Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 12(a) Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 12(a) Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain why propanol has a higher boiling point than that hydrocarbon-butane.
Answer:
Propanol has a higher boiling point (391 K) than that hydrocarbon butane (309K).
Reason: In propanol, strong intermolecular hydrogen bonding is present between the molecules. But in the case of butane weak van der Waals force of attractions are present.
Question 2.
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses. Explain this fact.
Answer:
Alcohols are comparatively more soluble in water than hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
Explanation: .
- Alcohols and water are both polar solvents. Alcohol is dissolves in water, due to formation of hydrogen bonding with water molecules.
- Hydro carbons are non polar and these dorv.t form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. So alcohols are soluble in water where as hydrocarbons are not soluble in water.
![]()
Question 3.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula, C7H8O.
Answer:
Given molecular formula of monnhydric phenols is C7H8O. The no. of possible isomers with molecular formula C7H8O are three.
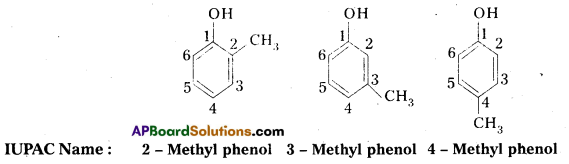
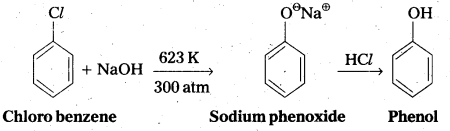
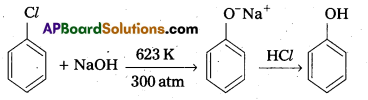
Question 4.
Give the reagents used for the preparation of phenol from chiorobenzene.
Answer:
Phenol is prepared from chiorobenzene as follows. Reagents required are
- NaOH, 623K, 300 atm
- HCl.
Chemical reaction :
Question 5.
Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method. Give reason.
Answer:
Only 1° – alcohols form Ethers on acid dehydration. But not 2° or 3°-alcohols.
Reason : In case of 2° or 3° alcohols steric hindrance arises. Due to this steric hindrance alkenes are formed but not Ethers.
![]()
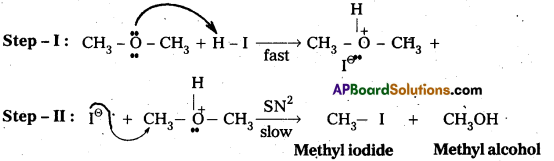
Question 6.
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Answer:
Case – I: When methoxy methane reacts with cold.dil. HI then methyl alcohol and methyl iodide are formed.
Mechanisms:
Case – II : When methoxy methane reacts with hot.conc.HI then only methyl iodide is formed.
Mechanisms:
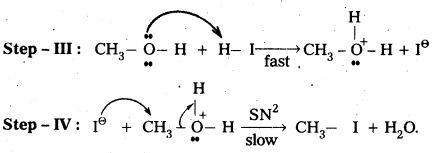
Question 7.
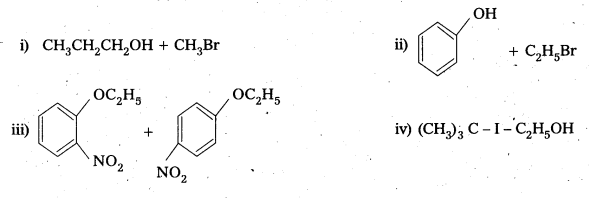
Name the reagents used in the following reactions.
- Oxidation of primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
- Oxidation of primary alcohol to aldehyde.
Answer:
- The reagents used for the oxidation of 1° – alcohols to carboxylicacid are acidified K2Cr2O77 (or) Acidic/alkaline KMnO4 (or) Neutral KMnO4
- The reagents used for the oxidation of 1°- alcohols to aldehyde are pyridine chloro chromate (PCC) in CH2Cl2.
Question 8.
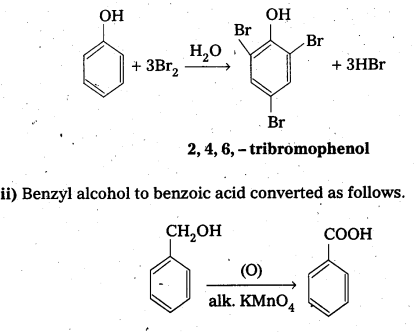
Write the equations for the following reactions.
i) Bromination of phenol to 2,4, 6-tribromophenol
ii) Benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid.
Answer:
i) Bromination of phenól to 2, 4, 6 tribromophenol.
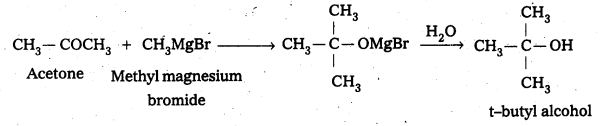
Question 9.
IdentIfy the reactant needed to form t-.butylalcohol from acetone.
Answer:
When acetone reacts with methyl magnesium bromide followed by the hydrolysis forms t-butyl alcohol.
![]()
Question 10.
Write the structures for the following compounds
- Ethoxyethane
- Ethoxybutane
- Phenoxyethane
Answer:
- Ethoxyethane → CH3 – CH2 – O – CH2 – CH3
- Ethoxybutane → CH3 – CH2 – O – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
- Phenoxyethane → C6H5 – O – CH2 – CH3
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula C5H12O2 and give their IUFAC names and classify them as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Answer:
- Given molecular formula of compound is C5H12O.
- It has eight isomeric alcohols.
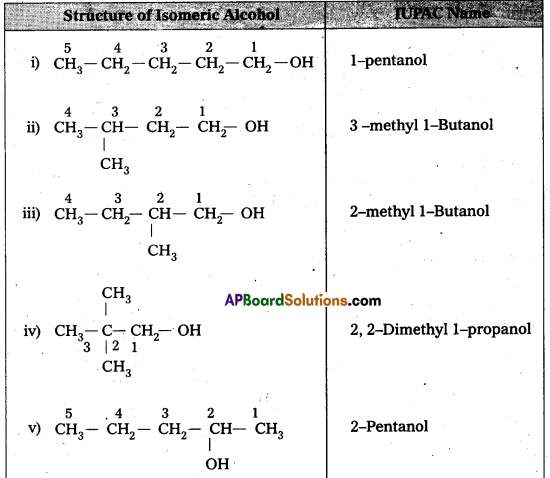
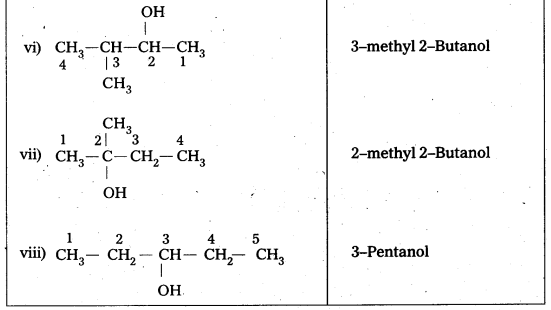
In the above isomeric alcohols (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) and 1°-alcohols; (v), (vi) and (viii) are 2°- alcohols, (vii) is 3°-alcohol.
Question 2.
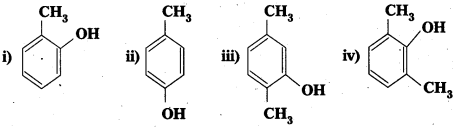
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenols by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give rèason.
Answer:
While separating a mixture of ortho and para nitrophenols by steam distillation, ortho nitrophenol is steam volatile.
Reason: In ortho nitrophenol intra molecular hydrogen bonding is present and in case of para nitrophenol inter molecular hydrogen bonding is present. So O-nitrophenol is steam volatile.
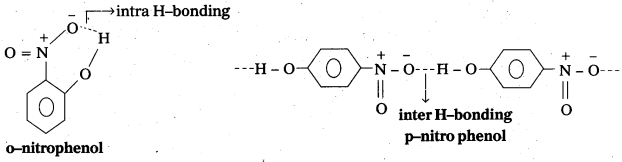
![]()
Question 3.
Give the equations for the preparation of phenol from Cumene. [Mar. 14]
Answer:
Phenol.is prepared from Cumene as follows.
- Oxidation of Cumene to Cumene hydroperoxide.
- Cumene hydroperoxide on acidic hydrolysis to form phenol.
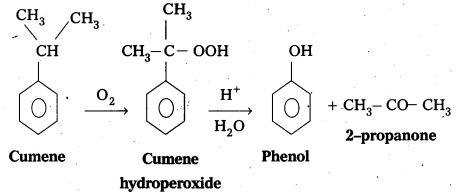
Question 4.
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
Answer:
Hydration of Ethene to yield ethanol involves 3—step mechanism.
Step – 1: In step – 1 formation of carbocation takes place by the protonation of ethene.
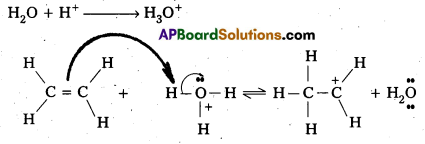
Step – 2 : In step – 2 carbocation formed in the above step attacked by water.
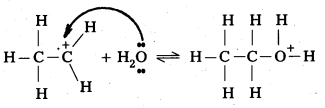
Step – 3 : Ethyl alcohol is formed by he deprotonation in step -3
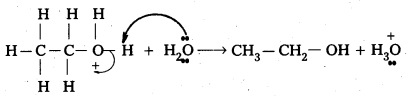
Question 5.
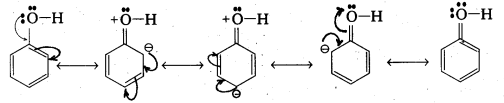
Explain the acidic nature of phenols and compare with that of alcohols.
Answer:
The reaction of phenol with sodium metal and with aq.NaOH indicates the acidic nature of phenol.
i) Phenol reacts with sodium metal to form sodium phenoxide.
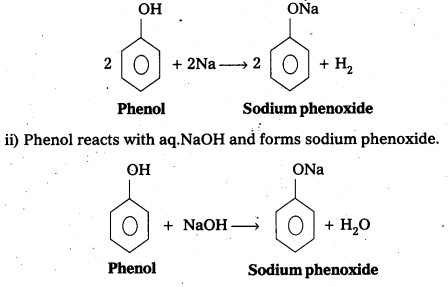
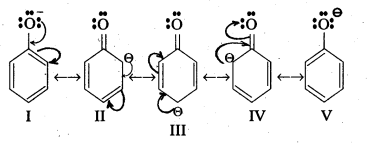
- In phenol hydroxyl group is attached to the Sp2 hydridised carbon of benzene ring which acts as electron with drawing group. The formed phenoxide ion from phenol is more stabilised due to delocalisation of negative charge.
Comparison of acidic character of Phenol and Ethanol:
- The reaction of phenol with aq. NaOH indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols.
- The hydroxyl group attached to an aromatic ring is more acidic than in hydroxyl group is attached to an alkyl group.
- Phenol forms stable phenoxide ion stabilised by resonance but ethoxide ion is not.
![]()
Question 6.
Write the products formed by the reduction and oxidation of phenol.
Answer:
a) Reduction of phenol: Phenol undergo reduction in presence of zinc dust to form benzene.
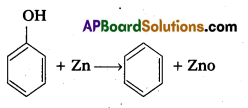
b) Oxidation of phenol : Phenol undergo oxidation with chromicacid and forms a conjugated diketone known as benzoquinone.
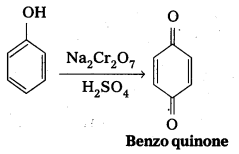
Question 7.
Ethanol with H2SO4, at 443K forms ethene while at 413 K it forms ethoxy ethane. Explain the mechanism.
Answer:
Case – 1: Ethanol reacts with Cone. H2SO4 at 443K forms ethene
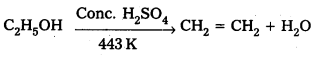
Mechanism:
Step – 1: Formation of protonated alcohol
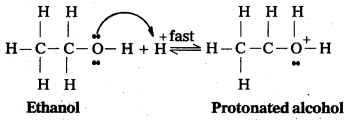
Step 2 : Formation of carbo cation
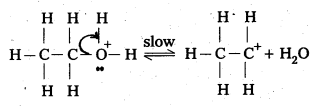
Step 3 : Formation of ethene by elimination of a proton
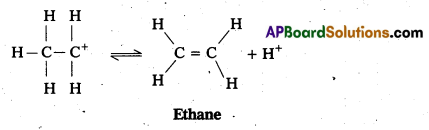
Case – II : Ethanol reacts with Cone. H2SO4 at 413 K to form ethoxy ethane.
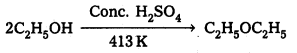
Mechanism:
In the above reaction ether formation is a SN reaction. This involve attack of alcohol molecule on a protonated alcohol.
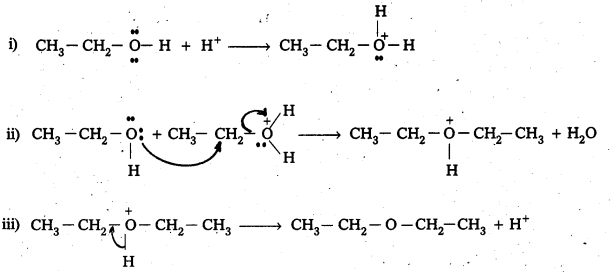
Question 8.
Account for the statement: Alcohols boil at higher temperature than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses.
Answer:
Alcohols boil at higher temperature than hydrocarbons and ethers of comparable molecular masses.
Explanation : Consider ethanol, propane and methoxy methane which are having comparable molecular masses. The boiling points, molecular masses and structures of the above compounds mentioned below.
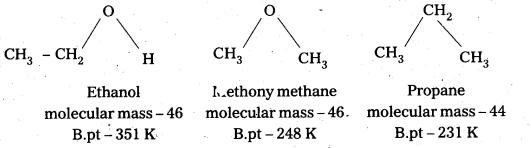
The higher boiling points of alcohols are due to the presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding in them which is lacking in ethers and hydrocarbons.
![]()
Question 9.
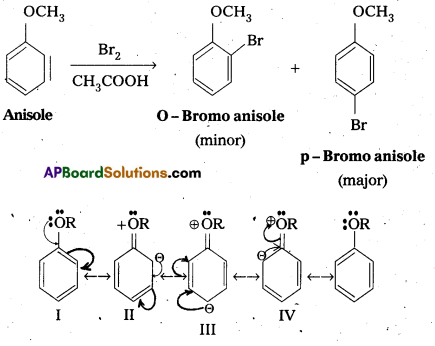
Explain why in anisole electrophilic substitution takes place at ortho and para positions and not at meta position.
Answer:
Anisole is an aryl alkyl ether. In anisole the group -OCH3 influences + R effect. This increases the electron density in the benzene ring and it leads to the activation of benzene ring towards electrophihic substitution reactions.
In Anisole eletron density is more at O-and P-Positions but not at m—position. So 0-and P-products are mainly formed during electrophillic substitution reactions.
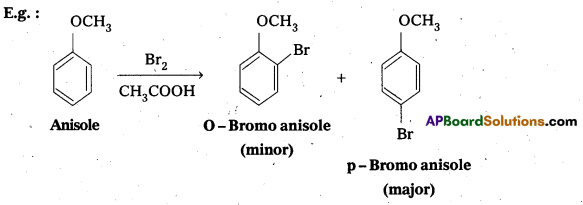
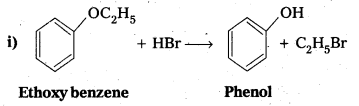
Question 10.
Write the products of the following reactions :
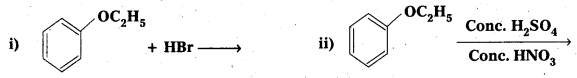
Answer:
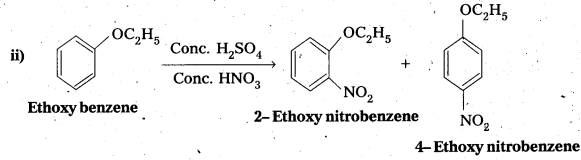
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compounds :
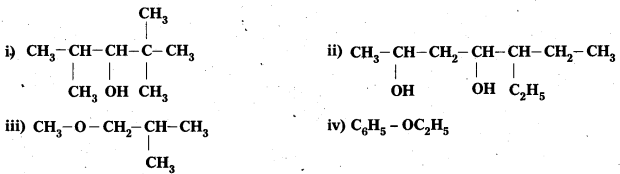
Answer:
Question 2.
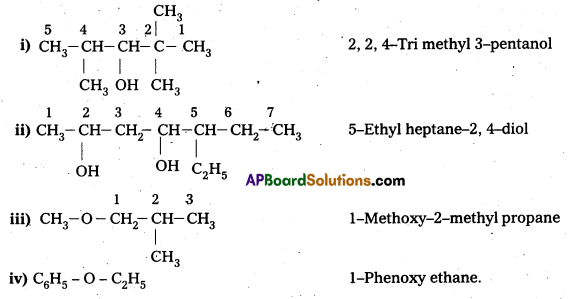
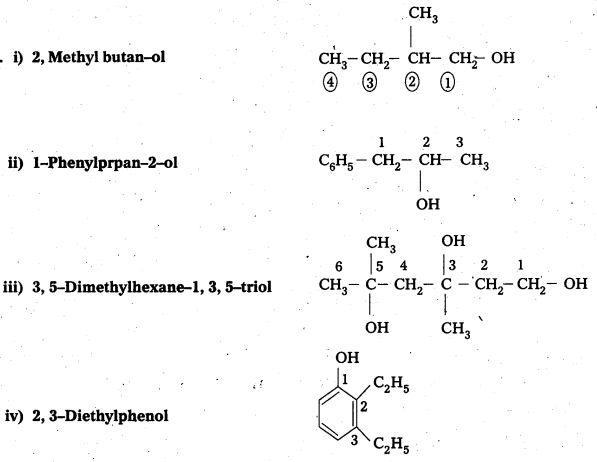
Write structures of the compounds whose IUPAC names are as follows:
i) 2, Methyl butan—ol
ii) 1-Phenylprpan-2-ol
iii) 3, 5-Dhuethylhexane-1, 3, 5-triol
iv) 2, 3-Diethylphenol
v) 1-Ethoxypropane
vi) 2-Ethoxy-3-methylpentane
vii) Cyclohexylmethanol
viii) 3-Chloromethylpentan-1-ol
Answer:
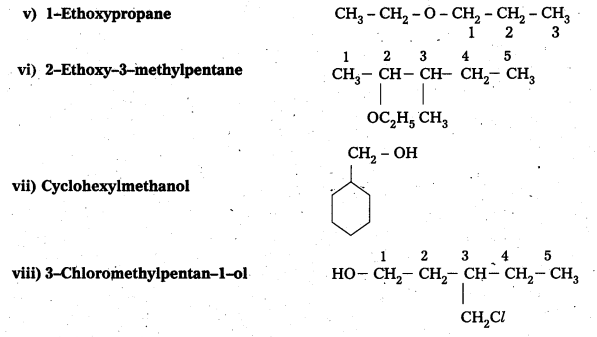
![]()
Question 3.
Write the equations for the preparation of phenol using benzene, conc. H2SO4 and NaOH. [Mar. 14]
Answer:
The equations for the preparation of phenol using conc.H2SO4 and NaoH as follows
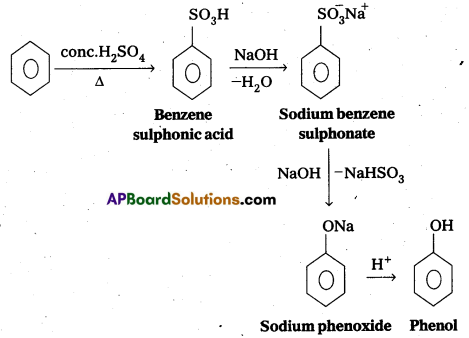
Question 4.
Illustrate hydroboration-oxidation reaction with a suitable example.
Answer:
When alkenes undergo addition reaction with diborane to form tri alkyl boranes. These followed by the oxidation by alkaline H2O2 to form alcohols. This reaction is called as hydroboration-oxidation reaction.
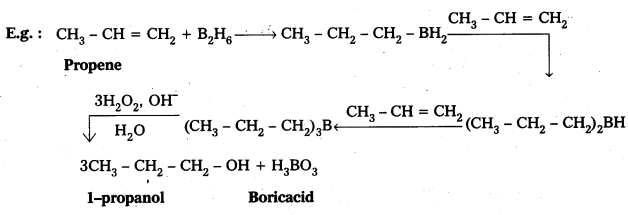
Question 5.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compounds:
Answer:
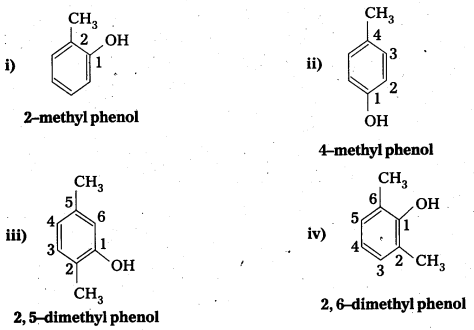
![]()
Question 6.
How will you synthesise:
i) 1 – Phenylethanol from a suitable alkene
ii) Cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by an SN2 reaction.
iii) Pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
Answer:
i) Synthesis of 1-phenylethanol from a suitable alkene : When styrene undergo hydrolysis in presence of dil.H2SO4 to form 1-phenyl ethanol. It is an example of Marknowni koff’s rule.
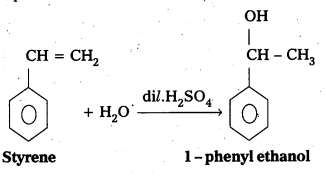
ii) Synthesis of cyclohexyl methanol using an alkyl halide by SN2 reaction : When cyclohexyl methyl bromide reacts with aq. NaOH to form cyclohexyl methanol.
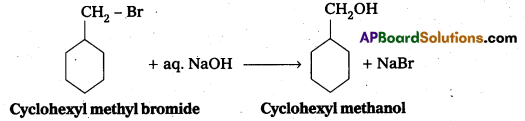
iii) Synthesis of 1-pentanol using a suitable alkyl halide: When 1-Bromo pentane reacts with aq.KOH to form 1-pentanol.
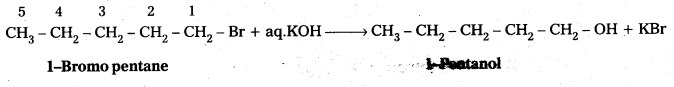
Question 7.
Explain why-
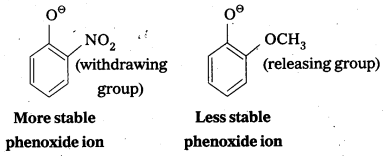
i) Ortho nitrophenol is more acidic than Ortho methoxyphenol.
ii) OH group attached to benzene ring activates it towards electrophilic substitution.
Answer:
i) Ortho nitrophenol is more acidic than Ortho methoxyphenol.
Explanation: .
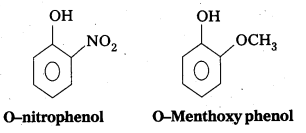
- -NO2 is an electron withdrawing group and -OCH3 is electron releasing group.
- By the presence of electron withdrawing group the phenoxide ion is more stabilized. By the presence of electron releasing group the phenoxide ion is less stabilized.
- Due to high stability of phenoxide ion, acidic nature increases.
ii) The -OH group attached to benzene ring activates it towards electrophilic substitution.
Explanation : When an electrophile is attacked, the – OH group exerts +R effect on the benzene ring. So electrodensity in the ring increases at ortho and para positions. When an electrophile attacks, substitution takes place at O and p-positions. So benzene ring activates towards electrophilic substitution.
![]()
Question 8.
Wth a suitable example write equations for the following:. [T.S. MAr. 19, 18; A.P. Mar. 18, 16] [A.P. Mar. 16]
i) Kolbe’s reaction
ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction
iii) Williamsons ether synthesis
Answer:
i) Kolbes reaction: Phenol reacts with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide. This undergoes electrophilhic substitution with CO2to form salicylic acid.
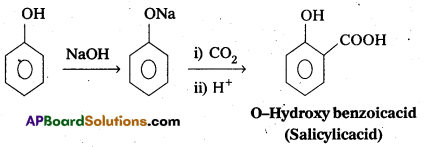
ii) Relmer-Tlemann reactIon : Phenol reacts with chloroform in presence of NaOH to form salicylaldehyde (O-Hydroxy benzaldehyde). This reaction is known as Reimer-Tiemann reaction. .
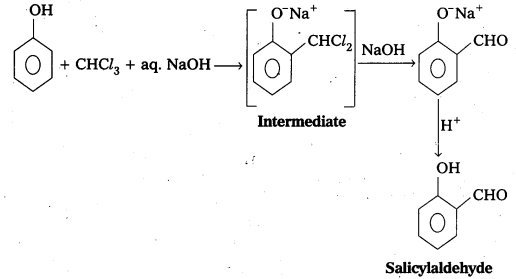
iii) Wilhiamsons ether synthesis:
- This method is used for the preparation of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers.
- The reaction of an alkyl halide with sodium alkoxide to form ethers is known as Williamsons Synthesis.
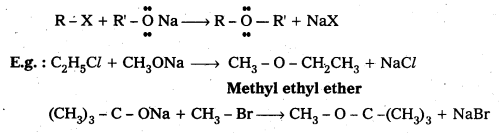
Question 9.
How are the following conversions carried out?
i) Benzyl chloride to Benzyl alcohol
ii) Ethyl magnesium bromide to Propan-1-ol
iii) 2-Butanone to 2-Butanol
Answer:
i) Conversion of Benzyl chloride to Benzyl alcohol : Ben.zyl chloride reacts with aq. NaOH to form benzyl alcohol.
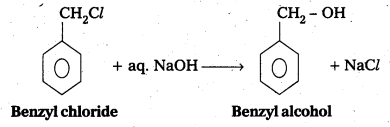
ii) Conversion of Ethyl magnesium bromide to Propan-1-ol : Ethyl magnesium bromide reacts with form aldehyde followed by hydrolysis to form 1-propanol.
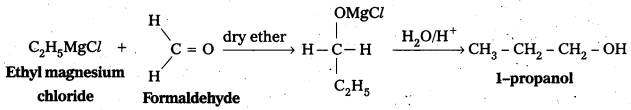
iii) Conversion of 2-Butanone to 2-Butanol: 2-Butanone undergo reduction in presence of LiA/H4 to form 2-Butanol.
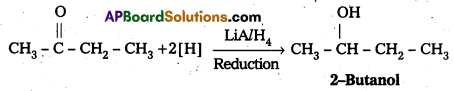
Question 10.
Write the names of the reagents and equations for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis:
i) 1-Propoxypropane
ii) Ethoxybenzene
iii) 2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
iv) 1 -Methoxyethane
Answer:
i) Preparation of 1-propoxy propane :
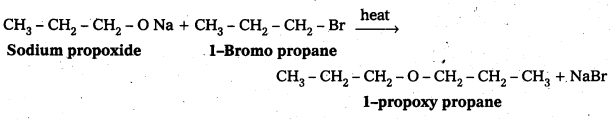
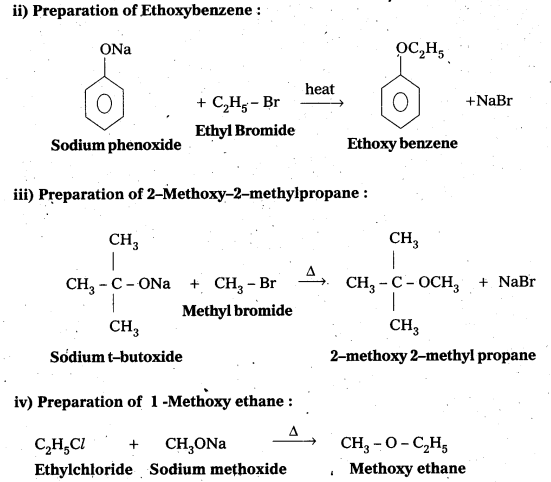
![]()
Question 11.
How is 1-propoxypropane synthesized from propan-1-ol ? Write mechanism of this reaction.
Answer:
1 – Proponal reacts with Conc. H2SO4 at 413 K to form 1-propoxy propane.
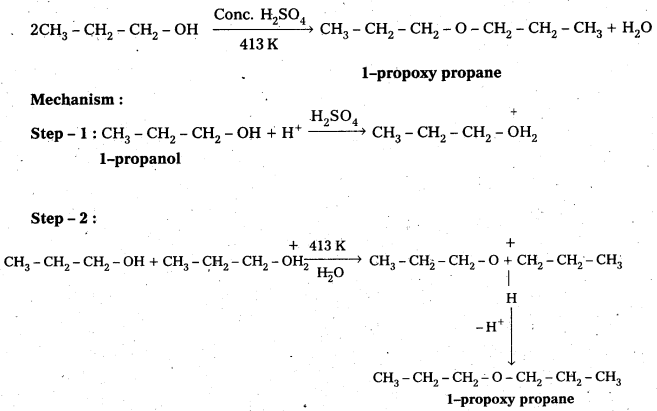
Question 12.
Explain the fact that in aryl alkyl ethers the alkoxy group activates the benzene ring towards electrophilic substitution.
Answer:
Anisole is an aryl alkyl ether. In anisole the group -OCH3 influences +R effect. This increases the electron density in the benzene ring and it leads to the activation of benzene ring towards electrophillic substitution reactions.
In Anisole eletron density is more at O-and P-Positions but not at m-position. So O-and P-products are mainly formed during electrophillic substitution reactions.
Question 13.
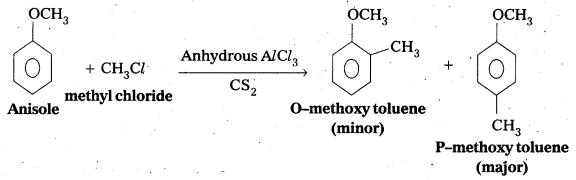
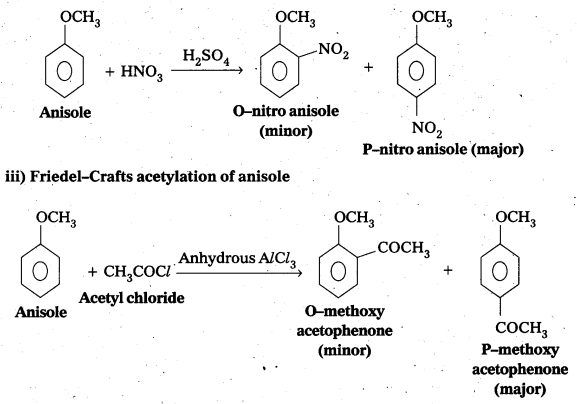
Write equations of the below given reactions:
i) Alkylation of anisole
ii) Nitration of anisole
iii) Friedel-Crafts acetylation of anisole
Answer:
i) Friedel crafts Alkylation of anisole :
ii) Nitration of anisole
![]()
Question 14.
Show how you would synthesize the following alcohols from appropriate alkenes?
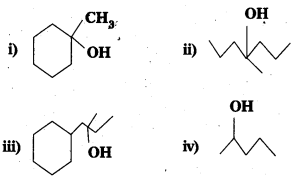
Answer:
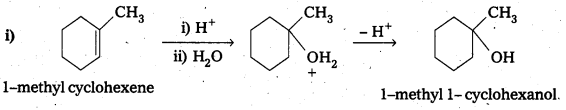
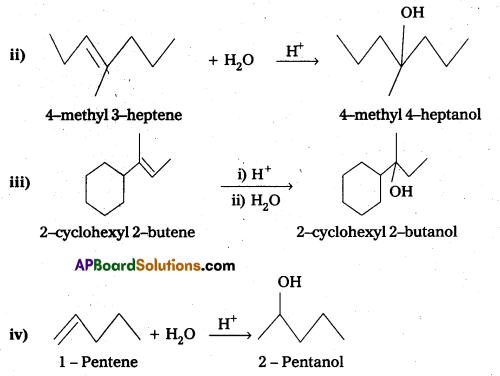
Question 15.
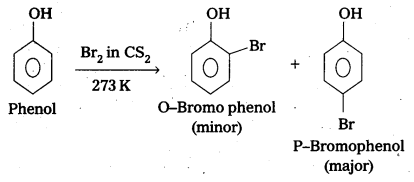
Explain why phenol with bromine water forms 2,4,6-tribromophenol while on reaction with bromine in CS2 at low temperatures forms para-bromophenol as the major product.
Answer:
a) Phenol under goes Bromination in presence of CS2 to form p-bromophenol as major product.
b) Phenol undergoes bromination in aqueous medium form 2,4,6 -tribromo phenol (white ppt).
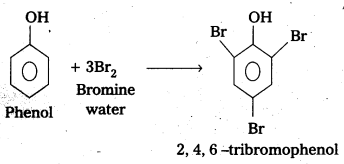
Explanation: In bromination of phenol, the polarisation of Br2 molecule takes place even in the absence of Lewis acid. This is due to the highly activating effect of -OH group attached to the benzene ring.
Textual Examples
Question 1.
Give IUPAC names of the following compounds:
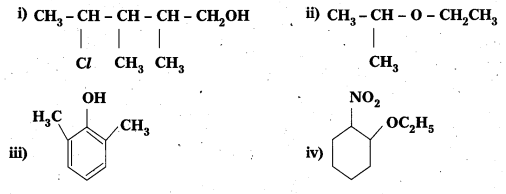
Solution:
i) 4-Chloro-2, 3-dimethylpentan-1-ol
ii) 2-Ethoxypropane
iii) 2, 6-Dimethyiphenol
iv) 1-Ethoxy-2-nitrocyclohexane
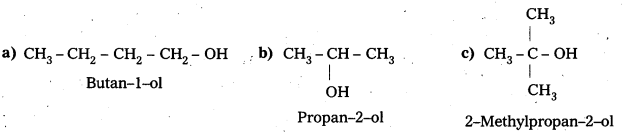
Question 2.
Give the structures and IUPAC names of the products expected from the following reactions :
a) Catalytic reduction of butanal.
b) Hydration of propene in the presence of dilute sulphuric acid.
c) Reaction of propanone with methylmagnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis.
Solution:
![]()
Question 3.
Arrange the following sets of compounds in order of their increasing boiling points :
a) Pentan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, ethanol, propan-1-ol, methanol.
b) Pentan-1-ol, n-butane, pentanal, ethoxyethane.
Solution:
a) Methanol, ethanol, propan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, pentan-1-ol.
b) n-Butane, ethoxyethane, pentanal and pentan-1-ol.
Question 4.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their acid strength:
Propan-1-ol, 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol, 3-nitrophenol, 3, 5-dinitrophenol, phenol, 4-methylphenol.
Solution:
Propan-1-ol, 4-methylphenol, phenol, 3-nitrophenol, 3, 5-dinitrophenol, 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol.
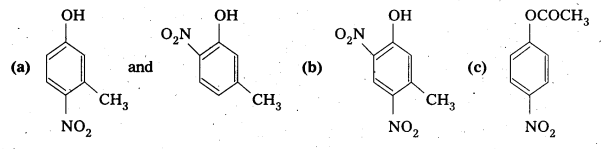
Question 5.
Write the structures of the major products expected from the following reactions:
a) Mononitratlon of 3-methylphenol .
b) Dinitratlon of 3methylphenol
c) Mononitration of phenyl methanoate.
Solution:
The combined influence of -OH and -CH3 groups determine the position of the incoming group.
Question 6.
The following is not an appropriate reaction for the preparation of t-butyl ethyl ether.
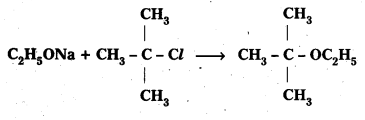
i) What would be the major product of this reaction?
ii) Write a suitable reaction for the preparation of t-butylethyl ether.
Solution:
i) The major product of the given reaction is 2-methylprop-1-ene.
It is because sodium ethoxide is a strong nucleophile as well as a strong base. Thus elimination reaction predominates over substitution.
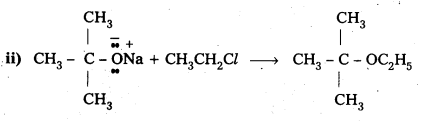
![]()
Question 7.
Give the major products that are formed by heating each of the following ethers with HI.
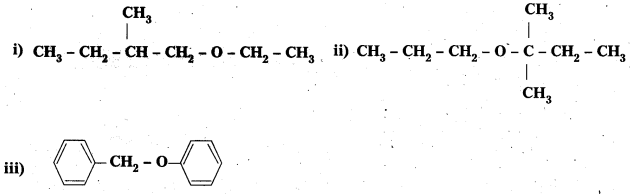
Solution:
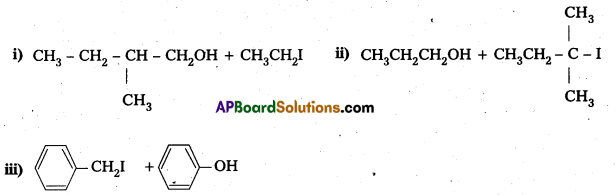
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols:
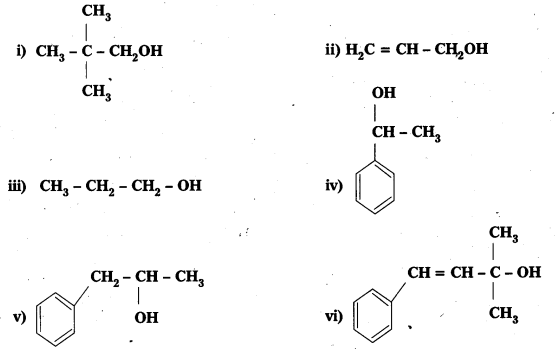
Answer:
Primary alcohols (i), (ii), (iii)
Secondary alcohols (iv) and (y)
Tertiary alcohols (vi)
Question 2.
Identify allylic alcohols in the above examples.
Answer:
Allylic alcohols are (ii) and (vi)
Question 3.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
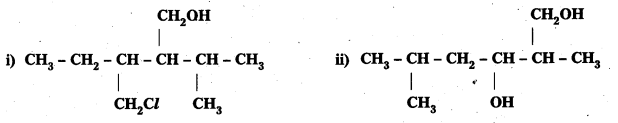

Answer:
i) 3-Chioremethyl 2-isopropylpentan-1-ol
ii) 2, 5-Dimethylhexane-1, 3-dial
iii) 3-Bromocyclohexanol
iv) Hex-1-en-3-ol
v) 2-Bromo-3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol.
![]()
Question 4.
Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent of methanol?

Answer:
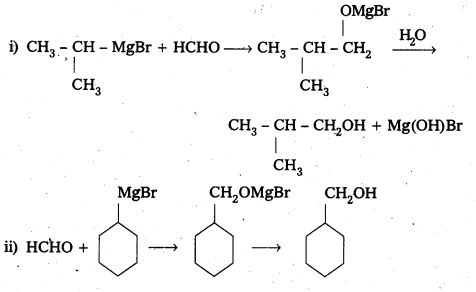
Question 5.
Write structures of the products of the following reactions :

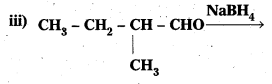
Answer:
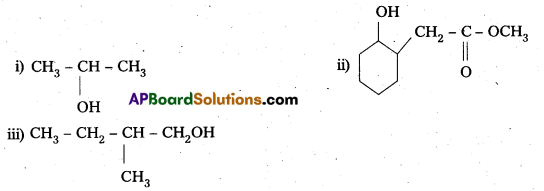
Question 6.
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of
- 1-methylcyclohexanol and
- butan-1-ol.
Answer:
- 1-Methylcyclohexene
- A mixture of but-1-ene and but-2-ene. But-1-ene is the major product formed due to rearrangement to give,secondary carbocation.
Question 7.
Write the reactions of Williamson synthesis of 2-ethoxy-3-methylpentane starting from ethanol and 3-methylpentan-2-ol.
Answer:
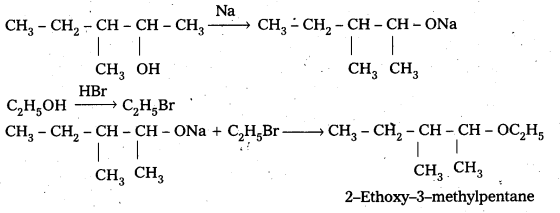
![]()
Question 8.
Predict the products of the following reactions:
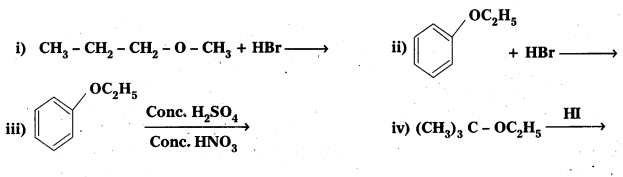
Answer: