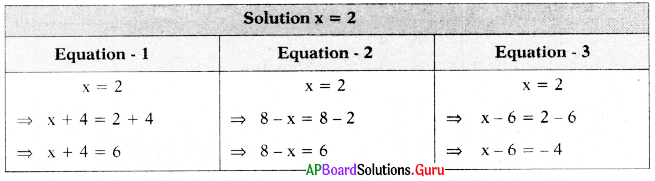
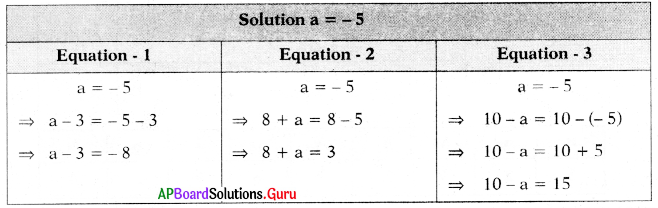
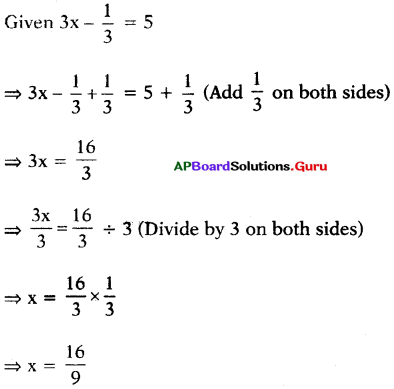
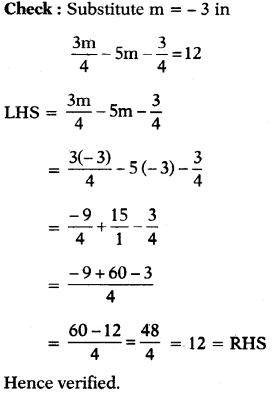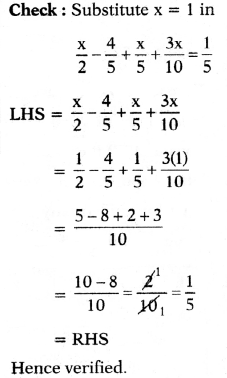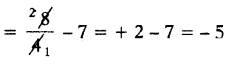SCERT AP 7th Class Maths Solutions Pdf Chapter 3 Simple Equations Unit Exercise Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Maths Solutions 3rd Lesson Simple Equations Unit Exercise
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer.
(i) Which of the following numbers satisfy the equation – 6 + m = – 10 ?
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) – 4
(d) – 2
Answer:
(c) – 4
Explaination:
– 6 + m = -10
⇒ – 6 + m + 6 = – 10 + 6
(Add 6 on both sides)
⇒ m = – 4

(ii) The equation having – 2 as solution is
(a) x + 2 = 5
(b) 7 + 3x = 1
(c) 2x + 3 = 7
(d) 2(x + 1) = 4
Answer:
(b) 7 + 3x = 1
Explaination
(a) x + 2 = 5
⇒ x + 2 – 2 = 5 – 2 (Subtract 2 on both sides)
⇒ x = 3 it is not – 2
(b) 7 + 3x = 1
⇒ 7 + 3x – 7 = 1 – 7 (Subtract 7. on both sides)
⇒ 3x = – 6
⇒ \(\frac{3 x}{3}\) = \(\frac{-6}{3}\) (Divide by 3 on both sides)
∴ x = – 2
so, solution is – 2
Similarly, check (c) and (d) also.
(iii) If a and b are positive integers, then the solution of the equation ax = b will always be a ____________ .
(a) positive number
(b) negative number
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer:
(a) positive number
Explaination:
If a and b are positive integers and b < a, then ax ± b also positive integer.
(iv) The equation which can’t be solved in integers is
(a) 2(x – 3) = 10
(b) \(\frac{x}{3}\) = 5
(c) 5 – 3m = 1
(d) 2k + 1 = 1
Answer:
(c) 5 – 3m = 1
Explaination:
(a) 2(x – 3) = 10
⇒ 2x – 6 = 10 (Distributive property)
⇒ 2x – 6 + 6 = 10 + 6 (Add 6 on both sides)
⇒ 2x = 16
⇒ \(\frac{2x}{2}\) = \(\frac{16}{2}\) (Divide by 2 on both sides)
⇒ x = 8 is an integer.

(b) \(\frac{x}{3}\) = 5
⇒ \(\frac{x}{3}\) × 3 = 5 × 3 (Multiply by 3 on both sides)
⇒ x = 15 is an integer.
(c) 5 – 3m = 1
⇒ 5 – 3m – 5 = 1 – 5 (Subtract 5 on both sides)
⇒ – 3m = – 4
⇒ \(\frac{-3 m}{-3}\) = \(\frac{-4}{-3}\)
⇒ m = \(\frac{4}{3}\) is not an integer.
(d) 2k + 1 = 1
⇒ 2k + 1 – 1 = 1 – 1 (Subtract 1 on both sides)
⇒ 2k = 0
⇒ \(\frac{2 k}{2}\) = \(\frac{0}{2}\) (Divide by 2 on both sides)
⇒ k = 0 is an integer
So, our answer is c.
(v) Which of the following is not allowed in a given equation?
(a) Adding the same number to both sides of the equation.
(b) Subtracting the same number from both sides of the equation.
(c) Multiplying both sides of the equation by the same non-zero number.
(d) Dividing both sides of the equation by the same number.
Ans.
(d) Dividing both sides of the equation by the same number.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks.
(i) If 2y – 1 = 5, then value of 5y + 3 is ____________
Answer:
Given 2y – 1 = 5
⇒ 2y – 1 + 1 = 5 + 1 (Add 1 on both sides)
⇒ 2y = 6
⇒ \(\frac{2 y}{2}\) = \(\frac{6}{2}\) (Divide by 2 on both sides)
∴ y = 3
then 5y + 3 = 5(3) + 3
= 15 + 3 = 18
(ii) Changing of term from one side of equation to other side is called __________
Answer:
Transposition.

(iii) If the sum of two numbers is 60. One is thrice the other, then the equation formed is ___________.
Answer:
Let one number be x.
Other number = thrice of first number = 3(x) = 3x
Sum of two numbers = 60
⇒ x + 3x = 60
⇒ 4x = 60
(iv) If ‘x’ is a natural number, then the solution of x – 8 = – 8 is _________ .
Answer:
x – 8 = – 8
x – 8 + 8 = – 8 + 8 (Add 8 on both sides)
x = 0 is not a natural number.
So, given equation has no solution.
(v) 13 subtracted from twice of a number gives 3, then the number
Answer:
Let the number be x.
Twice the number = 2x
13 is subtracted from twice the number
⇒ 2x- 13 = 3
⇒ 2x – 13 + 13 = 3 + 13 (Add 13 on both sides)
⇒ 2x = 16
⇒ \(\frac{2 x}{2}\) = \(\frac{16}{2}\) (Divide 2 on both sides)
⇒ x = 8
∴ Number is 8.
Question 3.
Check whether the value given in the brackets is a solution to the given equation or not.
(a) 2n + 5 = 19 (n = 7)
Answer:
Given 2n + 5 = 19
Substitute n = 7 in the given equation
2(7) + 5 = 19
⇒ 14 + 5 = 19
⇒ 19 = 19
∴ LHS = RHS
So, n = 7 is the solution of the given equation.

(b) \(\frac{3 m}{5}\) – 7 = 1 (m = 10)
Answer:
Given \(\frac{3 m}{5}\) – 7 = 1
Substitute m = 10 in the given equation
\(\frac{3(10)}{5}\) – 7 = 1
⇒ 3 × 2 – 7 = 1
⇒ 6 – 7 = 1
∴ – 1 = 1
LHS ≠ RHS
So, m = 10 is not the solution of given equation.
Question 4.
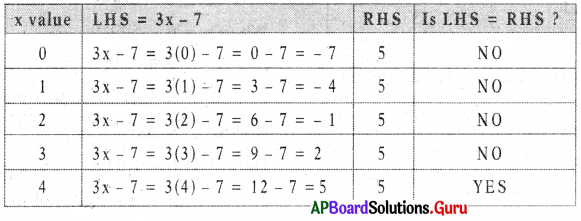
Solve 5 – 2k = – 3 using trial and error method.
Answer:
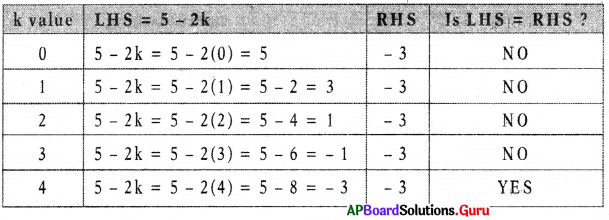
For k = 4, LHS = RHS
So, k = 4 is the solution of given equation.
Question 5.
Write the following equations in mathe-matical statement form.
(a) 2m + 7 = 21
Answer:
7 more than twice the m is 21.
(b) \(\frac{n}{7}\) = 4
Answer:
One seventh of n is 4.
Question 6.
Give the steps you will use to separate the variables and then solve the equation.
(a) 7(x – 3) = 28
Answer:
Given 7(x – 3) = 28
⇒ 7x – 21 = 28 (Distributive property)
⇒ 7x – 21 + 21 = 28 + 21 (Add 21 on both sides)
⇒ 7x = 49
⇒ \(\frac{7 x}{7}\) = \(\frac{49}{7}\) (Divide by 7 on both sides)
⇒ x = 7

(b) 8y – 9 = 15
Answer:
Given 8y – 9 = 15
⇒ 8y – 9 + 9 = 15 + 9 (Add 9 on both sides)
⇒ 8y = 24
⇒ \(\frac{8 y}{8}\) = \(\frac{24}{8}\) (Divide by 8 on both sides)
⇒ y = 3
Question 7.
Solve the following equations and check the result (Method of Transposition)
(a) 9(a + 3) + 7 = 22
Given 9(a + 3) + 7 = 22
⇒ 9(a + 3) + 7 – 7 = 22 – 7 (Subtract 7 on both sides)
⇒ 9(a + 3) = 15
⇒ 9a + 27 = 15 (Distributive property)
⇒ 9a + 27 – 27 = 15 – 27 (Subtract 27 on both sides)
⇒ 9a = – 12
⇒ \(\frac{9 a}{9}\) = \(\frac{-12}{9}\) (Divide by 9 on both sides0
⇒ a = \(\frac{-4}{3}\)
Check:
Substitute a = \(\frac{-4}{3}\) in the given equation.
LHS = 9(a + 3) + 7
= \(9\left(\frac{-4}{3}+\frac{3}{1}\right)\) + 7
= \(9\left(\frac{-4+9}{3}\right)\) + 7
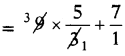
= 15 + 7 = 22 = RHS
Hence verified.
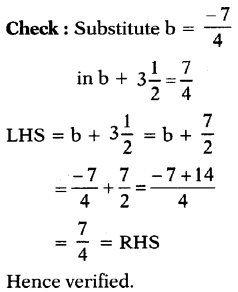
(b) 25 = 18 – 7(b – 6)
Answer:
Given 25 = 18 – 7(b – 6)
⇒ 25 – 18 = l8 – 7(b – 6) – 18 (Subtract 18 on both sides)
⇒ 7 = – 7(b – 6)
⇒ \(\frac{7}{-7}\) = \(\frac{-7(b-6)}{-7}\) (Divide by – 7 on both sides)
⇒ – 1 = b – 6
⇒ – 1 + 6 = b – 6 + 6 (Add 6 on both sides)
⇒ 5 = b
∴ b = 5 (By transposition)
Check: Substitute b = 5 in the
given equation.
RHS = 18- 7(b – 6) – = 18-7(5-6)
= 18 – 7(- 1)
= 18 + 7 = 25 = LHS
Hence verified.

Question 8.
Six times a number is 72. Find the number.
Answer:
Let the number be x.
Given, six times of number = 72
⇒ 6x = 72
⇒ \(\frac{6 x}{6}\) = \(\frac{72}{6}\)
⇒ x = 12
∴ The number is 12.
Question 9.
Three-fourth of a number is more than one-fourth of same number by 2. Find the number.
Answer:
Let the number be x.
Three fourth of number = \(\frac{3}{4}\) of x = \(\frac{3 x}{4}\)
One-fourth of number = \(\frac{1}{4}\) of x = \(\frac{x}{4}\)
Three-fourth of number
= One-fourth of number + 2
⇒ \(\frac{3 x}{4}=\frac{x}{4}+\frac{2}{1}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3 x}{4}=\frac{x+8}{4}\)
⇒ \(\frac{3 x}{4} \times 4=\frac{x+8}{4} \times 4\) (Multiply by 4 on both sides)
⇒ 3x = x + 8
⇒ 3x – x = x + 8 – x (Subtract x on both sides)
⇒ 2x = 8
⇒ \(\frac{2 x}{2}\) = \(\frac{8}{2}\) (Divide by 2 on both sides)
⇒ x = 4
Question 10.
In the given figure the perimeter of the square is 40m. Then find x.
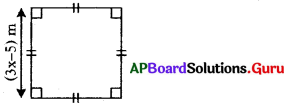
Answer:
From the above figure,
Side of square = (3x – 5) m
Perimeter of square = 40 m
⇒4 × side = 40
⇒ 4 × (3x – 5) = 40
⇒ \(\frac{4(3 x-5)}{4}\) = \(\frac{40}{4}\) (Divide by 4 on both sides)
⇒ 3x – 5 = 10
⇒ 3x – 5 + 5 = 10 + 5 (Add 5 on both sides)
⇒ 3x = 15
⇒ \(\frac{3 x}{3}\) = \(\frac{15}{3}\) (Divide by 3 on both sides)
∴ x = 5 m

Question 11.
Jeevan is 3 years younger than his brother Sasi. If the sum of their present ages is 19 years. What are their present ages ?
Answer:
Let the present age of Sasi is x years.
The present age of Jeevan = (x – 3) years
Sum of their present ages = 19
⇒x + x – 3 = 19
⇒ 2x – 3 = 19
⇒ 2x – 3 + 3 = 19 + 3 (Add 3 on both sides)
⇒ 2x = 22
⇒ \(\frac{2 x}{2}\) = \(\frac{22}{2}\) (Divide by 2 on both sides)
⇒ x = 11 years
∴ Present age of Sasi x = 11 years
Present age of Jeevan = x – 3
= 11 – 3 = 8 years
Question 12.
The length of a rectangle is 20m more than its width. If the perimeter of the rectangle is 100m, then find the length and breadth of rectangle.
Answer:
Let the width of a rectangle (b) = x m
Then the length of a rectangle (l)
= 20 more than its width
= (x + 20) m
Perimeter of the rectangle = 100 m
⇒ 2(1 + b) = 100
⇒ 2(x + 20 + x) = 100
⇒ 2(2x + 20) = 100
⇒ 4x + 40 = 100
⇒ 4x + 40 – 40 = 100 – 40 (Subtract 40 on both sides)
⇒ 4x = 60 4x 60
⇒ \(\frac{4 x}{4}\) = \(\frac{60}{2}\) (Divide by 4 on both sides)
⇒ x = 15 m
∴ Width x = 15 m
Length = x + 20 = 15 + 20 = 35 m

Question 13.
In a family, the consumption of rice is 4 times that of wheat. The total consumption of the two cereals in a month is 30kg. Find the quantities of rice and wheat consumed in the family.
Answer:
Let the quantity of wheat consumed in the month x kg. .
Quantity of rice = 4 times of wheat = 4x kg
Quantity of rice + Quantity of wheat = 30 kg
⇒ 4x + x = 30
⇒ 5x = 30
⇒ \(\frac{5 x}{5}\) = \(\frac{30}{5}\) (Divide by 5 on both sides)
⇒ x = 6 kg
∴ Quantity of wheat = 6 kg
Quantity of rice = 4x = 4 × 6 = 24 kg
Question 14.
The teacher tells the students in the class that the highest marks obtained by a student in the class is 7 more than twice the lowest marks. If the highest mark is 93, then what is the lowest mark ?
Answer:
Let the lowest mark = x then the highest mark
twice the lowest mark + 7 = 93
⇒ 2x + 7 = 93
⇒ 2x + 7 – 7 = 93 – 7 (Subtract 7 on both side)
⇒ 2x = 86
⇒ \(\frac{2 x}{2}\) = \(\frac{86}{2}\) (Divide by 2 on both sides)
⇒ x = 43
∴ Lowest mark = 43

Question 15.
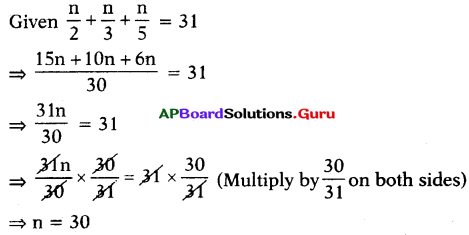
A man travelled \(\frac{4}{5}\) of his journey by train, \(\frac{1}{7}\) by bus and the remaining 16 km by auto. What is the length of his total journey ?
Answer:
Let the length of total journey = x km
Travelled by train = \(\frac{4}{5}\) of x = \(\frac{4x}{5}\) km
Travelled by bus = \(\frac{1}{7}\) of x = \(\frac{x}{7}\) km
Travelled by auto =16 km
Total length of journey = \(\frac{4x}{5}\) + \(\frac{x}{7}\) + 16
⇒ x = \(\frac{4 x}{5}+\frac{x}{7}+\frac{16}{1}\)
⇒ x = \(\frac{28 x+5 x+16 \times 35}{35}\)
⇒ x = \(\frac{33 x+560}{35}\)
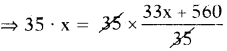
(Multiply 35 on both sides)
⇒ 35x = 33x + 560
⇒ 35x – 33x = 33x + 560 – 33x (Subtract 33x on both sides)
⇒ 2x = 560
⇒ \(\frac{2 x}{2}\) = \(\frac{560}{2}\) (Divide by 2 on both sides)
⇒ x = 280 km
Therefore, length of total journey = 280 km
![]()

![]()
![]()




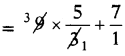

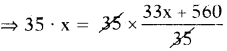

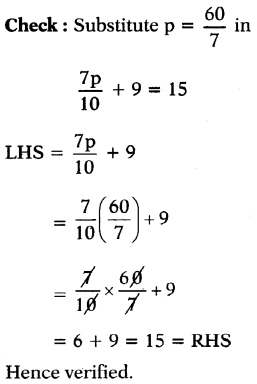
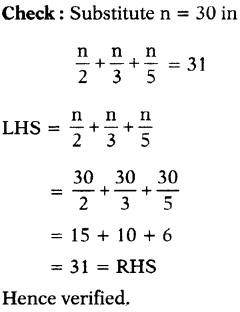
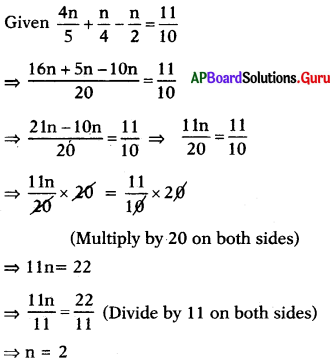
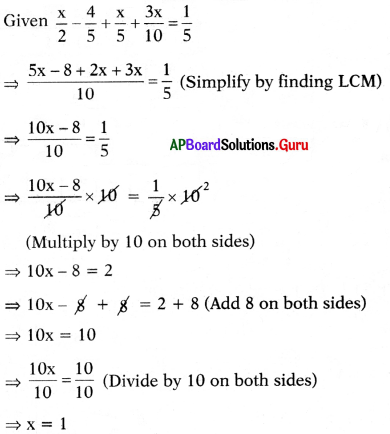
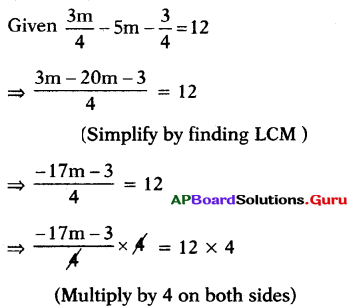 ⇒ – 17m – 3 = 48
⇒ – 17m – 3 = 48