Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 2nd Lesson Business Activities Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Commerce Study Material 2nd Lesson Business Activities
Essay Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by Industry? Explain various types of industries with suitable. [Mar. 2019, 18 – T.S. Mar. 16 – A.P.]
Answer:
Industry – Meaning :
Industry is concerned with the production of goods and services. Industry is involved to convert raw materials into finished goods. It creates form utility to goods.
Classification of Industries :
Industries can be classified into various types. They are
- Primary industry
- Genetic industry
- Extractive industry
- Manufacturing industry
- Construction industry
- Service industry
1) Primary Industry :
Primary industry is concerned with the production of goods with the help of nature. E.g : Agriculture, Farming, Fishing, Horticulture, etc.
2) Genetic industry :
This industry is concerned with the breeding of plants or animals, which are used in reproduction. E.g. : Poultry forms,’ Cattle breeding farms, Fish hatcheries, etc.
3) Extractive Industry :
This is concerned with extraction or drawing out goods from the soil, air or water. Generally products of extractive industries come in raw material, they are used for manufacturing and construction industries for produc¬ing finished products. E.g. : Mining, Fishing, Coal, Mineral, Iron ore, Oil industry, Timber, Rubber from forests, etc.
4) Manufacturing Industry :
This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw materials into semi-finished or finished goods. E.g.: Cotton Textiles, Sugar, Cement, etc.
Manufacturing industries are also sub-divided into four types. They are given below:
i) Analytical Industry :
In an analytical industry the basic raw material is broken into several useful materials. E.g.: Oil refinery. Crude oil is refined and several petroleum products are obtained.
ii) Synthetic Industry:
In this type of manufacturing industry two or more materials are mixed to form a new product. E.g. : Cosmetics, Soaps, Fertilizers, Paint industry etc.
iii) Processing Industry :
In this industry material is processed through various stages.
E.g.: The textile industry. Cotton passes through the spinning, weaving, dyeing, bleaching and printing processes.
iv) Assembling Industry :
In this type of industry, manufactured components or parts are combined together mechanically or chemically to produce a new product.
E.g.: Manufacturing of TV sets, and automobiles industries.
5) Construction Industry :
This industry is concerned with the construction and erection.
E.g.: Construction of Buildings, Roads, Dams, Bridges, and Canals.
6) Service industry:
These type of industries are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community. Service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation. E.g.: Hotels, Tourism, Entertainment industry, etc.
Question 2.
What is Commerce? Describe the various branches of Commerce.
Answer:
Commerce – Meaning:
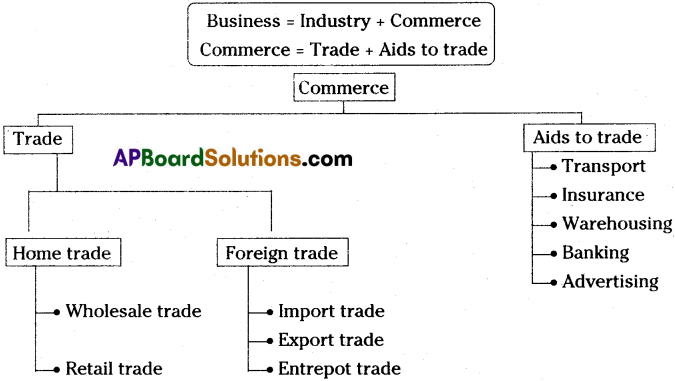
Commerce is the part of business. It deals with the buying and selling of goods. Commerce is concerned only with the exchange of goods. It includes all those activities which are related to the transfer of goods from production place to the consumption place. Commerce includes trade and aids to trades. Trade means buying and selling of goods. Aids to trade include transport, banking, insurance, warehousing, etc.
(Commerce = Trade + Aids to Trade )
Commerce – Definition:
“Commerce is an organized system for the exchange of goods between the members of the industrial world.” – James Stephenson
Branches of Commerce :
Commerce is divided into two branches. They are :
- Trade
- Aids to trade
1) Trade:
Trade is branch of commerce. It means purchase and sale of goods with profit motive. It involves exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers. Trade may be classified into two types, i) Home trade ii) Foreign trade
i) Home trade :
This is also known as inland trade or internal trade. Purchase and sale of goods with profit motive within the boundaries of the country is called internal trade.
Home trade is also divided into two types. They are :
- Wholesale trade
- Retail trade
1) Wholesale trade :
It implies buying and selling of goods in large quantities. Traders who engage themselves in wholesale trade are called “Wholesalers”. Wholesale serves as a connecting link between the producers and retailers.
2) Retail trade :
It involves buying and selling in small quantities. Traders engaged in retail trade are called “Retailers”. They serve as a connecting link between the wholesalers and consumers. Retail trade is the final stage of distribution.
ii) Foreign trade:
It refers to buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries, it is called foreign trade. In other words, the trade beyond the boundaries of the country is known as foreign trade.
Foreign trade is also known as “External trade” and “International trade”. Foreign trade may be classified into three types. They are
i) Export trade
ii) Import trade
iii) Entrepot trade
i) Export trade:
When domestic goods are sold to the other country it is called export trade. Selling and sending goods by Indian firms to other firms located outside India.
ii) Import trade :
In this type of trade, wherein goods are purchased from foreign countries. Purchasing goods by an Indian trader from a trader of the USA, the. UK, Japan, etc., is an example for import trade.
iii) Entrepot trade :
When the goods imported from one country are exported to an other country, it is known as entreport or re-export trade. E.g.: Oil import from Iraq by an Indian firm and export the same to Nepal, is called entrepot trade.
2) Aids to Trade :
Commercet is the sum total of those processes, which are engaged in the removal of hindrance of persons, place and time in the exchange of commodities, it is called Aids to trade.
Aids to trade is also called “Auxiliaries to trade.” Aids to trade include Transport, Communication, Warehousing, Banking, Insurance, Advertising.
i) Transport :
It means for the movement of commodities from one place to another place. The development of road, rail, air and water transport allows to move commodities all over the world. They create place utility to goods. Transport is broadly classified into three types – Land transport, Water transport, Air transport.
ii) Insurance :
Insurance reduces the problem of risks. Business is subject to risks and uncertainties. These are inevitable in the field of business. Risks may be due to fire, theft, accident or any other natural calamity. Insurance plays a vital role in removing risks. Insurance tries to reduce risks by spreading them out over a larger number of people.
iii) Warehousing :
There is a time gap between production and consumption. In other words, goods which are produced at one time, are not consumed at the same time. Hence it becomes necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing. Warehousing creates time utility and removes the hindrances of time.
iv) Banking :
Banking solves the problem of finance. Businessmen receive money and also pay money in large amounts. It is risky to carry large amount to cash from one place to another. Here comes banking as a solution. Banking and financial institutions solve the problem of payment and facilitate exchange between buyer and seller. Banks provide many services like accepting deposits, advance loans, agency services, overdraft facilities, etc.
v) Advertising :
Advertising means giving publicity regarding goods or services which are offered to the public for sale. It is intended to retain the existing market. Advertising creates mass market for the product. Advertisements can be made through different media.” E.g. : Newspaper, Magazines, Television, Radio, Outdoor publicity, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Define trade explain the various types of aids to trade.
Answer:
Trade :
Trade is branch of commerce. It means purchase and sale of goods with profit motive. It involves exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers.
Trade may be classified into two types.
- Home trade
- Foreign trade
1) Home trade :
This is also known as inland trade or internal trade. Purchase and sale of goods with profit motive within the boundaries of the country is called internal trade. Home trade is also divided into two types. They are :
i) Wholesale trade
ii) Retail trade
i) Wholesale trade :
It implies buying and selling of goods in large quantities. Traders who engage themselves in wholesale trade are called “Wholesalers”. Wholesale serves as a connecting link between the producers and retailers.
ii) Retail trade :
It involves buying and selling in small quantities. Traders engaged in retail trade are called “Retailers”. They serve as a connecting link between the wholesalers and consumers. Retail trade is the final stage of distribution.
2) Foreign trade :
It refers to buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries, it is called foreign trade. In other words, the trade beyond the boundaries of the country is known as foreign trade.
Foreign trade is also known as “External trade” and “International trade”. Foreign trade may be classified into three types. They are
i) Export trade
ii) Import trade
iii) Entrepot trade
i) Export trade :
When domestic goods are sold to the other country it is called export trade. Selling and sending goods by indian firms to other firms located outside india.
ii) Import trade :
In this type trade, wherein goods are purchased from foreign countries. Purchasing goods by an Indian trader from a trader of the USA, the UK, Japan, etc. is an example for import trade.
iii) Entrepot trade :
When the goods imported from one countiy are exported to an other country, it is known as entrepot or re-export trade. E.g.: Oil import from Iraq by an Indian firm and export the same to Nepal, is called entrepot trade.
Aids to trade :
Commerce is the sum total of those process, which are engaged in the removal of hindrance of persons, place and time in the exchange of commodities, it is called Aids to trade.
Aids to trade is also called “Auxiliaries to trade.” Aids to trade include, Transport, Communication, Warehousing, Banking, Insurance, Advertising.
i) Transport:
It means for the movement of commodities from one place to another place. The development of road, rail, air and water transport allows to move commodities all over the world. They create place utility to goods. Transport is broadly classified into three types – Land transport, Water transport, Air transport.
ii) Insurance:
Insurance reduces the problem of risks. Business is subject to risks and uncertainties. These are inevitable in the field of business. Risks may be due to fire, theft, accident or any other natural calamity. Insurance plays a vital role in removing risks. Insurance tries to reduce risks by spreading them out over a larger number of people.
iii) Warehousing :
There is a time gap between production and consumption. In other words, goods, which are produced at one time, are not consumed at the same time. Hence it becomes necessary to make arrangements for storage or warehousing. Warehousing creates time utility and removes the hindrances of time.
iv) Banking :
Banking solves the problem of finance. Businessmen receive money and also pay money in large amounts. It is risky to carry large amount to cash from one place to another. Here comes banking as a solution. Banking and financial institutions solve the problem of payment and facilitate exchange between buyer and seller. Banks provide many services like accepting deposits, advance loans, agency services, overdraft facilities, etc.
v) Advertising :
Advertising means giving publicity regarding goods or services which are offered to the public for sale. It is intended to retain the existing market. Advertising creates mass market for the product. Advertisements can be made through different media.
E.g.: Newspaper, Magazines, Television, Radio, Outdoor publicity, etc.
Question 4.
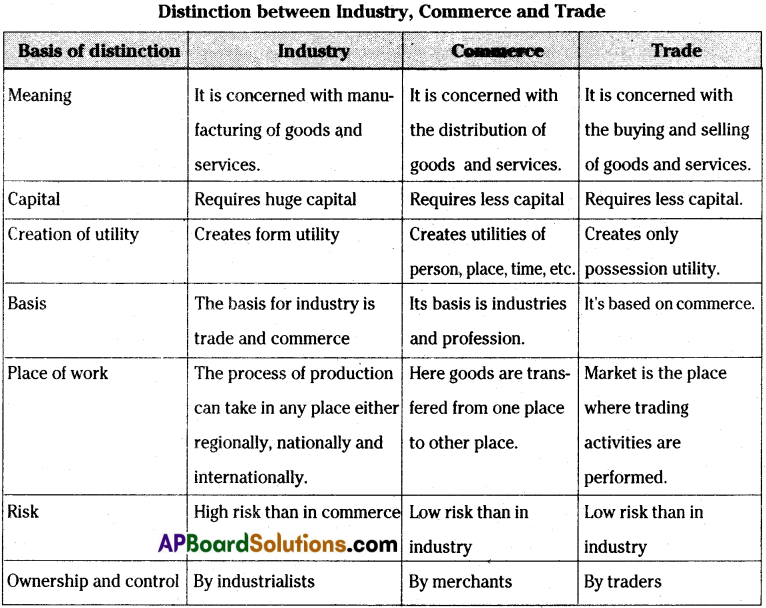
Explain the inter-relationship between Trade, Commerce and Industry, and also state differences between them.
Answer:
Inter-relationship between Industry, Trade and Commerce :
Business:
Business deals with production or purchase and sale of goods and services undertaken with the object of earning profit and acquiring wealth, through the satisfaction of human wants. .
Industry :
Industry deals with production of goods and services.
Commerce :
Commerce deals with distribution or exchange of goods and services.
Trade :
Trade deals with the buying and selling of goods and services.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define industry.
Answer:
Industry – Meaning :
Industry is concerned with the production of goods and services. Industry is involved to convert raw materials into finished goods. It creates form utility to goods.
Industry is a business activity which is related to the extracting, producing, processing or manufacturing of goods.
The goods may be consumer goods or producer goods. Consumer goods are the goods, which are used finally by consumers, e.g., Food grains, textiles, cosmetics, VCR, etc. Producer’s goods are the goods used by manufacturers for producing some other goods. E.g. Machinery, tools, equipment, etc.
Question 2.
What do you understand by commerce?
Answer:
Commerce is the part of business. It deals with buying and selling of goods and services and includes all those activities which directly or indirectly facilitate that exchange.
Commerce includes trade and aids to trade i.e. deals with the distribution aspect of the business. Whatever is produced it must be consumed, to facilitate this consumption there must be a proper distribution channel. Here comes the need for commerce which is concerned with the smooth buying and selling of goods and services.
Commerce is a very wide term. It involves the process of bringing goods from the place of production to the place of consumption. In other words, it supplies goods to ultimate consumers. Thus commerce in the sum total of those processes, which are engaged in the removal of hindrances of persons as place, time in the exchange of commodities. Importance of commerce :
- Commerce helps to increase our standard of living.
- Commerce links producers and consumers.
- Commerce generates employment opportunities.
- Commerce increases national income and wealth.
- Commerce encourages international trade.
COMMERCE = TRADE + AIDS TO TRADE”
![]()
Question 3.
What is trade?
Answer:
Trade :
Trade means purchase and sale of goods with profit motive. It involves exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers. Trade is a branch of commerce. It connects buying and selling activities. An individual who does trade is called a trader. Trader transfers the goods from the producer to the consumer. He earns profit from this activity.
Trade may be classified into (a) home trade (b) foreign trade.
Question 4.
State the types of foreign trade.
Answer:
Foreign trade :
It refers to buying and selling of goods and services between two or more countries through international airports and sea ports. Foreign trade is also known as ‘External Trade’ or ‘International Trade’.
Foreign trade may be classified into three types. They are :
- Import trade
- Export trade
- Entrepot trade
1) Import trade :
In this type of trade, wherein goods are purchased from foreign countries. Purchasing goods by an Indian firm from a trader of the USA, the UK, Japan, etc. is an example for import trade.
2) Export trade :
When domestic goods are sold to the other country it is called export trade. Selling and sending goods by Indian firms to other firms located outside India.
3) Entrepot trade :
When the goods imported from one country are exported to an other country, it is known as entrepot trade or re-export trade.
E.g.: Electronic goods are imported from Singapore and the same are exported to Bangladesh.
Question 5.
Explain the classification of industries.
Answer:
Classification of Industries : Industries can be classified into various types. They are
- Primary industry
- Genetic industry
- Extractive industry
- Manufacturing industry
- Construction industry
- Service industry
1) Primary industry :
It is concerned with the production of goods with the help of nature. E.g : Agriculture, Farming, Horticulture, etc.
2) Genetic industry :
This industry is concerned with the breeding of plants or animals, which are used in reproduction.
E.g. : Poultry forms, Cattle breeding farms, Fish hatcheries, etc.
3) Extractive industry :
This is concerned with extraction or drawing out goods from the soil, air or water. Generally products of extractive industries come in raw material, they are used for manufacturing and construction industries for producing finished products.
E.g. : Mining, Fishing, Coal, Mineral, Iron ore, Oil industry, Timber, Rubber from forests, etc.
4) Manufacturing Industry:
This industry is engaged in the conversion of raw materials into semi-finished or finished goods. E.g.: Cotton Textiles, Sugar, Cement, etc.
Manufacturing industries are also sub-divided into four types. They are given below :
i) Analytical Industry :
In an analytical industry the basic raw material is broken into several useful materials. E.g.: Oil refinery. Crude oil is refined and several petroleum products are obtained.
ii) Synthetic Industry:
In this type of manufacturing industry two or more materials are mixed to form a new product. E.g. : Cosmetics, Soaps, Fertilizers, Paint industry, etc.
iii) Processing Industry:
In this industry material is processed through various stages. E.g.: The textile industry. Cotton passes through the spinning, weaving, dyeing, bleaching, and printing processes.
iv) Assembling Industry:
In this type of industry, manufactured components or parts are combined together mechanically or chemically to produce a new product. E.g.: Manufacturing of TV sets, and automobiles industries.
5) Construction Industry:
This industry is concerned with the construction and erection. E.g.: Construction of Buildings, Roads, Dams, Bridges, and Canals.
6) Service industry:
These type of industries are engaged in the provision of essential services to the community. Service sector plays an important role in the development of the nation. E.g.: Hotels, Tourism, Entertainment industry, etc.
Question 6.
Define entrepot trade.
Answer:
Entrepot trade :
It means importing (buying) goods from one country for the purpose of exporting (selling) them to another country. This type of trade is also known as re-export trade.
Entrepot trade refers to a trade in one centre for the goods of other countries. Merchandise can be imported and exported without paying import duties in entrepot trade. Because of favorable trade conditions, profit is possible in entrepot trade.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the hindrances involved in commerce?
Answer:
Commerce is an organised system which facilitates free flow of goods and services. In busi¬ness, products and services are produced through industry. The produced goods and ser¬vices face various types of hindrances to reach the customers. Commerce removes all these hindrances and helps to distribute products and reach business desired goal.
| Hindrances | Removed By |
| Persons | Trade |
| Place | Transportation |
| Time | Warehousing |
| Finance | Banking |
| Risk | insurance |
| Promotion | Advertisement |
| Information | Communication |
Following are some important hindrances in commerce :
- Hindrance of person
- Hindrance of place
- Hindrance of exchage
- Hindrance of time and duration
- Hindrance of knowledge
1) Hindrance of person :
Trade treaty is done by buyers and sellers. In exchange of money, the sellers sell the value of the goods and services to the buyers. Therefore through the handover of products personal hindrances can be removed.
2) Hindrance of place :
The goods are produced at one place but their consumption in different places. The hindrance of distance is removed by various means of transport such as rail, road, air, and sea. Transport helps in removing the hindrance of place. It creates place utility.
3) Hindrance of exchange :
The payment of goods and services is generally made possible through banks. Bank as a part of commerce, acts to remove the hindrance of exchange. Bank helps in removing the hindrance of exchange.
4) Hindrance of time and duration :
There is a time gap between production and consumption. The goods produced are not immediately required for consumption. Warehousing removes the hindrances of time and duration. It preserves the goods from the time of production to the time of consumption. It creates time utility.
5) Hindrance of risk :
Business involves risk. Risk is involved in transporting goods from one place to another place. There can be a risk due to fire, theft, accident, etc. The risk of loss will removed by insurance. Insurance helps in the removal of hindrance of risk.
6) Hindrance of knowledge :
Advertisement removes the hindrance of knowledge. It informs to the customers about the availability of various products. Communication helps in the efficient operation of commercial activities. The hindrances of knowledge will be removed by advertisements.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Industry tf
Answer:
Basically industry is concerned with manufacturing of goods and services. Industry deals with extractive, genetic, manufacturing, construction, and service type industries.
Question 2.
Commerce.
Answer:
It deals with buying and selling of goods. Commerce is concerned only with the exchange of goods and services.
(Commerce = Trade + Aids to Trade)
Question 3.
Trade
Answer:
Trade is the central activity of commerce. Trade means purchase and sale of goods with profit motive. It involves exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers.
Question 4.
Home trade
Answer:
Purchase and sale of goods with profit motive within the boundaries of the country is called home trade. It is also known as Inland trade or Internal trade.
![]()
Question 5.
Entrepot trade.
Answer:
It is one of types of the foreign trade. When goods are imported from one country and the same are exported to another country such trade is called entrepot trade.
E.g.: Electronic goods are imported from Taiwan and same are exported to Nepal.
Question 6.
Transportation
Answer:
There is a vast distance between centers of production and centers of consumption. This difficulty is removed by transport. Transportation creates place utility.
Question 7.
Warehousing
Answer:
It is very important function of commerce. It involves storage or accumulation of goods for the purpose of equalizing supplies over a period of time. So, it creates time utility.
Question 8.
Genetic industries
Answer:
These industries are concerned with the breeding of plants or animals, which are used in reproduction. Eg : Poultry farms, etc.
Question 9.
Extractive industries
Answer:
These are concerned with extraction or drawing out goods from the soil, air or water. Eg : Mining, Fishing, Coal, Minerals, Iron ore, Oil industries, etc.
Question 10.
Banking
Answer:
Banking is one of the aids to trade. It solves the problem of finance. Businessmen receive money and also pay money in large amounts. It is risky to carry money from one place to another place. Here comes banking as a solution.
Question 11.
Ana lytica l industry
Answer:
In an analytical industry the basic raw material is broken into several useful materials. E.g.: Oil refinery. Crude oil is refined and several petroleum products are obtained.
Question 12.
Synthetic Industry
Answer:
In this type of manufacturing industry two or more materials are mixed to form a new product. E.g.: Cosmetics, Soaps, Fertilizers, Paint industry, etc.
Question 13.
Processing industry
Answer:
In the industry material is processed through various stages. E.g.: The textile industry. Cotton passes through the spinning, weaving, dyeing, bleaching and printing processes.
![]()
Question 14.
Assembling industry
Answer:
In this type of industry, manufactured components or parts are combined together mechanically or chemically to produce a new product.
E.g.: Manufacting of TV sets and automobile industries.