Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 12(b) Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Study Material Lesson 12(b) Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property indicated.
- Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Methyl t. butyl ketone reactivity towards HCN.
- Floroacetic acid, monochloroacetic acid, Acetic acid and Dichloroacetic acid (acid strength)
Answer:
- Due to the presence of groups around the carbonyl group the reactivity of a compound depends on the steric hindrance.
Greater the steric hindrance, less will be the reactivity of the compound. Reactivity towards HCN is in the following order.
Methyl tertiary butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde - Acid strength of given compounds is Dichloro acetic acid > fluoro acetic acid > chloro acetic acid > acetic acid.
![]()
Question 2.
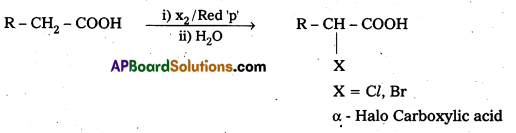
Write the reaction showing a-halogenation of carboxylic acid and give its name.
Answer:
Carboxylic acids having a-hydrogens are halogenated at the a-position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in presence of small amount of red phosphorous to give a-halo carboxylic acids.
This reaction is named as Hell-volhard – Zelinsky (HvZ) reactions
Question 3.
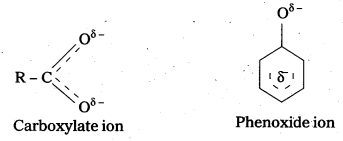
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures thancarboxylate ion carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Why ?
Answer:
- Phenoxide ion has non-equivalent resonance structures in which the negative charge is at the less electronegative carbon atom.
- The negative charge is delocalised over two electronegative oxygen atoms in carboxylate ion whereas in phenoxide ion the negative charge less effectively delocalised over one oxygen atom and less electronegative carbon atoms.
Question 4.
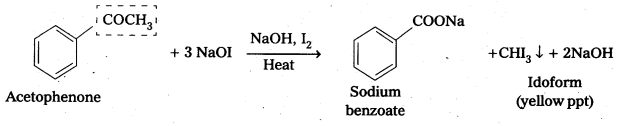
How do you distinguish acetophenone and benzophenone?
Answer:
On idoform test Acetophenone gives positive, where as benzophenone (C6H5COC6H5) does not
Question 5.
Explain the position of electrophilic substitution In benzolc acid.
Answer:
Benzoic acid undergo electrophilic substitution reactions in which carboxyl group acts as a deactivating and meta dirécting group.
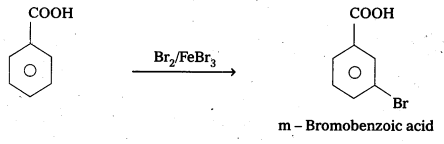
![]()
Question 6.
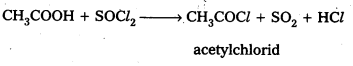
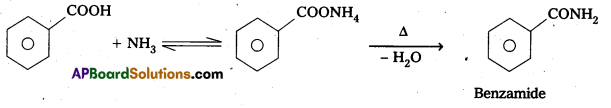
Write equations showing the conversion of
i) Acetic acid to Acetyl chloride
ii) Benzoic acid to Benzamide
Answer:
i) acetic acid reacts with PCl3 (or) PCl5 (or) SOCl6 to form acetyl chloride
ii) Benzoic acid reacts with ammonia to form benzamide
Question 7.
An organic acid with molecular formula C8H8O2 on decarboxylation forms Toluene. Identify the organic acid.
Answer:
The organic acid is phenyl acetic acid
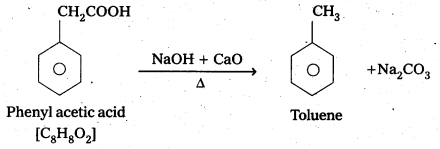
Question 8.
List the reagents needed to reduce carboxylic acid to alcohol.
Answer:
The Reagents required to reduce carboxylic acid to alcohol are
- LiAlH4/Ether (or) B2H6
- H4O+
Question 9.
Write the mechanism of esterification.
Answer:
Mechanism of esterification of carboxylic acids : The esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols is a kind of nucleophilic acyl substitution. Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen activates the carbonyl group towards nucleophilic addition of the alcohol. Proton transfer in the tetrahedral intermediate converts the hydroxyl group into – +OH2 group, which, being a better leaving group, is eliminated as neutral water molecule. The protonated ester so formed finally loses a proton to give the ester.
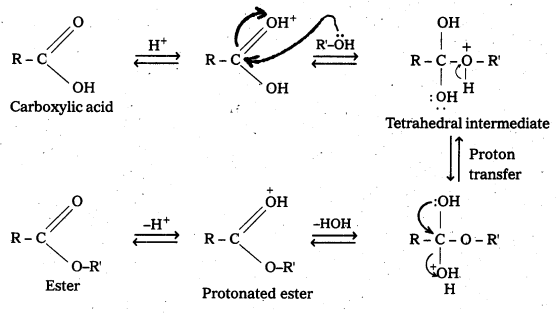
![]()
Question 10.
Compare the acidic strength of acetic acid, Chloroacetic acid, benzoic acid and Phenol. [Mar. 14]
Answer:
Benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) > Chloro acetic acid (ClCH2COOH) > Acetic acid (CH3COOH) > Phenol (C6H5OH)
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write the equations of any aldehyde with Fehlings reagent.
Answer:
Fehling’s reagent is mixture of two solutions Fehling’s A and Fehlings B.
Fehling’s A – aq. CuSO4 solution
Fehling’s B – Sodium potassium tartarate (Rochelle salt)
Acetaldehyde reacts with Fehlings .eagent and gives a redbrown ppt.
Reaction:
CH3 – CHO + 2CU+2 + 5OH– → RCOO– + CU2O + 3H3O (Red – brown ppt)
Question 2.
What is Tollens reagent? Explain Its reaction with Aldehydes.
Answer:
Tollens Reagent : Freshly prepared ammonicai silver nitrate solution is called Tollens reagent.
On warming an aldehyde with Tollens reagent a bright silver mirror is produced due to formation of silver metal.
R – CHO + 2 [Ag(NH3)2]+ + 3OH– → RCOO– + 2Ag + 2H2O + 4NH3
Question 3.
Write the oxidation products of : Acetaldehyc, Acetone and Acetophenone.
Answer:
a) Acetaldehyde under goes oxidation to foim acetic acid.
![]()
b) Acetone undergoes oxidation to form acetic acid
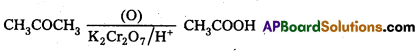
c) Acetophenone undergoes oxidation to form benzoicacid and chloroform
![]()
Question 4.
Explain why Aldehydes and ketones undergoes nucleophilic addition while alkenes undergoes electrophilic addition though both are unsaturated compounds.
Answer:
The carbon – oxygen double bond in carbonyl compounds is polarised due to higher electronegativity of oxygen relative to carbon. Hence the carbonyl carbon is an electrophilic and carboxyl oxygen is a nucleophilic centre. So aldehydes, ketones undergoes nucleophilic addition reaction.
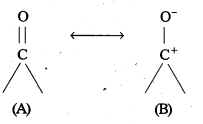
Alkenes contain ![]() which is a source of electron density so electrophiles add no to C = C to give addition products. Hence alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reaction.
which is a source of electron density so electrophiles add no to C = C to give addition products. Hence alkenes undergo electrophilic addition reaction.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the IUPAC names of the following:
i) CH3CH2CH(Br) CH3COOH
ii) Ph. CH3COCH3COOH
iii) CH3.CH (CH3) CH2COOC2H5
Answer:
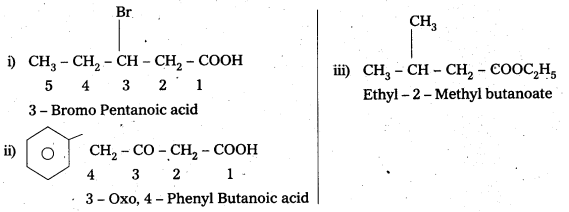
Question 6.
Arrange the following In the increasing order of their acidic strength:
Benzolc acid, 4 – Methoxybenzoic acid, 4 – Nitrobenzoic acid and 4 – Methylbenzoic acid.
Answer:
Electron donating group (-OCH3) decreases the acidic strength where as electron withdrawing group (NO2) increases the same.
Increases order of acidic strength is:
4-Methoxy benzoic acid < benzoic acid < 4-nitrobenzoic acid < 3, 4-dinitro benzoic acid.
Question 7.
DescrIbe the following: .
i) Cross aldol condensation
ii) Decarboxylation
Answer:
i) Cross Aldol Condensation : When aldol condensation ¡s earned out between two different aldehydes and (or) ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation.
If both the reactants contain α-hydrogen atoms, it gives a mixture of four products.
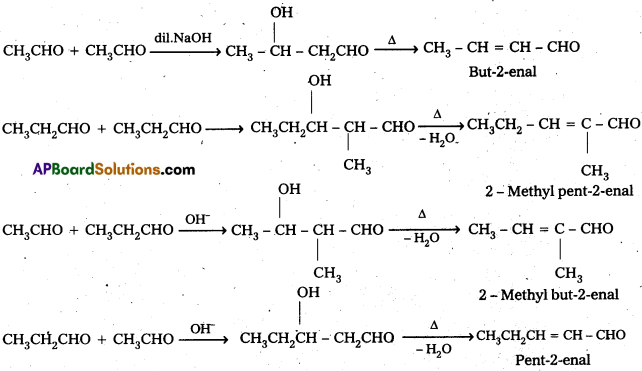
Ketones can also be used as one component in the cross aldol reactions
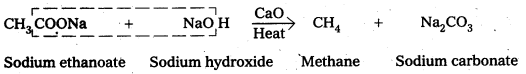
ii) Decarboxylatlon : Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide molecule to produce hydrocarbons on heating their sodium salts with sodalizne (a mixutre of NaOH & CaO in ratio 3 : 1)
.-, This reaction is called decarboxylation
![]()
Question 8.
ExplaIn the role of electron withdrawing and electron releasing groups on the acidity of carboxylic acids.
Answer:
- Electron with drawing groups increase the acidity of carboxylic acids by stabilising the conjugate base through decocalisation of the negative charge by inductive effect.
- Electron donating groups decreases the äcidity of carboxylic acids by destabilising the conjugate base.
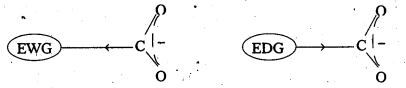
Eg : Cl– is a electron with drawing group acidic strength order in case of chloro acetic acids
CCl3COOH > CHCl2COOH > CH2ClCOOH > CH3COOH
Question 9.
Draw the structures of the following derivatives:
i) Acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
ii) The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
iii) The methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde.
Answer:
The structures of following are
i) Acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
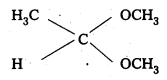
ii) Ethylene Ketal of hexan-3-one
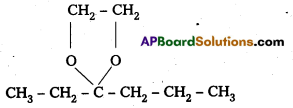
iii) Methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde
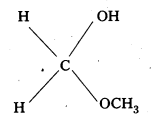
![]()
Question 10.
An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It doesnot reduce Tollens’ reagent but forms sodium hydrogensulphite adduct and gives +ve iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation forms ethanoic and propanoic acids. Write the possible structure of the compound.
Answer:
Step : 1 To determine the molecular formula of the compound.
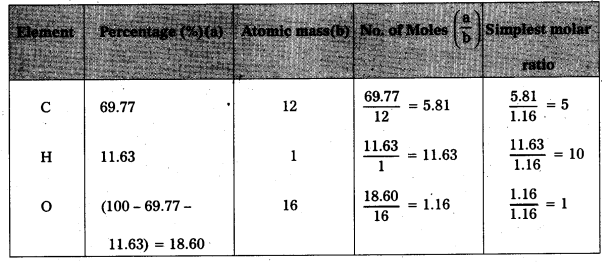
Emperical formula of the given compound = C5H10O
Molecular formula = n × (emperical formula)
Where n = \(\frac{\text { Molecular mass of the compound }}{\text { Emperical formula mass of compound }}\)
Given, molecular mass = 86
Emperical formula mass of C5H10O = (12 × 5) + (10 × 1) + 16 = 60 + 10 + 16 = 86
n = \(\frac{86}{86}\) = 1
Molecular formula = 1 × (C5H10O)
∴ Molecular formula = C5H10O
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the following terms. Give an example of the reaction in each case. [A.P. Mar. 18]
i) Cyanohydrin
ii) Acetal
iii) Semicarbazone
iv) Aldol
v) Hemiacetal
vi) Oxime
Answer:
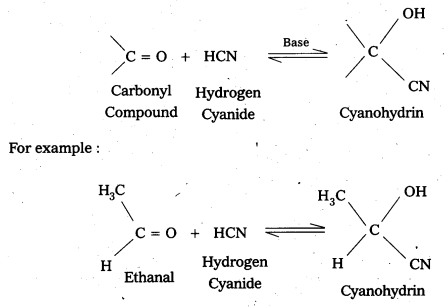
i) Cyanohydrin
Aldehydes and ketones react withk hydrogen cyanide (HCN) forms addition products called (or) known as cyanohydrins.
ii) Acetal
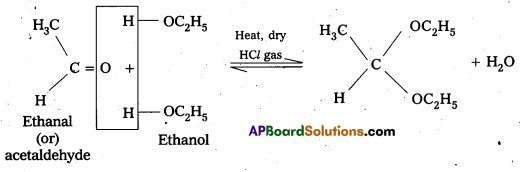
In the presence of dry HCl gas, an aldehyde reacts with two equivalents of a monohydric alchol forms gem-dialkoxy compounds are known as acetals.
—> In acetal two alkoxy groups are present on the terminal C-atom.
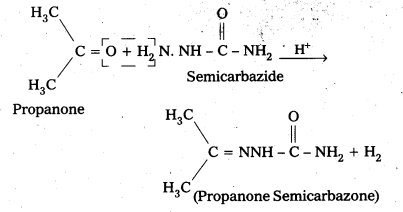
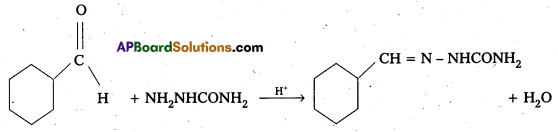
iii) Semicarbazone
Aldehydes/ketones react with semicarbazide forms certain compounds called as senilcarbazones.
For example:
iv) Aldol
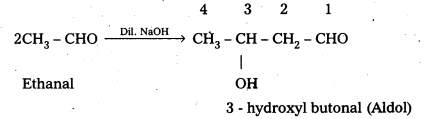
When an aldehyde ((or) ketone) having at least one a-hydrogen atom undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form aldol (or) β- hydroxy aldehydes ((or) ketals in case of ketones), the reaction is called aldol condensation.
For example:
v) Hemiacetat : In the presence of dry HCl gas an aldehyde reacts with one molecule of a monohydric alcohol forms gem-alkoxy alcohols. These are known as hemiacetals.
For example:
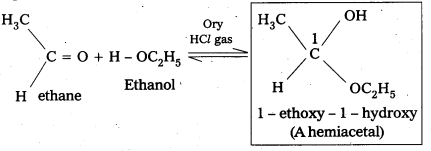
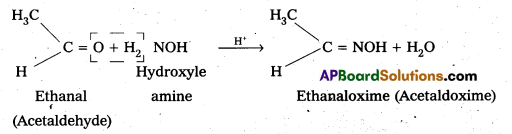
vi) Oxime: In weak acidic medium, an aldehyde ketone reacts with hydroxylamine forms products which are known as oxims.
Question 2.
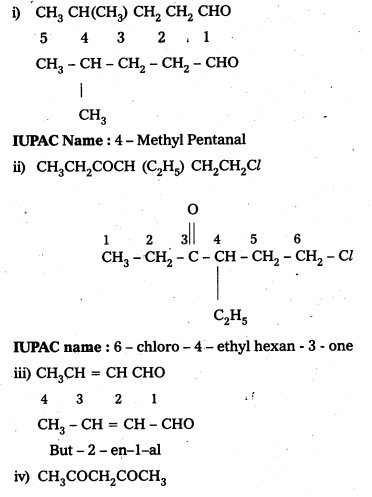
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
i) CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CHO
ii) CH3CH2COCH (C2H5)CH2CH2Cl
iii) CH3CH = CHCHO
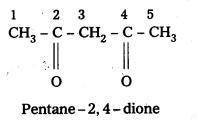
iv) CH3COCH2COCH3
Answer:
IUPAC names of following
![]()
Question 3.
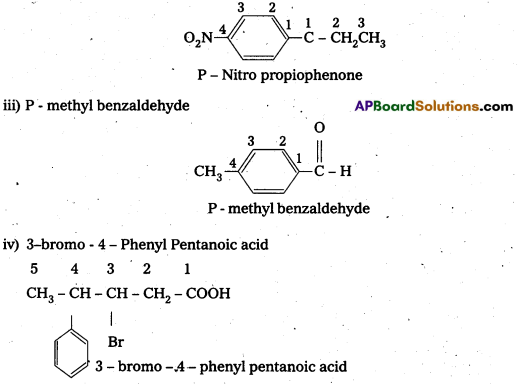
Draw the structures of the following compounds.
i) 3-Methylbutanal
ii) p-Nitropropiophenone
iii) p-Metylbenzaldehyde
iv) 3-Bromo-4-phenylpentanoic acid
Answer:
i) 3 – Methyl butanal
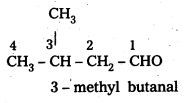
ii) p-Nitropropiophenone
Question 4.
Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and Aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names.
i) CH3CO(CH2)4 CH3
ii) CH3CH2CHBrCH2CH (CH3)CHO
iii) CH3(CH2)5CHO
iv) PhCH = CHCHO
v) 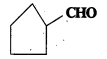
vi) PhCOPh
Answer:
i) CH3CO(CH2)4 CH3
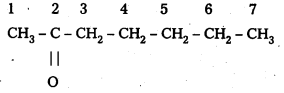
IUPAC Name: Heptan-2-one
Common Name: Methnyl n-pentyl ketone
ii) CH3CH2CHBrCH2CH (CH3)CHO
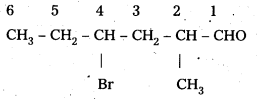
IUPAC Name : 4 – bromo – 2 – methyl hexanal
Common Name : γ – bromo – α – methyl caproaldehyde
iii) CH3(CH2)5CHO
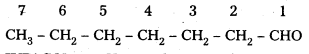
IUPAC Name: Heptanal
Common Name i n – heptyi aldehyde
iv) Ph – CH =CH – CHO
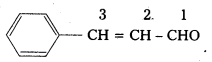
IUPAC Name : 3 – Phenyl Prop-2-en-1-al
Common Name: β – phenyl acrolein
v) 
IUPAC Name: Cyclopentane Carbaldehyde
vi) PhCOPh
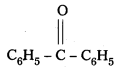
IUPAC Name : Diphenyl methanone
Common Name : Benzophenone
![]()
Question 5.
Draw the structures of the following derivatives.
i) The 2, 4 – dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde
ii) Cyclopropanone oxime
iii) Acetaldehyde hemiacetal
iv) The Semicarbazone of cyclobutanone
Answer:
i) The 2, 4 – dinitro phenyl hydrazone of benzaldehyde :
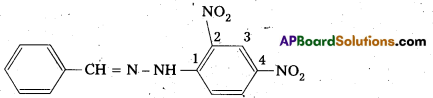
ii) Cyclopropanone oxime
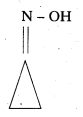
iii) Acetaldehyde hemiacetal
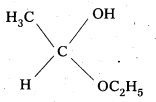
iv) The Semicarbazone of cyclobutanone
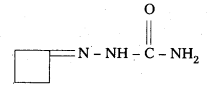
Question 6.
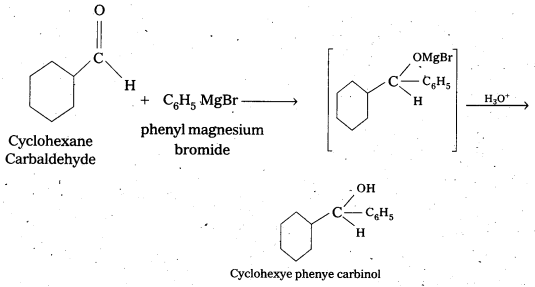
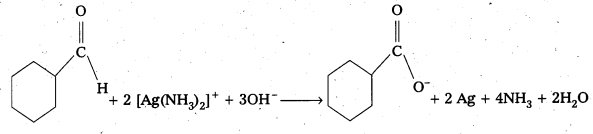
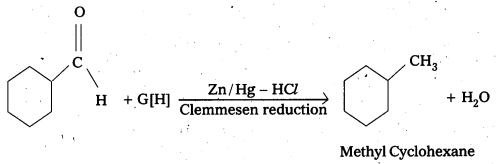
Predict the products formed when Cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with following reagents.
i) PhMgBr and then H3O+
ii) Tollens reagent
iii) Semicarbazide and weak acid
iv) Zinc amalgam and dilute HCl
Answer:
The products are formed when cyclohexane carbaldehyde reacts with following.
i) Ph MgBr and the H3O+
ii) Tollens reagent
iii) Semicarbazide and weak acid
iv) Zinc amalgam and dilute HCl
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following compounds would Undergo aldol condensation ? Write the structures of the products expected.
i) 2-Methylpentanal
ii) 1-Phenylpropanone
iii) Phenyl acetaldehyde
iv) 2,2 – Dimethylbutanal
Answer:
Compounds having one (or) more a-H atoms undergo aedol condensation.
So from above only first three compounds having α-H atoms. Therefore they undergo aldol condensation. They are namely
- 2-methyl Pentanal
- 1 – Phenyl propanone
- Phenyl acetaldehyde
i) 2 – Methyl Pentanal
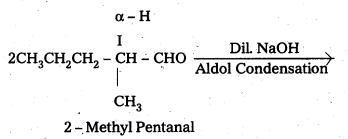
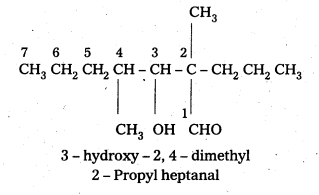
ii) 1 – Phenyl propanone
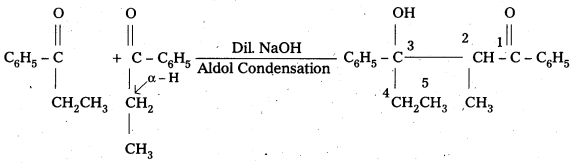
iii) Phenyl acetaldehyde
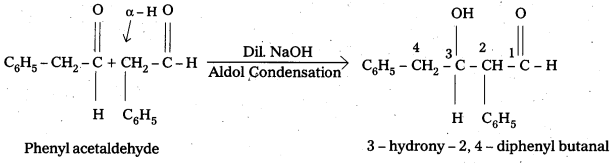
Question 8.
An organic compound A(C9H10O) forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’ reagent and undergoes Cannizaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation it gives 1, 2-benzene dicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
Answer:
- The compouhd having molecular formula C9H10O forms a 2, 4 – DNP derivative and reduces Tollen’s reagent. So it is an aldehyde.
- It undergoes cannizaro reaction, so the aldehyde group should be directly attached to the benzene ring.
- On vigorous oxidation it gives 1,2- benzene dicarboxylic acid, so it should be an ortho substituted benzaldehyde. For molecular formula C9H10O, the possibility is only O-ethyl benzaldehyde.
- The equations for all reactions are given below.
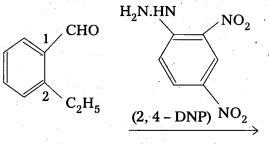
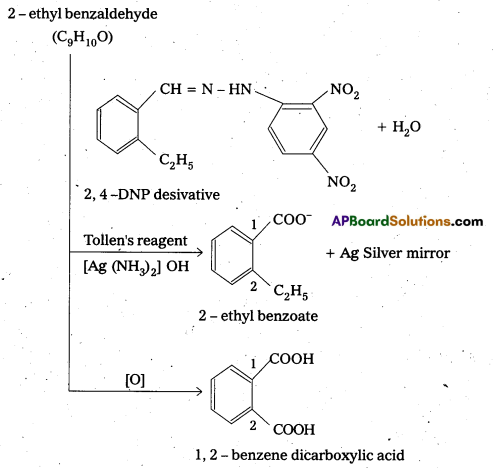
Question 9.
How do you distinguish the following pairs of compounds ?
i) Propanal and propanone
ii) Acetophenone and benzophenone
iii) Phenol and benzoic acid
iv) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
Answer:
i) Propanal and Propanone
On idoform test propanone responds, but absence of CH3CO – group in propanal (CH3CH2CHO) it does not respond.
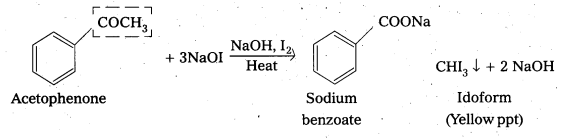
ii) Acetophenone and benzophenone
Acetophenone gives positive idoform test whereas benzophenone (C6H5COC6H5) does not
iii) Phenol and benzoic acid
Benzoic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to produce effervescences of carbon dioxide where as phenol (C6H5OH) does not
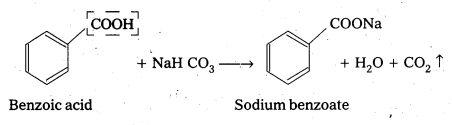
iv) Pentan-2-one and Pentan – 3 – One
On idoform test Pentan – 2 – One-responds whereas Pentan – 3 – one (C2H5 COC2H5) does not

![]()
Question 10.
How are the following conversions carried in not more than two steps ?
i) Ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal
ii) Bromobenzene to 1-Phenylethanol
iii) Benzaldehyde to ± Hydroxyphenylacetic acid
iv) Benzaldehyde to benzophenone
Answer:
i) Ethanol to 3-hydroxybutanal
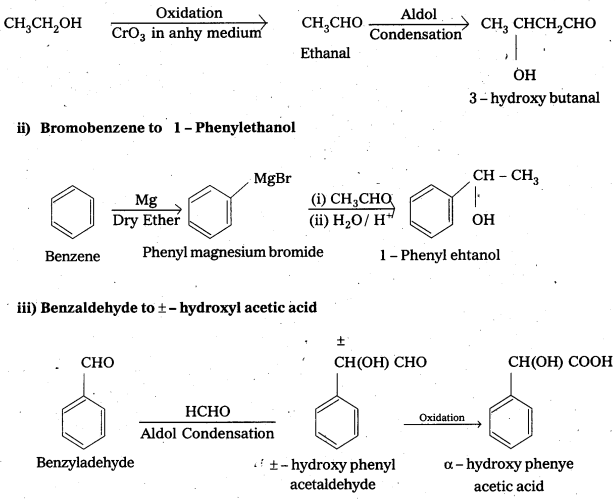
iv) Benzaldehyde to benzophenone
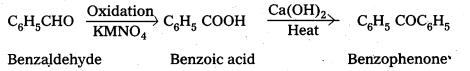
Question 11.
Describe the following. [A.P. & T.S. Mar. 19, 16] [A.P. Mar. 18]
i) Acetylation
ii) Cannizaro reaction
iii) Cross aldol condensation
iv) Decarboxylation
Answer:
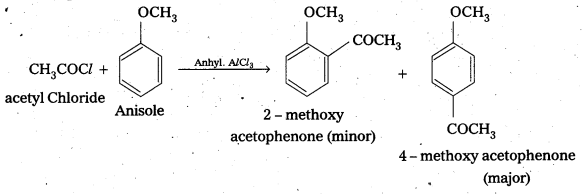
i) Acetylation : When active hydrogen atom of alcohol, phenol (or) an amine is replaced by acetyl (CH3CO–) group to form corresponding ester (or) amide, the reaction is known as acetylation.
Reagents used are acid chloride (or) acid anhydride in presence of a base like pyridine (or) dimethylaniline.
For example :
ii) Cannizaro reaction: On treating with concentrated alkali, aldehydes which do not have any α – hydrogen atom, undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction.
This reaction is called cannizaro reaction.
As a result, one molecule of aldehyde is reduced to alcohol while another is oxidised to carboxylic acid salt.
For example:
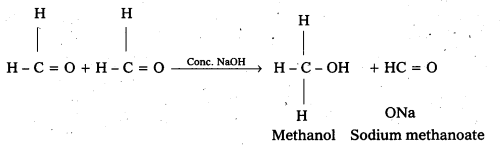
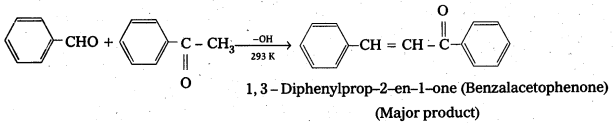
iii) Cross aldol condensation: When aldol condensation is carried out between two different aldehydes and (or) ketones, it is called cross aldol condensation.
If both the reactants contain a – hydrogen atoms, it gives a mixture of four products.
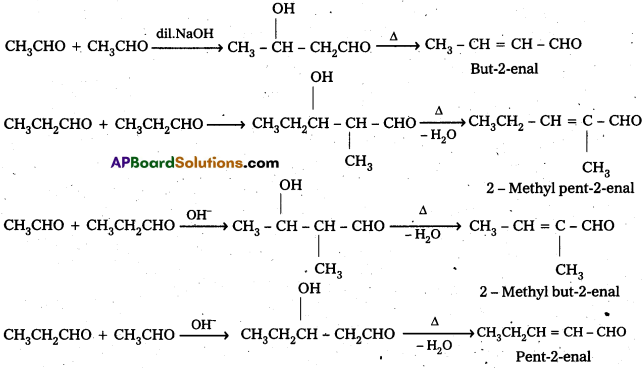
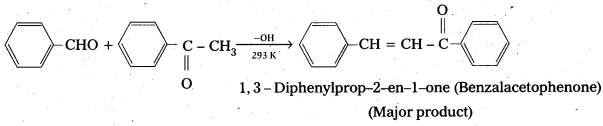
Ketones can also be used as one component in the cross aldol reactions
iv) Decarboxylation
Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide molecule to produce hydrocarbons on heating their sodium salts with sodalime (a mixutre of NaOH & CaO in ratio 3: 1). This reaction is called decarboxylation.
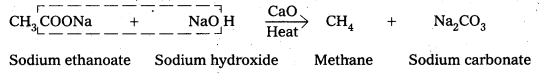
![]()
Question 12.
Complete each synthesis by giving the missing starting material, reagent or product.
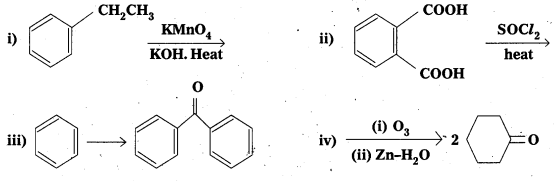
Answer:
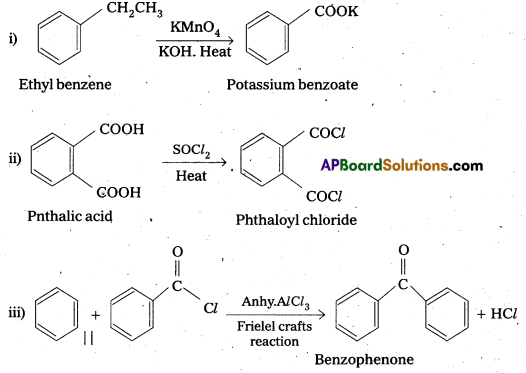
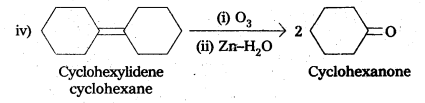
Question 13.
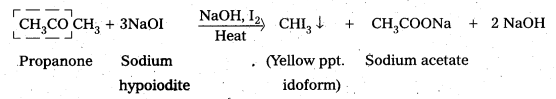
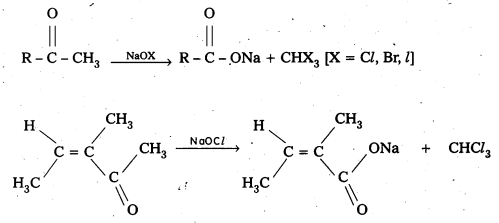
Explain how methyl ketones are distinguished from other ketones. Write the equations showing it.
Answer:
Oxidation of methyl ketones by haloform reactIon : Aldehydes and ketones having at least one methyl group linked to the carbonyl carbon atom (methyl ketones) are oxidisedby sodium hypohalite to sodium salts of corresponding carboxylic acids having one carbon atom less than that of carbonyl compound. The methyl group is converted to haloform. This oxidation does not affect a carbon-carbon double bond, If present in the molecule. lodoform reaction with sodium hypoiodite is also used for detection of CH3CO group or CH3CH(OH) group which produces CH3CO group on oxidation.
![]()
Question 14.
Write the equations showing the conversion of the following along with reagents.
i) 1-phenyipropane to Benzoic acid
ii) Benzamide to Benzoic acid
iii) Ethyl butanoate to Butanoic acid.
Answer:
i)
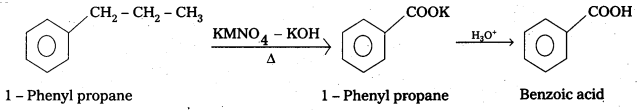
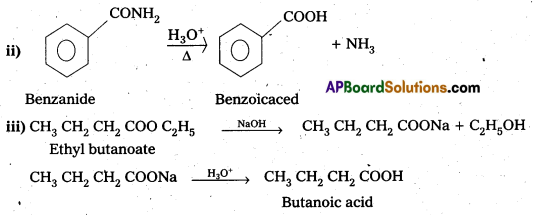
Question 15.
Write the products and reagents needed for the below given conversions
i) 3-Nitrobromobenzene to 3-Nitrobenzoic acid
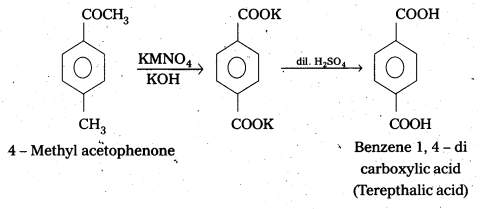
ii) 4-Methyl’acetophenone to Benzene- 1-4-dicarboxylic acid
Answer:
i) 3-Nitrobromobenzene to 3-Nitrobenzoic acid:
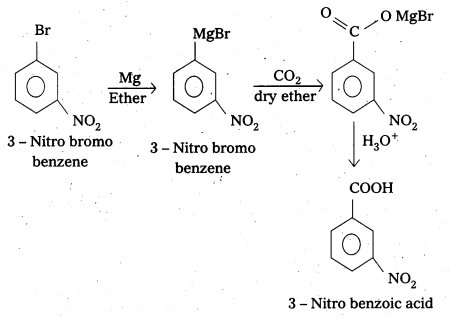
ii) 4-Methyl’acetophenone to Benzene- 1-4-dicarboxylic acid
Textual Examples
Question 1.
Give names of the reagents ot bring about the following transformations:
- Hexan – 1 – ol to hexanal
- Cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone
- p – Fluorotoluene to p – fluorobenzaldehyde
- Ethanenitrile to ethanal
- Allyl alcohol to propanal
- But-2-ene to ethanal
Solution:
- C5H5NH+ CrO3Cl– (PCC)
- K2Cr2O7 in acidic medium
- CrO3 in the presence of acetic anhydride/1. CrO2Cl25 2. HOH
- (Diisobutyl) aluminiinn hydride (DIBAL-H)
- PCC
- O3/H2O-Zn dust
Question 2.
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CH2CH2CHO, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH, H5C2-O-C2H5, CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
Solution:
The molecular masses of these compounds are in the range of 72 to 74. Since only butan-1- ol molecules are associated due to extensive intermolecular hydrogen bonding, therefore, the boiling point of butan-l-ol would be the highest. Butanal is more polar than ethoxyethane. Therefore, the intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction is stronger in the former. n-Pentane molecules have only weak vander Waals forces. Hence increasing order of boiling points of the given compounds is as follows :
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 < H5C2-O-C2H5 < CH3CH2CH2CHO < CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
![]()
Question 3.
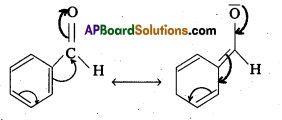
Would you expect benzaldehyde to be more reactive or less reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions than propanal ? Explain your answer.
Solution:
The carbon atom of the carbonyl group of benzaldehyde is less electrophilic them carbon . atom of the carbonyl group present in propanal. The polarity of the carbonyl group is reduced in benzaldehyde due to resonance as shown below and hence it is less reactive than propanal.
Question 4.
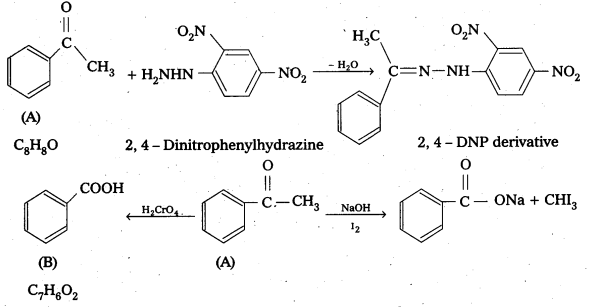
An organic compound (A) with molecular formula C8H8O forms an orange-red precipitate with 2,4 – DNP reagent and gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide. It neither reduces Tollens or Fehlings reagent, nor does it decolourise bromine water or Baeyer’s reagent. On drastic oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid (B) having molecular formula C7H6O2. Identify the compounds (A) and (B) and explain the reactions involved.
Solution:
(A) forms 2, 4 – DNP derivative. Therefore, it is an aldehyde or a ketone. Since it does not reduce Tollens or Fehling’s reagent, (A) must be a ketone. (A) responds to iodoform test. Therefore, it should be a methyl ketone. The molecular formula of (A) indicates high degree of unsaturation, yet it does not decolourise bromine water or Baeyers reagent. This indicates the presence of unsaturation due to an aromatic, ring.
Compound (B), being an oxidation product of a ketone should be a carboxylic acid. The molecular formula of (B) indicates that it should be benzoic acid and compound (A) should, therefore, be a monosubstituted aromatic methyl ketone. The molecular formula of (A) indicates that it should be phenyl methyl ketone (acetophenone). Reactions are as follows:
![]()
Question 5.
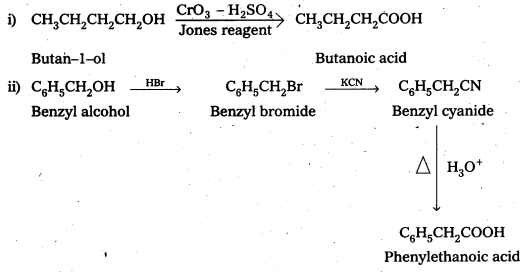
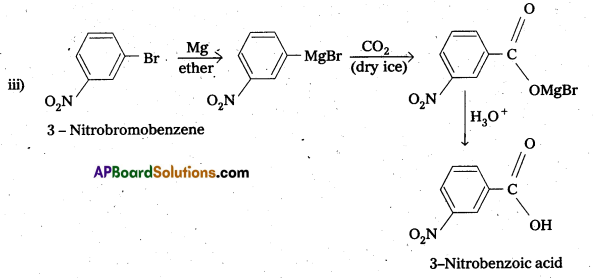
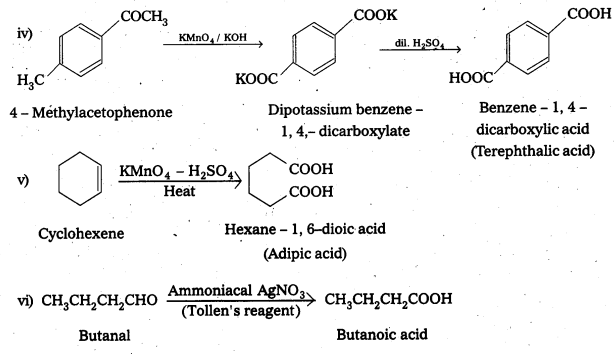
Write chemical reactions to affect the following transformations :
i) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid
ii) Benzyl alcohol to phenylethanoic acid
iii) 3-Nitrobromobenzene to 3-nitrobenzoic acid
iv) 4 – Methylacetophenone to benzene – 1, 4 – dicarboxylic acid
v) Cyclohexene to hexane-1, 6 – dioic acid
vi) Butanal to butanoic acid.
Solution:
Intext Questions
Question 1.
Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols:
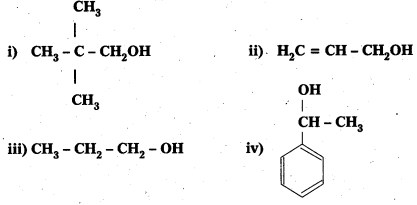
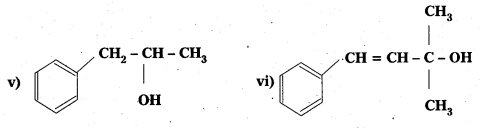
Answer:
Primary alcohols (1), (ii), (iii)
Secondary alcohols (iv) and (v)
Tertiary alcohols (vi)
Question 2.
Identify allylic alcohols In the above examples.
Answer:
Allylic alcohols (ii) and (vi)
Question 3.
Name of the following compounds according to IUPAC system.
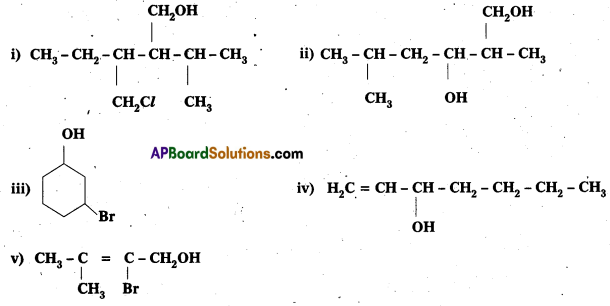
Solution:
i) 3-Chloromethyl – 2 isopropylpentan – 1 – ol
ii) 2, 5 – Dimethylhexane – 1, 3 – diol
iii) 3 – Bromocyclohexanol
iv) Hex- 1 -en-3-ol
v) 2-Bromo~3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol
![]()
Question 4.
Show how are the following alcohols prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanal ?

Solution:
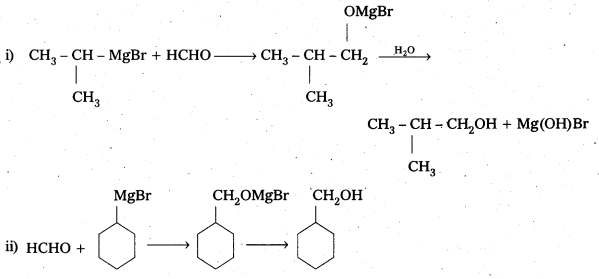
Question 5.
Write the structures of the products of the following reactions :
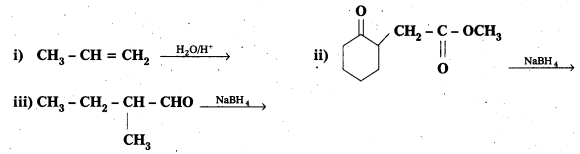
Solution:
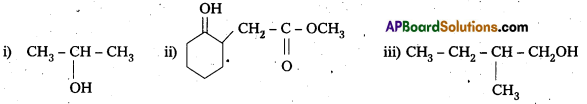
Question 6.
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration of
i) 1 – methylcyclohexanol and
ii) butan – 1 – ol
Solution:
i) 1 – Methylcyclohexene
ii) A mixture of but-1-ene and but-2-ene. But-1-ene is the major product formed due to rearrangement to give secondary carbocation.
Question 7.
Write the reactions of Williamson synthesis of 2-ethyoxy-3-methylpentane starting from ethanol and 3-methylpentan-2-ol.
Solution:
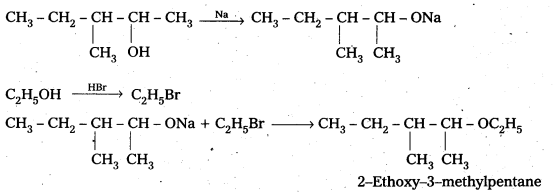
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following Is an appropriate set of reactants for the preparation of 1 – methoxy-4-nltrobenzene?

Solution:
ii)
Question 9.
Predict the products of the following reactions:
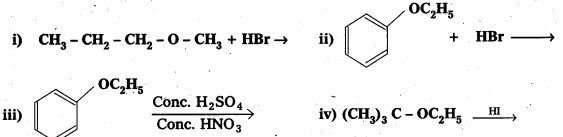
Solution:
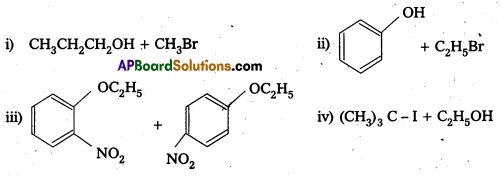
Question 10.
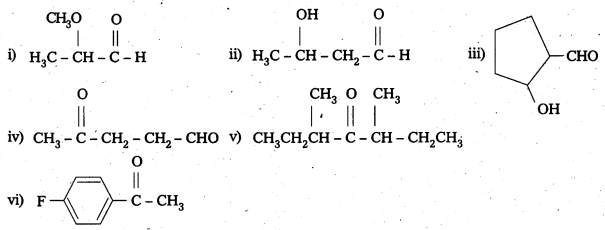
Write the structures of the following compounds.
i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
ii) 3- Hydroxybutanal
iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
iv) 4-Oxopentanal
v) Di-Sec. butyl ketone
vi) 4 – Fluoroacetophenone
Solution:
Question 11.
Write the structures of products of the following reactions;
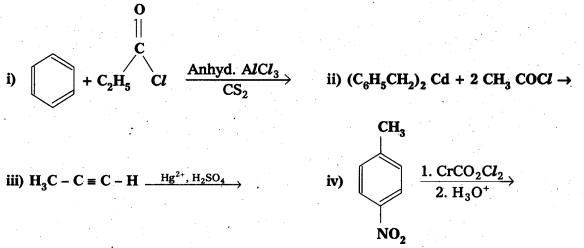
Solution:
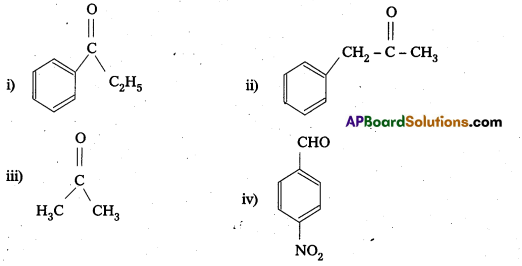
Question 12.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH2OCH3, CH3CH2CH3
Solution:
CH3CH2CH3 < CH3OCH3 < CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH
Question 13.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions.
- Ethanal, Porpanal, Propanone, Butanone.
- Benzaldehyde, p – Toualdehyde, p – Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone.
Solution:
- Butanone < Propanone < Propanal < Ethanal
- Acetophenone < p – Touladehyde, Benzaldehyde < p – Nitgrobenzaldehyde.
Hint: Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
![]()
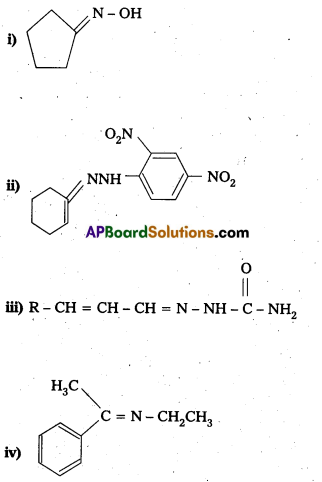
Question 14.
Predict the products of the following reactions :
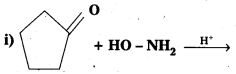
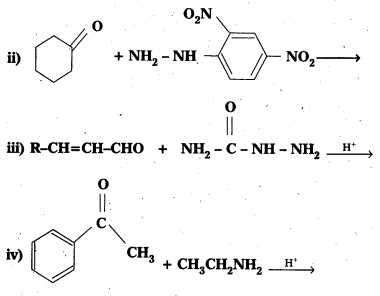
Solution:
Question 15.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
i) Ph CH2CH2COOH
ii) (CH3)2C = CHCOOH

Solution:
i) 3-Phenylpropanoic acid
ii) 3 – Mehtylbut-2-enoic acid
iii) 2-Metylcyclopentanecarboxylicacid
iv) 2, 4, 6 – Trinitrobenzoic acid
Question 16.
Show how each of the following compounds can be converted to benzoic acid.
i) Ethylbenzene
ii) Acetophenone
iii) Bromobenzene
iv) Phenylethene (Styrene)
Solution:
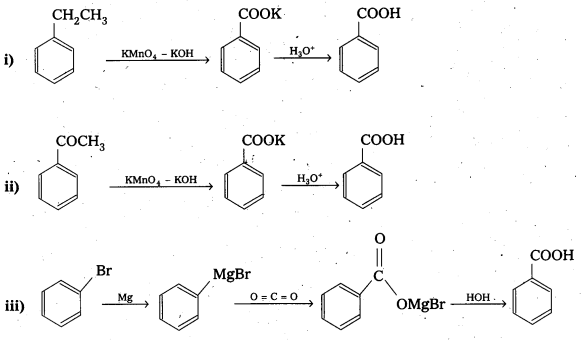
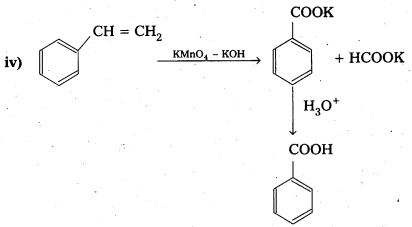
![]()
Question 17.
Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
i) CH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
ii) CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
iii) CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
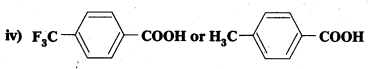
Solution:
i) CH3COOH
ii) CH2FCOOH
iii) CH3CHFCH2COOH
iv)