SCERT AP 7th Class Maths Solutions Pdf Chapter 5 Triangles InText Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Maths Solutions 5th Lesson Triangles InText Questions
Check Your Progress [Page No. 92]
Question 1.
Classify the following triangles according to the length of their sides:
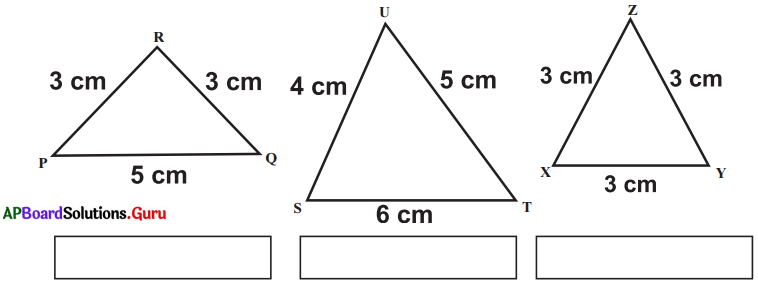
Answer:
[Page No. 93]
Question 2.
Classify the following triangles according to the measure of their angles.
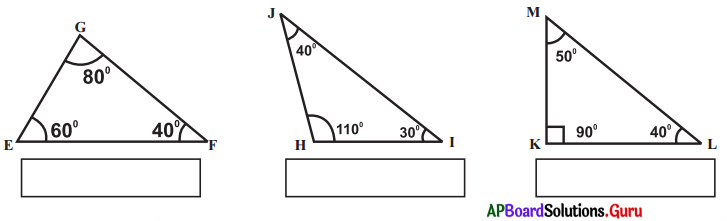
Answer:

Let’s Think [Page No. 97]
Question 1.
Can you find a triangle in which each angle is less than 60°?
Answer:
Sum of angles in a triangle is 180°.
If each angle is less than 60°, then the sum of angles of a triangle is < 180°. So, triangle cannot form. So, we cannot find a triangle in which each angle is less than 60°.
![]()
Check Your Progress [Page No. 99]
Question 1.
Find the value of ‘x’ in the given figure.
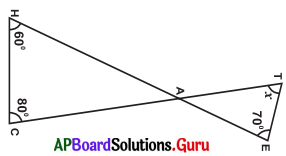
Answer:
In the given figure,
∠HAC = ∠TAE = a (∵ Vertically opposite angles)
In ∆AHC,
we know, ∠H + ∠C + ∠HAC 180°
⇒ 60° + 80° + a = 180°
⇒ 140° + a – 140° = 180°- 140° … a = 40°.
∴ ∠HAC = ∠TAE = a = 40°
In ∆ATE, we know,
∠T + ∠TAE + ∠E = 180°
⇒ x + a + 70° = 180°
⇒ x + 40° + 70° = 180°
⇒ x + 110°- 110° = 180°- 110°
∴ x = 70°
Let’s Do Activity [Page No. 101]
Question 1.
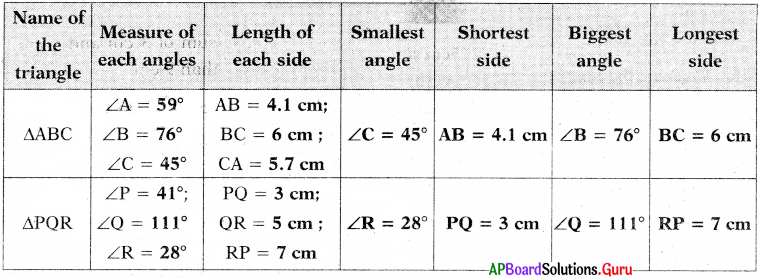
Measure the length of the sides of ∆ABC and fill the following table.
Answer:
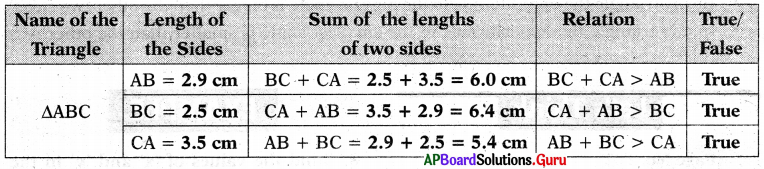
From the above table, we can conclude that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of the third side.
Question 2.
Take the same measurements of the previous activity and note the results as given below.
Answer:

From the above table we can conclude that the difference of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is less than the length of the third side.
Question 3.
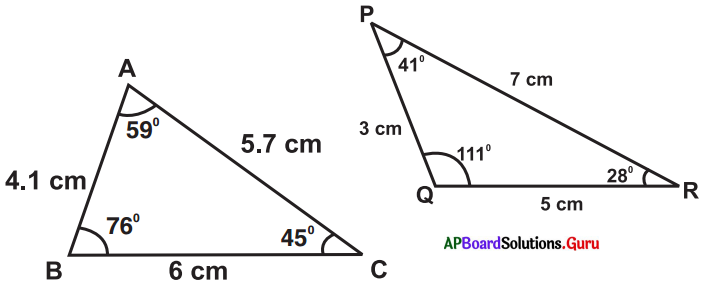
Fill the following table as per measurements given in the above triangles:
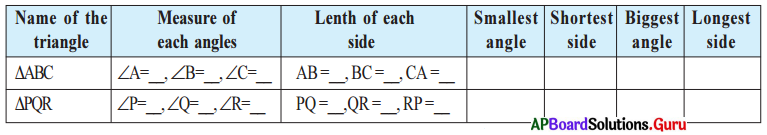
What do you observe from the last four columns in above table ?
- In any triangle the opposite side to the biggest angle is bigger than the other two sides.
- In any triangle the opposite side to the smallest angle is smaller than the other two sides.
Answer:
Let’s Think [Page No. 102]
Question 1.
What are the measurements of angles of an equilateral triangle?
Answer:
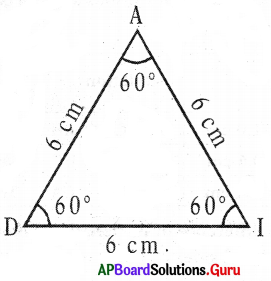
In ∆ADI
AD = DI – AI = 6 cm (All angles are equal)
∠A = ∠D = ∠I = 60° (All angles are equal)
So, in an equilateral triangle,
All Sides are equal in length. Each angle is equal to 60°.
![]()
Puzzle Time [Page No. 104]
Question 1.
Find the interior angles of all triangles by using given dues.
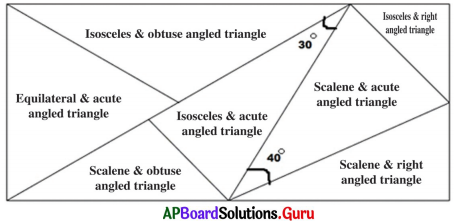
Answer:
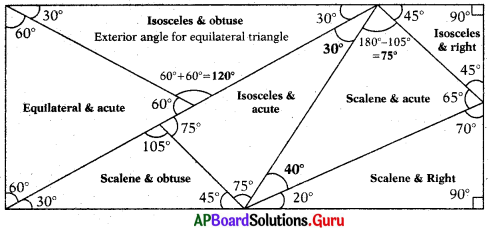
Hints:
Each angle in an equilateral triangle is 60°.
Straight angle = 180°
In an isosceles triangle, two angles are equal.
In a scalene triangle all angles are unequal.
Right angle = 90°.
Obtuse angle > 90°.
Examples:
Question 1.
In a triangle, two angles are 43° and 57°. Find the third angle.
Answer:
Given two angles of a triangle are 43° and 57°.
Sum of these two angles = 43° + 57° = 100°
In a triangle the sum of the interior angles is 180°.
∴ Third angle = 180° – 100° = 80°
Question 2.
Find the value of ‘x’ in the following triangles :
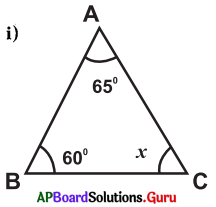
Answer:
From the figure
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° (v Sum of three angles in triangle is 180°)
⇒ 65° + 60° + x = 180°
⇒ 125° + x = 180°
∴ x =180°- 125° = 55°
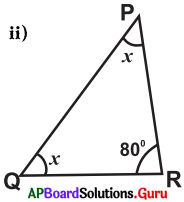
Answer:
From the figure
∠P + ∠Q + ∠R = 180°
x + x + 80° = 180°
⇒ 2x + 80° = 180°
⇒ 2x = 180°-80°
⇒ 2x = 100°
⇒ x = \(\frac{100^{\circ}}{2}\) = 50°
∴ x = 50°
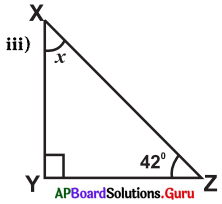
Answer:
From the figure
∠X + ∠Y + ∠Z – 180°
⇒ x + 90° + 42° = 180°
⇒ x + 132° = 180°
⇒ x = 180°- 132°
∴ x = 48°
Question 3.
Find the values of x and y in the given triangle.
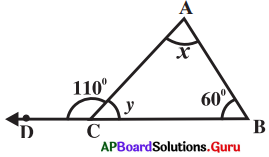
Answer:
In the ∆ABC
∠ACD + ∠ACB = 180° (linear pair of angles)
110° + y = 180°
⇒ y = 180°- 110°
∴ y = 70° ……………….(i)
∠BAC + ∠ACB + ∠CBA = 180°
⇒ x + y + 60° = 180°
⇒ x + 70° + 60° = 180° (From (i))
⇒ x + 130° = 180°
∴ x = 50°
![]()
Question 4.
In a right angled triangle one acute angle is 44°, then find the other acute angle.
Answer:
We know that, sum of the two acute angles in a right angled triangle is 90°.
Given that, in the right angled tri-angle one of the acute angles = 44°
Other acute angle in right angled triangle = 90° – 44° = 46°
Question 5.
The angles of a triangle are (x + 10)°, (x – 20)° and (x + 40)°. Find the value of x and the measure of the angles.
Answer:
Given that the angles of the triangle are
(x + 10)°, (x – 20)° and (x + 40)°
(x + 10)° + (x – 20)° + (x + 40)° = 180°
⇒ x + 10° + x – 20° + x + 40° = 180°
⇒ 3x + 30° = 180°
⇒ 3x – 180° – 30°
⇒ 3x = 150°
⇒ x = \(\frac{150^{\circ}}{3}\) = 50°
The angles are,
x + 10° = 50° + 10° = 60°
x – 20° = 50° – 20° = 30°
x + 40° = 50° + 40° = 90°
∴ Measure of the angles are 60°, 30° and 90°.
Question 6.
In the ∆ABC, exterior angle at ∠C = 105° and ∠A=65°. Find the other interior opposite angle.
Answer:
Given that, exterior angle at ∠C = 105°.
One of the interior opposite angle ∠A = 65°.
The other interior opposite angle is ∠B .
∠A + ∠B =105°(∵ Exterior angle property of a triangle)
65° + ∠B = 105°
⇒ ∠B = 105° – 65° = 40°
Question 7.
Find the exterior angle of the given triangle.
Answer:
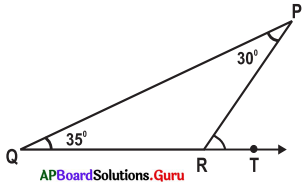
From the figure, ∠P = 30°, ∠Q = 35°
Exterior angle at R = ∠P + ∠Q (∵ Exterior angle property of a triangle)
= 30° + 35° = 65°
![]()
Question 8.
Find the values of ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the following figure.
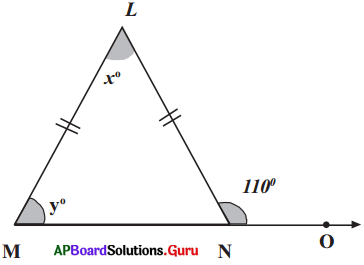
Answer:
∠LMN + 110° = 180° (Linear pair angles)
∠LNM = 180° -110° = 70°
∠LMN = ∠LNM (Angles opposite to equal sides)
y = 70°
⇒ x + y – 110° (Exterior angle property)
⇒ x + 70° = 110°
∴ x = 110°-70° – 40°