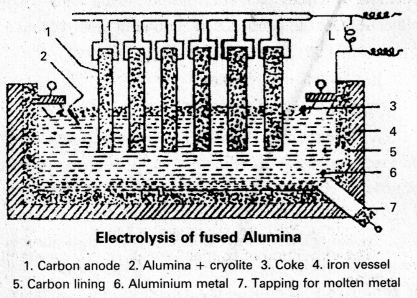
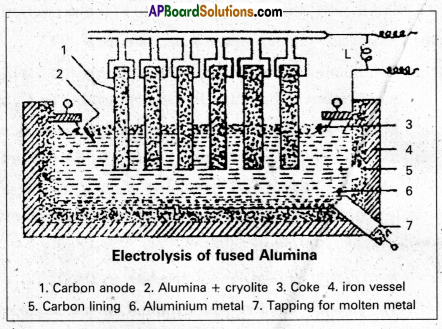
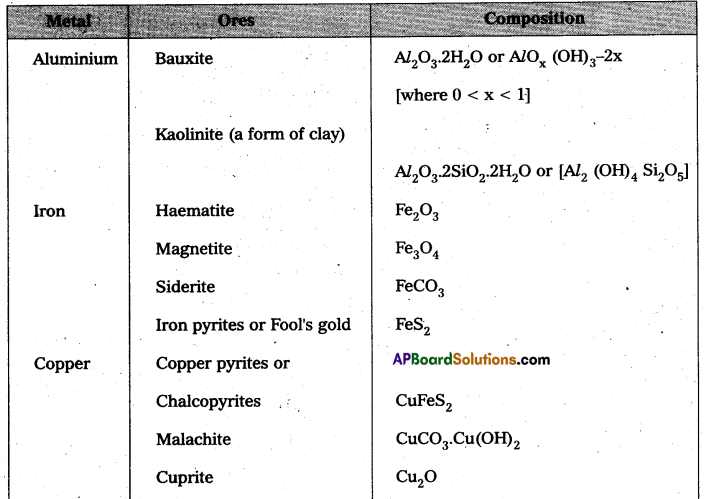
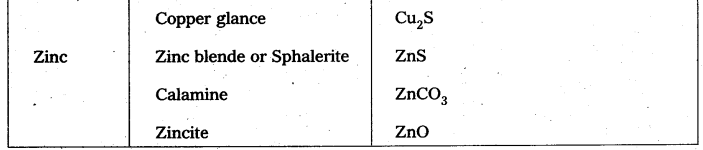
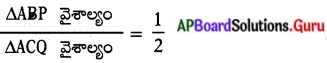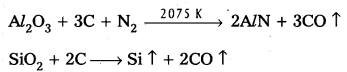These AP 10th Class Social Studies Important Questions 17th Lesson స్వతంత్ర భారత రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాణం will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 10th Class Social 17th Lesson Important Questions and Answers స్వతంత్ర భారత రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాణం
10th Class Social 17th Lesson ½ Mark Important Questions and Answers in Telugu Medium
1. భారతీయ ప్రజాస్వామ్యంలో వాస్తవ కార్యనిర్వహణాధి కారి ఎవరు
జవాబు:
ప్రధానమంత్రి.
2. అమెరికాలో పరిపాలనా శాఖలకు అధిపతులను ఏమంటారు?
జవాబు:
కార్యదర్శులు.
3. “భారత రాజ్యాంగాన్ని 1935 చట్టానికి నకలు మాత్రమే”నని విమర్శించింది ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
మౌలానా హస్రత్ మొహానీ.
4. 1976లో 42వ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ ద్వారా రాజ్యాంగ ప్రవేశికలో చేర్చిన పదాలు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
లౌకిక, సామ్యవాద.
5. నేపాల్ లో రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రూపొందించే ప్రక్రియ ఎప్పుడు మొదలయ్యింది?
జవాబు:
2007 లో.

6. రాజ్యాంగ (పరిషత్తు) సభలో షెడ్యూల్ కులాలకు చెందిన సభ్యులు ఎంతమంది ఉన్నారు?
జవాబు:
26 మంది.
7. భారత రాజ్యాంగ సభ్యులలో ఎక్కువ మంది ఏ పార్టీకి చెందిన వారున్నారు?
జవాబు:
భారత జాతీయ కాంగ్రెస్.
8. పాకిస్తాన్ రాజ్యాంగ సభ ఎప్పుడు ఏర్పాటయ్యింది?
జవాబు:
1947, ఆగస్టు 14 న.
9. బి. ఆర్. అంబేద్కర్ రాజ్యాంగసభ ముందు ఏ సంవత్సరంలో రాజ్యాంగ ముసాయిదాను ఉంచారు?
జవాబు:
1948 లో
10. అధికార విభజన ఏ ప్రభుత్వ ముఖ్య లక్షణం?
జవాబు:
సమాఖ్య
11. అంటరానితనాన్ని నిషేధించే భారత రాజ్యాంగ ప్రకరణ ఏది?
జవాబు:
17వ ప్రకరణం.
12. ఒక దేశం యొక్క ప్రభుత్వ స్వభావాన్ని, సిద్ధాంతాలను తెలియజేసేది?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగం.
13. భారతదేశంలో ఏర్పాటైన ప్రభుత్వ స్వరూపం ఏది?
జవాబు:
పార్లమెంటరీ వ్యవస్థ.

14. రాజ్యాంగం యొక్క స్వరూప, స్వభావాలను తెలియజేసేది ఏది?
జవాబు:
ప్రవేశిక.
15. అంటరాని తనానికి మూల కారణం ఏది?
జవాబు:
కుల వ్యవస్థ.
16. వివాహం, విడాకులు, వారసత్వ చట్టాలు, వాణిజ్యంలలో ఉమ్మడి జాబితాలో లేని అంశమేది?
జవాబు:
వాణిజ్యం
17. రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ చేయాలంటే పార్లమెంట్ లో ఎంత మెజారిటీ కావాలి?
జవాబు:
2/3 వంతు.
18. నేపాల్ లో మొదటి ఎన్నికలు ఏ సంవత్సరంలో జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1959.
19. రాజ్యాంగ సభ ఎన్నికలు ఏ పద్దతిలో జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
పరోక్ష పద్ధతిలో.
20. అమెరికా ప్రభుత్వ వ్యవస్థని ఏ తరహా ప్రభుత్వం అంటారు?
జవాబు:
అధ్యక్ష
21. ప్రతిపాదిత భారత రాజ్యాంగం ఒకే పౌరసత్వం ఉండే ద్వంద్వ….?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యతంత్రం.
22. రాజ్యాంగంలో ప్రభుత్వ విధానాలకు ఏ సూత్రాలు ఉన్నాయి?
జవాబు:
ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలు.
23. రాజ్యాంగంలోని అధికరణలను సవరించే అధికారం దేనికి మాత్రమే కలదు?
జవాబు:
పార్లమెంటుకు.

24. సామాజిక ఇంజనీరింగ్ సాధనలో ఎవరి హక్కులు ఒక ముఖ్యమైన అంశం?
జవాబు:
అల్ప సంఖ్యాక వర్గాల.
25. 2018 వరకు రాజ్యాంగానికి ఎన్ని సవరణలు చేసారు?
జవాబు:
99
26. శాంతి కాముకతను ఏ దేశ రాజ్యాంగ ప్రవేశిక కనబరిచింది?
జవాబు:
జపాన్.
మొదటి జతలోని రెండు అంశాల మధ్యగల సంబంధం ఆధారంగా రెండవ జతను పూరించండి.
27. ఇండియా : పార్లమెంటరీ విధానం : : అమెరికా : ?
జవాబు:
అధ్యక్షతరహా విధానం.
28. బ్రిటన్ : రాజు : : ఇండియా : ?
జవాబు:
అధ్యక్షుడు / రాష్ట్రపతి.
29. అధికరణలు : 315 : : షెడ్యూళ్ళు : ?
జవాబు:
08

30. ఒక సమాఖ్య (దేశం)లో ఇరవై రాష్ట్రాలు ఉన్నాయను కుంటే, ఇరవై రకాల (స్వతంత్ర) చట్టాలుంటే పరిస్థితి ఎలా ఉంటుందో గుర్తించి, జవాబు పత్రంలో రాయండి.
i) రాష్ట్రాలు బలహీన పరచటమవుతుంది.
ii) ఒక రాష్ట్రంలో చట్ట బద్ధమైంది మరొక రాష్ట్రంలో కాదు.
iii) రాష్ట్రాలలోని ప్రజల మధ్య గౌరవ భావం ఏర్పడుతుంది.
iv) రాష్ట్రాల నియంతృత్వం పెరుగుతుంది.
జవాబు:
(i) & (ii)
31. ఒక దేశ రాజ్యాంగాన్ని చేతిలో పెడితే చట్టానికి సంబంధించిన ‘భరత్’ అనే విద్యార్థి వేసే ప్రశ్నలు క్రిందివానిలో ఏమై ఉంటాయి?
i) ఏర్పాటు చేస్తున్న ప్రభుత్వ రూపం ఏమిటి?
ii) రాజ్యాంగ రూపం ఏమిటి?
iii)న్యాయ స్వరూపం ఏమిటి?
iv) ఆర్థిక స్వరూపం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
(i) & (ii)
32. నేపాలో రాచరికం ఎప్పుడు రద్దయ్యింది?
జవాబు:
2007 లో.
33. భారత రాజ్యాంగ సభకు ఏ సంవత్సరంలో ఎన్నికలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1946 లో.
34. భారత రాజ్యాంగ సభలో బ్రిటిషు ప్రత్యక్ష పాలనలోని సభ్యులు ఎంతమంది?
జవాబు:
292.
35. భారత రాజ్యాంగ సభలో స్వదేశీ సంస్థానాల సభ్యులు ఎంత మంది?
జవాబు:
93.

36. భారత రాజ్యాంగ సభలో మహిళలు ఎంతమంది ఉన్నారు?
జవాబు:
తొమ్మిది మంది.
37. భారత రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రాజ్యాంగ సభ ఎప్పుడు ఆమోదించింది?
జవాబు:
1949, నవంబరు, 26న.
38. భారత రాజ్యాంగం ఎప్పుడు అమల్లోకి వచ్చింది?
జవాబు:
1950, జనవరి 26న.
39. ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగంలో ఎన్ని అధికరణలు, ఎన్ని షెడ్యూళ్ళు ఉన్నాయి.
జవాబు:
315, 8.
40. భారత రాజ్యాంగంలోని కొన్ని (మౌలిక) అంశాలను ఎట్టి పరిస్థితులలోనూ సవరించటానికి లేదని ఏ కేసులో వాదించారు?
జవాబు:
కేశవానంద భారతి కేసు.
41. సామ్యవాద ప్రభుత్వంలోని ఏ సూత్రాన్ని నీవు ప్రశంసిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
జవాబు:
సమానత్వం
42. భారత సమాఖ్య అధిపతి ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
రాష్ట్రపతి.

43. సామాజిక నిర్మాణం కోసం భారత రాజ్యాంగం చేసిన ఏర్పాటు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
రిజర్వేషన్లు / అంటరానితనం నిషేధం / బలహీన వర్గాలకు రక్షణ.
44. భారత రాజ్యాంగంలోని ఏ అధికరణం రాష్ట్రపతి పాలన గురించి చెబుతుంది?
జవాబు:
356.
45. ‘లింగం” అన్న పదాన్ని ఏ దేశ రాజ్యాంగ ప్రవేశిక పేర్కొంది?
జవాబు:
నేపాల్.
46. స్వతంత్ర భారత తొలి రాష్ట్రపతి ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
బాబు రాజేంద్ర ప్రసాద్.
47. “ఏ దేశ రాజ్యాంగ ప్రవేశిక ప్రభుత్వం అన్నది ప్రజల పవిత్ర నమ్మకం” అని పేర్కొంది?
జవాబు:
జపాన్.
48. జవహర్లాల్ నెహ్రూ, వల్లభాయ్ పటేల్, గాంధీజీ, సరోజిని నాయుడు లలో ఎవరు భారత రాజ్యాంగ సభ సభ్యులు కారు?
జవాబు:
గాంధీజీ.
49. భారత రాజ్యాంగసభ అధ్యక్షుడు ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
డా|| బాబు రాజేంద్ర ప్రసాద్.
50. భారత రాజ్యాంగ ముసాయిదా సంఘం యొక్క అధ్యక్షులు ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
డా|| బి.ఆర్. అంబేద్కర్.
51. ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగాన్ని ఎన్ని నెలలు, ప్రజలు ముందు ఉంచారు?
జవాబు:
8 నెలలు.
52. భారత దేశంలో అత్యున్నత న్యాయస్థానం ఏది?
జవాబు:
సుప్రీంకోర్టు.

53. కేంద్రం, రాష్ట్రం రెండూ చట్టాలు చేసే అవకాశం ఉన్నా జాబితా ఏది?
జవాబు:
ఉమ్మడి జాబితా.
54. ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలు రాజ్యాంగంలోని ఏ భాగంలో ఉన్నాయి?
జవాబు:
నాలుగవ భాగంలో.
55. రాచరిక పాలనను రద్దు చేస్తూ నేపాలను ఏవిధమైన రాజ్యాంగ ప్రకటించారు?
జవాబు:
సమాఖ్య, ప్రజాస్వామిక, గణతంత్ర.
56. కొన్ని విషయాలలో ఏ చట్టంలోని అంశాలను అనుసరించాలని రాజ్యాంగ సభ నిర్దేశించింది?
జవాబు:
భారత ప్రభుత్వ చట్టం – 1935.
57. అమెరికా ప్రభుత్వంలో కార్యనిర్వాహక వర్గానికి అధిపతిగా ఎవరు వ్యవహరిస్తారు?
జవాబు:
అధ్యక్షుడు.
58. భారత సమాఖ్య అధ్యక్షుడు సాధారణంగా ఎవరి సలహాలకు కట్టుబడి ఉంటాడు?
జవాబు:
మంత్రుల.
59. ద్వంద్వ ప్రభుత్వ విధానాన్ని ఏ వ్యవస్థలో ఏర్పాటు చేస్తారు?
జవాబు:
సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థలో.
60. భారత రాజ్యాంగం ……. పౌరసత్వం కల్పించింది?
జవాబు:
ఏక
61. ముఖ్యమైన పదవులలో నియమించటానికి దేశమంతటికి ఏవిధమైన సర్వీసులు కలవు?
జవాబు:
అఖిల భారత సర్వీసులు.
62. కేంద్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలపై చట్టంచేసే అధికారం ఎవరికి ఉంది?
జవాబు:
కేంద్రానికి.

63. రాష్ట్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలపై చట్టాలు చేసే అధికారం ఎవరికి ఉంది?
జవాబు:
రాష్ట్రాలకు.
64. సమానత్వ హక్కు నేపథ్యంలో ఏ ఆచారానికి చట్టపరంగా అంతం పలకాలని నిర్ణయించినారు?
జవాబు:
అంటరానితనం.
65. “మతం, కులం లేదా చట్టబద్ద జీవనోపాధి ఆధారంగా వివక్షత చూపే ఏ చర్యకైనా అంటరానితన మంటారు” అన్న నిర్వచనం ఇచ్చినది ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
రోహిణి కుమార్ చౌదరి.
66. అమెరికాలోని ద్వంద్వ ప్రభుత్వాలలో ఉండే ప్రభుత్వాలు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
ఫెడరల్, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాలు.
67. జపాన్ పార్లమెంట్ నేమంటారు?
జవాబు:
నేషనల్ డైట్.
68. రాజ్యాంగ సభ సభ్యులను ఎన్నుకొన్నది ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
రాష్ట్ర శాసన సభ సభ్యులు.
69. 1946 డిసెంబర్ 13న రాజ్యాంగ సభలో “భారత దేశానికి మనం కోరుకుంటున్న భవిష్యత్ ఒక బృందానికో లేక ఒక వర్గానికో లేదా రాష్ట్రానికో కాక మొత్తం 40 కోట్ల జనాభాకు సంబంధించినది” అని ప్రకటన చేసిన వారు?
జవాబు:
జవహర్లాల్ నెహ్రూ.
70. రాజ్యాంగ ముసాయిదాలో భారత సమాఖ్య అధిపతి?
జవాబు:
అధ్యక్షుడు / రాష్ట్రపతి.
71. భారతీయ ప్రజాస్వామ్యంలో వాస్తవ కార్య నిర్వహణాధికారి ఎవరు?\
జవాబు:
ప్రధానమంత్రి.

72. అమెరికా ప్రజాస్వామ్యంలో వాస్తవ కార్యనిర్వహణాధికారి ఎవరు?\
జవాబు:
అధ్యక్షుడు.
73. అమెరికాలో పరిపాలనా శాఖలకు అధిపతులు ……..?
జవాబు:
కార్యదర్శులు.
74. భారతదేశంలో పరిపాలనా శాఖకు అధిపతులు …. ?
జవాబు:
మంత్రులు.
75. భారతదేశ ఐక్యతను కాపాడేందుకు రాజ్యాంగం రూపొందించిన మౌలిక అంశం/లు ఏది/ఏవి? గుర్తించి రాయండి.
i) ఒకే న్యాయ వ్యవస్థ.
ii) అఖిల భారత సివిల్ సర్వీసెస్.
iii)మౌలిక చట్టాలలో సారూప్యత.
iv) రిజర్వేషన్లు.
జవాబు:
(i), (ii) & (iii)
76. భారత న్యాయవ్యవస్థ చాలా దగ్గరగా ఏ దేశ న్యాయ వ్యవస్థను పోలి ఉంటుంది?
జవాబు:
కెనడా.

77. సాక్ష్యాల చట్టం, ఆస్తి బదిలీ చట్టం, వివాహ, విదాకులు, పౌర విచారణ స్మృతి, శిక్షా స్మృతి వంటి పౌర నేర చట్టాల స్మృతులు వంటివి ఏ జాబితాలో ఉన్నాయి?
జవాబు:
ఉమ్మడి జాబితా.
78. సోవియట్ యూనియన్ నుంచి ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగం ఏమీ తీసుకోలేదని, భారతీయ నేపథ్యంలో కీలకమైన గ్రామాలను విస్మరించారని విమర్శించినది ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
డి. ఎస్. సేథ్
79. “అంటరానితనాన్ని ఏ రూపంలోనైనా నిషేధిస్తున్నాం, దాని ఆధారంగా విధించే వివక్షత నేరం అవుతుంది” అన్నది ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
శ్రీ ప్రోమథ రంజన్ ఠాకూర్.
80. “గత రాజకీయ, సామాజిక నిర్మాణాన్ని తిరస్కరించి ముందుకు కదులుతూ తనకు తాను కొత్త వస్త్రాలను రూపొందించుకుంటున్న దేశానికి రాజ్యాంగ సభ ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహిస్తున్నట్టుగా” ఉందని పేర్కొన్నది ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
జవహర్లాల్ నెహ్రు.
81. శాసన సభలలో చట్టాలు చేయటానికి ఉండవలసిన మెజారిటీ ఎంత?
జవాబు:
సగంకంటే ఎక్కువ / 2/3 వంతు.
82. రాజ్యాంగ సభ సభ్యుల ఎన్నికకు, సంబంధించి, క్రింది వానిని సరిగా జతపరచండి.
i) బ్రిటిషు ఇండియా ( ) a) 292
ii) స్వదేశీ సంస్థానాలు ( ) b) 93
iii)ఢిల్లీ, అజ్మీర్, కూర్గ్, బ్రిటిష్, బెలూచిస్తాన్ ( ) c) 4
iv)మొత్తం సభ్యులు ( ) d) 389
జవాబు:
i – a, ii – b, iii – c, iv – d
83. క్రింది వానిలో భిన్నంగా ఉన్న దానిని గుర్తించండి. బి.ఆర్. అంబేద్కర్, K. M. ముల్టీ, సరోజిని నాయుడు, గాంధీజీ
జవాబు:
గాంధీజీ.

84. అమెరికా, స్విట్జర్లాండ్, భారతదేశం లలో ఏక పౌరసత్వాన్ని కల్గి ఉన్న దేశమేది?
జవాబు:
భారతదేశం.
ఇవ్వబడిన గ్రాను పరిశీలించి, క్రింద ఇచ్చిన ప్రశ్నలకు జవాబులు రాయండి.
రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు
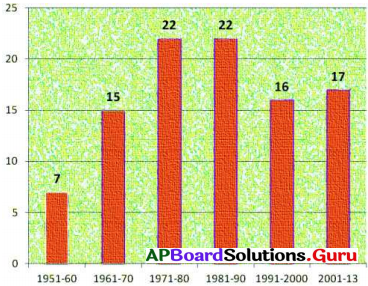
85. ఏ దశాబ్ద కాలంలో రాజ్యాంగానికి తక్కువ సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1951 – 60.
86. 2013 నాటికి రాజ్యాంగానికి ఎన్ని సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
99.
87. ఏయే దశాబ్ద కాలాల్లో రాజ్యాంగానికి సమాన సవరణలు
జవాబు:
1971 – 80, 1981 – 90.
88. రాజ్యాంగం అమల్లోకి వచ్చి 2020, జనవరి 26 నాటికి ఎన్ని సంవత్సరాలు పూర్తయ్యాయి?
జవాబు:
70 సంవత్సరాలు.
89. రాజ్యాంగాన్ని సవరించే అధికారం ఎవరికి ఉంది ? జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
పార్లమెంట్కు

90. 16 సార్లు రాజ్యాంగానికి సవరణలు ఏ దశాబ్ద కాలంలో జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1991 – 2000.
10th Class Social 17th Lesson 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers in Telugu Medium
ప్రశ్న 1.
AIADMK ని విస్తరింపుము.
జవాబు:
All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazagam (అఖిల భారత అన్నా ద్రవిడ మున్నేట్ర కజగం)
ప్రశ్న 2.
సమాఖ్యవాదం లక్షణాలు వ్రాయుము.
(లేదా)
భారత సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థ లక్షణాలను వివరించుము.
జవాబు:
- రెండు స్థాయిలలో ప్రభుత్వాలు
- అధికార విభజన
- లిఖిత రాజ్యాంగం
- ద్వంద్వ పౌరసత్వం
- స్వతంత్ర్య న్యాయశాఖ
- దృఢ రాజ్యాంగం
- రాజ్యాంగ ఆధిక్యత మొ||వి సమాఖ్యవాదం లక్షణాలు.
ప్రశ్న 3.
రాజ్యాంగంలో కల్పించిన సామాజిక మార్పునకు దోహదం చేసే అంశాలు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
- అంటరానితనాన్ని నిషేధించటం.
- S.C., S.T., లకు రిజర్వేషన్లు కల్పించటం.
- సార్వజనీన వయోజన ఓటు హక్కు
- ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలు మొదలైనవి సామాజిక మార్పునకు దోహదం చేసే అంశాలు.

ప్రశ్న 4.
భారత్, జపాన్ రాజ్యాంగ ప్రవేశికలలో గల రెండు పోలికలు వ్రాయండి.
జవాబు:
భారత్, జపాన్ రాజ్యాంగ ప్రవేశికలలో గల రెండు పోలికలు :
- సర్వసత్తాక అధికారం
- ప్రజాస్వామ్యం
- న్యాయం
- ధర్మం
ప్రశ్న 5.
పాఠశాల మొత్తానికి ఒక రాజ్యాంగం ఏర్పాటు చెయ్యాల్సి వుంటే ఎవరెవరు అందులో భాగస్వాములు కావాలి?
జవాబు:
పాఠశాల మొత్తానికి ఒక రాజ్యాంగం ఏర్పాటు చెయ్యాల్సి ఉంటే,
- అన్ని తరగతుల బాలబాలికల ప్రతినిధులు
- ప్రధానోపాధ్యాయులు
- ఉపాధ్యాయులు మరియు బోధనేతర సిబ్బంది
- పాఠశాల యాజమాన్య కమిటీ సభ్యులు మొదలగువారు భాగస్వాములు కావాలి.
ప్రశ్న 6.
ఏకీకృత రాజ్యాంగంలోని రెండు ముఖ్యమైన అంశాలేవి?
జవాబు:
ఏకీకృత రాజ్యాంగంలోని రెండు ముఖ్యమైన అంశాలు:
- ఒకే న్యాయవ్యవస్థ
- పౌర, నేర అంశాలలోని మౌళిక చట్టాలలో సారూప్యత
- అఖిల భారత సర్వీసులు
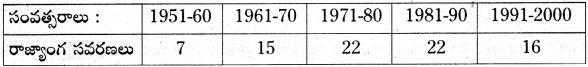
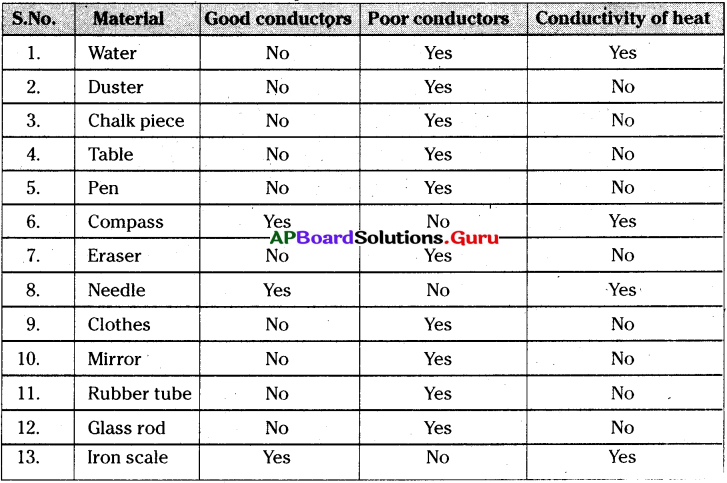
* కింది బార్ గ్రాఫ్ ను పరిశీలించి 7-10 ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
1950 – 2013 మధ్య జరిగిన 99 రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు

ప్రశ్న 7.
రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు ఎక్కువగా ఏ కాలంలో జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు ఎక్కువగా 1971-80, 1981-90 మధ్య జరిగాయి.
ప్రశ్న 8.
1951-60లో రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు తక్కువగా ఉండడానికి కారణాలు ఏమి?
జవాబు:
1961-60లో రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు తక్కువగా ఉండడానికి కారణాలు
- రాజ్యాంగం అమలులోకి వచ్చి తక్కువ కాలం అవడం.
- ఎక్కువ సమస్యలు ఉత్పన్నం కాకపోవడం.
ప్రశ్న 9.
ఏ ఏ దశాబ్దాలలో రాజ్యాంగానికి సమాన సంఖ్యలో సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1971-80 మరియు 1981-90.00
ప్రశ్న 10.
భారతదేశంలో రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ ఎవరు చేయగలరు?
జవాబు:
పార్లమెంట్ మాత్రమే చేయగలదు.
ప్రశ్న 11.
క్రింది చిత్రంలో ఇవ్వబడిన వ్యక్తికి సంబంధించిన అంశాలను గుర్తించి జవాబు పత్రంలో రాయండి.
జాతి పిత
రాజ్యాంగ రచనా సంఘం అధ్యక్షుడు
రాజ్యాంగ సభ అధ్యక్షుడు
తొలి న్యాయ శాఖామంత్రి

జవాబు:
i) రాజ్యాంగ రచనా సంఘం అధ్యక్షుడు.
ii) తొలి న్యాయశాఖా మంత్రి.
ప్రశ్న 12.
మొదటి జతలోని రెండు అంశాల మధ్య గల సంబంధం ఆధారంగా రెండవ జతను పూరించండి. ఇండియా : పార్లమెంటరీ విధానం : : అమెరికా : ?
జవాబు:
అధ్యక్ష తరహా విధానం.
ప్రశ్న 13.
నేపాల్ లో మొదటి ఎన్నికలు ఎప్పుడు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1969లో రాజు మహేంద్ర జారీ చేసిన రాజ్యాంగం కింద నేపాల్ లో మొదటి ఎన్నికలు జరిగాయి.
ప్రశ్న 14.
1991లో నేపాల్ లో ఎన్నికలు ఎందుకు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
ప్రజాస్వామిక ప్రాతినిధ్య ప్రభుత్వం కోసం ప్రజల నిరంతర పోరాటం ఫలితంగా 1991లో ఎన్నికలు జరిగాయి.
ప్రశ్న 15.
ముసాయిదా సంఘానికి నాయకుడు ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
ముసాయిదా సంఘానికి నాయకుడు డా|| బి.ఆర్ అంబేద్కర్.

ప్రశ్న 16.
రాజ్యాంగంను ఎప్పుడు ఆమోదించారు?
జవాబు:
1949 నవంబరు 26న రాజ్యాంగాన్ని ఆమోదించారు.
ప్రశ్న 17.
భారత రాజ్యాంగం ఎప్పటి నుండి అమలులోకి వచ్చింది?
జవాబు:
1950 జనవరి 26 నుంచి భారత రాజ్యాంగం అమలులోకి వచ్చింది.
ప్రశ్న 18.
ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగంలో ఎన్ని అధికరణాలు, ఎన్ని షెడ్యూళ్ళు ఉన్నాయి?
జవాబు:
ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగంలో 315 అధికరణాలు, 8 షెడ్యూళ్ళు ఉన్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 19.
అమెరికాలో అధిపతిగా ఎవరు ఉంటారు?
జవాబు:
అమెరికాలో అధ్యక్షుడు కార్యనిర్వాహక వర్గానికి అధిపతిగా ఉంటాడు.
ప్రశ్న 20.
రాజ్యాంగాలు ఎన్ని రకాలు? అవి ఏవి?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగాలు రెండు రకాలు :
- ఏకీకృత విధానం
- సమాఖ్య విధానం.
ప్రశ్న 21.
ఏకీకృత రాజ్యాంగం అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
ఏకీకృత రాజ్యాంగంలో రెండు ముఖ్యమైన అంశాలున్నాయి.
- కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వం
- ఇతర రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాలు లేకపోవటం.
ప్రశ్న 22.
సమాఖ్య రాజ్యాంగమనగా నేమి?
జవాబు:
సమాఖ్య రాజ్యాంగంలో రెండు రకాలైన ప్రభుత్వాలుంటాయి.
- కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వం
- రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వం
ప్రశ్న 23.
అమెరికాలోని ద్వంద్వ విధానమేమిటి?
జవాబు:
అమెరికాలో రెండు రకాల ప్రభుత్వాలుంటాయి. అవి
- ఫెడరల్ ప్రభుత్వం
- రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వం
ప్రశ్న 24.
చట్టాలు చేసే అంశాలను ఎన్ని రకాలుగా విభజించారు?
జవాబు:
చట్టాలు చేసే అంశాలను మూడు జాబితాలుగా విభజించారు. అవి :
- కేంద్ర జాబితా
- రాష్ట్రాల జాబితా
- ఉభయ జాబితా.
ప్రశ్న 25.
మౌలానా హస్రత్ మొహానీ ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగాన్ని ఏ విధంగా విమర్శించారు?
జవాబు:
మౌలానా హస్రత్ మొహానీ ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగం 1935 చట్టానికి నకలు మాత్రమేనని ఆరోపించారు.

ప్రశ్న 26.
ప్రొమథ రంజన్ రాకూర్ ‘అంటరానితనం’ గూర్చి ఏమన్నారు?
జవాబు:
అంటరానితనం అనేది కులవ్యవస్థ అనే వ్యాధి యొక్క లక్షణం మాత్రమే. మనం కులవ్యవస్థని సమూలంగా నిర్మూలిస్తే తప్ప అంటరానితనానికి పైపై చికిత్సలు చేసి ప్రయోజనం లేదు.
ప్రశ్న 27.
రాజ్యాంగంలో ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలు ఎక్కడ ఉన్నాయి?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగంలో నాలుగవ భాగంలో ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 28.
రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు ఎవరు చేయవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగంలోని అధికరణాల సవరణను పార్లమెంటు మాత్రమే చెయ్యాలి.
ప్రశ్న 29.
రాజ్యాంగానికి ప్రధానమార్పులు ఎప్పుడు జరిగాయి? ఎందుకు?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగానికి ప్రధానమార్పులు 1970లో చేశారు. రాజ్యాంగ ప్రవేశికలో “లౌకిక”, “సామ్యవాద” అనే పదాలను చేర్చారు.
ప్రశ్న 30.
కేశవానంద భారతి కేసులో సుప్రీంకోర్టు ఇచ్చిన తీర్పులో వేటిని అస్సలు మార్చకూడదని చెప్పింది?
జవాబు:
ప్రాథమిక హక్కులకు సంబంధించిన వాటిని అస్సలు మార్చకూడదని సుప్రీంకోర్టు తీర్పు ఇచ్చింది.
ప్రశ్న 31.
రాజ్యాంగంలో ‘అంటరానితనం’ గూర్చి అంతిమంగా తీసుకున్న నిర్ణయమేమిటి?
జవాబు:
అంతిమంగా రాజ్యాంగంలో అంటరానితనానికి నిర్వచనం ఇవ్వగూడదని, భవిష్యత్తులో అవసరమైన చట్టాలను చేసే బాధ్యతను శాసనసభకు వదిలివెయ్యాలని నిర్ణయించారు.
ప్రశ్న 32.
రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు రాజ్యాంగ రూపకల్పనకు ముందు భారత సమాజంలో ఉన్న ఏ లక్షణాలను గుర్తించారు?
జవాబు:
భారత రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు భారతీయ సమాజం అసమానతలు, అన్యాయం, లేమి వంటి సమస్యలను ఎదుర్కొంటోందని, ఆర్థిక దోపిడీకి పాల్పడిన వలస పాలకుల విధానాలకు బలి అయ్యిందనీ గుర్తించారు.

ప్రశ్న 33.
“లౌకిక”, “సామ్యవాదం” అన్న పదాలను ఏ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ ద్వారా రాజ్యాంగంలోని ఏ భాగంలో చేర్చినారు?
జవాబు:
1976వ సంవత్సరంలో 42వ సవరణ ద్వారా “లౌకిక”, “సామ్యవాదం” అనే పదాలను రాజ్యాంగంలోని ప్రవేశిక’ కు చేర్చినారు.
ప్రశ్న 34.
ఉమ్మడి జాబితాలోని అంశాలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
మొత్తం ఉమ్మడి జాబితాలో 47 అంశాలున్నాయి. వాటిలో ముఖ్యమైనవి వివాహాలు, విడాకులు, వ్యవసాయేతర భూములు, ఆస్తుల మారకం, కాంట్రాక్టులు, పౌరన్యాయం మొదలైనవి.
10th Class Social 17th Lesson 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers in Telugu Medium
ప్రశ్న 1.
కింది పేరాగ్రాఫ్ ను చదివి భారతదేశ సామాజిక, ఆర్థిక రంగాలలో వచ్చిన మార్పులను విశ్లేషించండి.
భారతదేశమంతటా భూసంస్కరణలు మనఃస్ఫూర్తిగా అమలు చేయలేదు. జమీందారీ వ్యవస్థను రద్దు చేశారు కానీ, భూమి లేని వాళ్ళకి భూపంపిణీ జరుగలేదు. గ్రామీణ ప్రాంతాల్లో ధనికులు, శక్తిమంతులు భూమిలోని అధిక భాగాలపై నియంత్రణ కొనసాగిస్తూనే ఉన్నారు. దళితులు ఇంకా భూమిహీనులుగానే ఉన్నారు. కాని వెట్టి చాకిరి నిర్మూలన, అంటరానితనం నిషేధం వల్ల ప్రయోజనం పొందారు.
జవాబు:
- రాజ్యాంగ సభ సామాజిక, ఆర్థిక, రాజకీయ న్యాయాన్ని, హోదా, అవకాశాలలో సమానత్వాన్ని కోరుకుంది. కొత్త రాజ్యాంగాన్ని ఆవిష్కరించిన నెల రోజులకు ప్రణాళికా సంఘాన్ని ఏర్పరిచారు.
- మొదటి పంచవర్ష ప్రణాళిక వ్యవసాయం మీద కేంద్రీకరించి ఆహార ఉత్పత్తిని పెంచడానికి ఉద్దేశించబడింది.
- వ్యవసాయ రంగంలోని మార్పును నెహ్రూ కేవలం ఆర్థిక అంశంగా చూడలేదు. దానిని గ్రామీణ రంగ రాజకీయ, సామాజిక, ఆర్థిక మార్పుగా పరిగణించాడు.
- కావున సామాజిక – ఆర్థిక మార్పు తీసుకురావడానికి నెహ్రూ ఈ క్రింది చర్యలను చేపట్టినాడు. ప్రధానంగా మూడు అంశాలున్నాయి. అవి :
1) భూసంస్కరణలు,
2) వ్యవసాయ సహకార సంఘాలు,
3) స్థానిక స్వపరిపాలన
1) భూసంస్కరణలు :
మూడు రకాలైన భూసంస్కరణలను నెహ్రూ ప్రతిపాదించాడు.
ఎ) జమిందారీ వ్యవస్థ రద్దు,
బి) కౌలు విధానాల సంస్కరణ,
సి) భూ పరిమితి విధానాలు. ఈ మూడు సంస్కరణల ముఖ్య ఉద్దేశం దున్నేవానికి భూమి చెందేలా చూసి మరింత ఉత్పత్తి చెయ్యటానికి ప్రోత్సహించటం.
2) వ్యవసాయ సహకార సంఘాలు :
సహకార సంఘాల ద్వారా ఆర్థికంగా లాభసాటి పరిమాణాన్ని చేరుకోవటమే కాకుండా విత్తనాలు, ఎరువులు, రసాయనాలు వంటి విలువైన ఉత్పాదకాలను అందించాలి.
3) స్థానిక స్వపరిపాలన :
భూసంస్కరణలు అమలు అయ్యేలా చూసి, గ్రామ ఉమ్మడి ప్రయోజనాలకు అనుగుణంగా సహకార సంఘాలు నడిచేలా చూస్తాయి.
- మొదటి పంచవర్ష ప్రణాళికలో పెద్ద ఆనకట్టలు కట్టి విద్యుత్తు ఉత్పత్తి, సాగునీటి కల్పనల ద్వారా వ్యవసాయాన్ని వృద్ధి చేయుటపై దృష్టి సారించారు.
- ఆనకట్టల వల్ల వ్యవసాయ, పారిశ్రామిక రంగాలు వృద్ధి చెందాయి.
- దేశం ప్రగతి సాధించాలంటే పరిశ్రమలను అభివృద్ధి చేసి, ఎక్కువ మంది కర్మాగారాలలోనూ, సేవారంగంలోనూ పనిచేసేలా మళ్లించాల్సిన అవసరం ఉందని ప్రణాళిక కర్తలు గుర్తించి, రెండవ పంచవర్ష ప్రణాళిక నుంచి ప్రాధాన్యత పరిశ్రమల వైపునకు మళ్ళించారు.

ప్రశ్న 2.
రాజ్యాంగ ముసాయిదా రూపకల్పనలో అంబేద్కర్ పాత్రను గురించి వ్రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- 1947 ఆగష్టు 29న రాజ్యాంగ రచనా కమిటీని ఏర్పాటు చేయడం జరిగింది. దానికి చైర్మన్ డా|| బి.ఆర్. అంబేద్కర్.
- అంబేద్కర్ తనతోపాటు ఉన్న మిగతా సభ్యుల సహకారంతో ఇతర దేశాల రాజ్యాంగాలను క్షుణ్ణంగా చదివే మనకు అవసరమైన అంశాలను మన రాజ్యాంగంలో చేర్చడం జరిగింది.
- అంటరానితనాన్ని నిర్మూలించేందుకు మరియు అణగారిన వర్గాలను అభివృద్ధిపరచడానికి అంబేద్కర్ కృషి చేశారు.
- అన్నివర్గాల వారితో చర్చలు జరిపిన తరువాత భారతదేశానికి అవసరమైన ఒక విశాలమైన రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రూపొందించారు.
ప్రశ్న 3.
ఏకీకృత రాజ్యాంగంలోని రెండు ముఖ్య లక్షణాలు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
i) కేంద్రం రాజ్యతంత్రం యొక్క సర్వాధిక్యత.
ii) ఉప సర్వసత్తాక రాజ్యతంత్రాలు లేకపోవటం.
ప్రశ్న 4.
1950 నుండి 2013 వరకు జరిగిన రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు తెలిపే బార్ ను పరిశీలించండి.

A) ఏ దశాబ్దంలో తక్కువ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1951 – 60
B) 1950 – 2013 మధ్య ఎన్ని రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
99 సవరణలు
ప్రశ్న 5.
భారత రాజ్యాంగం యొక్క నాలుగు ప్రధాన లక్షణాలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- లిఖిత రాజ్యాంగము
- దృఢ, అదృఢ రాజ్యాంగము
- పార్లమెంటరీ తరహా ప్రజాస్వామ్యం
- ఏక పౌరసత్వం
- ఏకకేంద్ర మరియు సమాఖ్య ప్రభుత్వం
ప్రశ్న 6.
“భారత రాజ్యాంగం కాలానుగుణంగా మార్పులకు లోనయ్యే ఒక సజీవ జీవన పత్రము” అన్న వ్యాఖ్యతో నీవు ఏకీభవిస్తావా? మీ జవాబును సమరించుకోండి.
జవాబు:
- అవును. నేను దీనితో ఏకీభవిస్తాను.
- చట్టాలను అప్పుడప్పుడూ సవరించాల్సిన అవసరం ఏర్పడుతుందని రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు గుర్తించారు. కాబట్టి చట్టాలను సవరించే అవకాశం కల్పించారు.
ప్రశ్న 7.
సామాజిక మార్పుకు దోహదం చేసే రాజ్యాంగ అంశాలను పేర్కొనండి.
జవాబు:
- అంటరానితనాన్ని నిషేధించడం
- రిజర్వేషన్లు
- అల్పసంఖ్యాక వర్గాలకు ప్రత్యేక రక్షణ
ప్రశ్న 8.
అధ్యక్ష తరహా ప్రభుత్వమునకు, పార్లమెంటరీ తరహా ప్రభుత్వమునకు గల ఏవైనా రెండు భేదాలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
| అధ్యక్ష తరహా ప్రభుత్వము | పార్లమెంటరీ తరహా ప్రభుత్వము |
| 1. అధ్యక్షుడు కార్యనిర్వాహక వర్గానికి అధిపతి. | 1. అధ్యక్షుడు రాజ్యానికి అధిపతి. కానీ కార్యనిర్వాహక వర్గానికి కాదు. |
| 2. అధ్యక్షుని క్రింద వివిధ శాఖలకు బాధ్యత ఆవహిస్తూ సెక్రటరీలు ఉంటారు. | 2. అధ్యక్షుని క్రింద వివిధ శాఖలకు బాధ్యత వహిస్తూ మంత్రులు ఉంటారు. |
| 3. సెక్రటరీలు ఇచ్చే సలహాకు అధ్యక్షుడు కట్టుబడి ఉండాల్సిన పనిలేదు. | 3. అధ్యక్షుడు సాధారణంగా మంత్రుల సలహాకు కట్టుబడి ఉంటాడు. |
| 4. అధ్యక్షుడు ఏ సెక్రటరీనైనా ఎప్పుడైనా తొలగించవచ్చు. | 4. అధ్యక్షుడు ఆ విధంగా చేయలేడు. |
| 5. ఉదా : అమెరికా | 5. ఉదా : భారతదేశం |
ప్రశ్న 9.
ఈ క్రింది సమాచారం ఆధారంగా ఒక కమ్మీ చిత్రాన్ని గీయండి.
జవాబు:
కమ్మీ చిత్రం
ప్రశ్న 10.
భారతదేశం సమాఖ్య విధానం కల్గినదని ఎట్లా చెప్పగలవు?
జవాబు:
భారతదేశం సమాఖ్య విధానం :
1. ద్వంద్వ రాజ్యతంత్రం :
i) సమాఖ్య విధానం ప్రకారం అధికారాల విభజనకు మూలం అనేది “1935 భారత ప్రభుత్వ చట్టం” లోనే ఉంది.
ii) సమాఖ్య విధానం ప్రకారం కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్రాల మధ్య అధికారాల విభజన జరిగింది.
iii) ఈ రెండు కూడా వాటి పరిధిలో సర్వసత్తాకమైనవి. అయినప్పటికి భారత రాజ్యాంగం, ఈ సమాఖ్య విధానంలో కేంద్రాన్ని బలమైన సంస్థగా మార్చింది.
2. అధికారాల విభజన :
i) చట్టాలు చేసే అంశాలను కేంద్ర జాబితా, రాష్ట్రాల జాబితా, ఉభయ జాబితాగా విభజించారు.
ii) కేంద్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలపై కేంద్రం మాత్రమే చట్టాలు చెయ్యగలదు, రాష్ట్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలపై రాష్ట్రం మాత్రమే చట్టాలు చెయ్యగలదు.
iii) ఉభయజాబితాలోని అంశాలపై రాష్ట్రాలు, కేంద్రం చట్టాలు చేయవచ్చు. అయితే కేంద్రం చేసే చట్టానికి విరుద్ధంగా రాష్ట్రం చట్టం చేస్తే, కేంద్రం చేసిన చట్టం మాత్రమే చెల్లుబాటవుతుంది. పై అంశాలను బట్టి భారతదేశం సమాఖ్య విధానం కల్గి ఉన్నదని చెప్పగలము.

ప్రశ్న 11.
రాజ్యాంగం నిర్వర్తించే విధులేమిటి?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగం రెండు విధులు నిర్వర్తిస్తుంది :
(అ) పౌరుల హక్కులు, బాధ్యతలను పేర్కొనటం; ప్రభుత్వం దాని అంగాలైన కార్యనిర్వాహక, శాసన, న్యాయశాఖల వంటివాటి నిర్మాణం, అధికారాలను పేర్కొనటం;
(ఆ) ప్రభుత్వమూ, సమాజమూ కలిసి నిర్మించాల్సిన భవిష్యత్తు సమాజ స్వభావాన్ని సూచించటం, అంటే దేశం ముందుకు వెళ్లటానికి ప్రస్తుత అంశాలను ఎలా మార్చాలో రాజ్యాంగం సూచిస్తూ ప్రధానంగా భవిష్యత్తు చట్టాన్ని పేర్కొంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 12.
నేపాల్ రాజ్యాంగం 2007లో మొదలయ్యి 2014 నాటికి కూడా పూర్తికాకపోవడానికి కారణాలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
నేపాల్ లో రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రూపొందించే ప్రక్రియ 2007లో మొదలయ్యింది. కానీ 2014 నాటికి కూడా ఇది పూర్తికాలేదు. దీనికి కారణం అనేక మౌలిక అంశాలపై నేపాల్ లోని అనేక రాజకీయ ధోరణులు ఒక ఏకాభిప్రాయానికి రాలేకపోవడం. అంటే రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రూపొందించే ప్రక్రియ-చర్చలు, వాదోపవాదాలు, అభిప్రాయ భేదాలను పరిష్కరించటం, పరస్పర విరుద్దభావాలు ఉన్న వాళ్లందరికీ ఆమోదయోగ్యమయ్యే చట్రాన్ని రూపొందించడం.
ప్రశ్న 13.
భారతదేశ రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రూపొందించినది ఎవరు? రాజ్యాంగ అవసరం ఎందుకు ఏర్పడింది?
జవాబు:
భారతదేశ రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రాజ్యాంగ సభ రూపొందించి, ఆమోదించింది. బ్రిటిష్ వలస పాలనకు వ్యతిరేకంగా స్వాతంత్ర్యం కోసం భారతీయ ప్రజల సుదీర్ఘ పోరాటఫలితం ఇది. భారతదేశానికి స్వాతంత్ర్యం ఇవ్వాలని బ్రిటిష్ ప్రభుత్వం నిర్ణయించటంతో తమను తాము పరిపాలించుకోటానికి, తమకు దీర్ఘకాల లక్ష్యాలు నిర్దేశించుకోటానికి భారత ప్రజలకు కొత్త రాజ్యాంగం అవసరమయ్యింది.
ప్రశ్న 14.
రాజ్యాంగ సభ, రాజ్యాంగం రూపొందించడానికి ముందు ఏర్పాటు చేసిన సలహా సంఘాలేవి?
జవాబు:
ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు, అల్పసంఖ్యాక వర్గాలు, గిరిజన ప్రాంతాలు వంటి వాటిపై సలహాల కొరకు కమిటీలను ఏర్పాటు
చేయుట జరిగింది. అవి :
- కేంద్ర అధికారాల సంఘం
- కేంద్ర రాజ్యాంగ సంఘం
- రాష్ట్రాల రాజ్యాంగ సంఘం
- నిబంధనల కమిటీ
- స్టీరింగ్ కమిటీ
ప్రశ్న 15.
దేశ ఐక్యతను కాపాడటానికి ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగం అవలంబించిన విధానాలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
భారతదేశం సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థగా ఉండి, అదే సమయంలో భారతదేశ ఐక్యతను కాపాడటానికి అవసరమైన అన్ని మౌలిక అంశాలలో సారూప్యతను కలిగి ఉండేలా విధానాలను, పద్ధతులను రూపొందించటానికి ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగం ప్రయత్నించింది. ఇందుకు ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగం మూడు విధానాలను అవలంభించింది.
- ఒకే న్యాయవ్యవస్థ.
- పౌర, నేర అంశాలలోని మౌలిక చట్టాలలో సారూప్యత.
- ముఖ్యమైన పదవులలో నియమించటానికి దేశమంతటికీ అఖిల భారత సివిల్ సర్వీస్.
ప్రశ్న 16.
సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థలో అధికారాల విభజన ఏ విధంగా జరుగుతుంది?
జవాబు:
చట్టాలు చేసే అంశాలను కేంద్ర జాబితా, రాష్ట్రాల జాబితా, ఉభయ జాబితాగా విభజించారు. కేంద్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలపై కేంద్రం మాత్రమే చట్టాలు చెయ్యగలదు, రాష్ట్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలపై రాష్ట్రం మాత్రమే చట్టాలు చెయ్యగలదు. ఉభయ జాబితాలోని అంశాలపై రాష్ట్రాలు, కేంద్రం చట్టాలు చేయవచ్చు. అయితే కేంద్రం చేసే చట్టానికి విరుద్ధంగా రాష్ట్రం చట్టం చేస్తే, కేంద్రం చేసిన చట్టం మాత్రమే చెల్లుబాటవుతుంది.

ప్రశ్న 17.
రాజ్యాంగ సభ గురించి జవహర్లాల్ నెహ్రూ ఏవిధంగా పేర్కొన్నాడు?
జవాబు:
అభివృద్ధితోపాటు సామాజిక మార్పుకి కూడా రాజ్యాంగం దోహదం చెయ్యాలని గుర్తించారు. “గత రాజకీయ, సామాజిక నిర్మాణాన్ని తిరస్కరించి ముందుకు కదులుతూ తనకు తాను కొత్త వస్త్రాలను రూపొందించుకుంటున్న దేశానికి” రాజ్యాంగ సభ ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహిస్తున్నట్టుగా జవహర్ లాల్ నెహ్రూ పేర్కొన్నాడు.
ప్రశ్న 18.
ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
- భారత రాజ్యాంగం ఉదారవాద ప్రజాస్వామ్యాన్ని ఏర్పాటు చేసింది. ప్రజలందరికి వారి స్వేచ్ఛలకు, వ్యక్తిగత ఔన్నత్యానికి భంగం కలగని పద్ధతిలో సాంఘిక న్యాయం సాధించాలని దాని లక్ష్యాలలో నిర్దిష్టించింది.
- రాజ్యాంగంలోని నాలుగవ భాగం నిర్దేశిక నియమాలను ప్రస్తావిస్తుంది.
- ప్రభుత్వం సాధించవలసిన లక్ష్యాలను నిర్దేశిక నియమాలు ఆదేశిస్తాయి.
- ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు వ్యక్తి స్వేచ్ఛకు ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహిస్తాయి. నిర్దేశిక నియమాలు సమాజ ప్రయోజనాలను ప్రతిబింబిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 19.
‘కేశవానంద భారతి’ కేసులో సుప్రీంకోర్టు ఇచ్చిన తీర్పు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
సుప్రీంకోర్టు కేశవానంద భారతి కేసులో తీర్పు ఇస్తూ – “దేశ మనుగడ కొన్ని మౌలిక సూత్రాలపై ఆధారపడి ఉంటుందని వాదించింది. భారత రాజ్యాంగంలోని కొన్ని అంశాలను ఎట్టి పరిస్థితులలోనూ సవరించటానికి లేదని ఈ కేసులో వాదించారు.”
ప్రశ్న 20.
కేంద్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
కేంద్ర జాబితాలో మొత్తం 97 అంశాలు కలవు. దేశ రక్షణ, సాయుధ బలగాలు, ఆయుధాలు, మందుగుండు సామగ్రి, అణుశక్తి, విదేశీ వ్యవహారాలు, యుద్ధం, శాంతి, పౌరసత్వం, నేరస్థుల అప్పగింతలు, కరెన్సీ, తంతితపాలా, విదేశీ వ్యాపారం, బ్యాంకులు, బీమా, తూనికలు వంటివి ముఖ్యమైన అంశాలు.
ప్రశ్న 21.
రాష్ట్ర జాబితాలోని అంశాలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
రాష్ట్రాల జాబితాలలో మొత్తం 60 అంశాలున్నాయి. వాటిలో ముఖ్యమైనవి – శాంతిభద్రతలు, పోలీసు, న్యాయ నిర్వహణ, స్థానిక పరిపాలన, ప్రజారోగ్యం , పారిశుద్ధ్యం, విద్య, మత్తుపానీయాలు, వ్యవసాయం, పశుపాలన, నీటి పారుదల, – అడవులు, రాష్ట్ర పబ్లిక్ సర్వీస్ కమిషన్ మొదలైనవి.
ప్రశ్న 22.
రాజ్యాంగం యొక్క రెండు ప్రధాన విధానాలను తెల్పండి.
జవాబు:
- చరిత్రలో ముఖ్యంగా రెండు రాజ్యాంగ రూపాలున్నాయి.
- ఒకటి ఏకీకృత విధానమని, రెండవ దానిని సమాఖ్య విధానమని అంటారు.
- ఏకీకృత రాజ్యాంగంలో కేంద్ర రాజతంత్రం, ఉప సర్వసత్తాక రాజతంత్రాలు ఉండకపోవడం ముఖ్య లక్షణాలు.
- సమాఖ్య విధానంలో కేంద్ర రాజతంత్రంతోపాటు ఉపరాజ తంత్రాలుండటం, అవి సర్వసత్తాకంగా ఉండటం ముఖ్య లక్షణాలు.
ప్రశ్న 23.
ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగాన్ని ప్రజలతో చర్చించాల్సిన అవసరమేమి?
జవాబు:
- ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగాన్ని ప్రజలతో చర్చించాల్సిన అవసరం ఉంది.
- దాంట్లోని అంశాల పట్ల ప్రజలు తమ స్పందనలను తెలియజేయడానికి అవకాశం ఇవ్వాలి.
- ముసాయిదాను అంగీకరించేందుకు, విమర్శించేందుకు మిత్రులకు, విమర్శకులకు, ప్రత్యర్థులకు తగినంత సమయం ఇవ్వాలి.
- రాజకీయ వ్యవస్థకు సంబంధించి ప్రజల సూచనలను అవసరానుగుణంగా వాడుకోవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 24.
అధికారాన్ని మరీ కేంద్రీకరిస్తే అది మరీ నిరంకుశ అధికారంగా మారుతుంది మరియు ఫాసిస్టు ఆదర్శాలవైపు తీసుకెళ్ళుతుంది. పై వ్యాఖ్యపై విశ్లేషించండి.
జవాబు:
- అధికారాన్ని మరీ కేంద్రీకరిస్తే అది నిరంకుశంగా మారుతుంది మరియు ఫాస్ట్ ఆదర్శాలవైపు తీసుకెళ్తుంది.
- 1971 ఎన్నికల రికార్డు విజయం తర్వాత ఇందిరాగాంధీ పార్టీ, పార్లమెంట్లపై పట్టు సాధించింది.
- అధిక శాతం ప్రజలు ద్రవ్యోల్బణం, నిత్యావసర వస్తువుల ధరల పెరుగుదల, ఆహార కొరత, నిరుద్యోగంతో బాధపడి జెపీ ఉద్యమాన్ని బలపర్చారు.
- తీవ్రతరమైన ఆ ఉద్యమాన్ని ఆపడానికి ఇందిరాగాంధీ అత్యవసర పరిస్థితిని విధించి ప్రజల హక్కులను కాలరాశారు. ఇది భారత ప్రజాస్వామ్యాన్ని వెనుకకు తీసుకుపోయింది.
ప్రశ్న 25.
“ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగం … చాలా పెద్ద పత్రం. దీంట్లో 315 అధికరణాలు, 8 షెడ్యూళ్ళు ఉన్నాయి. ముసాయిదా రాజ్యాంగం అంత పెద్ద రాజ్యాంగం ఉన్న దేశం మనదేశమే.
ప్రశ్న : రాజ్యాంగాన్ని అధికరణలు, షెడ్యూళ్ళుగా విభజించడం అవసరమా ….. విశ్లేషించండి.
జవాబు:
- రాజ్యాంగాన్ని షెడ్యూళ్ళు, అధికరణాలుగా విభజించడం అవసరమే.
- ఒకే అంశానికి సంబంధించి కొన్ని అధికరణాలు ఉంటాయి.
- అలాగే కొన్ని అధికరణాలు ఒకే షెడ్యూల్ లో ఉండి మొత్తం కలిసి ఒకే విషయం గురించి వివరిస్తాయి.
- షెడ్యూళ్ళు ప్రస్తుతం 12 మాత్రమే ఉన్నాయి మరియు అధికరణాలు 445 ఉన్నాయి.

ప్రశ్న 26.
దేశంలోని ప్రతి రాష్ట్రానికి వేరు వేరు చట్టాలుంటే ఏర్పడే పరిణామాలను ఊహించండి.
జవాబు:
- స్థానిక అవసరాలు, స్థానిక పరిస్థితులకు అనుగుణంగా ప్రభుత్వ అధికారాలను మార్చుకొంటే పర్వాలేదు కాని అది ఒక స్థాయి దాటితే గందరగోళం సృష్టిస్తుంది.
- వేరు వేరు రాష్ట్రాలలోని వేరు వేరు చట్టాలు రాష్ట్రాలను బలహీన పర్చడమే కాక ఒక రాష్ట్రం నుంచి మరొక రాష్ట్రం వెళ్ళే పౌరులను సహించదు.
- ఆ పౌరులు ఒక రాష్ట్రంలో చట్టబద్ధమైనది మరొక రాష్ట్రంలో కాదని తెలుసుకుంటారు.
10th Class Social 17th Lesson 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers in Telugu Medium
ప్రశ్న 1.
భారతదేశాన్ని లౌకిక రాజ్యం అని ఎలా అనవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
భారతదేశాన్ని లౌకిక రాజ్యం అని కచ్చితంగా చెప్పవచ్చు, ఎలాగంటే
- భారతదేశం మత ప్రమేయం లేని రాజ్యం . ప్రభుత్వమంటూ ఉండదు. ఏ మతాన్ని ప్రోత్సహించదు, ఆక్షేపించదు.
- పరిపాలనాపరంగా మతం అనేది నిరపేక్ష భావన.
- మతపరంగా అల్ప సంఖ్యాక వర్గాలవారి హక్కులు వాని పరిరక్షణ రాజ్యాంగంలో పొందుపరచడం జరిగింది.
- ప్రభుత్వం మత విశ్వాసాలలో జోక్యం చేసుకోదు. తటస్థంగా ఉంటుంది.
- రాజ్యాంగంలోని ప్రాథమిక హక్కుల ద్వారా పౌరులకు మత స్వేచ్ఛనివ్వటం జరిగింది. దీని ప్రకారం పౌరులు ఏ మతాన్నైనా స్వీకరించవచ్చు, ప్రచారం చేసుకోవచ్చు. అభివృద్ధి చేసుకోవచ్చు.
- ప్రభుత్వం మత సహనాన్ని పాటిస్తుంది. శాంతి యాత్రలను ప్రోత్సహిస్తుంది.
- అనాదిగా మన దేశానికున్న సర్వధర్మ సమభావన సంస్కృతి లౌకికస్ఫూర్తికి ఆదర్శంగా నిలుస్తుంది.
- ప్రభుత్వ విద్యాసంస్థలలో, ప్రభుత్వ గ్రాంట్లతో నడిచే విద్యాసంస్థలలో మత విషయాల చోదన నిషేధించటం జరిగింది.
- అలాగే రాజకీయాలలో మతపర గుర్తులను, మతపర జోక్యాన్ని నిషేధించటం జరిగింది.
- మతస్వేచ్ఛను కల్పిస్తూనే సామాజిక సామరస్యానికి శాంతికి భంగం కలుగకుండా పరిమితులు విధించటం జరిగింది.
ప్రశ్న 2.
పార్లమెంటరీ, అధ్యక్ష ప్రభుత్వ విధానాల మధ్య తేడాలు వివరించండి.
(లేదా)
పార్లమెంటరీ తరహా ప్రభుత్వం అధ్యక్ష తరహా ప్రభుత్వం కంటే ఎలా భిన్నమైందో పేర్కొనుము.
జవాబు:
పార్లమెంటరీ, అధ్యక్ష ప్రభుత్వ విధానాల మధ్య ఈ క్రింది తేడాలున్నాయి.
| పార్లమెంటరీ ప్రభుత్వం | అధ్యక్ష విధాన ప్రభుత్వం |
| 1) భారత సమాఖ్య అధ్యక్షుడు నామమాత్రుడు. | 1) అధ్యక్ష ప్రభుత్వంలో అధ్యక్షుడు యధార్థ కార్యనిర్వాహకుడుగా వ్యవహరిస్తాడు. |
| 2) కార్యనిర్వాహక శాఖ, శాసన నిర్మాణ శాఖలో అంతర్భాగం. మంత్రులందరూ శాసనసభలో సభ్యత్వాన్ని పొంది ఉంటారు. | 2) కార్యనిర్వాహక వర్గం శాసన నిర్మాణశాఖలో అంతర్భాగంగా ఉండదు. అంటే అధ్యక్షుడు, అతని సలహాదారులు శాసనసభలో సభ్యులు కారు. |
| 3) రాజ్యా ధిపతి, ప్రభుత్వాధిపతి పదవులు వేరుగా ఉంటాయి. రాజ్యాధిపతిగా బ్రిటన్లో లాగ చక్రవర్తిగాని, ఇండియాలో లాగ రాష్ట్రపతిగాని వ్యవహరిస్తారు. ప్రభుత్వాధిపతులుగా, భారత్, ఇంగ్లాండులలో ప్రధానమంత్రులు వ్యవహరిస్తారు. | 3) రాజ్యా ధిపతిగా, ప్రభుత్వాధిపతిగా ఒకే వ్యక్తి ఉంటాడు. |
| 4) శాసన, కార్యనిర్వాహక, న్యాయశాఖల మధ్య అధికార పంపిణీ జరగదు. ప్రభుత్వ అధికారాలు 3 అంగాల మధ్య కలిసి ఉంటాయి. | 4) ప్రభుత్వాంగమైన శాసన, కార్యనిర్వాహక, న్యాయశాఖల మధ్య అధికార పంపిణీ జరుగుతుంది. వాటికి స్వతంత్రాధికారాలు ఉంటాయి. |
| 5) పార్లమెంటులో మెజారిటీ మద్దతు ఉన్నంతవరకు భారత సమాఖ్య అధ్యక్షుడికి మంత్రులను తొలగించే అధికారం లేదు. పార్లమెంటరీ తరహా ప్రభుత్వం అధ్యక్ష తరహా ప్రభుత్వం కన్న భిన్నమైనదని చెప్పవచ్చు. | 5) అమెరికా అధ్యక్షుడు ఏ సెక్రటరీనైనా, ఎప్పుడైనా తొలగించవచ్చు. |
ప్రశ్న 3.
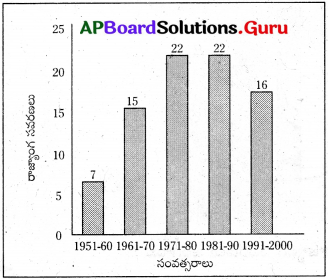
ఈ కింది బార్ గ్రాఫ్ ఆధారంగా ప్రశ్నలు 2 నుండి 4 వరకు సమాధానం రాయుము.

a) 1951-1960 మధ్యకాలంలో ఎన్ని రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
b) ఏయే సంవత్సరాల మధ్యకాలంలో ఎక్కువ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
c) ఏ దశాబ్దాలలో రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు సమానంగా జరిగాయి?
d) 2013 వరకు జరిగిన మొత్తం రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు ఎన్ని?
జవాబు:
a) 1951-1960 మధ్యకాలంలో 7 రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి.
b) 1971-81 మరియు 1981-90 సంవత్సరాల మధ్యకాలంలో ఎక్కువ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి.
c) 1971-81 మరియు 1981-90 దశాబ్దాలలో రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు సమానంగా జరిగాయి.
d) 2013 వరకు జరిగిన మొత్తం రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు 99.
ప్రశ్న 4.
భారత రాజ్యాంగంలోని మౌలిక అంశాలకు సంబంధించిన వివరణలు, ఉదాహరణలు పేర్కొనండి.
జవాబు:
- పార్లమెంటరీ వ్యవస్థ : భారతదేశం ప్రపంచంలో అతి పెద్ద ప్రజాస్వామ్య దేశంగా పార్లమెంటరీ వ్యవస్థను కలిగి ఉన్నది.
- పౌర హక్కులు : ప్రతి భారతీయుడు ఆరు ప్రాథమిక హక్కులను కలిగి ఉంటాడు.
- ప్రాథమిక విధులు : ప్రతి భారతీయుడు 10 ప్రాథమిక విధులను ఆచరిస్తాడు.
- సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థ : భారత రాజ్యాంగం అధికారాలను 3 జాబితాలలో కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర, ఉమ్మడి జాబితాలుగా విభజించింది.
- స్వతంత్ర న్యాయవ్యవస్థ : భారత న్యాయవ్యవస్థ స్వయం ప్రతిపత్తిని కలిగి ఉంది. దీనికి రాజ్యాంగం రక్షణ కల్పిస్తుంది.
- ఏక పౌరసత్వం : భారత రాజ్యాంగం దేశంలో పౌరులకు ఏక పౌరసత్వాన్ని ఇచ్చింది.
- ఆదేశ సూత్రాలు : భారత రాజ్యాంగం కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాలకు సలహాపూర్వక సూచనలు చేసింది. వీటినే ఆదేశ సూత్రాలు అంటారు.

ప్రశ్న 5.
సమాఖ్య విధానమనగానేమి? దాని లక్షణాలేమిటి?
(లేదా)
భారత సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థ లక్షణాలు వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
ప్రభుత్వాధికారులు కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్రాల మధ్య రాజ్యాంగబద్ధంగా పంపిణీ అయి ఉన్న ప్రభుత్వ విధానమే సమాఖ్య ప్రభుత్వం. భారతదేశంలో కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్రాల మధ్య అధికార పంపిణీ రాజ్యాంగబద్ధంగా జరిగింది.
సమాఖ్య లక్షణాలు :
1) రెండు స్థాయిలలో ప్రభుత్వాలు :
కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర స్థాయిలలో సర్వసత్తాకమైన వేర్వేరు ప్రభుత్వాలుంటాయి.
2) అధికార విభజన :
కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాల మధ్య అధికారాల విభజన ఉంటుంది. జాతీయ ప్రాధాన్యం ఉన్న దేశ , రక్షణ, విదేశీ వ్యవహారాలు, తంతితపాలా, రవాణా మొదలైనవి కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వ ఆధీనంలో ఉంటాయి.
3) లిఖిత రాజ్యాంగం :
సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థలో కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాల వ్యవస్థలను నిర్ణయించి, నిర్దేశించేది లిఖిత రాజ్యాంగమే.
4) దృఢ రాజ్యాంగం :
కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వం కాని, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వం కాని ఏకపక్షంగా రాజ్యాంగాన్ని మార్చలేవు.
5) రాజ్యాంగ ఆధిక్యత :
సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థలో రాజ్యాంగమే అత్యున్నతమైన శాసనం. రాజ్యాంగం విధించే పరిమితులకు లోబడి కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాలు అధికారాలను చెలాయిస్తాయి.
6) స్వతంత్ర న్యాయశాఖ :
కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాల మధ్య వచ్చే వివాదాలను పరిష్కరించి, సమాఖ్యను సరిగ్గా నడిపించడానికి, రాజ్యాంగం ఆధిక్యాన్ని పరిరక్షించడానికి స్వతంత్ర ప్రతిపత్తి, సర్వాధికారాలు ఉన్న ఒక ఉన్నత న్యాయవ్యవస్థ ఉంటుంది.
7) ద్వంద్వ పౌరసత్వం :
సమాఖ్య రాజ్యాల్లో పౌరులకు రెండు పౌరసత్వాలు ఉంటాయి. అవి
- వారి రాష్ట్ర పౌరసత్వం
- దేశ పౌరసత్వం. కాని భారతదేశంలో ఏక పౌరసత్వం మాత్రమే ఉంది. అదే దేశ పౌరసత్వం.
ప్రశ్న 6.
భారత రాజ్యాంగ మౌలిక సూత్రాలను వివరింపుము.
జవాబు:
భారత రాజ్యాంగం జనవరి 26, 1950 నుండి అమలులోకి వచ్చింది. భారత రాజ్యాంగంలోని మౌలిక సూత్రాలు ఈ క్రింది విధంగా ఉన్నాయి.
1) పార్లమెంటరీ విధానం :
భారతదేశం పార్లమెంటరీ ప్రజాస్వామ్యాన్ని అనుసరిస్తూ ప్రపంచంలోనే అతి పెద్ద ప్రజాస్వామ్య దేశంగా ఉంది.
2) ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు :
భారతదేశ పౌరులందరికి ఆరు రకాలైన ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు ఉన్నాయి.
3) ప్రాథమిక విధులు :
భారత పౌరులకు ప్రాథమిక హక్కులతో పాటు 10 రకాల ప్రాథమిక విధులు ఉన్నాయి.
4) ఏక పౌరసత్వం :
భారతీయులంతా రాజ్యాంగం ప్రకారం ఒకే పౌరసత్వాన్ని కలిగి ఉంటారు.
5) సమాఖ్య వ్యవస్థ :
భారతదేశంలో రాష్ట్రాలు స్వతంత్ర ప్రతిపత్తి కలిగి కేంద్ర ప్రభుత్వానికి లోబడి పనిచేస్తాయి.
6) స్వతంత్ర న్యాయ వ్యవస్థ :
భారతదేశం స్వతంత్ర న్యాయ వ్యవస్థ కలిగి ఉంది. ఇది రాజ్యాంగాన్ని రక్షిస్తుంది. న్యాయ సమీక్షాధికారాన్ని కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
7) ఆదేశిక సూత్రాలు :
కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్ర ప్రభుత్వాలు ఎలా నడుచుకోవాలో ఇవి సూచిస్తాయి.
8) సార్వజనీన వయోజన ఓటు హక్కు :
18 సంవత్సరాలు నిండిన స్త్రీ, పురుషులందరికీ ఓటుహక్కు కల్పించబడింది.
ప్రశ్న 7.
సామాజిక మార్పునకు దోహదం చేసే అంశాలు మన రాజ్యాంగంలో అనేకం ఉన్నాయి. అవి నేడు ఎలా అమలవుతున్నాయి?
జవాబు:
మన రాజ్యాంగంలో సామాజిక మార్పునకు దోహదం చేసే అంశాలు:
- అంటరానితనాన్ని నిషేధించడం వలన అస్పృశ్యత నివారణ అయింది.
- విద్య, ఉద్యోగాలలో రిజర్వేషన్లు కల్పించబడ్డాయి.
- స్వేచ్ఛ, సమానత్వం, న్యాయం అందరికీ అందుబాటులోనికి వచ్చాయి.
- ఆదేశ సూత్రాలు ఇవ్వబడ్డాయి.
- ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు కల్పించబడ్డాయి.

ప్రశ్న 8.
డా|| బి.ఆర్. అంబేద్కర్ వెలువరించిన దిగువ అభిప్రాయం మీద మీ వ్యాఖ్యలను రాయండి.
1950, జనవరి 26న మనం వైరుధ్యాలతో కూడిన జీవనంలోకి ప్రవేశించబోతున్నాం. రాజకీయాల్లో సమానత్వం ఉంటుంది, కానీ సామాజిక, ఆర్థిక అంశాల్లో అసమానత్వం ఉంటుంది.
జవాబు:
- డా|| బి. ఆర్. అంబేద్కర్ యొక్క ఈ అభిప్రాయం అక్షర సత్యము.
- అందరికీ ఓటుహక్కు ఉంది గనుక, ఒక ఓటుకు ఒక విలువ ఉంది. కనుక రాజకీయాలలో సమానత్వం ఉందని భావించవచ్చు.
- అనేక అంశాలలో వివక్షత ఉన్నందున సామాజిక సమానత్వం ఒక ప్రశ్నగా మారుతున్నది.
- ప్రజల ఆదాయాలలో తీవ్ర అసమానతలు ఉన్నందున ఆర్థిక సమానత్వం లోపిస్తున్నది.
- ఈ అసమానతలు సాధ్యమైనంత తొందరగా పరిష్కరింపబడాలి.
ప్రశ్న 9.

పై లో 1951 నుండి 2013 మధ్య జరిగిన రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ గ్రాఫ్, దానిని అధ్యయనం చేసి, మీరు గమనించిన విషయాలను చర్చించండి.
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగంలోని అధికరణాలను సవరణ చేసే అవకాశాన్ని రాజ్యాంగం కల్పించింది. ఈ సవరణలను పార్లమెంటు మాత్రమే చేయాలి. పై ను పరిశీలించినట్లయితే ఈ క్రింది విషయాలు తెలుస్తున్నాయి.
- మన రాజ్యాంగం 1950లో అమలులోకి వచ్చింది రాజ్యాంగం అమలులోకి వచ్చిన పది సంవత్సరాలలో అనగా 1951 నుండి 60 మధ్య రాజ్యాంగానికి ఏడు సవరణలు చేయబడినాయని తెలుస్తుంది.
- 1961 నుండి 70 మధ్య పది సంవత్సరాలలో రాజ్యాంగానికి 15 సవరణలు చేయబడినాయి.
- 1971 నుండి 80 మధ్య పది సంవత్సరాలలో రాజ్యాంగానికి 22 సవరణలు చేశారని తెలుస్తుంది.
- 1981 నుండి 90 మధ్య పది సంవత్సరాలలో కూడా రాజ్యాంగానికి 22 సవరణలు చేశారు.
- 1991 నుండి 2000ల మధ్య పది సంవత్సరాలలో రాజ్యాంగానికి 16 సవరణలు చేయబడినాయి.
- 2001 నుండి 2013 సంవత్సరాల మధ్య రాజ్యాంగానికి 17 సవరణలు చేశారు.
- 1951 నుండి 2013వ సంవత్సరం వరకు పరిశీలించినట్లయితే అత్యల్పమైన సవరణలు 7 సవరణలు, ఇవి 1951 నుండి 1960ల మధ్య చేయబడినాయి.
- అత్యధిక సవరణలు 22. ఇవి 1971 నుండి 80ల మధ్య మరియు 1981 నుండి 1990ల మధ్య కూడా రాజ్యాంగానికి 22 సవరణలు చేశారు. ఈ విధంగా 1951 నుండి 2013 వరకు రాజ్యాంగానికి మొత్తం 99 సవరణలు చేయబడినాయి.
ప్రశ్న 10.
సమాఖ్య, ఏకకేంద్ర విధానాల మధ్య భేదాలు వ్రాయండి.
(లేదా )
ఏకకేంద్ర మరియు సమాఖ్య ప్రభుత్వ వ్యవస్థల మధ్య గల తేడాలను తెల్పండి.
జవాబు:
| సమాఖ్య విధానం | ఏకకేంద్ర విధానం |
| 1) కేంద్ర రాజ్య తంత్రంతో పాటు ఉపరాజ్య తంత్రాలు ఉంటాయి. | 1) కేంద్ర రాజ్య తంత్రం యొక్క సర్వాధిక్యత. |
| 2) ద్వంద్వ పౌరసత్వం కొన్ని దేశాలలో ఉంటుంది. | 2) ఏక పౌరసత్వం. |
| 3) ద్వంద్వ న్యాయవ్యవస్థ, ద్వంద్వ న్యాయ సూత్రాలు ఉంటాయి. | 3) ఏకీకృత న్యాయవ్యవస్థ మరియు ఉమ్మడి పౌరస్మృతి. |
| 4) కేంద్ర, రాష్ట్రాల మధ్య రాజ్యాంగబద్ధమైన అధికార విభజన. | 4) అధికారాలు అన్నీ కేంద్రం పరిధిలో ఉంటాయి. |
ప్రశ్న 11.
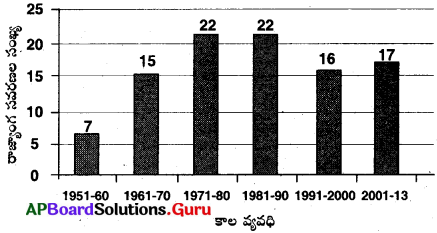
క్రింద ఇవ్వబడిన సమాచారానికి ఒక కమ్మీ రేఖాచిత్రము గీయుము.
| కాల వ్యవధి | జరిగిన రాజ్యాంగ సవరణల సంఖ్య |
| 1951-60 | 7 |
| 1961-70 | 15 |
| 1971-80 | 22 |
| 1981-90 | 22 |
| 1991-2000 | 16 |
| 2001-2013 | 17 |
జవాబు:
ప్రశ్న 12.
ఈ క్రింది రేఖాచిత్రం ఆధారంగా దిగువ ఇచ్చిన ప్రశ్నలకు తగు సమాధానములు వ్రాయుము.
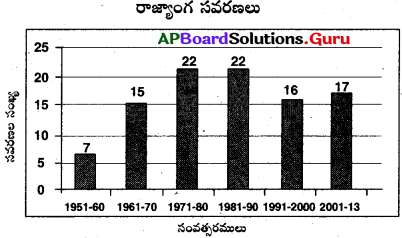
a) భారత రాజ్యాంగం ఎప్పటి నుంచి అమలులోనికి వచ్చింది?
జవాబు:
1950
b) ఏ దశాబ్దంలో అతితక్కువ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
1951-60
c) రాజ్యాంగమును ఎందుకు సవరించాలి?
జ. మారుతున్న పరిస్థితులను, విధానాలను బట్టి చట్టాలలో మార్పులు అవసరం.
d) 1951-1980 మధ్య కాలంలో మొత్తం ఎన్ని రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి?
జవాబు:
44 సవరణలు
(లేదా)
పైన ఇవ్వబడ్డ రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలకు సంబంధించిన గ్రాఫును విశ్లేషించి, మీ పరిశీలనలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- 1951-60 దశాబ్దంలో అత్యల్పంగా రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు జరిగాయి.
- 2013 వరకు జరిగిన మొత్తం రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు 99.
- 1971-80 మరియు 1981-90 దశాబ్దాల కాలంలో అత్యధికంగా సవరణలు జరిగాయి.
- 1971-80 మరియు 1981-90 దశాబాలలో సమానంగా సవరణలు జరిగాయి.

ప్రశ్న 13.
‘భారత రాజ్యాంగంలోని మౌలిక సూత్రాల గురించి ఒక వ్యాసం వ్రాయండి.
జవాబు:
భారత రాజ్యాంగంలోని మౌలిక సూత్రాలు :
ఏ రాజ్యాంగమైనా ఆ దేశ ప్రజల మనోభావాలను, ఆదర్శాలను ప్రతిఫలిస్తుంది. రాజ్యాంగం శాశ్వత విలువను కలిగి ఉన్నప్పటికీ, అది రచించబడిన కాలంనాటి పరిస్థితులను ప్రతిబింబిస్తుంది. మన భారత రాజ్యాంగం కూడా ఇదే విధంగా ఉండి ఈ క్రింది మౌలిక సూత్రాలను కలిగి ఉంది.
- సార్వభౌమాధికారము
- ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు
- ఆదేశసూత్రాలు
- పార్లమెంటరీ తరహా ప్రభుత్వ విధానము
- లౌకికతత్వము
- సామ్యవాదము
- సమాఖ్యవాదము
- స్వతంత్ర్య న్యాయవ్యవస్థ
ప్రశ్న 14.
క్రింది గ్రాఫ్ ని పరిశీలించి, విశ్లేషణ చేయండి.
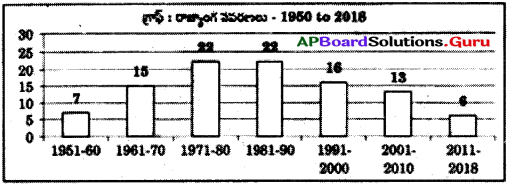
జవాబు:
పైన ఇవ్వబడిన గ్రాఫ్ మన రాజ్యాంగం అమలులోనికి వచ్చినప్పటినుండి ఇప్పటివరకు అనగా 1950 నుండి 2018 వరకు చేసిన రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలను ఇవ్వడం జరిగింది.
ఇప్పటివరకు 101 సార్లు మనం రాజ్యాంగాన్ని సవరించాం. రాజ్యాంగం అమలులోకి వచ్చిన మొదటి దశాబ్దంలో 7 సార్లు మాత్రమే సవరించాం. కాలం మారుతున్న సందర్భంగా సవరణల సంఖ్య కూడా పెరుగుతూ వచ్చింది. 1971 నుండి 1990 వరకు మనం ఎక్కువగా అనగా 44 సార్లు రాజ్యాంగాన్ని సవరించాం. దానికి ప్రధానకారణం అప్పుడు ఉన్న రాజకీయ పరిస్థితులు. సాధారణంగా అత్యవసర పరిస్థితులలో మాత్రమే మారుతున్న ప్రజల ఆసక్తుల ప్రకారం ఎటువంటి ఇబ్బందులు ఎదురవకుండా ఉండటం కోసం మరియు సమాజంలోని అన్ని రంగాలవారి అభివృద్ధి కోసం రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ చేయడం జరుగుతుంది.
ఉదా : లౌకిక, సామ్యవాద అంశాలను 1976వ సంవత్సరంలో మన రాజ్యాంగ పీఠికలో పొందుపరచడం జరిగింది. 1975 – 1980- 1984 సంవత్సరాల మధ్యలో అత్యవసర పరిస్థితి విధింపు మరియు ప్రభుత్వము వాటి మనుగడ సాగించడం కోసం కూడా కొన్ని రాజకీయ సవరణలు చేయడం జరిగింది.
1991 – 2000 మధ్యకాలంలో మనదేశ ఆర్థిక పరిస్థితులను మెరుగుపరచడం కోసం ఆర్థిక సవరణలు చేయడం జరిగింది.
కేశవానంద భారతీ కేసులో సుప్రీంకోర్టు తీర్పును ఇస్తూ రాజ్యాంగంలోని ప్రాథమిక మరియు మౌలిక అంశాలను ఎటువంటి పరిస్థితులలోనూ సవరించడానికి వీలులేదని వాదించారు.
ఉదా :
ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు.
కొన్ని సందర్భాలలో కాంగ్రేసేతర ప్రభుత్వాలు ఏర్పడినప్పుడు కూడా రాజ్యాంగాన్ని సవరించడం జరిగింది.
సాధారణంగా రాజ్యాంగంలోని అధికరణాల సవరణను పార్లమెంటు మాత్రమే చేపట్టాలి. అంతే కాకుండా రాజ్యసభ, లోకసభ రెండింటిలో మూడింట రెండువంతుల సభ్యుల ఆమోదం అవసరం. కొన్ని అధికరణలను రాష్ట్ర శాసనసభలు అంగీకరించిన తరువాత మాత్రమే సవరించవచ్చు.
కొన్ని సందర్భాలలో చేసిన రాజ్యాంగ సవరణలు కొన్ని విమర్శలకు కూడా అవకాశం కల్పించాయి. రాజ్యాంగాన్ని అత్యవసర పరిస్థితులలో కాకుండా ప్రభుత్వాలకు అనుగుణంగా మార్చుకుంటూ పోతే రాజ్యాంగం మీద ప్రజలకు నమ్మకం పోతుంది. రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతల మరియు రాజ్యాంగం యొక్క ఆశయాలకు భంగం వాటిల్లకుండా చూసే బాధ్యత మన అందరి మీద ఉన్నది.
2011 నుండి 2018 మధ్యకాలంలో 6 సార్లు మాత్రమే సవరించడం జరిగింది. ఇది గమనించినట్లయితే రాజ్యాంగ సవరణల సంఖ్య గణనీయంగా తగ్గుతుంది అని మనం గమనించవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 15.
“సామాజిక మార్పునకు దోహదం చేసే అనేక అంశాలు రాజ్యాంగంలో ఉన్నాయి. దీనికి ఒక మంచి ఉదాహరణ రాజ్యాంగంలో షెడ్యూల్ కులాలు, షెడ్యూల్ తెగలకు రిజర్వేషన్లను కల్పించటం. ఈ వర్గాలు తరతరాలుగా ఎదుర్కొన్న అన్యాయాలను అధిగమించటానికి, వారి యొక్క ఓటు హక్కుకు సరైన అర్థాన్ని ఇవ్వడానికి కేవలం సమానత్వపు హక్కు ఇస్తే సరిపోదని రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు విశ్వసించారు. వాళ్ల ప్రయోజనాలను ప్రోత్సహించేందుకు ప్రత్యేక రాజ్యాంగ చర్యలు ‘ అవసరం. అందుకనే షెడ్యూల్డ్ కులాల, షెడ్యూల్డ్ తెగల ప్రయోజనాలను కాపాడటానికి శాసనసభా స్థానాల రిజర్వేషన్ వంటి అనేక ప్రత్యేక అంశాలను రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు కల్పించారు. ఈ వర్గాలకు ప్రభుత్వరంగ ఉద్యోగాలలో రిజర్వేషన్లకు కూడా రాజ్యాంగం అవకాశం కల్పించింది.” వ్యాఖ్యానించండి.
జవాబు:
- అంటరానితనాన్ని నిషేధించటం, అస్పృశ్యత నేరం.
- షెడ్యుల్డ్ కులాలు, షెడ్యూల్డ్ తెగలకు రిజర్వేషన్లు కల్పించబడ్డాయి. వీరికి శాసనసభ, పార్లమెంట్ వంటి చట్ట సభల్లో రిజర్వేషన్ వంటి ప్రత్యేక అంశాలను రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు కల్పించారు.
- షెడ్యుల్డ్ కులాలు, తెగలకు విద్య, ఉద్యోగాలలో కూడా రాజ్యాంగం రిజర్వేషన్లు కల్పించింది.
- పౌరులందరికి కుల, మత, వర్గ, ధనిక, పేద వంటి తేడాలు చూపకుండా ప్రాథమిక హక్కులు (ఓటుహక్కు, స్వేచ్ఛా స్వాతంత్ర హక్కు మొ||వి) కల్పించినారు.
- స్వేచ్ఛా, సమానత్వం, న్యాయం అందరికీ అందుబాటులోకి వచ్చేలా రాజ్యాంగం రూపకల్పన చేశారు.
- పై విధంగా సామాజిక మార్పునకు దోహదం చేసే అనేక అంశాలు రాజ్యాంగంలో పొందుపరిచినారు.

ప్రశ్న 16.
రాజ్యాంగ సభ నిర్మాణం ఏ విధంగా జరిగింది?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగం కోసం 1946లో రాష్ట్రాలకు ఎన్నికలు జరిగిన తరువాత రాజ్యాంగ సభకు ఎన్నికలు జరిగాయి. రాజ్యాంగ సభ సభ్యులను రాష్ట్ర శాసన సభలు పరోక్షంగా ఎన్నుకున్నాయి. 1946లో ఏర్పాటైన కేబినెట్ మిషన్ ప్రతి రాష్ట్రానికి, ప్రతి సంస్థానానికి లేదా కొన్ని సంస్థానాలతో కూడిన బృందాలకి కొన్ని స్థానాలను కేటాయించింది. ఈ ప్రకారం బ్రిటిష్ ప్రత్యక్ష పాలనలోని రాష్ట్రాలు 292 సభ్యులను ఎన్నుకోగా, అన్ని సంస్థానాలు కలిసి 93 సభ్యులను ఎన్నుకున్నాయి. ప్రతి రాష్ట్రం నుంచి ఎన్నికయ్యే సభ్యులలో ఆ రాష్ట్రాలలో ఆయా వర్గాల జనాభాను బట్టి ముస్లిములు, సిక్కులు, ఇతరులు ఉండేలా ఈ ఎన్నికలు నిర్వహించారు. రాజ్యాంగ సభలో షెడ్యూల్డ్ కులాలకు చెందిన 26 మంది సభ్యులు ఉండేలా కూడా చూశారు. రాష్ట్రాల శాసనసభలలో ఎన్నికలు నిర్వహించగా సంస్థానాల ప్రతినిధులను సంప్రదింపుల ద్వారా ఎంపిక చేశారు. మొత్తం మీద దీంట్లో తొమ్మిది మంది మాత్రమే మహిళలు. దీంట్లో 69% సీట్లతో భారత జాతీయ కాంగ్రెస్ అతి పెద్ద పార్టీ కాగా ఆ తరువాత స్థానంలో ముస్లింలకు కేటాయించిన స్థానాల్లో అధికశాతాన్ని గెలుచుకున్న ముస్లింలీగు ఉంది. మొదట్లో బ్రిటిష్ ఇండియాకి చెందిన అన్ని ప్రాంతాల సభ్యులు దీంట్లో ఉన్నారు. అయితే 1947 ఆగస్టు 14న పాకిస్థాన్, భారతదేశంగా దేశ విభజన జరగటంతో పాకిస్థాన్ కి చెందిన సభ్యులు పాకిస్థాన్ రాజ్యాంగ సభగా ఏర్పడ్డారు.
ప్రశ్న 17.
1946 డిసెంబరు 13న రాజ్యాంగ సభలో జవహర్లాల్ నెహ్రూ చేసిన ప్రకటన ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
“భారతదేశానికి మనం కోరుకుంటున్న భవిష్యత్తు ఒక బృందానికో లేక ఒక వర్గానికో, లేదా ఒక రాష్ట్రానికో పరిమితమైనది కాదు. ఇది దేశ 40 కోట్ల జనాభాకు సంబంధించినది…… ఇక్కడ లేనివాళ్లను గుర్తు చేసుకోవటం మన విధి. ఇక్కడ ఒక పార్టీ కోసమో, లేక ఒక బృందం కోసమో పని చెయ్యటానికి లేము; దేశం మొత్తం కోసం మనం ఆలోచన చెయ్యాలి, భారతదేశ 40 కోట్ల ప్రజల సంక్షేమాన్ని దృష్టిలో ఉంచుకోవాలి. మన స్వార్థాల నుంచి, పార్టీ వివాదాల నుంచి సాధ్యమైనంత వరకు బయటపడి మన ముందున్న పెద్ద సమస్య గురించి అత్యంత విస్తృత, సహనశీల ప్రభావవంత పద్దతిలో ఆలోచించి మనం రూపొందించేది దేశమంతటికీ అర్హమైనదిగా ఉండాలి. ఈ అత్యంత బాధ్యతాయుత కార్యక్రమంలో ప్రవర్తించవలసిన విధంగా మనం ప్రవర్తించామని ప్రపంచం గుర్తించేలా ఉండాలి.”
ప్రశ్న 18.
షెడ్యూల్డ్ కులాలు, షెడ్యూల్డ్ తెగలు తరతరాలుగా ఎదుర్కొన్న అన్యాయాలను అధిగమించడానికి రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు తీసుకున్న చర్యలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
రాజ్యాంగంలో షెడ్యూల్డ్ కులాలు, షెడ్యూల్డ్ తెగలకు రిజర్వేషన్లను కల్పించటం. ఈ బృందాలు తరతరాలుగా ఎదుర్కొన్న అన్యాయాలను అధిగమించటానికి, వాళ్ల ఓటుహక్కుకి సరైన అర్థాన్ని ఇవ్వడానికి కేవలం సమానత్వానికి హక్కు ఇస్తే సరిపోదని రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు విశ్వసించారు. వాళ్ల ప్రయోజనాలను ప్రోత్సహించేందుకు ప్రత్యేక రాజ్యాంగ చర్యలు అవసరం. అందుకనే షెడ్యూల్డ్ కులాల, షెడ్యూల్డ్ తెగల ప్రయోజనాలను కాపాడటానికి శాసనసభ స్థానాల రిజర్వేషను వంటి అనేక ప్రత్యేక అంశాలను రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు కల్పించారు. ఈ వర్గాలకు ప్రభుత్వరంగ ఉద్యోగాలలో రిజర్వేషన్లకు కూడా రాజ్యాంగం అవకాశం కల్పించింది.
ప్రశ్న 19.
రాజ్యాంగ సవరణ ప్రక్రియను వివరించుము.
జవాబు:
శాసనసభలలో సగం కంటే ఎక్కువమంది ఆమోదంతో తరచు చట్టాలు చెయ్యవచ్చు. అయితే రాజ్యాంగంలోని అధికరణాల సవరణను పార్లమెంటు మాత్రమే చేపట్టాలి. అంతేకాకుండా రాజ్యసభ, లోక్సభల రెండింటిలో మూడింట రెండు వంతుల సభ్యుల ఆమోదం అవసరం. కొన్ని అధికరణాలను రాష్ట్ర శాసనసభలు అంగీకరించిన తరువాత (లేదా రాటిఫై చేసిన తరువాత) మాత్రమే సవరించవచ్చు. అంతేకాకుండా ఇతర చట్టాలలాగే కొత్త సవరణలను దేశ అధ్యక్షుడు కూడా ఆమోదించాల్సి ఉంది.

ప్రశ్న 20.
రాజ్యాంగం – సామాజిక నిర్మాణం (Constitution and Social Engineering)
భారత రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు భారతీయ సమాజం అసమానతలు, అన్యాయం, లేమి వంటి సమస్యలను ఎదుర్కొంటోందని, ఆర్థిక దోపిడీకి పాల్పడిన వలస పాలకుల విధానాలకు బలి అయ్యిందని గుర్తించారు. కాబట్టి అభివృద్ధితోపాటు సామాజిక మార్పుకి కూడా రాజ్యాంగం దోహదం చెయ్యాలని గుర్తించారు. “గత రాజకీయ, సామాజిక నిర్మాణాన్ని తిరస్కరించి ముందుకు కదులుతూ తనకు తాను కొత్త వస్త్రాలను రూపొందించుకుంటున్న దేశానికి ” రాజ్యాంగ సభ ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహిస్తున్నట్టుగా జవహర్ లాల్ నెహ్రూ పేర్కొన్నారు.
ప్ర. “గత రాజకీయ, సామాజిక నిర్మాణాన్ని తిరస్కరించి ముందుకు కదులుతూ తనకు తాను కొత్త వస్త్రాలను రూపొందించుకుంటున్న దేశానికి ” రాజ్యాంగ సభ ప్రాతినిధ్యం వహిస్తున్నట్టుగా జవహర్ లాల్ నెహ్రూ వ్యాఖ్యానంతో మీరు ఏకీభవిస్తారా? కారణాలు తెలియచేయండి.
జవాబు:
జవహర్లాల్ నెహ్రూగారి వ్యాఖ్యానంతో నేను ఏకీభవిస్తాను. పై వ్యాఖ్యానాన్ని బలపరుస్తూ రాజ్యాంగంలో అనేక అంశాలున్నాయి. సామాజిక మార్పునకు దోహదం చేసే అనేక అంశాలు రాజ్యాంగంలో ఉన్నాయి.
- అంటరానితనాన్ని నిషేధించటం జరిగింది. షెడ్యూల్డ్ కులాలు, షెడ్యూల్డ్ తెగలకు రిజర్వేషన్లు కల్పించబడ్డాయి. – వీరికి శాసనసభా స్థానాల రిజర్వేషన్ వంటి అనేక ప్రత్యేక అంశాలను రాజ్యాంగ నిర్మాతలు కల్పించారు.
- షెడ్యూల్డ్ కులాలు, వర్గాలకు ప్రభుత్వ రంగ – ఉద్యోగాలలో కూడా రాజ్యాంగం రిజర్వేషన్లు కల్పించింది.
- రాజ్యాంగంలో అల్ప సంఖ్యాక వర్గాల హక్కులకు ప్రత్యేక రక్షణ, ఆదేశ సూత్రాలు రూపంలో కల్పించినారు. మత పర అల్ప సంఖ్యాక వర్గాలు తమ సొంత విద్యా సంస్థలను నిర్వహించుకునే హక్కు కల్పించబడింది.
- ప్రజలందరికి కుల, మత, వర్గ, ధనిక, పేద వంటి తేడాలు చూపకుండ ఓటు హక్కును కల్పించినారు. ఇది – సమానత్వపు హక్కును సూచిస్తుంది. ఈ అంశాల ద్వారా నెహ్రూగారి వ్యాఖ్యానంతో నేను ఏకీభవిస్తున్నాను.
![]()
![]()
![]()





































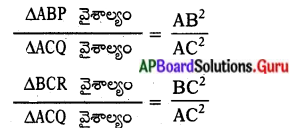
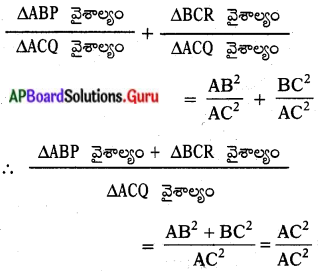
 (పైథాగరస్ సిద్ధాంతం నుండి)
(పైథాగరస్ సిద్ధాంతం నుండి)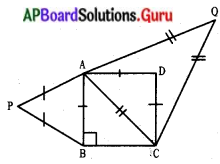
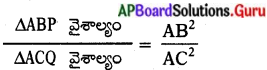 [∵ ∆ABP ~ ∆ACQ]
[∵ ∆ABP ~ ∆ACQ]