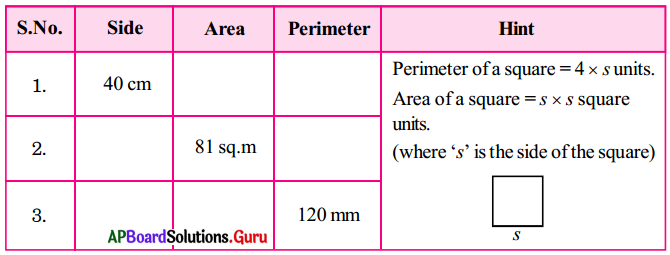
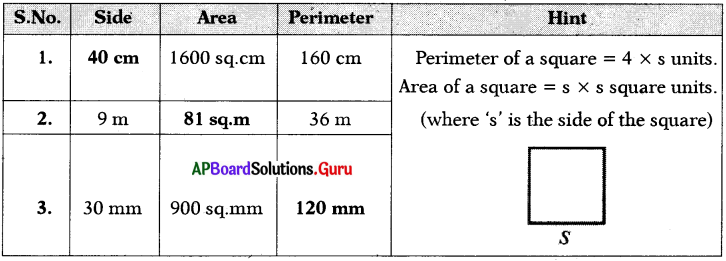
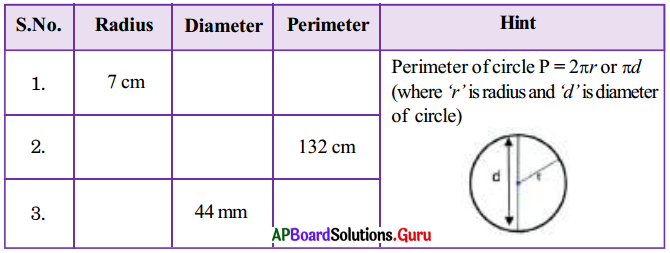
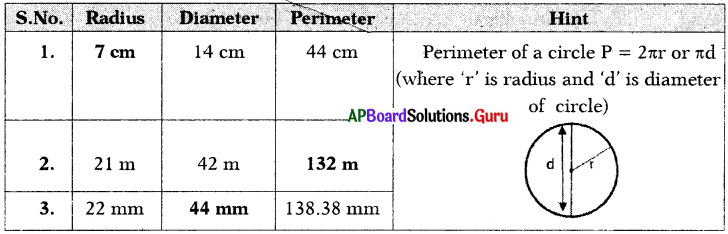
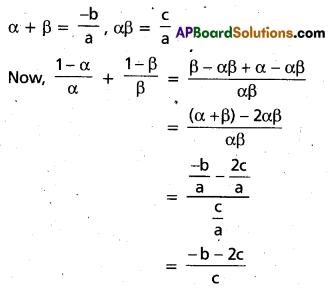
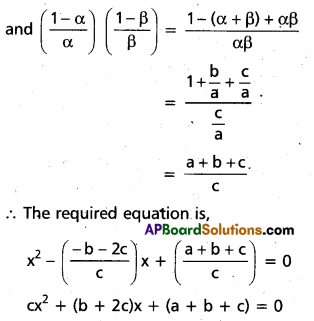
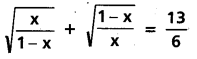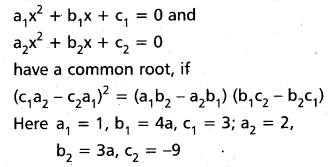These AP 7th Class Science Important Questions 2nd Lesson Nature of Substances will help students prepare well for the exams.
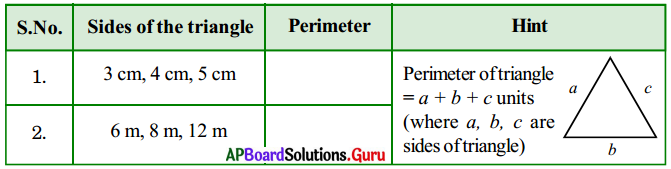
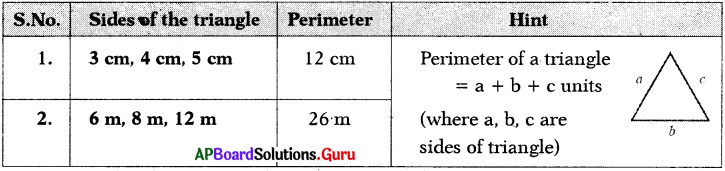
AP Board 7th Class Science 2nd Lesson Important Questions and Answers Nature of Substances
Question 1.
From which language does the word ‘Acid’ derived?
Answer:
The word acid came from the Latin word ‘acere’ means sour.
Question 2.
Give some examples for substances containing acids.
Answer:
Tamarind, Lemon, Tomato, Apple, Curd, Raw mango etc.
Question 3.
What is the chemical name of vitamin C?
Answer:
The chemical name of vitamin C is Ascorbic acid.
Question 4.
Name some substance in which vitamin C is available.
Answer:
Vitamin C is available in citrus fruits and in amla (usiri).
![]()
Question 5.
What will happen when carbon dioxide is added to water?
Answer:
When carbon dioxide is added to water, it become carbonic acid/soda.
Question 6.
How are bases to touch?
Answer:
Bases are slippery to touch.
Question 7.
Which base is used to prepare bath soap?
Answer:
Bath soap is prepared using potassium hydroxide.
Question 8.
Which base is used to prepare detergent soap?
Answer:
Detergent soap for washing clothes is prepared using Sodium hydroxide.
Question 9.
What are the main components in the tooth paste?
Answer:
Main components in the tooth paste are calcium carbonate, aluminum hydroxide and sodium bi carbonate. All these chemicals are bases.
Question 10.
What are alkalis?
Answer:
Bases that can dissolve in water are called alkalis.
Question 11.
Give some examples for alkalis.
Answer:
Some examples of alkalis are sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide.
![]()
Question 12.
What are neutral substances?
Answer:
The substance which is neither an acid nor a base is known as neutral substance.
Question 13.
Give examples for neutral substances.
Answer:
Distilled water, salt solution, sugar solution etc are example for neutral substances.
Question 14.
Who gave the most modern definition of acids and alkalis?
Answer:
Svante Arrhenius Swedish physical chemist gave the most modern definition of acids and alkalis.
Question 15.
What are indicators?
Answer:
Substances which are used to test acids or bases are called acid base indicators.
Question 16.
From what does litmus extracted?
Answer:
Litmus is extracted from lichens.
Question 17.
What are olfactory indicators?
Answer:
Substances which change their smell when mixed with acid or base are known as olfactory indicators. Ex: onion, vanilla and clove oil.
Question 18.
What happens when a metal piece is dropped in an acid?
Answer:
If you drop a metal piece in an acid it reacts with acid and releases hydrogen gas.
![]()
Question 19.
How can you test hydrogen gas?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas make the flair e to put off with a pop sound.So we can test it by introduc¬ing a incense stick into the mouth of the container having gas.
Question 20.
Why does balloon fill with hydrogen gas fly?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas has less weight than air. So balloon fill with hydrogen gas flies high.
Question 21.
How can you test carbon dioxide gas?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide gas put off the fire. So we can test it by introducing a lighting match stick into the mouth of the container having gas.
Question 22.
What is neutralization reaction?
Answer:
Reaction of an acid and a base is called neutralization reaction.
Question 23.
What are the substances formed in neutralization reaction?
Answer:
The substances formed in neutralization reaction are water and salt.
Question 24.
What do antacids contain?
Answer:
Antacids contain bases, eg: aluminum hydroxide, milk of magnesia.
Question 25.
Why do we get pain and itching, when an ant bites us?
Answer:
When an ant bites us, it injects formic acid into our skin. It causes pain and itching.
Question 26.
What is Acid rain?
Answer:
Rain water with slight acidic nature is called Acid rain.
![]()
Question 27.
All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis. Give one example in support of this statement.
Answer:
Zinc hydroxide is a base but not an alkali. It doesn’t dissolve in water.
7th Class Science 2nd Lesson Nature of Substances Short Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Mention some food items containing acids and write the name of the acid present in them.
Answer:
| Food item | Acid present |
| Lemon | Citric acid |
| Tamarind | Tartaric acid |
| Apple | Malic acid |
| Tomato | Oxalic acid |
| Amla | Ascorbic acid |
Question 2.
What are mineral acids? Give examples.
Answer:
- Some acids are prepared artificially from minerals which are extracted from the earth. Such acids are known as mineral acids or synthetic acids.
- Hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acids are examples for mineral acids.
Question 3.
Mention any four daily life situations where acids are being used.
Answer:
- Hydrochloric acid is used for bath room cleaning.
- Sulphuric acid is used in batteries.
- Soda water and cool drinks contain carbonic acids.
- Fatty acids are used in manufacturing of soaps.
- Citric acid, tartaric acid, acetic acid etc, are used in the preparation and preserva¬tion of some foods.
Question 4.
Mention any four daily life situations where bases are being used.
Answer:
- Bath soap is prepared using potassium hydroxide.
- Detergent soap for washing clothes is prepared using Sodium hydroxide.
- Aluminium hydroxide is used in the preparation of tooth paste.
- Aluminium hydroxide and milk of magnesia are used in preparation of antacids.
- Quick lime and Potassium hydroxide are used to treat acidic soils.
![]()
Question 5.
Is it possible to test all the acids and bases simply by tasting or touching them? Why?
Answer:
- No, It is not possible to test all the acids and bases simply by tasting or touching them.
- Some acids like hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acids and bases like so¬dium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide are very harmful and strong.
- We cannot test them by touch or taste.
- We should use indicators to test them.
Question 6.
How to prepare turmeric indicator?
Answer:
- Take a table spoon of turmeric powder in a plate.
- Add little water and make it into a paste.
- Take a white paper and apply the paste over it on both sides and let it dry.
- After drying, cut the paper into strips.
- Now turmeric paper strips are ready for use as indicator.
Question 7.
Do the turmeric strip act as a indicator? How?
Answer:
- Yes, turmeric strip act as a indicator.
- This is because turmeric is a natural indicator.
- The colour of turmeric strip will change into reddish brown in basic solutions.
- It remain yellow in acidic solutions.
Question 8.
How can you identify acids and bases using hibiscus indicator?
Answer:
- Hibiscus is a natural indicator that changes its colour in acids and bases.
- It changes its colour from violet to pink in acids.
- It changes its colour from violet to green in bases.
- Thus it can be used to identify acids and bases.
Question 9.
Mention the colours of different indicators in acidic and basic mediums.
Answer:
| Indicator | In acid | In base |
| 1. Blue litmus | Red | – |
| 2. Red litmus | – | Blue |
| 3. Methyl orange | Red | Yellow |
| 4. Phenolphthalein | – | Pink |
| 5. Turmeric | – | Reddish brown |
| 6. Hibiscus | Pink | Green |
Question 10.
Magicians bring blood out of a lemon when they cut it with a knife. How is it pos-sible?
Answer:
- It is simply a science trick.
- Magician prepares a knife by applying an indicator like methyl orange or hibiscus solution on it.
- Then he cut the lemon before us.
- Due to the reaction the lemon juice (acid) turns red and we are made to believe that blood is coming out of the lemon.
![]()
Question 11.
Who introduced pH scale? How is it used?
Answer:
- pH scale was introduced by Sorensen.
- Strength of acid or base solution is measured in pH scale.
- The range of pH scale is from 0 to 14.
- pH of acids is less than 7, pH of bases is more than 7 and pH of neutral substance is 7.
- Strength of acids decreases from 0 to 7 and strength of bases increases from 7 to 14.
Question 12.
Classify the following in to strong acid, weak acid, strong base, weak base.
Hydrochloric acid, Acetic acid, oxalic acid, Sodium hydroxide, Sulphuric acid, Po-tassium Hydroxide, Nitric acid, Ammonium hydroxide,Citric acid.
Answer:
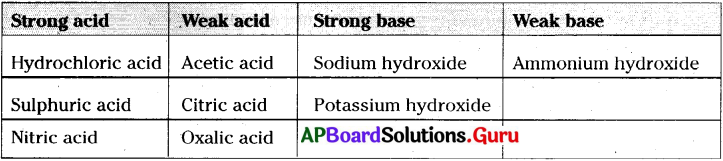
Question 13.
Pickles are not stored in aluminum or steel or copper vessels. Why?
Answer:
- Pickles contain acids.
- These acids react with metal containers and releases toxic substances.
- So, we should store them in metal containers.
- Generally, they are stored in ceramic or glass containers which do not react.
Question 14.
How can you prove carbon dioxide releases when acid reacts with calcium carbonate?
Answer:
- Take some crushed egg shells in a test tube and pour dilute sulphuric acid until the egg shells completely sink. Egg shell is made of calcium carbonate.
- We will observe that a gas being released.
- Bring a lighting match stick near the mouth of test tube.
- The gas that put off the lighting match stick indicating that the gas is carbon diox¬ide.
- This confirms that carbon dioxide releases when acid reacts with calcium carbon¬ate.
Question 15.
What is neutralization? Give examples for neutralization reaction from day-to-day life.
Answer:
- Neutralization is a chemical reaction where acid and base react with each other to form salt and water.
- The bases in the antacids neutralize gastric juice and give us relief from acidity.
- When an ant bites, it injects formic acid into the skin. It causes pain and itching. We can neutralize the acid by rubbing the paste of baking soda on the place of bite. Baking Soda is a base and it neutralizes the formic acid.
- When soil becomes too acidic, farmers neutralize it by adding basic substances like quick lime (sunnam), potassium hydroxide etc,.
- When soil becomes too basic they neutralize it with organic substances like com¬post which release acidic substances into the soil.
Question 16.
What is acid rain? How is it caused?
Answer:
- Rain water with slight acidic nature is called Acid rain.
- Air pollution is a major cause of acid rains.
- Fuels like coal and petroleum emissions have sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide etc. which react with rain water droplets and form sulphuric acid and nitric acid.
- These acids come along with rain water to cause acid rain.
Question 17.
Bhasker said that some plants help us to find out the nature (pH)of the soil. Do you support his statement?
Answer:
- Yes, I support his statement.
- Hydrangea plants have different colours of flowers based on the pH of the soil.
- If the pH of the soil is below 5.5 it gives blue flowers.
- If the pH of the soil is below 6.5 it gives pink flowers.
- Thus, they helps us to find the nature (pH) of soil.
![]()
Question 18.
Why do Neem/ miswak/ kanuga sticks are used as chew sticks from olden days?
Answer:
- Neem, miswak, kanuga sticks are used as chew sticks (pandupulla) from olden days.
- Because they have basic substances.
- The bases in these sticks neutralizes the acids released by the bacteria in our mouth.
- Thus they protect our oral health.
Question 19.
Write some acids and there uses in our daily life in the form of a table.
Answer:
| Name of the acid | Uses |
| Vinegar (Acetic acid) | Preservation of pickles and other food substances |
| Citric acid | Food preservation and in soft drinks |
| Nitric acid and sulphuric acid | Manufacture of chemical fertilizers, paints, dyes etc. |
| Sulphuric acid | Automobile battery |
| Tannic acid | Production of ink and leather |
Question 20.
Write some bases and their uses in our daily life in the form of a table.
Answer:
| Name of the Base | Uses |
| Calcium hydroxide | neutralize the acidity of soil, white washing |
| Magnesium hydroxide (milk of magnesia) | antacid and laxative |
| Ammonium hydroxide Sodium hydroxide | windows cleaner, cleaning agent manufacturing of paper, soaps and detergent |
| Potassium hydroxide | manufacturing of soaps and batteries |
Question 21.
What is soap? How is it prepared?
Answer:
- Soap is a salt with basic nature.
- It is prepared by adding fatty acids like coconut oils to alkalis like Sodium hydroxide or Potassium hydroxide.
- Detergent soap used to wash cloths contains Sodium hydroxide.
- Bath soap contains Potassium hydroxide.
Question 22.
What are the precautions to be taken while handling chemicals?
Answer:
- Do not taste and smell. Do not let it fall on the body.
- Use a dropper while transferring acid from bottle.
- While adding water to make dilution, pour small quantities of acid slowly into water taken in a beaker.
- Use a holder to hold a test tube.
- Read the precautions given on the containers of substances.
![]()
Question 23.
What precautions should be taken if the body burns due to chemicals?
Answer:
- Start first aid immediately.
- Remove contaminated clothes from the person.
- Wash the affected area with plenty of water.
- Don’t pierce the blisters.
- Shift the person to hospital.
7th Class Science 2nd Lesson Nature of Substances Long Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the properties of Acids.
Answer:
- Acids are sour to taste.
- They turn blue litmus to red colour, methyl orange to red colour, hibiscus indicator to pink colour.
- They don’t change the colour of phenolphthalein and turmeric indicators.
- pH of acids is less than 7.
- Acids react with metals and release hydrogen gas.
- Acids react with calcium carbonate to release carbon dioxide.
- Acids react with base to form water and salt. This reaction is called neutralisation reaction.
- Hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid are examples for acids.
Question 2.
Write the properties of Bases.
Answer:
- Bases are bitter to taste.
- They are slippery to touch.
- They turn red litmus to blue colour, methyl orange to yellow colour, phenolphtha- lein to pink and hibiscus indicator to green colour.
- They change the colour of turmeric indicator to reddish brown.
- pH of acids is more than 7.
- Bases like sodium hydroxide react with metals and releases hydrogen gas.
- Bases react with acid to form water and salt. This reaction is called neutralisation reaction.
- Sodium hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide and calcium hy-droxide are examples for bases.
![]()
Question 3.
How can you demonstrate the neutralisation reaction in the laboratory?
Answer:
Aim: To demonstrate the neutralisation reaction.
What you need:
1) Conical flask, 2) Dropper, 3) Sodium hydroxide solution, 4) Hydro-chloric acid, 5) Phenolphthalein indicator
How to do:
Take sodium hydroxide solution in a conical flask and observe its colour. Now add 2-3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator to it. Now observe the colour. It is pink in colour. Using a dropper add dilute hydrochloric acid drop by drop to this solution, and stir gently.
What you see:
The pink colour of the solution disappears. On crystallisation water evaporates from this solution leaving the salt in the flask.
What you learn:
In this reaction acid and base reacts with each other to form salt and water. Such reactions are called neutralisation reactions.
Hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium chloride + water
Question 4.
Take the following solutions in to test tubes. Test them with a) red litmus, b) blue litmus, c) methyl orange and d) phenolphthalein indicators. Tabulate your results. 1)Dilute hydrochloric acid, 2) Sodium hydroxide, 3) Acetic acid, 4) Salt solution, 5) Sugar solution and 6) Soap water
Answer:
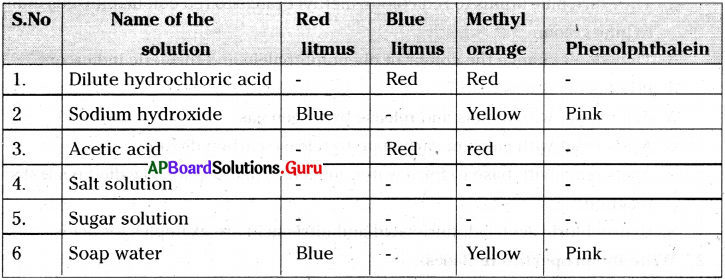
Question 5.
How can you prove that hydrogen gas releases when acid reacts with metals?
(or)
How can you produce hydrogen gas in the laboratory?
Answer:
Aim: Acid reacts with metals and produces hydrogen gas.
Materials required:
Conical flask, hydrochloric acid, zinc pieces, incense stick, match box.
Procedure:
Take 5g of zinc metal pieces in a conical flask. Pour 20 ml of dilute hydro-chloric acid into it. Now, observe what happens.
Observation:
The zinc pieces reacted with the hydrochloric acid and releases a gas. Test for hydrogen gas
Now, introduce a incense stick into mouth of the conical flask. The flame of burning stick will put off with a pop sound. This is a test for hydrogen gas. Hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc metal and forms zinc chloride, releases hydrogen gas. This reaction can be written as a word equation,
Zinc + hydrochloric acid → zinc chloride + hydrogen
Conclusion:
Hence, we can conclude that acids react with metals and release hydrogen gas.
AP Board 7th Class Science 2nd Lesson 1 Mark Bits Questions and Answers Nature of Substances
I. Multiple Choice Questions
1. Table salt contains
A) Sodium chloride
B) Sodium bicarbonate
C) Potassium chloride
D) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
A) Sodium chloride
2. Baking soda contains
A) Sodium chloride
B) Sodium bicarbonate
C) Potassium chloride
D) Sodium hydroxide
Answer:
B) Sodium bicarbonate
3. Gastric juice means
A) Sulphuric acid
B) Citric acid
C) Antacid
D) Hydrochloric acid
Answer:
D) Hydrochloric acid
![]()
4. Sulphuric acid reacts with eggshell and releases
A) Carbondioxide
B) Hydrogen
C) Oxygen
D) None
Answer:
A) Carbondioxide
5. Substance/s formed in a neutralization reaction is/are
A) Water
B) Salt
C) A and B
D) Hydrogen
Answer:
C) A and B
6. Which of the following does not contain acid?
A) lemon
B) Bitter gourd
C) Amla
D) Tomato
Answer:
B) Bitter gourd
7. This acid is present in cool drinks
A) Sulphuric acid
B) Hydrochloric acid
C) Carbonic acid
D) Vinegar
Answer:
C) Carbonic acid
8. Bath soap is prepared using
A) Sodium hydroxide
B) Aluminum hydroxide
C) Calcium carbonate
D) Potassium hydroxide
Answer:
D) Potassium hydroxide
9. Olfactory indicator from the following
A) Hibiscus
B) Phenolphthalein
C) Clove oil
D) Methyl orange
Answer:
C) Clove oil
10. lichens are used in the preparation of
A) Litmus
B) Methyl blue
C) Phenolphthalein
D) Olfactory indicators
Answer:
A) Litmus
![]()
11. Phenolphthalein shows colour change with
A) Acids
B) Bases
C) both A & B
D) Neutral substances
Answer:
B) Bases
12. Which of the following is a strong acid?
A) Citric acid
B) Acetic acid
C) Sulphuric acid
D) Malic acid
Answer:
C) Sulphuric acid
13. This gas is lighter than air
A) Hydrogen
B) Nitrogen
C) Oxygen
D) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
A) Hydrogen
14. Product of neutralisation
A) Salt
B) Water
C) Both A & B
D) Acid
Answer:
C) Both A & B
15. Example for salt
A) Common salt
B) Antacid
C) Tooth paste
D) Clove oil
Answer:
A) Common salt
16. Acid produced in stomach
A) Sulphuric acid
B) Hydrochloric acid
C) Nitric acid
D) Carbonic acid
Answer:
B) Hydrochloric acid
17. This can be used to treat ant bite
A) Baking soda
B) Common salt
C) Vinegar
D) Turmeric
Answer:
A) Baking soda
18. pH of bases
A) 0-14
B) 7
C) more than 7
D) less than 7
Answer:
C) more than 7
19. This is responsible for acid rains
A) Sulphur dioxide
B) Nitrogen dioxide
C) Both A & B
D) Oxygen
Answer:
C) Both A & B
20. Flowers that change their colour according to the nature of soil
A) Hydrangea
B) Marigold
C) Hibiscus
D) Jasmine
Answer:
A) Hydrangea
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Rain with slight ………….. nature is called acid rains.
2. Wash the affected burning area on skin with ………….. .
3. ………….. will be prepared by adding fatty acids to alkalis.
4. ………….. are used in making soaps.
5. ………….. are used to test the nature of substances.
6. ………….. acid is also called as Vitamin C.
7. ………….. acid is used for bath room cleaning.
8. ………….. acid is used in batteries.
9. Soda water and cool drinks contain ………….. acids.
10. Bases are ………….. to taste.
11. Bath soap is prepared using ………….. .
12. Detergent soap is prepared using
13. Bases that can dissolve in water are called ………….. .
14. The substance which is neither an acid nor a base is known as ………….. .
15. Purewater is a ………….. substance.
16. Substances which are used to test acids or bases are called ………….. .
17. Indicators obtained from natural sources are called as ………….. .
18. The most commonly used natural indicator is ………….. .
19. The colour of turmeric strip will change into ………….. in soap water.
20. Soda water turns into ………….. on adding hibiscus indicator.
21. Soap solutions turns ………….. on adding hibiscus indicator.
22. An indicator prepared from artificialsources is known as ………….. .
23. Methyl orange turns in acids and ………….. in bases.
24. Phenolphthalein turns ………….. in bases, but ………….. in acids.
25. Substances which change their smell when mixed with acid or base are known as ………….. .
26. ………….. is a mixture of different indicators and shows different colours in different solutions.
27. ………….. can show the strength of acid or alkaline substance.
28. Strength of acid or base solution is measured in ………….. scale.
29. pH of acids is ………….. .
30. pH of bases is ………….. .
31. pH of neutral substance is ………….. .
32. Natural acids are ………….. acids.
33. Acids react with metals and release gas.
34. Acids react with ………….. and release carbon dioxide gas.
35. Reaction of an acid and a base is called ………….. reaction.
36. The substances formed in neutralization reaction are ………….. and ………….. .
37. Antacids contain ………….. .
38. When an ant bites, it injects acid into the skin.
39. When soil becomes too acidic, farmers treat it by adding
40. When soil becomes too basic,farmers treat it with
41. Rain water with slight acidic nature is called
42. ………….. acid is used in the preservation of pickles and other food substances.
43. ………….. acid is used in the production of ink and leather.
44. Base used in windows cleaner is ………….. .
45. Magnesium hydroxide is used in ………….. and ………….. .
Answer:
- acidic
- plenty of water
- Soap
- Bases
- Indicators
- Ascorbic
- Hydrochloric
- Sulphuric
- carbonic
- bitter
- potassium hydroxide
- Sodium hydroxide
- alkalis
- neutral substance
- Neutral
- acid base indicators
- Natural indicators.
- litmus
- reddish brown
- pink
- green
- Synthetic indicator.
- red, yellow
- pink, does not change
- olfactoryin dicators.
- Universal indicatoris
- Universal indicator
- pH
- less than 7
- more than 7
- 7
- weak
- hydrogengas.
- calcium carbonate
- neutralization reaction.
- water, salt
- bases.
- formic
- quick lime/ potassium hydroxide.
- compost.
- Acid rain.
- Acetic
- Tannic
- Ammonium hydroxide
- antacid and laxative
III. Match the following
1.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| A) Blue litmus in acid | 1) Yellow |
| B) Methyl orange in base | 2) No change |
| C) Hibiscus in acid | 3) Red |
| D) Phenolphthalein in acid | 4) Brown |
| E) Turmeric in base |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| A) Blue litmus in acid | 3) Red |
| B) Methyl orange in base | 1) Yellow |
| C) Hibiscus in acid | 5) Pink |
| D) Phenolphthalein in acid | 2) No change |
| E) Turmeric in base | 4) Brown |
2.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| A) Hydrangea plants | 1) Air pollution |
| B) Neem | 2) pH of the soil |
| C) pH scale | 3) Chew sticks |
| D) Nitric acid | 4) Manufacture of fertilizers |
| E) Acid rain | 5) Automobile battery |
| 6) Sorensen |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| A) Hydrangea plants | 2) pH of the soil |
| B) Neem | 3) Chew sticks |
| C) pH scale | 6) Sorensen |
| D) Nitric acid | 4) Manufacture of fertilizers |
| E) Acid rain | 1) Air pollution |
3.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| A) Antacid | 1) Formic acid |
| B) Ant | 2) Salt and water |
| C) Neutralisation | 3) Bases that can dissolve in water |
| D) Olfactory indicator | 4) Stomach |
| E) Alkalis | 5) Hibiscus |
| 6) Clove oil |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| A) Antacid | 4) Stomach |
| B) Ant | 1) Formic acid |
| C) Neutralisation | 2) Salt and water |
| D) Olfactory indicator | 6) Clove oil |
| E) Alkalis | 3) Bases that can dissolve in water |
Do You Know?
Arrhenius
→ Svante Arrhenius Sweadish physical chemist gave the most modern definition of acids and alkalis. He got Noble prize in 1903 for his contribution in chemistry.
BLOOD IN LEMON…!
→ You might have seen the trick by magicians … blood coming out from a lemon when cut with a knife. This is made possible by applying an indicator like Methyl orange or hibiscus flower solution on the knife before cutting the lemon. The indicator reacts with lemon juice to give out red coloured juice. Next time you see such a trick reveal the secret.
→ Hydrangea plants have different colours of flowers based on the pH of the soil. If the pH of the soil is below 5.5 it gives blue flowers. If the pH of the soil is below 6.5 it gives pink flowers. This may helps us to find the nature of soil.
→ Neem, miswak, kanuga sticks are used as chew sticks (pandu pulla) from olden days.
Do you know why? Because they have basic substances. The bases in these sticks neutralizes the acids released by the bacteria in our mouth.
![]()
→ Soap is a salt with basic nature. It is prepared by adding fatty acids like cocohut oils to alkalis like Sodium hydroxide or Potassium hydroxide. Detergent soap is used to wash cloths contains Sodium hydroxide where as bath soap contains Potassium hydroxide. Zinc hydroxide is a. base but not an alkali. This is used in cosmetic products. All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis. Discuss with your friends.