Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 12th Lesson Final Accounts Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 1st Year Accountancy Study Material 12th Lesson Final Accounts
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
List out advantages of Final accounts.
Answer:
List out advantages of Final accounts :
- To know the profit or loss: Business profit or loss can be known to the trader through the trading account and profit and loss account.
- Financial position: Balance sheet reflects the financial position of the organization.
- Financial planning : Final accounts are important source of finance information which helps the management to plan the financial activities of the business concern.
- Decision making: Financial statements of current year can be compared with results of the previous year statements, which helps the trader to take business decisions.
- To pay the taxes: Final accounts help in completion of tax.
- To borrow money : Final accounts reveal the solvency position of the organization. This helps to take loan from banks.
Question 2.
Explain the capital and revenue expenditures and incomes with examples.
Answer:
Capital and Revenue Expenditures: Business expenditure of an enterprise are of three kinds as :
1. Capital Expenditure,
2. Revenue Expenditure,
3. Deferred Revenue Expenditure.
1) Capital Expenditure : It is the expenditure which is normally incurred for acquiring fixed assets or assets which increase the earning capacity of the business. Benefits of this expenditure are extended over a number of years. E.g.: Purchase of furniture, Machinery, Buildings, etc.
2) Revenue Expenditure : It is the expenditure incurred in the normal course of business activities. The benefit of this expenditure is restricted to only one accounting year.
E.g.: Rent, Salaries, Selling expenses.
3) Deferred Expenditure : It consists of revenue and capital items. Benefits from these expenses are spread over several years.
E.g.: Huge amount of expenditure on advertisement.
Capital and Revenue Incomes: The business incomes are of three kinds as :
1. Capital Income,
2. Revenue Income and
3. Deferred Income.
1) Capital Income: Any amount received as investment by the owners, raised by way of loans and incomes received on sale of fixed assets is called capital income.
E.g.: Capital, Sale of machinery, etc.
2) Revenue Income: It means an income which arise, during normal course of regular business transactions. E.g.: Commission received, Sale of goods, etc.
3) Deferred Income : This consists of items of revenue and capital nature and spread over several years. E.g.: Rent or Interest received for more than a year.
![]()
Question 3.
Draw an imaginary Balance Sheet Pro forma.
Answer:
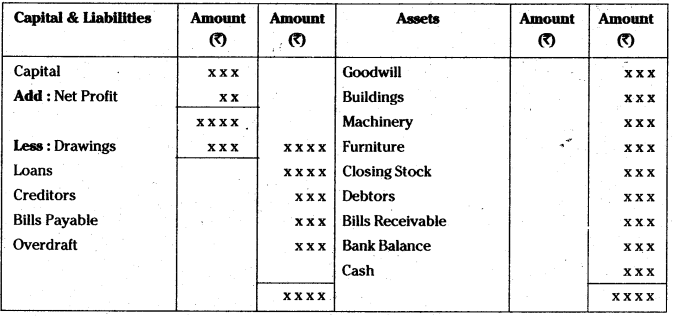
Balance sheet may be prepared in any one of the following orders.
- Liquidity order
- Permanency order
Proforma of Balance sheet on the basis of Liquidity order:
Balance sheet of ____ as on _____
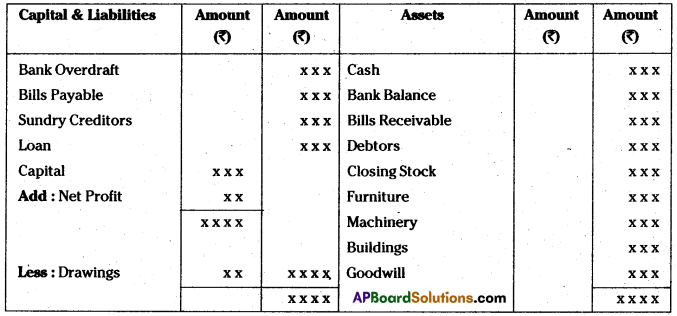
Balance sheet on the order of Permanency: Balance sheet of ____ as on ____
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the meaning and uses of final accounts.
Answer:
Final accounts (Final statements) are the statements that are prepared at the end of an accounting period. These consist of trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Uses:
- To know the profit or loss at the end of a particular period.
- To know the financial position of the organization.
- It helps to plan the financial activities of business concern.
- It helps to take business decision.
- With the help of financial statements business concerns can get the loans from the banks.
Question 2.
Explain the meaning and advantages of trading account.
Answer:
An account is to be prepared to know the results of trading activities carries during the accounting period. This account is termed as Trading Account.
Advantages:
- It reveals either gross profit or gross loss
- Gross profit / loss ratio can be calculated
- Trading expenses and incomes of the current year can be compared with that of previous year.
- The trader can estimate his trade revenue for future years.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the meaning and importance of profit and loss account.
Answer:
After trading account, the Profit & Loss a/c is to be prepared to find out the net profit or net loss of the business. It is a nominal account. Hence all the expenses and losses should be debited and all the incomes and gains to be credited to this account.
Importance of Profit & Loss Account
- It reveals net profit or net loss.
- Net profit ratio can be calculated.
- Current year’s administrative, selling and other expenses can be compared with the previous year’s amounts.
- It facilitates for the preparation of balance sheet.
Question 4.
Explain the following with examples:
a) Current Assets
b) Current Liabilities
Answer:
a) Current Assets : The assets which are held for resale or can be converted into cash on a later date are called current assets. E.g.: Stock, Debtors, Bills receivable, etc.
b) Current Liabilities : These liabilities payable by the organization within one accounting period (short term liabilities) not more than 12 months from the date of balance sheet E.g.: Bills payable, Trade creditors, Bank overdraft, etc.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define capital expenditure and give two examples.
Answer:
Capital expenditure is the expenditure which is normally incurred for acquiring fixed assets or assets which increase the earning capacity of the business. Benefits of capital expenditure are extended over a number of years. E.g,: Purchase of fixed assets like furniture, Machinery and Buildings.
Question 2.
Define revenue expenditure with two examples. (Mar. ’17 – A.P.)
Answer:
Revenue expenditure means an expenditure incurred in the normal course of business activities. The benefit of revenue expenditure is restricted to only one accounting year.
E.g.: Office expenses like rent, Salaries, etc.
Question 3.
Define capital income and give two examples. (Mar. 2019, 15 – A.P.)
Answer:
Any amount received as investments by the owners, raised by way of loans and income received on sale of fixed assets is called capital income. E.g.: Capital, Sale of machinery, etc.
Question 4.
Explain the terms tangible and intangible assets with examples.
Answer:
Assets which can be seen and touch are called tangible assets E.g.: Furniture, Machinery, etc. Assets which can neither be seen nor touched are called intangible assets. E.g.: Patents, Good will etc.
Question 5.
Define the term drawings. (Mar. 2019 – T.S.)
Answer:
Drawings may be defined as the amount withdrawn by the proprietor from the business either in cash or in kind for personal use. Drawings should be deducted from capital in the balance sheet on liabilities side.
Problems
Question 1.
Prepare trading account of Srikanth Traders for the year ended 31.12.2013.
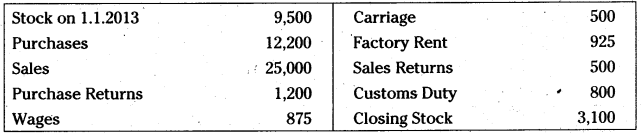
Answer:
Dr. Tracing Account of Srikanth Traders for the year ended 31.12.2013
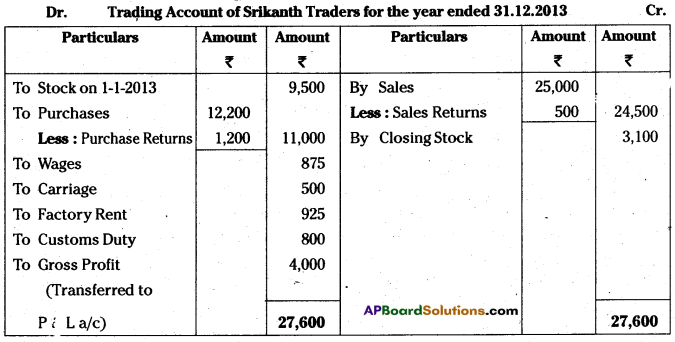
Question 2.
Prepare trading account from the following particulars for the year ended 31.03.2014:
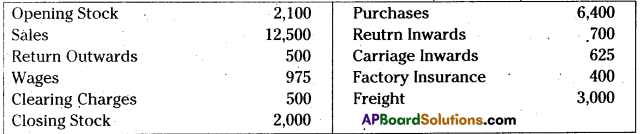
Answer:
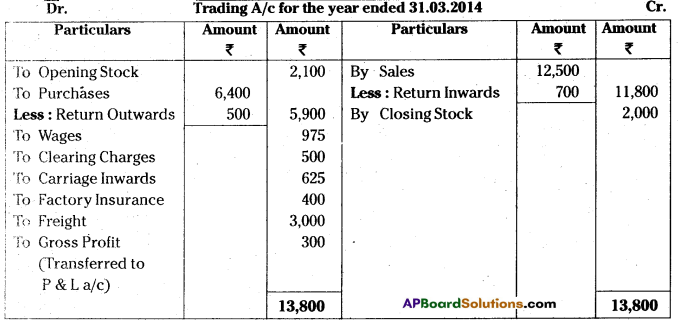
![]()
Question 3.
Prepare trading account.
Purchases
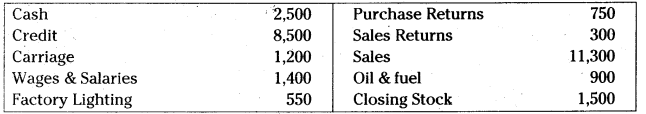
Answer:
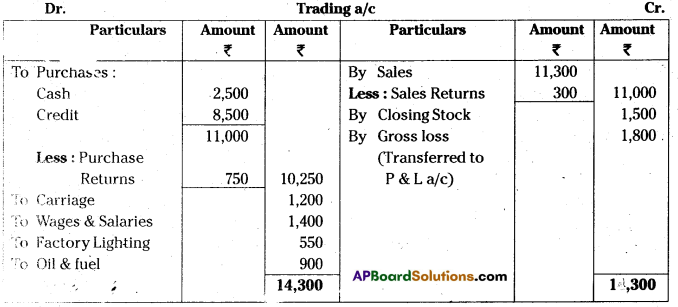
Question 4.
Prepare trading account of Hyderabad Traders as on 31.12.2012:
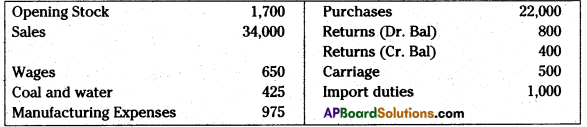
Answer:
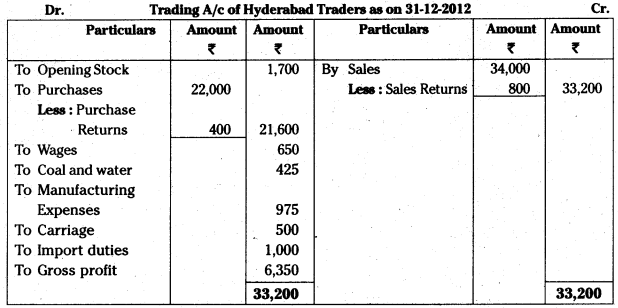
Question 5.
From the following particulars, prepare Profit & Loss A/c as on 31.12.2013:
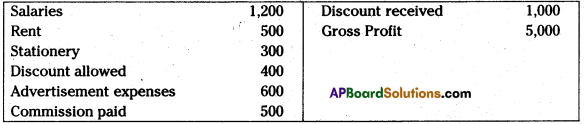
Answer:
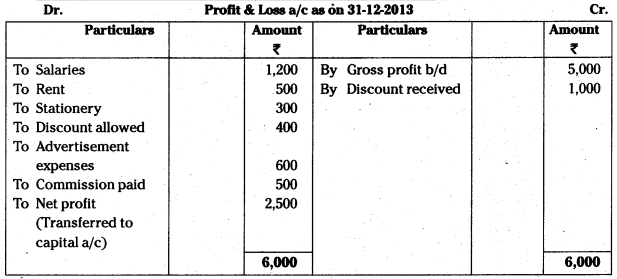
Question 6.
Prepare Profit & Loss A/c from the following particulars:
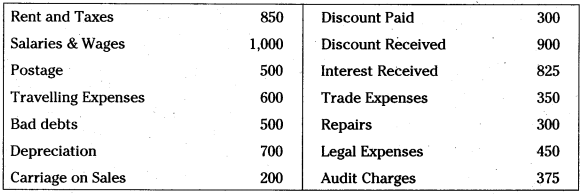
Answer:
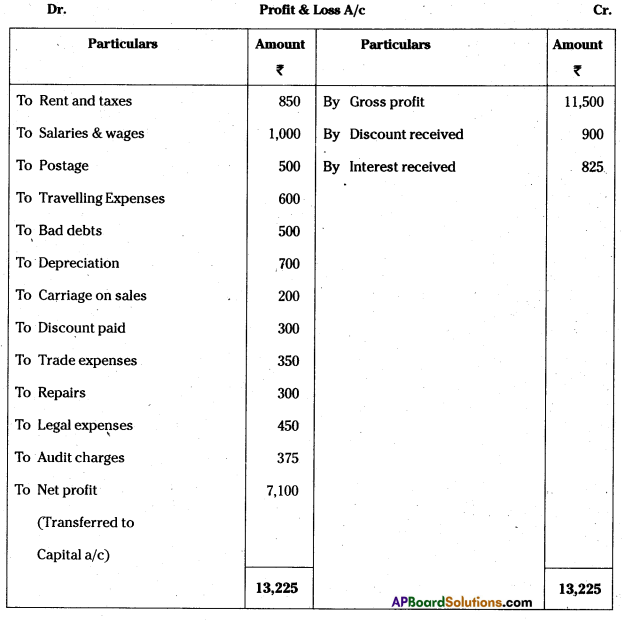
Question 7.
From the following Particulars, prepare Profit & Loss A/c.
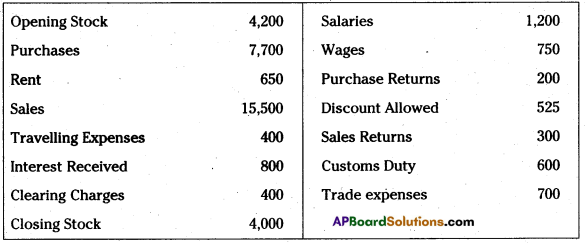
Answer:
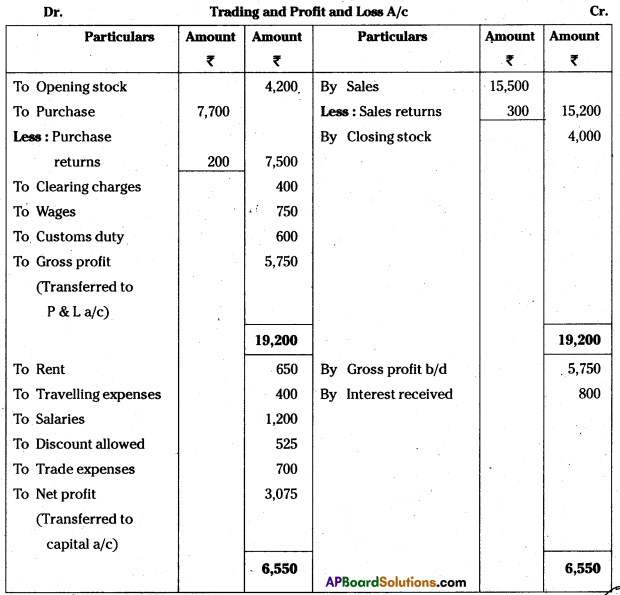
Question 8.
Prepare Trading A/c, Profit & Loss A/c of Suresh Traders for the year ending 31.12.2012.
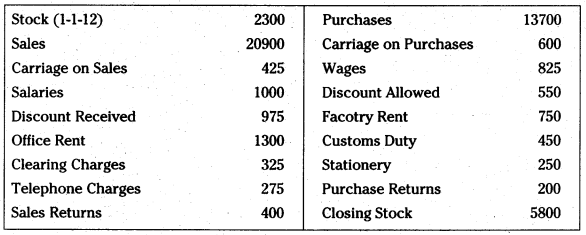
Answer:
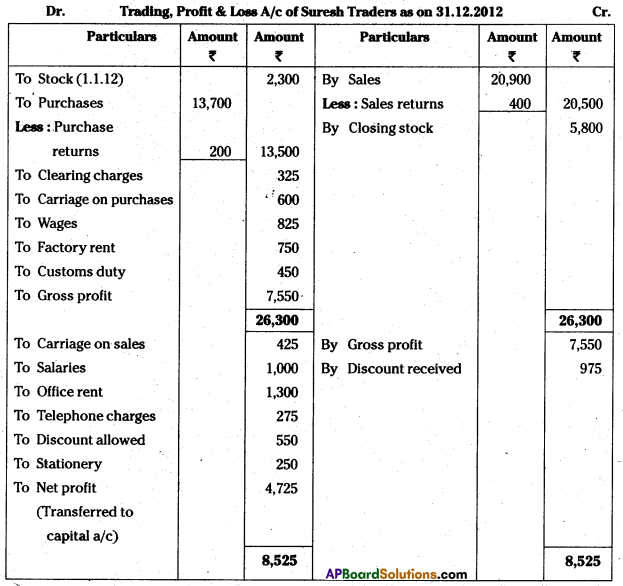
Question 9.
From the following trial balance, prepare Trading A/c, Profit & Loss A/c for the year ended 31.12.2013:
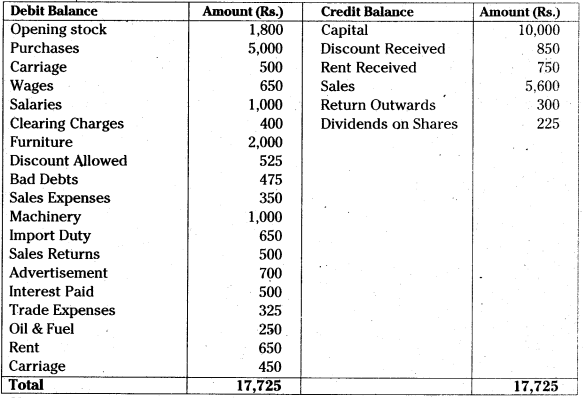
Answer:
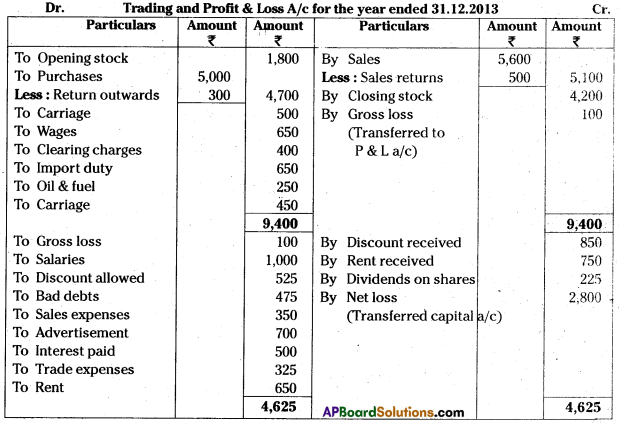
Question 10.
Prepare Trading account and Profit & Loss A/c. (amounts in rupees)
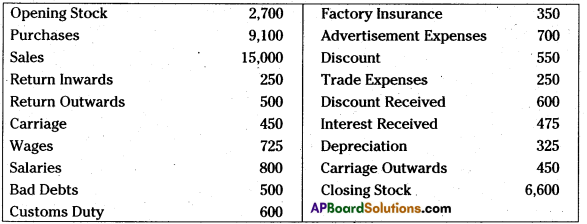
Answer:
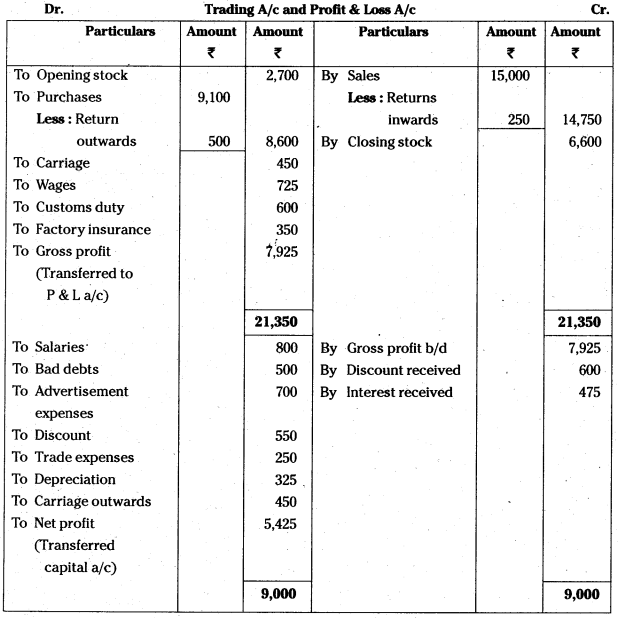
![]()
Question 11.
Prepare Balance sheet from the following;
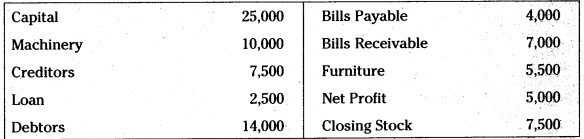
Answer:
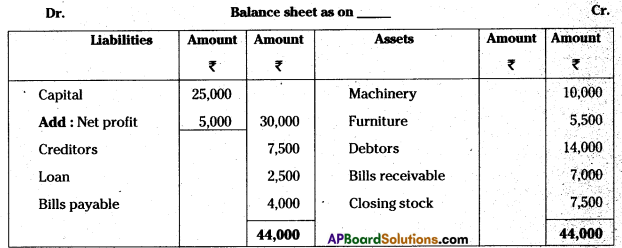
Question 12.
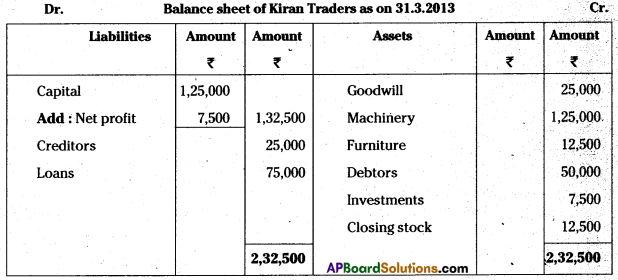
Prepare balance sheet of Kiran Traders from the following as on 31.03.2913:
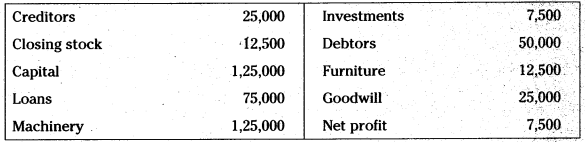
Answer:
Question 13.
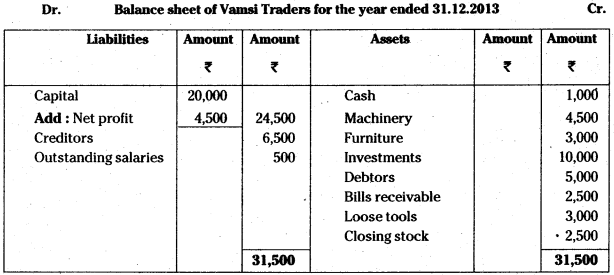
Prepare balance sheet of Vamsi Traders for the year ended 31.12.2013:
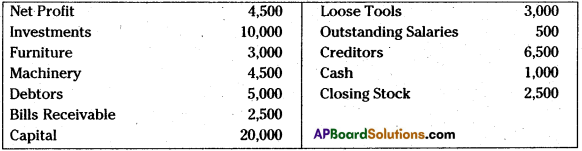
Answer:
Question 14.
From the following Trial Balance, prepare Trading, P& L Account and Balance Sheet:
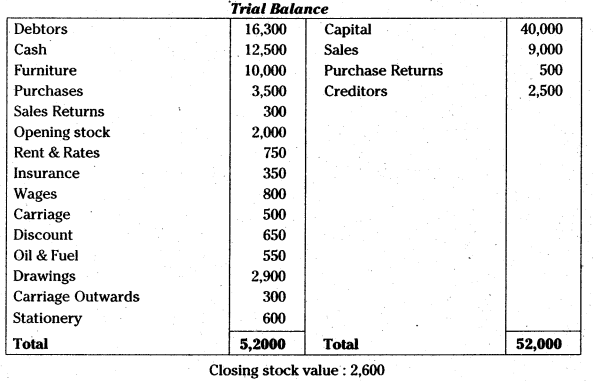
Answer:
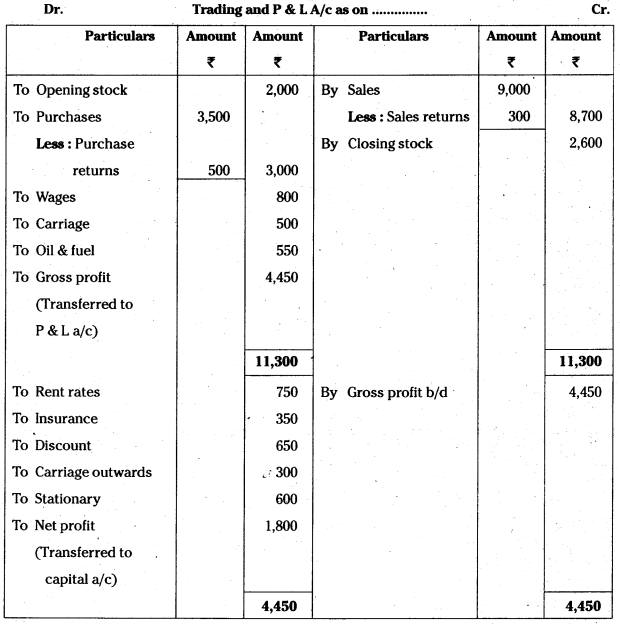
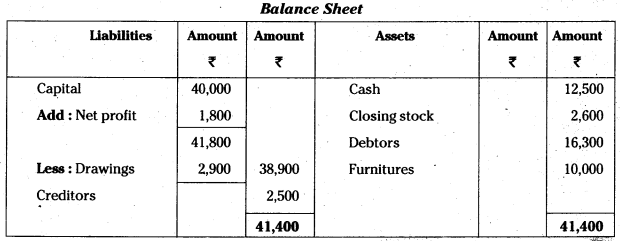
![]()
Question 15.
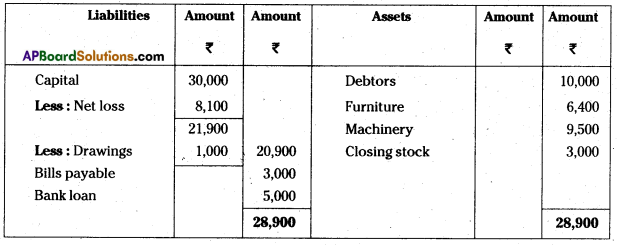
From the following a trial balance prepare final accounts for the year ending 31.03.2014 :
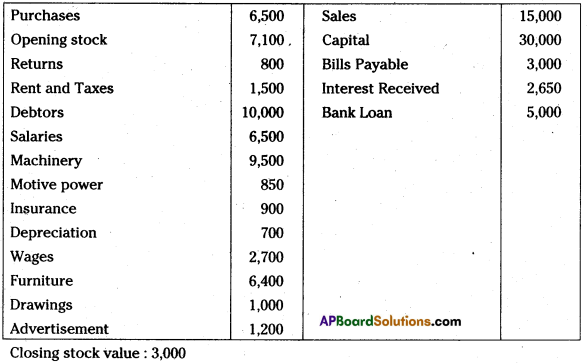
Answer:
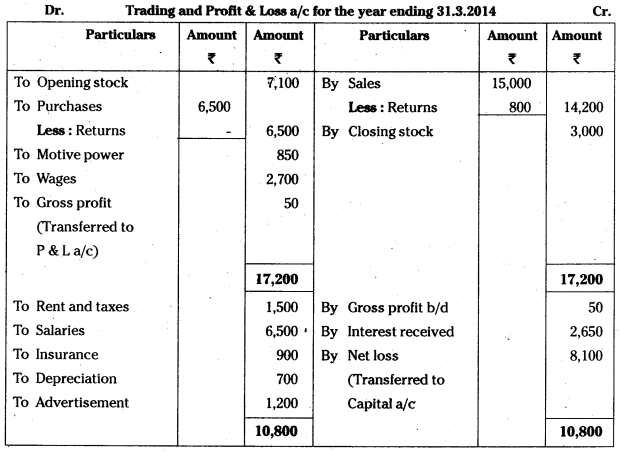
Balance sheet for the year ending 31.3.2014
Student Activity
Visit any small undertaking and collect its expenses, income, assets and liabilities during the latest accounting period, and prepare Trading and Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet in vertical form.