Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 8th Lesson Environment and Sustainable Economic Development Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 8th Lesson Environment and Sustainable Economic Development
Essay Questions
Question 1.
Define environment and explain the components of environment
Answer:
The word Environment is derived from the French word environner which means to surround or encircle. Everything which surround us may collectively be termed as the environment, we are surrounded by both living and non living things. The living things are called as biotic part (Physical environment) and non-living things as abiotic part (Biological environment) of the environment.
Components of Environment : According to National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) of USA, 1969, the term “Environment” includes physical, social, cultural, economic and aesthetic dimensions. According to Rau & Wooten, environment can be viewed in four dimensions.
1) Physical Environment: It covers the physical, chemical and biological elements such as land, climate, vegetation, wild life surrounding land uses and physical character of the area, infrastructure, air and noise pollution levels.
2) Social Environment: It includes a large number of factors such as population and its density, community, composition, religious, education, community facilities like schools, parks, hospitals, recreational and cultural facilities. Some social factors will overlap the economic factors.
3) Economic Environment: All economic factors like employment, unemployment levels and sources of income, availability of factors of production, demand patterns, poverty level etc., are come under this category.
4) Aesthetic Environment : This category comprises historical archeological or architecture of objects or sites, scenic areas, views and landscapes. People derive pleasure by seeing such objects.
As the environment consists of all these different components, it is considered to be completely interdisciplinary discipline. We need the knowledge of Physics, Botany, Zoology, Geology, Geography, Agriculture, Chemistry, Economic Education, Demography, Ecology, Sociology, Philosophy, Political Science, Biotechnology, Biochemistry and Genetics to understand what an environment is.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the relationship between environment and the economy.
Answer:
Relationship between environment and economy: The functions of the environment explain the importance of environment. It acts as the supplier of raw materials to the economy and absorbs the wastes discharged by the economy.
In economic terms, the resources supplied by the environment can be called as environmental goods. These goods are public goods. They can be used by many individuals at the same time without any competition from other individuals.
However, in modem days, the reckless and exploitative behaviour of the economic activity is setting a limit to the efficiency of environment to supply to the resources. Economist warned the world about the consequences of overuse of environmental resources. He said that earth is a spaceship with a limited amount of life support resources. He warned the mankind to minimize the consumption rather than to maximize it.
In the other words, there should be a balance between inputs and outputs. When we receive the inputs to produce goods and services, it must be equal to the consumption and the discharge of wastes. The quality of wastes and emission must be less, so that the environment can absorb them. Material balance model.provides and excellent.answer for the relationship that must exist between environment and the economy.
R = F + W1
The household sector consumes all the ‘F units of produced goods and services. While doing so, it also produces W2 units of wastes.
So in the consumption sector F = W2
Hence, in the consumption economy R = F = (W1 + W2)
Therefore R = (W1 + W2)
These equations show that the entire mass of inputs (raw materials) equal the entire mass of output (wastes). This entire amount of wastes is returned to the environment. Thus, the materials taken from the environment are again returned the environment in equal amounts. Hence, R = W1 + W2.
This equality shows the accounting identing of the material balance. Assuming this two sector model, material balance can be explained by the diagram.
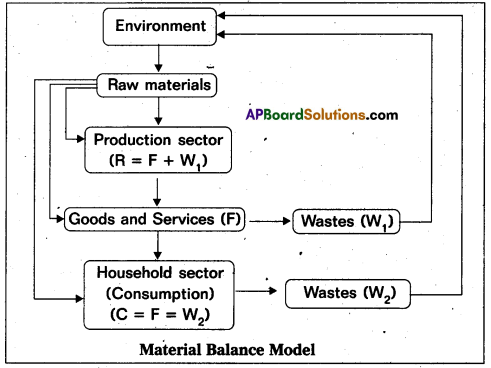
Note: F = W and R = W1 + W2; F = Final goods and services; W = Wastes; R = Raw material the production sector uses R (Raw materials) units of raw materials from the environrhent to product F unit of final products./While producing the final products, it also produces W1 amount of wastes. So in the production sector.
R = F + W1
The household sector consumes all the ‘F units of produced goods and services. While doing so it also produces W2 units of wastes.
So in the consumption sector F = W2
Hence, in the economy R = F = (W1 + W2)
Therefore R = (W1 + W2)
These equations show that the entire mass of inputs (raw materials) equals the entire mass of output (wastes). This entire amount of wastes is returned to the environment. Thus, the materials taken from the environment are again returned to the environment in equal amounts. Hence, R = W1 + W2. This equality shows the accounting identity of the material balance.
It can be concluded that this material balance model depends upon the first two laws of thermodynamics. The first law explains that the energy can be changed from one form to another. But it can neither be created nor destroyed. The second law is the law of entropy. Economic activities of production and consumption are dependent on these two laws. Similarly generation and assimilation of wastes are also dependent on the two laws.
![]()
Question 3.
What is air pollution ? Explain the causes and consequences for air pollution.
Answer:
“The excessive concentration of contaminated substance in the air which adversely affects the well being of the individuals, living organs and property of all forms” is called as air pollution.
Causes for air pollution : It is estimated that 2 billion tonnes of air pollutants are released every year. Besides natural sources, a number of man-made sources are causing air pollution. Burning of fire woods for domestic purposes, burning of fossil fuels, industrialization, agricultural activities, vehicular emissions, nuclear tests, deforestation, mining power generation, refrigeration industries, etc., are the sources of air pollution.
Effects of Air Pollution :
- Air pollution adversely affects people, plants, animals, aquatic life and materials.
- It leads to health disorders in human beings.
- Damages the leaves of the plants and trees; interferes with photosynthesis and plant growth.
- Air pollution discolours the historical monuments; breakdown the exterior paint on cars and houses and deteriorates the quality of natural beauty sites. Ex : Taj Mahal in 1998, when the white marble of the famous monument began to turn yellow.
- Air pollution affects the stratosphere and climatic conditions.
- Global warming, acid rains, depletion of ozone layer, changes in the distribution of solar energy, rising temperatures, occurrence of droughts, changes in the natural plants, crops, insects, livestock
- Increased ultraviolet radiation are the effects of air pollution.
Question 4.
Briefly discuss the sources, effects of water pollution ?
Answer:
Water is blue gold like air, water is very essential for the existence of all the living organisms. It accounts tor about 70 percent of the weight of the human body. About 80 percent of the earths surface is covered by water.
Water pollution is defined as “the addition of some substance or factor which degrades the quality of water, so that it becomes unit for use”.
We have two sources of water surface and ground water.
Water that is found in streams, tanks, rivers and artificial reservoirs is called surface water. Water that per colates into the ground is called as ground water.
Sources of Water Pollution: The major pollutants that pollute water are :
- Domestic wastes and Sewage
- Surface run-off
- Silt
- Industrial effluents
- Hot effluents.
- Fertilizers and Pesticides
- Accidental Oil spills
- Compounds of toxic metals
- Mining wastes
- Untreated waste water and garbage etc.,
Effects of Water Pollution: Water pollution generates the following effects.
- Transmits the water – borne diseases.
- Deteriorates the quality of drinking water.
- Affects the productivity of irrigated agricultural lands.
- Sea food becomes contaminated.
- Depletes oxygen in water. Brings undesirable changes in temperature and breeding of fish.
- Makes water unfit even for swimming
- Produces offensive odours in water.
- Water-related diseases cause a heavy economic burden, particularly for poor people.
- Leads to loss of human days due to illness.
- Children suffer from intestinal diseases.
![]()
Question 5.
Define noise pollution and explain how it affects the quality of environment?
Answer:
Sound is different from ‘Noise’, though these words are used similarly. Not all sounds are noise. A deep, loud and unpleasant sound is called noise. It is undesirable and unwanted. To be precise, anything between 50 to 90 dB is considered as noise. The human ear can safely responds to pressures upto 120 dB. As per the Environment (protection) (Second Amendment) Rules, 1997, the permitted noise levels is 125 dB.
“Any noise generated above 125 dB and produces harmful effects in effects in environment and causes health hazards to human being” is called as noise pollution.
Noise becomes a pollutant when it exceeds certain limits. Noise pollution remains in the environment only for hazards to human being is called as noise pollution limited time. It is not so dangerous as air and water pollutions. They are
- Indoor sources
- Outdoor sources.
Sources of Noise Pollution : There are two board categories of sources for noise pollution. They are 1. Indoor sources 2. Outdoor sources.
1) Indoor Sources: Sounds generated by the use of home appliances, libraries, living rooms, business offices, sounds generated by alarm clocks, breathing, conversation, computer rooms etc., are the sources of indoor noise pollution.
2) Outdoor Sources: Noise generated by transport vehicles, loud speakers, industries, marriages, aeroplanes, cinema theatres, firing of crackers, heavy road traffic, festivals etc., are the outdoor noise pollutants.
Effects of Noise Pollution: Noise pollution affects the quality of environment as well as life on earth. Noise pollution leads to the following effects.
- Pollutes the essence of music and speech.
- Affects communications.
- Leads of temporary or permanent hearing loss.
- Affects the functioning of various systems of human body. Hypertension, sleeplessness, digestive disorders, peptic hinders, blood pressure changes are some of the ill effects of noise pollution.
- Disturbs the brain waves of the people at sleep.
- Causes irregular or faster pulse beats and increases in blood cholesterol levels.
- Causes increased heart-beat rate of the foetus.
- Causes irrepairable damage, to unborn babies.
- Ears, the first organ that develop of the unborn babies, are badly affected.
Question 6.
What are the economic implications of environmental degradation ?
Answer:
Environmental degradation is slightly different from pollution. Environmental degradation is decrease in the quality of environment, whereas, the pollution is the contamination of the nature (air, soil, water) with harmful substances. Environmental changes may be driven by many factors including economic growth, population growth, urbanization, intensification of agriculture, rising energy use and transportation etc. The basic factors for environmental degradation are discussed below.
1) Social factors: Social factors, which are responsible for environmental degradation are briefly discussed below.
a) Population : Population is an important source of development yet it is a major source of environmental degradation when it exceeds the threshold limits of the support systems.
b) Poverty : Poverty is said to be both the cause and effect of environmental degradation. The circular link between both concepts is an extremely complex phenomenon. Inequality may faster unsustainability because, the poor, who rely on natural resources more than the rich, deplete natural resources faster as they have no real prospects of gaining access to other types of resources.
c) Urbanisation : Lack of opportunities for gainful employment in villages and the ecological stresses is leading to an ever-increasing movement of poor families to town, Mega cities are emerging and urban slums are expanding. Such rapid and unplanned expansion of cities has resulted in degradation of urban environment.
2) Economic factors : Environmental degradation is the result of market failure. In this context, environmental degradation is a particular case of consumption or production of externalities reflected by divergence between private social costs.
3) Institution factors: The Ministry of Environment and Forest of the government of India is responsible for protection, conservation and development of environment. Environment Act, 1986 is the key legislation governing environment management. Wild life Act 1972, the forest conservation Act 1980 etc.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the various factors resulting in environmental pollution ?
Answer:
Pollutions are classified into different ways. They are classified according to their form, exsistence and natural disposal.
According to their natural disposal, the pollutants are classified into three groups.
1) Degradable pollutants: The pollutants are can be rapidly broken down by natural processes are called degradable pollutants. Ex : discorded vegetables, domestic sewage etc. These pollutants are called as Biodegradable pollutants.
2) Slowly Degradable pollutants : Some pollutants remain in the environment for many years in unchanged condition pollution results when their discharge exceeds the capacity of the environmental degrade them. These pollutants are actually waste products. Ex : DDT, Plastic etc.
3) Non – Degradable pollutants: The pollutants which can not be degraded by natural processes are called as nondegradable pollutants once they enter into the environment, it is difficult to eradicate them. They continue to accumulate in the environment. For Ex : Nuclear waste.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain various concepts of Environment.
Answer:
Environment around us consists of living and non living things with their inter dependency and mutual interaction. A study of all these aspects is called as ecology. To understand environment and its nature, a primary information of its basic concepts is needed. Eco-system biodiversity, greenhouse effects, global warming, climate change, acid rains, ozone depletion are some of the basic concepts of environment.
A) Eco-System: The British Ecologist AG.Tansley coined the term Ecosystem in 1935. An ecosystem is a region with a specific and recognizable land, scape (form) such as forest, grassland, desert, or coastal area. The living community of plants and animals in any area together with the non-living components of the Environment constitute as ecosystem.
B) Biodiversity : The word biodiversity was coined by Walter Rosen in 1986. Living organisms are different in their size, colour, shape and structure. The genes, environment and ecosystem decide this variety and complexity in the living organisms. The variety and variability among living organisms is called as biodiversity.
C) Greenhouse effect: It is a phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a planet traps radiation emitted by the sun, caused by gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapour and methane that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but retain heat radiated back from the planet’s surface. It is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases and is re-radiated in all directions.
Greenhouse effect may leads to many serious environmental issues such as radiation, climate change, mansoon, directions and its efficiency and so on.
D) Global Warming : Global warming is the increase of Earth’s average surface temperature due to the effect of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide emissions from burning fossil fuels or from deforestation. Which trap heat that would otherwise escape from Earth.
E) Acid Rain : Acid rain is a broad term referring to a mixture of wet and dries deposition (deposited material) from the atmosphere containing higher than normal amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids. These acid rains are the result from both natural sources such as volcanoes and decaying vegetation and man-made sources, primarily emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) resulting from fossil fuel combustion.
F) Ozone Depletion : Reduction in the amount of Ozone (O3) in the stratosphere is called ozone depletion. It happens due to high levels of chlorine and bromine compounds in that layer.
As ozone depletes more ultraviolet (UV) radiation comes to earth and causes damages to all living organisms. UV radiation seems responsible for skin cancer and other skin complications.
![]()
Question 2.
Causes for soil or land pollution.
Answer:
Soil pollution is defined as “Unfavourable alteration of soil quality by disturbing the natural composition which decreased soil productivity.
Causes for Soil Pollution :
- Soil pollution or land degradation is primarily caused by soil erosion, in which the fertile upper surface of the land erode and land become barren. It happens due to deforestation, extensive cultivation, mining activities etc.
- Desertification is spreading due to over grazing, extensive use of poor soils, alkalization and salination of soil.
- Soil is also degrading because of excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides leads to acidification which changes chemical properties and destroy plants and agricultural sector on the whole.
- Filling of wastages and other disposals into the land also causes land degradation.
Question 3.
Types of natural resources with suitable examples. [A.P. Mar. 16]
Answer:
Natural resources are classified on the basis of their quantity, mutability and re¬usability. However, it would be convenient to classify the natural resources in the following general categories.

Natural Resources
1) Renewable Resources : The natural resources which cam be used permanently without depletion are called renewable resources. They are not exhaustible. They have the capacity to regenerate themselves, within a short period. Ex: Solar; wind, tidal etc.
2) Non-Renewable Resources : The natural resources which will exhaust by use are called as non-renewable resources. They cannot be regenerated. Once we exhaust these resources, they will not be available for use. Ex : Gold, silver, copper etc.
Question 4.
What is pollution ? Explain the types of pollution.
Answer:
Pollutant is a physical agent which is found more than the normal levels, changes the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of the resources that environment is supplying.
Types of Pollution : Pollution can be classified into various types among which air, water, soil, noise pollutions are important forms.
Air Pollution: The excessive concentration of contaminated substance in the air which adversely affects the well being of the individuals, living organs and property of all forms is called as air pollution.
Water Pollution : It is defined as the addition of some substance or factor present in water which degrades its quality. So that it becomes health hazard or unfit for use”.
Soil Pollution : Unfavourable alteration of soil quality by disturbing the natural composition which decreases soil productivity.
Noise Pollution : Any noise generated above 125 dl. B and produces harmful effects in environment and causes health hazards to human being is called noise pollution.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you mean by ”Sustainability” ? Explain the Components of Sustainability.
Answer:
Sustainability can also be defined as achievement of constant real consumption through time keeping the capital intact. A flow of consumption without reducing the capital is called sustainability.
There are three basic components of sustainable developments namely economic, social and environmental components. These three components are interdependent.
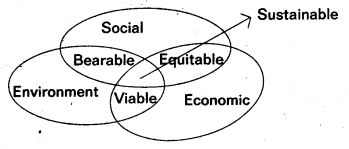
Economic Component: Economic components of sustainability require that societies pursue growth path that generate, optimum flow of income while maintaining the basic stock of man-made capital, human capital and natural capital.
Social Components : Social components of sustainability are built on the twin principles of justice and equity. For development path to be sustained, wealth, resources and oppo’rtunities should be equally shared. All citizens should have access to minimum standards of security, human rights and social benefits such as food, health, education and opportunities of self-development.
Environmental Components : Environment components of sustainability require sustainable resource use, efficient sink function and maintainance of natural capital. The environment should be able to perform its three functions efficiently and uninterrupted so that ecological stability and resilience are not affected.
Question 6.
Explain the effects of pollution on human health.
Answer:
Enviommental degradation has adverse effects on human health; which may lead to raise the labour absenteesism. Ill health causes to decrease the efficiency of labour which intum leads to low productivity.
i) Air Pollution: Air pollutants like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, particulate matter etc., attack human health through respiratory system. Diseases like bronchitis, lung cancer, eye irritation and skin irritation etc., are caused by air pollution.
ii) Water Pollution : Water is significant vehicle in transmission of diseases, various, disease – producing organisms such as viruses, bacteria and protozoa are transmitted through water. These organisms cause dysentery, typhoid, cholera and infectious hepatitis.
iii) Sound Pollution: Sound pollution affects human health in many ways. Loud noise causes disturbances in sleep and lead to different side effects. It leads to damage of hearing, interference with work tasks and speech, diversion of concentration, hypertension, tachycardia (fast heart beat) and irritation.
![]()
Question 7.
Measures for the conservation of forests. [A.P. Mar. 18, 17]
Answer:
Forests are the carbon sinks and treasures of scenic beauty. The following are some protective measures such important forests.
- Forest land should not be alloted to poor for house sites.
- Specific areas must be developed under social forestry programmes.
- Waste land must be brought under plantations.
- Forest must be protected from fires particularly in summer.
- Measures must be taken to refill the depleted forest area.
- Establishment of Joint Forest Management Communities is necessary.
- Cattle grazing and illegal cutting of trees should not be allowed.
- Local communities must be involved in the conservation of forests.
Question 8.
Need for environmental preservation.
Answer:
1) Moral persuasion, which is an appeal to reduce pollution in the broader interests of the society and making people involved in the environmental protection activities.
2) Methods of recycling should be made compulsory in which production units are restricted to maintain certain level of environmental quality or to install a specific treatment of pollutants.
3) Fiscal controlling techniques should be implemented such as
a) Levying of an affluent charge or pollution charge and revenue so collected should be redirected for the purpose of environmental protection.
b) Giving subsidies on pollution control equipment and encouragement of eco-friendly techniques of manufacturing.
c) Refundable deposit, which is collected from the polluters and refunded after his activities cease.
d) Pollution permits should be fixed and to see each production unit is functioning with in the limits.
e) Industrial permits should be linked with the maintenance of plantation in proportion to its production activity.
4) Government investment programmes such as waste treatment plants, slum clearance and management of wild like refugees, reforestration and afforestation are some policy instruments available to control pollution and preserve environmental equity.
5) As the children are the future citizens, awareness on environment and its protection should be introduced as a part of their curriculum. An effort is made by the government in this direction and now environmental education is mandatory part in education system from school level and onwards.
6) So far, government of India enacted some of the following acts for environmental protection.
a. The Wild life Protection Act, 1972.
b. The Water (prevention and control of pollution) Act, 1974 amended in 1978 and 1988.
c. The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
d. The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Rules, 1982.
e. The Forest (conservation) Act, 1980 amended in 1988.
f. The Environment (protection) Act, 1986.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Environment.
Answer:
The word environment is derived from French word environner which means to surround or encircle. Everything which surrounds us is collectively called as environment.
![]()
Question 2.
Ecosystem. [A.P. Mar. 16]
Answer:
The British ecologist A.G.Tansley coined the term Ecosystem in 1935. Eco system is the combination of natural and physical environment in a given geographical arc. It is two types. 1. Natural eco-system 2. Artificial eco-system.
Question 3.
Greenhouse effect. [A.P. Mar. 17]
Answer:
It is a phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a planet traps radiation emitted by the sun caused by gases such as CO2, water vapor and methane, that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but retain heat radiated back from the planet’s surface. It leads radiation climate changes etc.
Question 4.
Air Pollution.
Answer:
The excessive concentration of contaminated substance in the air which adversely affect the well being of the individuals, living organs and properly of all forms is called air pollution.
Question 5.
Water Pollution. [A.P. Mar. 18, 17]
Answer:
It is defined as “the addition of some substance or factor which degrades the quality of water, so that it becomes unfit for use”. The major pollutants that pollute water are, domestic wastes and sewage, slit etc.
Question 6.
Ozone Layer. [A.P. Mar 18, 17, 16]
Answer:
The Ozone layer is present in the stratosphere which is immediately above the troposphere at a height of 12 k.m from the earth. It is 40 k.m thick layer. Ozone absorbs the dangerous ultra violet rays from the sun and protects life on earth from death.
![]()
Question 7.
Global Warming.
Answer:
Global warming is the increase of Earth’s average surface temperature due to the effects of green house gases such as carbon dioxide emissions from burning fossil fuels or from deforestation, which trap heat that would otherwise escape from earth.
Question 8.
Sustainable Development [A.P. Mar. 18, 16]
Answer:
The process of development which sustains the human well being in future also.
Question 9.
Cost – benefit analysis of environment.
Answer:
Evaluation and comparison of capital and environmental costs of a project to estimate its relative merits and demerits. Every economic activity consists of both benefits as well as costs.
Question 10.
Reasons for Deforestation.
Answer:
Forests are deforestation due to various causes such as population growth, poverty and unemployment, fire wood, overgrazing, construction of danis, roads etc.
Question 11.
Biodiversity. [A.P. Mar. 18, 17]
Answer:
The word biodiversity was coined by Waiter Rosen in 1986. The variety and variability among living organisms is called as biodiversity or totality of genes species and ecosystems in a region.
![]()
Question 12.
What is “Noise”?
Answer:
A deep, loud and unpleasant sound which is undesirable and unwanted.
Question 13.
What is Land Degradation? .
Answer:
Land is a valuable resource wedepend for food, habitations and for all the basic necessities on land. The land is said to be degraded. Deforestation cultivation industrialisation, wind erosion, soil acidity are important sources for land degradation.
Question 14.
Environmental Externalities.
Answer:
An externality is a consequence of an economic activity that is experienced by unrelated third parties. It is either positive or negative. Whenever economic activity is held environmental externalities should be considered.
Question 15.
Swachh BharatAbhiyan. [A.P. Mar. 16]
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi communicated a quintessential message to the ration through his efforts, to educate people around him about cleanliness. He wished to see a ‘Clean India’. To work seriously towards this vision of Gandhiji, R M. Shri Narendra Modi – External website that opens Swachh Bharat in October 2, 2014. This mission seeks to achieve the goal.