Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions 10th Lesson Chemistry In Everyday Life which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions 10th Lesson Chemistry In Everyday Life
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are drugs ?
Answer:
Drug : The chemicals of low molecular masses ranging from 100 to 500 U that react with macromolecular targets to produce biological response are called drugs.
E.g. : Morphine, Codeine, Heroin etc.,
Question 2.
When are the drugs called medicines ?
Answer:
When the biological response of a drug is therapeutic and useful then the chemical substances (drugs) are called medicines.
![]()
Question 3.
Define the term chemotherapy.
Answer:
Chemotherapy: The use of medicines (chemical substances) in the treatment of diseases is called chemotherapy.
In chemotherapy diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases are involved.
Question 4.
What are antagonists and agonists ?
Answer:
- Antagonists : The drugs that bind to the receptor site and inhibit its natural function are called antagonists. ’
- These are useful when blocking of message is required.
- Agonists : The drugs that mimic the natural messenger by switching on receptors are called agonists.
- These are useful when there is lack of natural chemical messenger.
Question 5.
What are antacids ? Give example. [IPE – 2014, 2016 (TS)] [Mar. 14]
Answer:
Antacids : Chemicals that remove the excess of acid in the stomach and maintain the pH to normal level are antacids.
E.g. : Omeprozole, Lansoprozole etc.
Question 6.
What are antihistamines ? Give example. [IPE 2014]
Answer:
Antihistamines : Chemicals that prevent the interaction of histamines with receptors of the stomach wall thus producing less amount of acid are antihistamines.
E.g. : Dimetapp, Terfenadine (Seldane).
Question 7.
What are tranquilizers ? Give example. [IPE 2015 (TS)]
Answer:
Tranquilizers : The drugs which are used in the management (or) treatment of psychoes and neuroses are called tranquilizers. ‘
E.g.: Luminal, Seconal, Barbituric acid etc.
![]()
Question 8.
What are analgesics ? How are they classified ?
Answer:
Analgesics : These are to reduce or totally abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, incoordination, paralysis, disturbances of nervous system etc.
Analgesics are classified as
- Narcotic analgesics : These are most potent and clinically useful agents causing depression of central nervous system and at the same time act as strong analgesics. E.g. : Morphine, Codeine etc.
- Non-narcotic analgesics : These drugs are analgesics but they have no addictive
properties. Their analgesic use is limited to mild aches and pains. .
E.g.: Aspirin, Ibuprofen etc.
Question 9.
What are antimicrobials ?
Answer:
Antimicrobials : The chemical substances which destroy (or) prevent the development (or) inhibit the pathogenic action of microbes such as bacteria, fungi, virus are called antimicrobials.
E.g.: Lysozyme, Lactic acid etc.
Question 10.
What are antibiotics ? Give example. [A.P. Mar. 16]
Answer:
Antibiotics: The chemical substances produced by micro organisms and inhibit the growth or destroy microorganisms are called antibiotics.
(Or)
The substance produced totally or partly by chemical synthesis which in low concentration inhibits the growth (or) destroy microorganism by intervening in their metabolic process are called antibiotics.
E.g.: Penicillin, Chloramphenicol etc.
Question 11.
What are antiseptics ? Give example. [A.P. Mar. 15]
Answer:
Antiseptics : The chemical compounds that kill (or) prevent the growth of micro organism are called antiseptics.
Antiseptics are the chemical substances applied on the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces.
E.g.: Dettol, Bithional etc.
Question 12.
What are disinfectants ? Give example. [A.P. Mar. 17]
Answer:
Disinfectants : The chemical compounds used for killing (or) preventing the growth of microorganism are called disinfectants.
i) These are applied to inanimate objects like floors, drainage systems etc.
E.g.:
- 4% aqueous solution of formaldehyde called formalin is a disinfectant
- 0.3 ppm chlorine aqueous solution is disinfectant.
- SO2 in very low concentration is disinfectant.
![]()
Question 13.
What is the difference between antiseptics and disinfectants ?
Answer:
Antiseptics are the chemical substances applied on the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces.
Disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments etc.
Question 14.
What are antifertility drugs ? Give example.
Answer:
Antifertility drugs: These are birth control pills and contain a mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone derivatives.
E.g. : Norethindrone, Ethynylestradiol (novestrol)
Question 15.
What are artificial sweetening agents ? Give example. [IPE – 2016 (A.P.), (T.S.)]
Answer:
The chemical substances which are used instead of sucrose (or) sugar are called artificial sweetening agents.
E.g. : Aspartame, Alitame, saccharin.
These decrease the calorific intake and at the same time several times sweeter than sucrose.
Question 16.
Why is the use of aspartame limited to cold foods and drinks ?
Answer:
Aspartame is unstable at cooking temperature so it’s use is limited to cold foods and soft drinks.
Question 17.
What problem does arise in using alitame as artificial sweetener ?
Answer:
While using alitame as artificial sweetener, the control of sweetness of food is difficult. Alitame is a high potency sweetner.
![]()
Question 18.
Why do soaps not work in hard water ?
Answer:
In hard water Ca, Mg-dissolved salts are present. Ca+2, Mg+2 ions form insoluble Ca, Mg, soaps respectively when sodium (or) potassium soaps are dissolved in hard water.

- These insoluble soaps separate as scum in water and are useless as cleansing agent. ’ These are problematic to good washing because the ppt adheres into the fibres of cloth
as gummy mass. - Hair washed with hard water looks dull.
- Dye does not absorb evenly on cloth washed with soap using hard water due to this gummy mass.
Question 19.
What are synthetic detergents ?
Answer:
The cleansing agents which are having all the properties of soaps but donot contain any soap are called synthetic detergents.
Synthetic detergents can be used both in soft and hard water as they give foam even in hard water.
E.g.: Sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate.
Question 20.
What is the difference between a soap and a synthetic detergent ?
Answer:
- Generally soaps are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fattyacids.
- Synthetic detergents are cleansing agents having all the properties of soaps and donot cpntain any soap.
- Soaps donot work in hard water but synthetic detergents can be used both in soft and hard water as they give foam even in hard water. Some of the detergents give foam even in ice cold water.
Question 21.
What are food preservatives ? Give example. [A.P. Mar. 17 – IPE 2016 (T.S)]
Answer:
The chemical substances which prevent the spoilage of food due to microbial growth are called food preservatives.
E.g.: Sodium benzoate, Salt of sorbic acid etc.
Question 22.
How are synthetic detergents better than soaps ?
Answer:
Soaps donot work in hard water but synthetic detergents can be used both in soft and hard water as they give foam even in hard water. Some of the detergents give foam even in ice cold water.
![]()
Question 23.
Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well as disinfectant.
Answer:
Phenol is used as antiseptic as well as disinfectant.
- 0.2% phenol is antiseptic
- 1% phenol is disinfectant.
Question 24.
Why chemicals are added to food ?
Answer:
Chemicals are added to food for i) preservation ii) enhancing their appeal iii) adding nutritive value in them.
Question 25.
Name different categories of food additives.
Answer:
The following are the categories of food additives.
- Food colours
- Flavours and sweetners
- Fat Emulsifiers and stabilising agents
- Anti oxidants
- Flour improvers – antistaling agents and bleaches
- Preservatives
- Nutritional supplements such as minerals, vitamins and amino acids.
Question 26.
Why do we require artificial sweetening agents ?
Answer:
- Artificial sweetening agents are very useful to diabetic persons.
- These decrease the calorific intake and at the same time several times sweeter than sucrose.
- These are harmless.
Question 27.
Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
Answer:
The sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient is saccharin (or) sucralose. It is stable at cooking temperature.
![]()
Question 28.
Name two most familiar antioxidants used as food additives.
Answer:
The most familiar antioxidants are butylated hydroxy toluene (BHT) and butylated hydroxy anisole (BHA).
Question 29.
What is saponification ?
Answer:
The process of formation of soaps containing sodium salts by heating esters of fatty acid with aq. NaOH solution is called saponification.
Question 30.
What are the main constituents of dettol ?
Answer:
Dettol (antiseptic) is a mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol.
Question 31.
What is tincture of iodine ? What is its use ?
Answer:
Tincture of iodine (antiseptic) is a mixture of 2 – 3% Iodine solution in alcohol-water.
Question 32.
What are enzymes and receptors ?
Answer:
Enzymes : The proteins which perform the role of biological catalysts in the body are called enzymes.
Receptors : The proteins which are crucial to communication system in the body are called receptors.
Question 33.
Which forces are involved in holding the drug to the active site of enzymes ?
Answer:
The forces involved in holding the drugs to the active site of enzymes are ionic bonds, vander waal’s forces, hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions etc.
![]()
Question 34.
What are enzyme inhibitors ?
Answer:
The drugs which inhibits the catalytic activity of enzymes and can block the binding site of the enzyme and prevent the binding of substrate are called enzyme inhibitors.
Question 35.
While antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with the function of histamines why do not these interfere with the function of each other ?
Answer:
Antacids and antiallergic drugs donot interfere with the function of each other because they work on different receptors in the body.
Question 36.
What are antipyretics ? Give example.
Answer:
The medicines which reduce body temperature during fever are called antipyretics.
E.g.: Paracetamol
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are analgesics ? How are they classified ? Give examples.
Answer:
Analgesics : These are to reduce or totally abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, incoordination, paralysis, disturbances of nervous system etc. Analgesics are classified as
- Narcotic analgesics : These are most potent and clinically useful agents causing depression of central nervous system and at the same time act as strong analgesics.
E.g. : Morphine, Codeine etc. - Non-narcotic analgesics : These drugs are analgesics but they have no addictive properties. Their analgesic use is limited to mild aches and pains.
E.g. : Aspirin, Ibuprofen etc.
Question 2.
What are different types of microbial drugs ? Give one example for each.
Answer:
Antimicrobials : The chemical substances which destroy or prevent the development (or) inhibit the pathogenic action of microbes such as bacteria, fungi, virus are called antimicrobials.
E.g.: Lysozyme, Lactic acid etc.,
Different types of antimicrobial drugs are antibiotics, antiseptics, disinfectants.
- Antibiotics : The chemical substances produced by micro organisms and inhibit the growth or destroy microorganisms are called antibiotics.
(Or)
The substance produced totally or partly by chemical synthesis in low concentration inhibits the growth (or) destroy microorganism by intervening in their metabolic process are called antibiotics. - Antiseptics: The chemical compounds that kill (or) prevent the growth of micro organism are called antiseptics.
Antiseptics are the chemical substances applied on the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces. - Disinfectants : The chemical compounds used for killing (or) preventing the growth of microorganism are called disinfectants.
These are applied to inanimate objects like floors, drainage systems etc.
E.g. :- 4% aqueous solution of formaldehyde called formalin is a disinfectant
- 0.3 ppm chlorine aqueous solution is disinfectant.
- SO2 in very low concentration is disinfectant.
![]()
Question 3.
Write notes on antiseptics and disinfectants. [T.S. Mar. 17]
Answer:
Antiseptics : The chemical compounds that kill (or) prevent the growth of micro organism are called antiseptics.
Antiseptics are the chemical substances applied on the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces.
E.g.: Dettol, Bithional etc.
Phenol is used as antiseptic as well as disinfectant. 0.2% phenol is antiseptic.
Dettol (antiseptic) is a mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol.
Tincture of iodine (antiseptic) is a mixture of 2 – 3% Iodine solution in alcohol-water.
Disinfectants : The chemical compounds used for killing (or) preventing the growth of microorganism are called disinfectants.
These are applied to inanimate objects like floors, drainage systems etc.
E.g.:
- 4% aqueous solution of formaldehyde called formalin is a disinfectant.
- 0.3 ppm chlorine aqueous solution is disinfectant.
- SO2 in very low concentration is disinfectant.
Phenol is used as antiseptic as well as disinfectant. 1% phenol is disinfectant.
Question 4.
How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants ? Does the same substance be used as both ? Give one example for each.
Answer:
Antiseptics are the chemical substances applied on the living tissues such as wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces.
Disinfectants are applied to inanimate objects such as floors, drainage system, instruments etc.
Phenol is used as antiseptic as well as disinfectant.
i) 0.2% phenol is antiseptic.
ii) 1% phenol is disinfectant.
- Examples of Antiseptics :
- Dettol (antiseptic) is a mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol.
- Tincture of iodine (antiseptic) is a mixture of 2.3% Iodine solution in alcohol-water.
- Examples of disinfectants :
- 4% aqueous solution of formaldehyde called formalin is a disinfectant.
- 0.3 ppm chlorine aqueous solution is disinfectant.
- SO2 in very low concentration is disinfectant.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples.
i) Cationic detergents
ii) Anionic detergents
iii) Non-ionic detergents
Answer:
Synthetic detergents are classified into three types.
i) Cationic detergents : These are synthetic detergents.
a) Cationic detergents are quarternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides (or) bromides as anions.
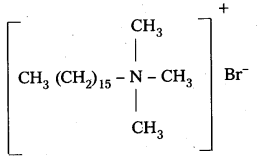
b) Cationic part possess a long hydrocarbon chain and a positive charge on nitrogen atom. Hence these are called cationic detergents.
E.g.: Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
It is used in hair conditioners.
ii) Anionic Detergents : These are synthetic detergents.
a) Anionic detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols (or) hydrocarbons.
b) Anionic detergents are formed by the treatment of long chain alcohols with cone. H2SO4 followed by the neutralisation with alkali.
E.g.: Sodium lauryl sulphate.
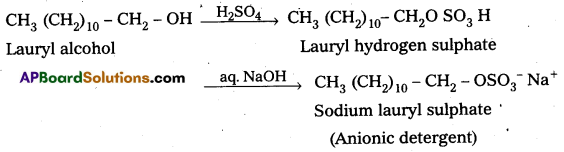
These are used for house hold work and in tooth pastes.
iii) Non-ionic detergents : These are synthetic detergents.
a) Non-ionic detergents donot contain any ion in their constitution..
b) The detergent formed by the reaction of stearic acid with poly ethylene glycol is an example of non ionic detergent.
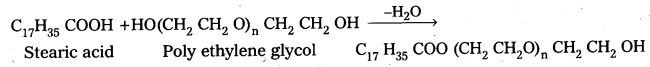
Non-ionic detergents are used in liquid dish washing purpose.
Question 6.
What are biodegradable and non-bio degradable detergents ? Give one example for each.
Answer:
i) Biodegradable detergents :
- The detergents which are degraded (or) decomposed by micro organisms are called biodegradable detergents. Biodegradable detergents have less branching.
- These do not cause water pollution.
E.g. : n-dodecyle benzene sulphonate, soap (non synthetic)
ii) Non Biodegradable detergents :
- The detergents which are not decomposed (Or) degraded by microbes (or) micro organisms are called non-biodegradable detergents. These have more branching.
- These cause water pollution.
E.g.: ABS detergent.
![]()
Question 7.
What are broad spectrum and narrow spectrum antibiotics ? Give one example for each.
Answer:
The range of bacteria (or) other micro organisms that are effected by a certain antibiotic is expressed as its spectrum of action.
Broad spectrum antibiotics : Antibiotics which kill (or) inhibit a wide range of gram¬positive and gram-negative bacteria are called broad spectrum antibiotics.
Narrow spectrum antibiotics: Antibiotics which are effective mainly against gram-positive (or) gram-negative bacteria are called narrow spectrum antibiotics.
E.g.: Penicillin – G is a narrow spectrum antibiotic.
Limited spectrum antibiotics : Antibiotics which are effective mainly against a single organism (or) disease are called as limited spectrum antibiotics.
Question 8.
Name different types of soaps.
Answer:
The following are the different types of soaps.
- Toilet soaps
- Soaps that float in water
- Medicated soaps
- Shaving soaps
- Laundry soaps
- Soap powders and scouring soaps etc.
![]()
Question 9.
Write notes on antioxidants in food.
Answer:
Antioxidants :
- Antioxidants are important and necessary food additives.
- Antioxidants help in food preservation by retarding the action of oxygen on food.
- Antioxidants are more reactive towards oxygen than the food material which they protect.
- The most familiar antioxidants are Butylated hydroxy toluene (BHT) and Butylated hydroxy anisole (BHA).
- The addition of BHA to butter increases its shelf life from months to years.
- BHT and BHA along with citric acid are added to produce more antioxidant effect.
- SO2 and sulphites are useful anti oxidants for wine and beer, sugar syrups and cut, peeled (or) dried fruits and vegetables.