AP State Syllabus 7th Class Social Important Questions 19th Lesson Livelihood and Struggles of Urban Workers
Question 1.
The details of workers in a paper mill are given in the table below. Study the table and answer the following questions.
| Nature of Employment | Nature of Work | Monthly Salary | Other Benefits | Number of Workers |
| Permanent | Technical work | 15,000 | Provident fund. Free medical facility, paid leave, Bonus | 1800 |
| Contractual | Unloading wood, packing and loading paper | 8,000 | Get work throughout the year. May become permanent worker after 3 years | 1000 |
| Casual | Cleaning the floors, Pasting labels on paper packets. | 2,500 | Nil | 500 |
a) How is the nature of the work of a permanent worker different from a contractual worker?
Answer:
The permanent worker is using his mental labour. But contract worker is using his physical labour.
b) How are contractual workers different from casual workers in terms of “Other benefits”?
Answer:
Contract labour job may or may not become permanent after 3 years.
But permanent worker enjoys all benefits along with the permanent job.
c) Why do you think a large number of workers in the mill are not permanent? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Skilled labour is need throughout the year. But unskilled labour is needed whenever the work is there. So companies appoint more labour temporarily why because if ‘ the worker is temporary in manner, there is no need to provide all facilities. This is the benefit to the owner.
![]()
Question 2.
Read the table and answer the following questions.
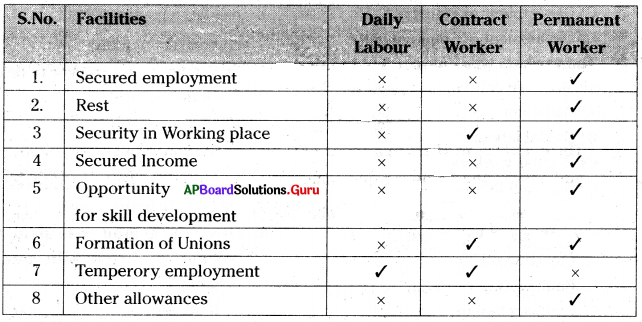
i) Write any two facilities of contract labour.
Answer:
- Security in working place.
- Formation of unions.
- Temporary employment.
ii) Which type of workers get paid holiday?
Answer:
Permanent workers.
iii) How can you. say the permanent worker get better facilities than oil…
Answer:
According to the above information maximum, all facilities are enjoyed by the permanent worker.
iv) What do you understand about daily labour?
Answer:
Daily labour enjoys only temporary employment if he did not do the work, not gaining any wage.
![]()
Question 3.
What rights and securities have the workers been fighting for?
Answer:
- Right to Productive and Safe Employment.
- Right to Leisure and Rest.
- Right to Employment Security.
- Income Security.
- Work Security.
- Skill Improvement.
- Collective Voice so that they can form unions to express their problems and needs.
Question 4.
Who are called regular workers and who are called contract or casual workers?
Answer:
Workers in the factories who are properly registered with the government and who are provided security and workers’ rights under the laws of the government are called regular workers.
Workers in factories, registered and unregistered with the government; and who are not provided security and worker’s rights and who have not been given basic needs of the workers are called casual or contract workers.
Question 5.
What are the benefits available to the permanent workers?
Answer:
- Their wages were fixed through agreements with the union.
- Medical facilities through employees State Insurance and Provident Fund are provided for the permanent workers.
- Health checkups in big private hospitals and leave in case workers become sick are provided for the workers.
- Educational allowance for their children, travelling allowance and conveyance allowance for the workers are given.
- Companies provide quarters for the workers to live in.
- They will be given loans when needed.
- The company also provide training for workers.
- Contract workers should be regularised after a definite period of work.
![]()
Question 6.
What is the difference between a permanent worker and a badli worker?
Answer:
Workers who are employed permanently, who are provided with regular and high wages and whose employment is secured, and who can enjoy all the facilities such as Provident Fund, Employees State Insurance and all types of allowances are called permanent workers.
Workers who are employed on a casual basis, who replaced permanent workers in their absence, are called badli workers. They get very little salary and very few benefits like Provident Fund and Health Insurance etc.,
Question 7.
Describe the process of making bricks.
Answer:
- Clay is to be prepared by mixing sand, clay and water.
- Clay is to be put in brick moulds.
- Once the clay is shaped into bricks, they are to be smoothened and the seal of the brick company is to be fixed on the bricks.
- They are allowed to dry and then loaded on bullock carts and taken to kilns for baking.
Question 8.
What kind of machines tools and sources of power are used in brick production?
Answer:
Any machines and tools are not used in brick making except the moulds to shape the clay into bricks. No power is used for making bricks. Only the muscle power of the workers is used for mixing the clay, shaping the clay into bricks by using moulds. In all levels of brick making, no machinery is used. For transport of the clay, sand and dried bricks to the kilns, bullock carts or tractors are used.
![]()
Question 9.
Describe a lot of brick workers.
Answer:
- The workers have to work for 14 to 16 hours a day.
- They are paid Rs. 108 per 1000 bricks. They normally manage to make about 1000 bricks a day.
- If they are ill they are not paid anything.
- Most of the days they don’t get proper feed to eat-they neither have the time nor the money for it.
- Their children don’t get any education.
- Though the government frees from their bonded labour they are forced to come back to the kilns since they don’t have any employment opportunities at their home.
- There are no trade unions that fight for their rights.
Question 10.
Read the following passage.
Over the last two hundred years, workers all over the world have fought to get these rights recognised even though they may not be implemented in all places. In most countries, the governments have agreed that these are the basic needs of workers and made laws that ensure workers these rights. Governments also have Labour Departments which have the responsibility to ensure that these laws are followed. If the laws are not followed workers can file cases in courts.
Now answer the following questions.
a. What did the workers all over the world fight for?
Answer:
To get their rights recognised
b. Are the rights of the workers being implemented everywhere?
Answer:
No. Not in all places
c. What are considered the basic needs by the governments?
Answer:
The rights of the workers are considered as basic needs by the governments.
d. What did the governments do?
Answer:
The governments made laws that ensure workers these rights.
e. Which department has the responsibility to ensure that their laws are followed?
Answer:
The labour department.
![]()
Question 11.
Read the following passage:
In our country, we find that many factories which are properly registered with the government often follow many of these laws. However even they try to give these rights only to some workers who are called the ‘Regular Workers’ of the factory and not to those called ‘casual’ or ‘contract workers’ who are employed irregularly. At the same time, there are many factories that are not properly registered with the government and the government does not supervise them.
Now answer the following questions.
a. Which factories follow the laws of the workers?
Answer:
Factories registered with the government.
b. Which workers have been given the rights of the workers?
Answer:
The regular workers.
c. What kind of workers have not been given the rights of the workers?
Answer:
Casual or contract workers.
d. Which type of factory is not supervised by the government?
Answer:
The factories are not properly registered with the government.
e. Which workers are employed irregularly?
Answer:
Casual or contract labour.
Question 12.
Read the following passage:
This company (not a real name) mixes and packs medicines for another big medicine company. It employed about 118 workers of whom about 104 workers were employed as daily casual workers. That is only 14 workers were regular and permanent and were used for the skilled work of mixing the chemicals to prepare the medicine powder. They were paid about Rs. 1500 to Rs 2500 per month and had security of employment. They also got ESI and PE The remaining 104 workers who were engaged on a daily basis mainly did the packaging and labelling of the medicine. About 56 of them were women. These daily workers were engaged by a labour contractor who was told every day by the manager how many workers to engage.
Now answer the following questions.
a. Which company is talked about in the above passage?
Answer:
A multinational medicine company.
b. How many workers work in the factory in total?
Answer:
118
c. How many workers are regular and permanent workers?
Answer:
Only 14 are permanent workers.
d. How many workers are skilled labour?
Answer:
Only 14
e. What are the benefits availed by the permanent workers?
Answer:
They get Rs. 2500/- as salary, they have the security of employment. They also get ESI, medical insurance and Provident Fund.
![]()
Question 13.
Read the given passage.
A Trade Union is an organisation formed by workers to protect their interests. If every single worker has to negotiate with the employer separately, they will not be in a strong position. However, if all of them negotiate, their position will become stronger. Trade Unions negotiate on behalf of all workers with the government and the employers. They seek to ensure proper wages, other benefits and decent working conditions for their members. Collectively with their member workers, they secure social security benefits, medical facilities, houses, Provident Fund and pension. If any worker is harassed or is in need of help, the Trade Union takes up his or her cause. Unions adopt a variety of measures like negotiations, filing cases in the law courts and even strikes or stoppage of work to pressurise the employers.
Now answer the following questions :
a. What is a trade union?
Answer:
An organisation formed by workers for protecting their rights.
b. What do the trade unions work for?
Answer:
Ensuring proper wages, other benefits and decent working conditions for its number.
c. What are the measures adopted by the trade unions to pressurise the employers?
Answer:
Negotiations, filing cases in the law courts and even strikes or stoppage of work to pressurise the employers.
d. What is it that conducts negotiations with the government and employers?
Answer:
The trade union.
e. What are the social security benefits the workers should get?
Answer:
Medical facilities, houses, provident fund and pension.
Question 14.
Read the following Passage.
In Andhra Pradesh and other states of India, towns and cities are becoming bigger and bigger. People are rapidly shifting from villages to these towns. But many of them do hot get sufficient regular employment there and are doing a variety of odd jobs. They sell vegetables or other items, make and sell snacks, work in tea stalls, or small factories, stitch clothes, load and unload in markets, work as domestic maids, etc.
Many of them produce goods at home – weavings clothes, papads, pickles, doing embroidery, etc. and are engaged through the putting-out system.
Now answer the following questions:
a. Why are towns and cities becoming bigger and bigger?
Answer:
Because people are rapidly shifting from village to village.
b. Why, do the people end up as casual workers in cities?
Answer:
Because in cities they do not get any regular jobs.
c. Write some jobs that come under the informal sector.
Answer:
Selling vegetables, making snacks and selling, working in tea stalls and small factories.
d. What is the system that the workers of the informal sector are engaged through?
Answer:
Putting out system.
e. Growth of cities leads to the growth of ……….. labour in cities.
Answer:
Casual
![]()
Question 15.
Here is a bar diagram. Based on the answer the questions below:
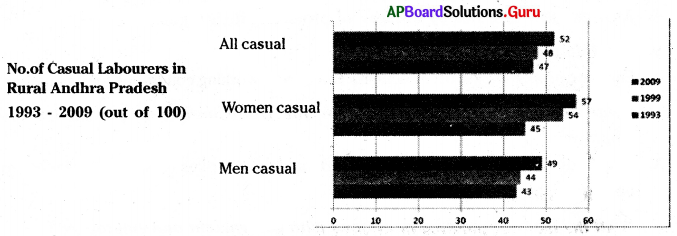
Fill in the blanks.
i) In 2009 of all the 100 people employed ………… were causal labourers.
(54,52,57,51)
Answer:
52
ii) In 1999 of all the 100 people employed ………….. were women, casual workers.
(52, 54, 57, 51)
Answer:
54
iii) In 1993 of all the 100 people employed ………….. were men casual workers
(47, 45, 43, 48)
Answer:
43
iv) The total number of women casual labourers increased faster than male casual labourers between ………….. (a. 1993 to 1999; b. 1999 to 2009)
Answer:
a. 1993 to 1999
Question 16.
Correct the false statement,
a. The total number of casual labourers in rural Andhra Pradesh has decreased from 1993 to 2009.
Answer:
The total number of casual labourers in rural Andhra Pradesh has increased from 1993 to 2009.
b. There are more women casual labourers than male casual labours during all three years.
Answer:
The statement is true.
![]()
Question 17.
Write a short note on how gender differences are making an impact on the labour market, drawing from previous chapters as well.
Answer:
Yes. Gender differences are making a great impact on the labour market. From the above bar diagram, it is proved. There are more women casual labourers than male casual labourers during all three years. It is because the female labourers are employed at cheaper rates than the male ones. Thus the gender differences are making a great impact on the labour market.
Question 18.
Below are three pie charts of working people in the entire Andhra Pradesh, rural and urban areas. Study them and answer the questions.
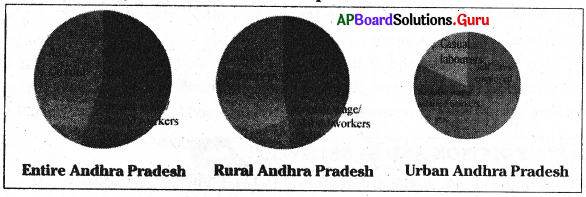
a. Of all the working persons in Andhra Pradesh 45% are …………….
(self-employed, salaried, casual labourers)
Answer:
Casual labourers.
b. Of all the rural working people in Andhra Pradesh 7% are …………….
(self-employed, salaried, casual labourers)
Answer:
Salaried
c. Of all the urban working people in Andhra Pradesh 37% are ……………
(self-employed, salaried, casual labourers)
Answer:
self-employed
d. There are more …………. in the rural area than urban area (self-employed, salaried casual labourers) but there are more ………… in an urban area than rural area (self-employed; salaried; casual labourers)
Answer:
casual labourers; regular salaried workers.
e. More than half of the rural population are …………. (self-employed, salaried, casual labourers)
Answer:
casual labourers
![]()
Question 19.
Write a short note on the differences in the rural and urban contexts of employment conditions.
Answer:
a) While casual labourers are more than half of the rural population, in urban areas only 18% of casual labourers are there.
b) Whole self-employed people occupy 41% of the rural population 37% of the working persons in urban areas are self-employed.
c) While 7% of the rural working persons are regular waged / salaried workers, but in urban areas regular waged / salaried workers occupy 45% of the urban working people.
d) In urban areas skilled employment in the organised sector than in the rural areas.
e) In rural areas unskilled employment in the unorganised primary sector is more than in urban areas.
Question 20.
Why do you think people migrate for work in other distant states?
Answer:
In their own place, people may have a small plot of land, with which they cannot get on. They are in debt and on the verge of selling their land. They don’t get regular employment in their villages. Because of the closing down of the factories and mills, the workers of these factories migrate to cities and join the ranks of casual workers.
![]()
Question 21.
Which of the seven rights are available to brick kiln workers like Bandhani?
Answer:
- Right to productive and Safe Employment: Though the brick kiln workers’ employment is productive, their employment is not safe.
- Right to Leisure and Rest: They don’t have any Leisure and time to rest. They have to work for 14 to 16 hours a day.
- Right to Employment Security: No. Their employment is not at all called employment in legal terms. It is called a bonded labour. Moreover, it is seasonable employment.
- Income Security: The kiln workers do not have an adequate and regular income for taking care of the needs of their families and savings for living a dignified life in their old age.
- Work Security: If they fall ill or meet with an accident they won’t get proper care and won’t get paid for the period of illness.
- Skill Improvement: It is not a job in which skill is needed.
- Collective voice: There are not trading unions that fight for their rights as they are migrant workers and spread out in a number of sites.