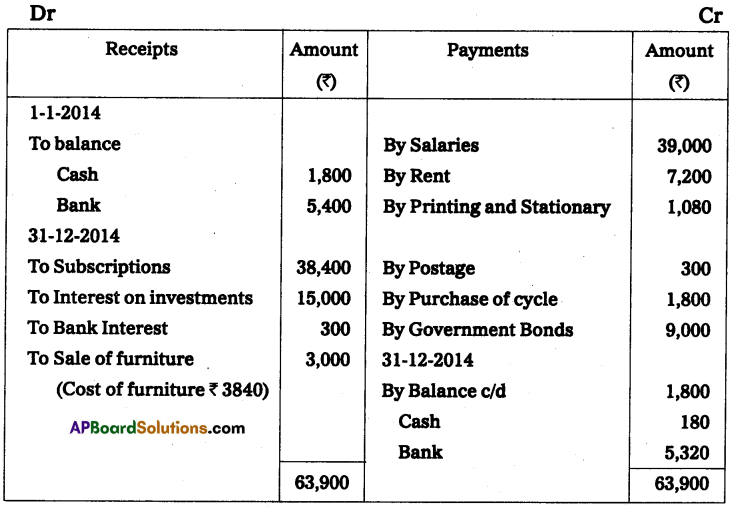
Sri Hari Sports Club’s, Ongole receipts and payments for the year ending 31-Dec-2014. Is given below.
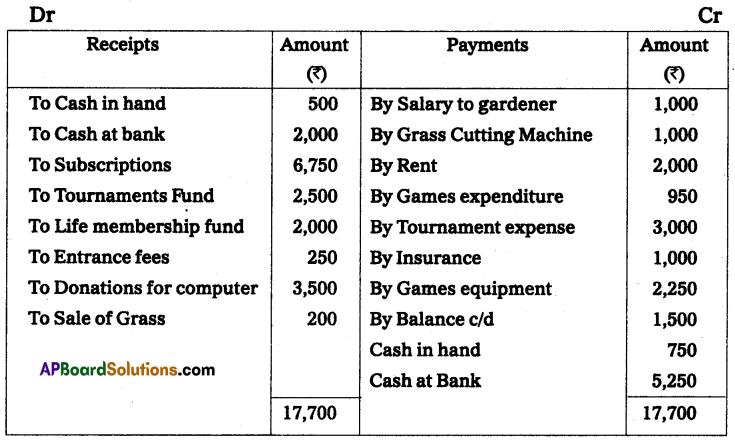
Additional Information:
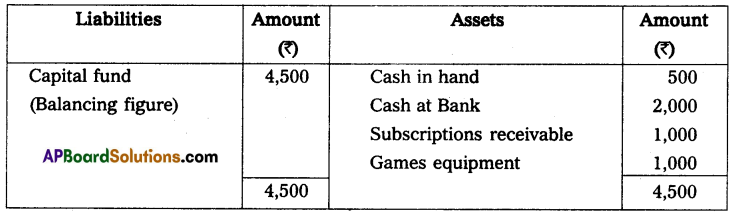
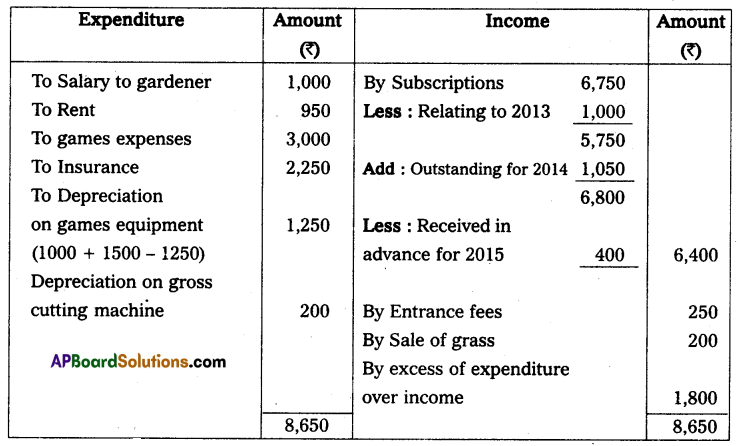
(a) Subscription receivable for 2013 were ₹ 1,000 and for 2014 ₹ 1,050. A subscription has already been received including ₹ 400 for the year 2015.
(b) Games equipment, in the beginning, was ₹ 1,000 and at the end ₹ 1,250.
(c) Provide depreciation @ 10% Grass cutting machine.
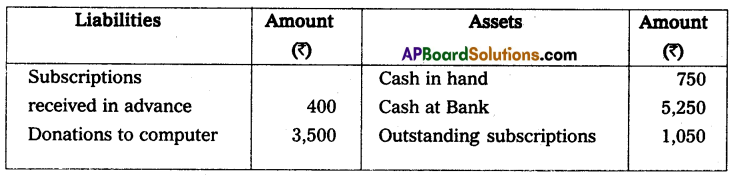
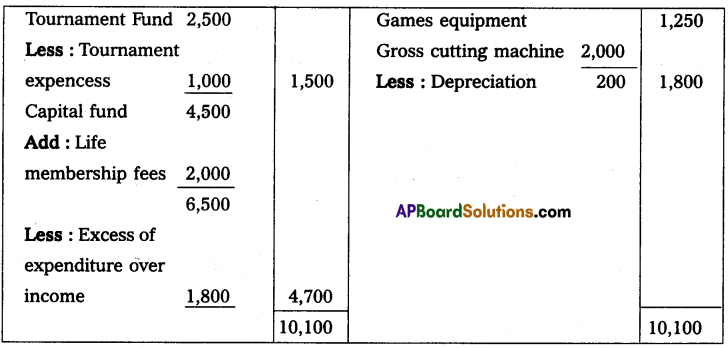
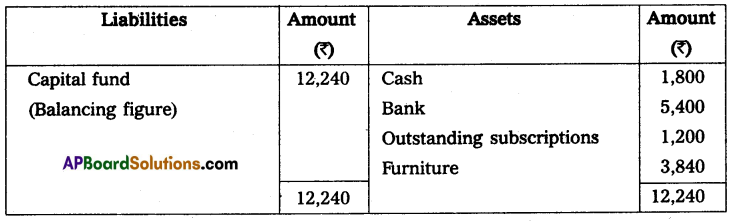
Prepare income and expenditure A/c for the year ending 31-Dec-2014. And opening, and closing the balance sheet.
Solution:
Balance sheet as on 1-1-2014
Income and expenditure A/c for the year ended 31-12-2014
Balance sheet as on 31-12-2014
![]()
Question 11.
From the following receipts and payments accounts of other information of Kadapa City Club, Prepare income and expenditure A/c as of 31-Dec-2014 and balance sheet as of that date.
Adjustments:
(a) Subscription received included ₹ 1,200 for the year 2013, and ₹ 2,400 for the year 2015.
(b) Subscriptions due for the year 2014 – ₹ 1,800
(c) Printing Charges payable for 2014 – ₹ 240
(d) Salaries payable for the year 2014 – ₹ 3,600
Solution:
Balance sheet as on 1-1-2014
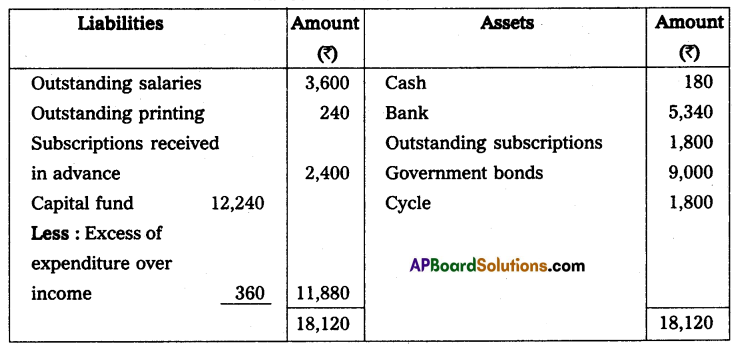
Income and expenditure account for the year ended 31st December 2014.
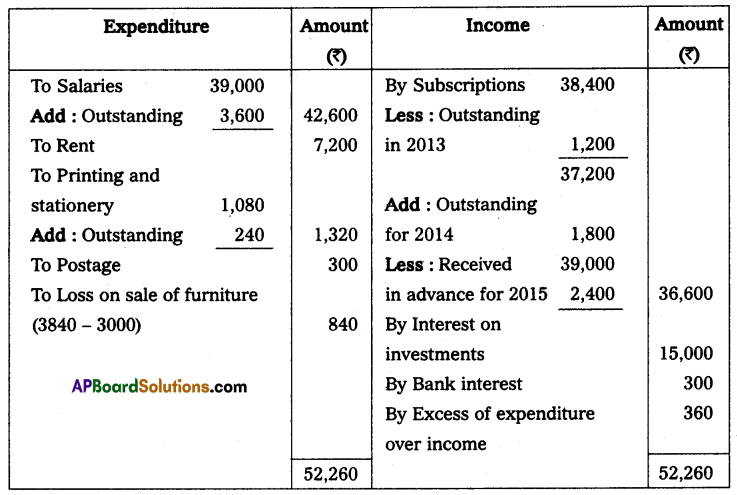
Balance sheet as on 31.12.2014
Question 12.
From the following Receipts and payments a/c of Amaravathi Sports Club for the year ended 31st Dec-2008, prepare income and expenditure account.
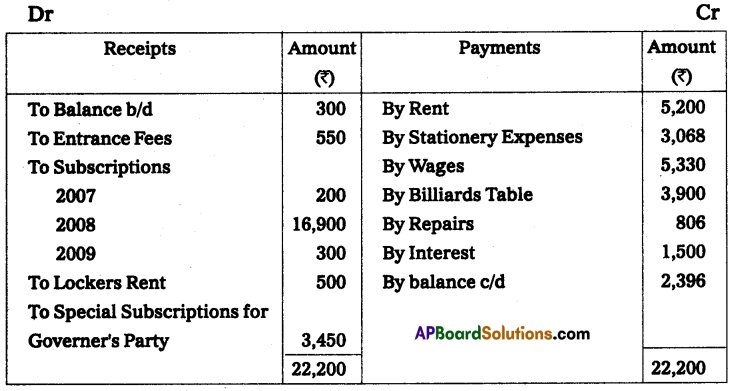
Lockers rent ₹ 60, pertaining to 2007 and ₹ 90 is still owing. Rent ₹ 1,300 pertained to 2007 and ₹ 1,300 is still due. Stationery Expenses ₹ 312 relating to 2007 and ₹ 364 is still owing.
Subscriptions Receivable for 2008 is ₹ 468.
Solution:
Income and expenditure A/c of Amaravathi sports club for the year ended 31st December 2008
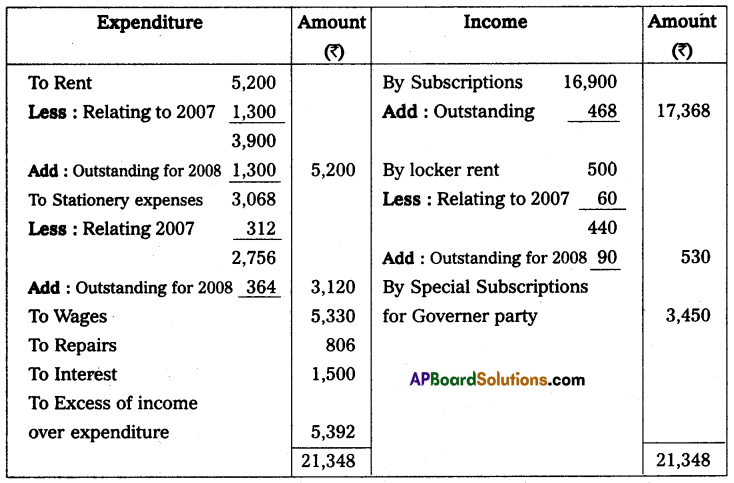
Note: Entrance fees are capitalized.
Question 13.
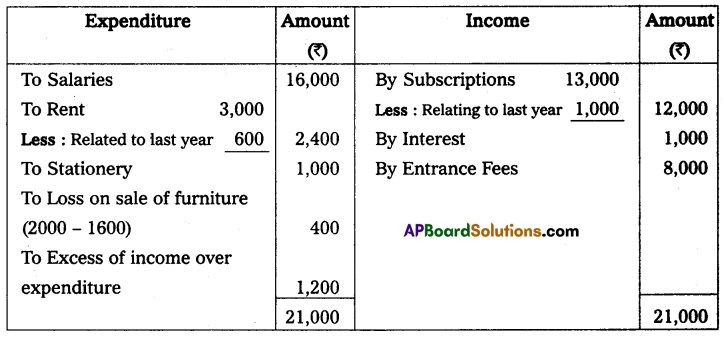
From the following Receipts and Payments of Nethajee Sports Club, prepare income and Expenditure A/c for the year ended on 31 -Mar-2012.
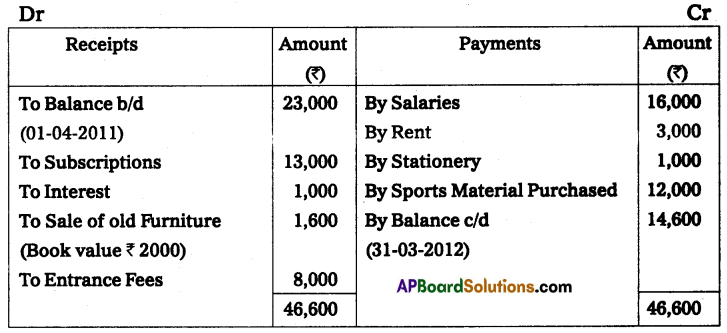
Additional Information:
(a) Subscriptions Include ₹ 1,000 Received for the last year.
(b) Rent Includes ₹ 600 paid for the last year.
From the above particulars Prepare Income and Expenditure A/c for the year ending 31-03-2012.
Solution:
Income and expenditure of Nethajee sports club for the year ended 31st March 2012
![]()
Question 14.
Visakha Town Club provided Receipts and Payments A/c for the year ended 31-Mar-2013. Prepare Income and Expenditure A/c.
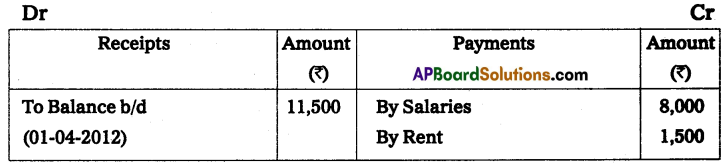
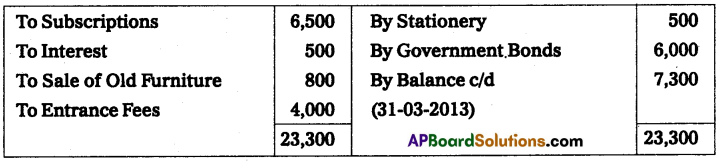
Adjustments:
(a) Subscriptions Include ₹ 500 received for the last year.
(b) Rent Includes ₹ 300 paid for the last year.
(c) Book value of Furniture sold ₹ 1,000
Solution:
Income and expenditure A/c for the year ended 31.3.2013
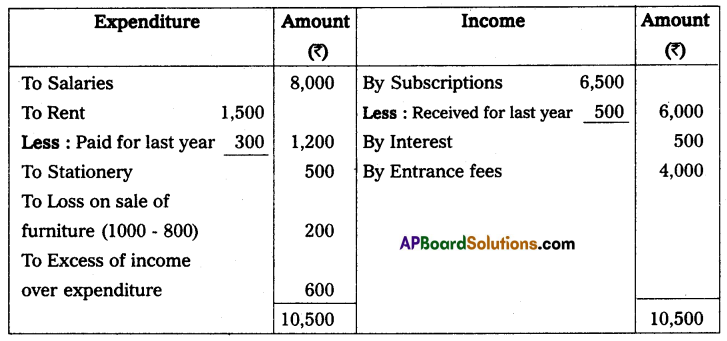
Question 15.
From the following Receipts and Payments A/c of Guntur Sports Club for the year ending 31-Mar-2012, Prepare income and Expenditure A/c.
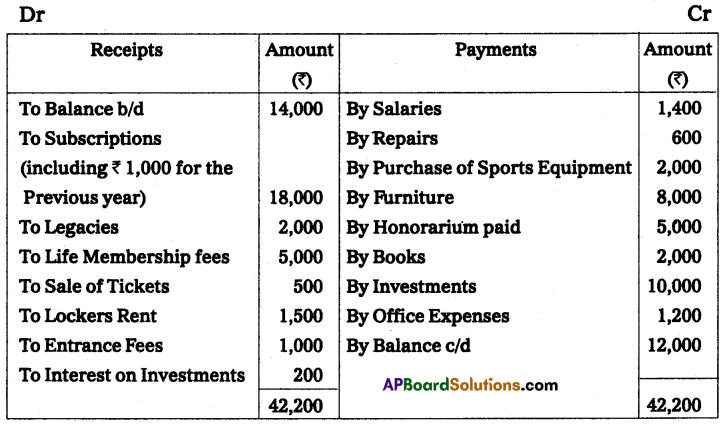
Additional Information:
(a) Outstanding Salaries ₹ 600
(b) Opening value of sports equipments ₹ 1,000, closing value ₹ 500
(c) Interest accrued on investments of ₹ 200
(d) Subscription receivable for the year 2012, ₹ 3,000
Solution:
Income and expenditure of Guntur sports club for the year ended 31st March 2012
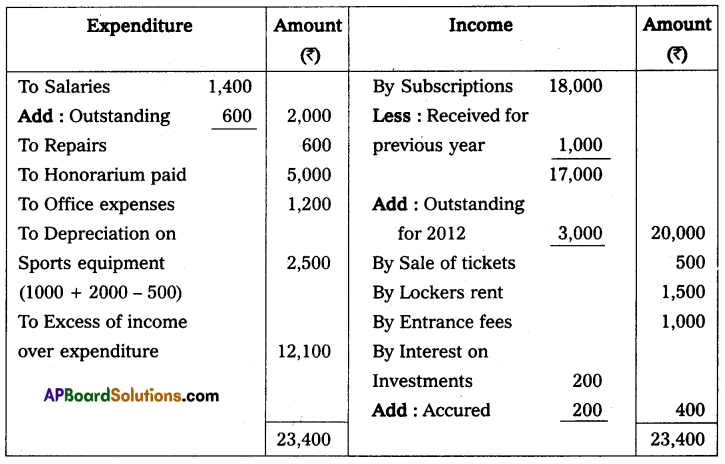
Question 16.
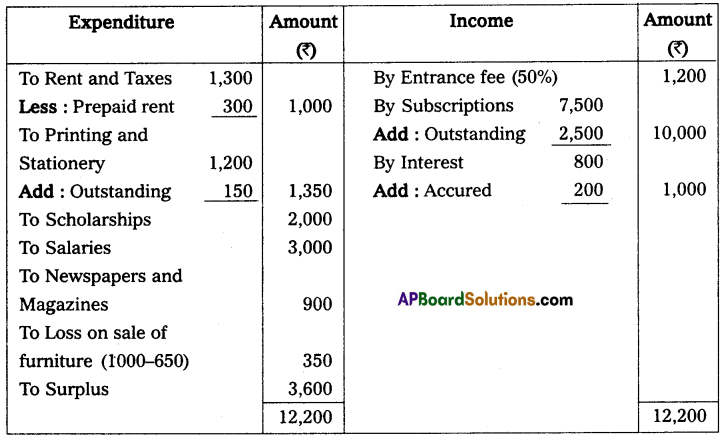
From the following Receipts and Payments A/c of Sai Charitable Trust, Anantapur, Prepare Income and Expenditure A/c.
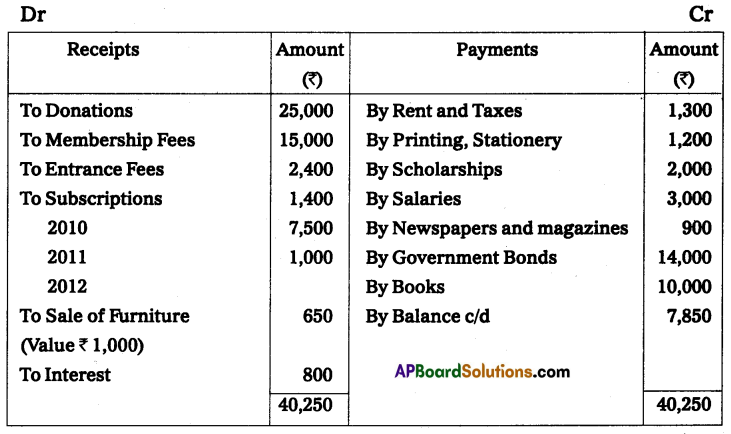
Additional Information:
(a) Subscriptions Receivable for the year 2011 – ₹ 2,500.
(b) Prepaid Rent ₹ 300.
(c) Outstanding Stationery Bill ₹ 150.
(d) Capitalize donations.
(e) Half of the Entrance fees are capitalized.
(f) Interest Receivable for the year 2011 – ₹ 200.
Solution:
Income and expenditure A/c of Sai Charitable Trust for the year ended Dec 31, 2011
![]()
Question 17.
Nellore Sports Club started on 01-01-2010. Their Receipts and Payments A/c for the year ended 31-Dec-2010.
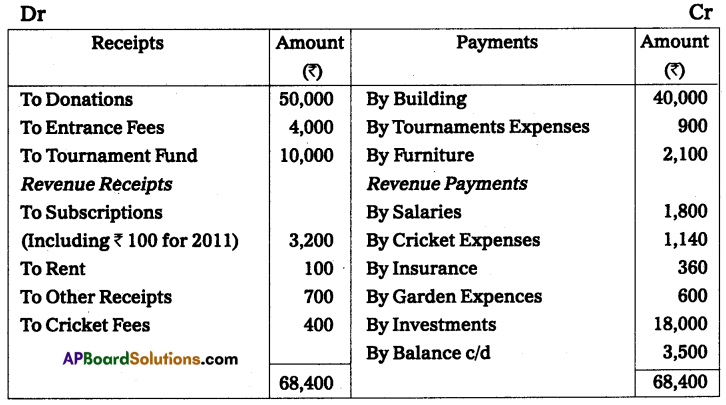
Additional Information:
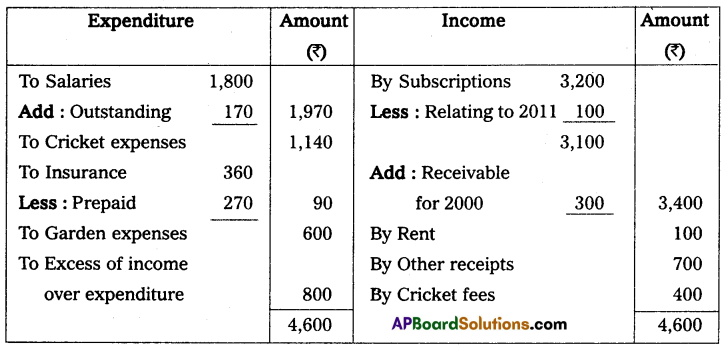
(a) Subscription is receivable for 2010 – ₹ 300.
(b) Salaries Unpaid – ₹ 170.
(c) Entrance fees are to be capitalized.
(d) Insurance includes 9 months’ premium for 2011.
Solution:
Income and expenditure of Nellore Sports Club for the year ended 31st Dec. 2010.
Question 18.
From the following Receipts and Payments A/c of Balaji Trust, prepare Income and Expenditure A/c for the year ending 31-December-2008.
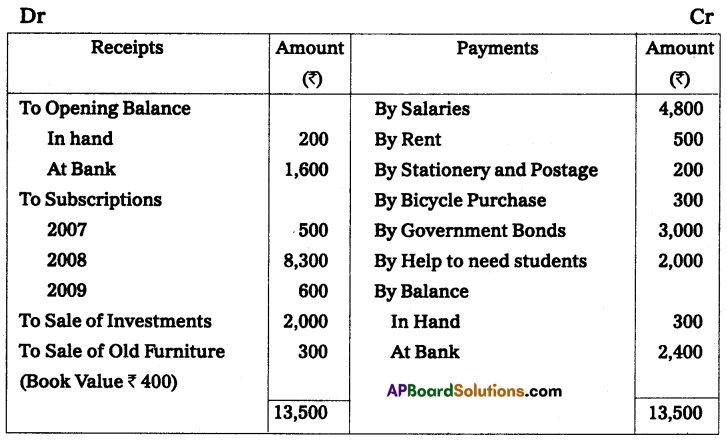
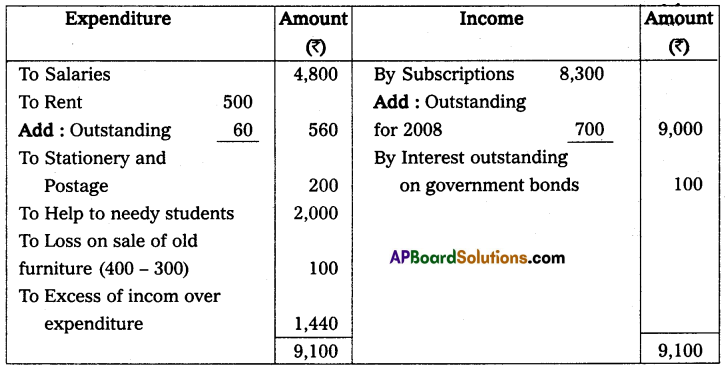
Adjustments:
Subscriptions for the year 2008 still receivable were ₹ 700, interest due on Government Bonds ₹ 100, and rent outstanding ₹ 60.
Solution:
Income and expenditure account of Balaji trust for the year ended 31st, Dec. 2008
Textual Examples
Question 1.
From the following particulars, prepare Receipts and Payments Account.

Solution:
![]()
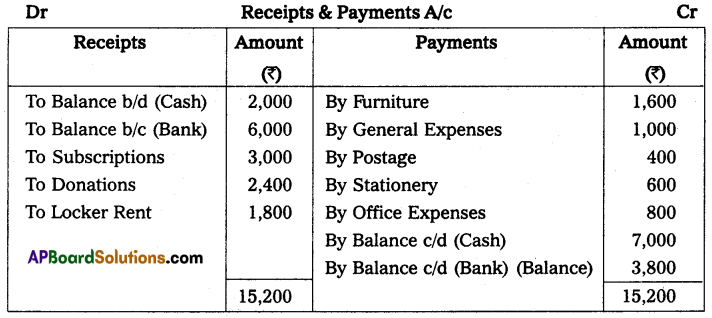
Question 2.
Prepare Receipts and Payments Account of Kurnool Sports Club for the year ended on 31-3-2015

Solution:
Receipts & Payments of Kurnool Sports Club for the year ending 31-3-2015