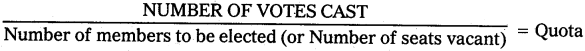Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Study Material 11th Lesson Elections and Representation Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Civics Study Material 11th Lesson Elections and Representation
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write an essay on the Election System in India.
Answer:
Elections are very important for the political system of modem democratic states. Modem democratic states have representative governments. People participate in the process of government through their elected representatives. The election system is a political device through which the modern state creates among its citizens a sense of involvement and participation in public affairs.
Features of the Indian Election System :
The following features of the Indian Election system highlight its good structure nature.
1. Direct Election of Representatives:
The Constitution provides for a direct election of the representatives of the people. Members of the Lok Sabha, the State Legislative Assemblies, Municipalities, and Village Panchayats are directly elected by the people. These legislative bodies are the real centres of people’s power in the Indian democratic system.
2. Indirect Election for some Institutions :
However, the Constitution also provides for an indirect election in respect of the Rajya Sabha, State Legislative Councils, and the President and the Vice President of India. These are elected indirectly and in accordance with a system of proportional representation vote.
3. Universal Adult Franchise :
The constitution provides for a uniform Franchise to all the citizens. The right to vote was granted to all the citizens of 18 years of age without any discrimination on the basis of caste, religion, gender, education, property and place of birth. All the citizens whose names appear in the electoral lists, are eligible to exercise their vote in elections.
4. Reservation of seats for SCs and STs :
With a view to safeguard the interests of the people belonging to the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, the Constitution provided the reservation of seats for them. Article 330 of the Constitution provides the reservation of seats to these classes in the Lok Sabha and Article 332 lays down this provision in respect of elections to every state Assembly. In the reserved constituencies, persons belonging to SC and ST only can contest in the elections.
5. Provision for Nominations :
The Constitution, under its Article 337, lays down that the President may, if he is of the opinion that the Anglo-Indian community is not adequately represented in the Lok Sabha, nominate not more than two members of the community to the Lok Sabha. Likewise, the Governor can also nominate not more than one person from this Anglo – Indian community to the State Legislative Assembly.
6. Regular revision of Electoral Rolls:
The Election Commission revises and prepares the electoral rolls enumerating the names of the eligible voters for every ten years. Besides this, the Election Commission can order the revision of electoral rolls before any election. Provision also exists for a regular annual revision of electoral lists. Only those persons whose names appear in the electoral rolls of the constituency can exercise their franchise on the Election Day.
7. Territorial and Single Member Constituencies :
Indian Election System provides for the creation of single-member territorial constituencies. All the voters living in a particular and defined territory constitute one constituency. Each territorial constituency elects one representative. Each state is divided into as many territorial constituencies as is the number of seats of its Legislative Assemblies and Parliamentary Constituencies and each constituency elects one representative.
8. Delimitation of Constituencies :
After every census the boundaries of the constituencies are delimited. This work is done by a three member Delimitation Commission. This commission can change the boundaries of constituencies, and its decision is final. This cannot be challenged before any court of law.
9. Secret Ballot:
Secret voting enables the voters to exercise their votes in accordance with their wishes and opinions. Special steps are taken in elections for maintaining secrecy and for checking impersonation in voting. This system is essential for making elections free and fair.
10. Introduction of Voting Machines :
The Election Commission has introduced the using of electronic voting machines (EVMs) for casting of votes by people and counting of votes in India.
11. Relative Majority of Votes System :
In the election, the candidate who secures more votes than every other contestant in his constituency is declared elected as representative to the Lok Sabha or the State Legislative Assemblies. In this system, valid votes are taken into consideration for counting.
12. Independent Machinery for the conduct of Elections in India:
According to the Article 324 of the Constitution, the conduct of elections in India is the responsibility of the Election Commission. It is the Constitutional body which is conducting the elections freely, fairly, impartially and independently.

Question 2.
Explain the Functions of Election Commission in India.
Answer:
Article 324(1) of the constitution provides the Election Commission to supervise and conduct the elections to parliament, state legislatures, the offices of the Preside ans the Vice-President of India.
Composition :
The Election Commission of India consists of the Chief Election Commissioner and Two other Commissioners.
Appointment :
The Chief Election Commissioner and other commissioners are appointed by the president of India.
Tenure :
The Chief Election Commissioner and other commissioners hold office for a period of 6 years or until they attain the age of 65 years whichever is earlier.
Removal:
The Chief Election Commissioner and other commissioners can be removed by the president on the basis of a resolution passed to that effect by both the Houses of Parliament with special majority either on the ground of proved misbehaviour or in capacity.
Salary and Allowances :
The Chief Election Commissioner and two other commissioners shall receive salary and Allowances which are similar to that of a Judge of the Supreme Court.
Powers and Functions of Election Commission:
The Constitution of India in its Articles 324-328 enumerates the powers and functions of the Election Commission. These can be mentioned here under.
- It prepares all periodically revised electoral rolls.
- It makes every effort to ensure that the voters’ list is free of errors like non-existence of names of registered voters or existence of names of that non-eligible or non¬existent.
- It notifies the dates and schedules of election and scrutinizes nomination papers.
- During this entire process, the Election Commission has the power to take decisions to ensure a free and fair poll.
- It can postpone or cancel the election in the entire country or a specific State or constituency on the grounds that the atmosphere is vitiated and therefore, a free and fair election may not be possible.
- The Commission also implements a model code of conduct for parties and candidates. It can order a re-poll in a specific constituency.
- It can also order a recount of votes when it feels that the counting process has not been fully fair and just.
- The Election Commission accords recognition to political parties and allots symbols to each of them.
- It advices the President whether elections can be held in a state under President’s rule in order to extend the period of emergency after one year.
- It advices the Governor on matters relating to the disqualifications of the,members of Stage Legislature.
Question 3.
What is Representation? How many types of representative systems are there in India?
Answer:
Representation:
In Democracy people elect members to the Legislatures. The elected members are the representatives of the people. They represent the people in the Legislature. This process is called representation.
Types of Representative systems in India:
Many methods are in practice for electing the representatives of Legislative bodies in India. They may be explained under the following heads :
i) Direct Method :
This is widely practiced and easy method. The voter takes part in the election directly and casts his vote to the condidate of his choice. The elected representatives serve for a fixed term.
Ex : The members of Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies are being elected through this method.
ii) In Direct Method :
In this method the voters elect their representatives indirectly. Accordingly, first voters (Primary electors) elect the Intermediatoiy electors known as secondary Electors. These secondary electors in turn, elect the Representatives on behalf of the first voters. The sequence is
Voters → Intermediatory voters → Representatives
Or
Primary voters → Secondary voters Representatives
(Members of Electoral College)
Ex: In India, voters elect the members of Legislative Assemblies in the states, who in turn, elect the members of Upper house, Popularly known as the RAJYA SABHA in the centre in accordance with the provisions, Rules and Regulations in force. They also elect the members of Legislative council and form a part and parcel of electoral college for electing the President of India.
iii) Territorial Representation:
Under Territorial Representation, the country will be divided into geographical units called “Constituencies”. Voters in every constituency elect their representatives in periodically held elections, i.e., for every five years.
Ex : a) Representatives of Local bodies.
b) Members of State Legislative Assemblies and
c) Members of Lok Sabha
iv) Functional Representation:
Under this method people are divided into functional groups, such as for example Doctors, Lawyers, Engineers, Teachers, Graduates, Capitalists, Workers etc. representatives from each functional group will be returned to legislative bodies. It is hoped that these representatives will ventilate all the problems related to their occupations.
Ex: In India
- The president of India nominates 12 members to the Rajya Sabha having special knowledge or practical experience in respect of matters such as literature, science, arts and social service.
- 1/3 of the total members of the state legislative council shall be elected by the electorate consisting of the members of local bodies such as Municipalities, Zillaparishads etc.
- 1/12 of the total members of state legislative council are elected by the electorate consisting of university graduates.
- 1/12 of the total members of state legislative council are elected by the electorate consisting of secondary school teachers or those in higher educational institutions.
- 1/6th of the total members of state legislative council are nominated by the governor on the basis of their special knowledge in literature, science, arts, co-operative movement or social service.
v) Proportional Representation :
Under this system each party gets representation strictly in Accordance with its voting strength, it means majority of electors would have majority of the representatives, but a minority of electors would have minority of representatives. There are two methods in proportional representation. These are
A) Single Transferable Vote System :
The election of President, Vice President and members of Rajya Sabha etc. in India is based on this system.
The main features of this system are
- Each voter will have only one vote.
- But the voter has to distribute this vote according to his preference (First preference, second preference etc).
- The condidate to be declared elected should secure the required QUOTA of votes.
- Provision for transfer of votes.
QUOTA :
Under this system as stated above, A candidate in order to be declared elected need not secure majority votes. But he requires only quota of votes. For determining quota, two methods are followed.
A) Hare and Andrae method of fixing quota :
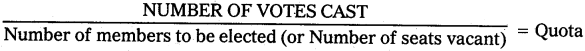
Ex:
Number of votes cast – 14000
Number of seats vacant – 14
Quota – 1400 votes
B) Drop method:
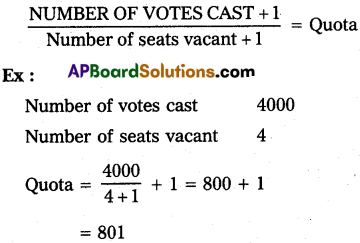
Question 4.
Do you think that Indian Election System needs to be Reformed.
Answer:
The overall health of a representative form of Government depends, to a very large extent, on the fairness and effectiveness of the electoral process. In order to strengthen the foundatipns of our democratic polity, several reforms need to be undertaken in the electoral system. The system should provide equal opportunities to all citizens and help to build an egalitarian society. This would call for a careful review and reforms of existing features governing legislative, administrative and institutional dimensions of the electoral system in the country.
Within the broad framework of the existing constituency system of elections, geographies delimitation, multi-party system with right to individual to contest, the main issues that need to be examined include plugging loopholes in the present Representation of People Act and Anti-Defection Act.
The various committees and commissions which were appointed to examine our electoral system, election machinery as well as election process have recommended various reforms that have to be introduced in our electoral system. These can be mentioned briefly here under.
- The donation of companies to the political parties should be strictly banned.
- The accounts of the political parties are to be audited by the Election commission periodically.
- The number of members of the Election commission shall be raised.
- The limit on election expenditure of the candidates must be proper, practical and realistic.
- The announcement of new policies, projects and programmes by the party in power during elections should be banned.
- The members of the election commission should be appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister, leader of the opposition in the Lok Sabha and the chief justice of India.
- The government should meet the election expenditure of the candidates.
- The election commission should be authorised to invalidate the election of a candidate if it was proved that he had used government machinery during elections.
- Notification should be issued to the voters and electronic voting machines should be introduced after fool-proof arrangements.
- The candidate who secures 51 percent of the polled votes shall be declared as winner.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a Short Note on Electoral Functions.
Answer:
The electoral functions are different for the individual voter and for the political system. For the individual voter, elections may be regarded as a means of political participation and to some extent, of policy choice, although for many voters. Even in democratic societies, elections may be a customary at to which little significance is attached. For the political system, elections are important devices for assuring legitimacy and for system maintenance and support building. Hence, the electoral functions may be considered into four broad categories. They are :
a) Political choice
b) Political participation
c) Support-building and system – maintenance, and
d) Linkage functions.
a) Political choice :
The elections may be used or interpreted as a plebiscite, a referendum, or a mandate. They are the instruments for choosing the leaders and also determining the will of the people. They are devices for controlling political leaders. Control of leaders involves some degree of control of governmental choice and policies. They provide the means for the peaceful and orderly transfer of power.
b) Political participation :
The major electoral function is to provide opportunities and channels for political participation. This function of elections is a central one as political participation is essential in the democratic system. The participation strengthens the democratic system.
c) Support-building and system – maintenance :
The elections support the political system by providing legitimacy, political stability, integration and identification. The elections, are therefore a contributing rather than a controlling factor of a political system. Rosenau uses the term support-building as function of elections and hence, all other functions could be subsumed under it.
d) Linkage functions :
Elections are important agencies of political communication between the people and the government in the sense of political linkages. They provide a chance for the people to have more direct contact with their leaders.

Question 2.
Discuss the Election process in India.
Answr:
The electoral process in India is operationalized in several stages which can be explained as under.
1. Delimitation of Constituencies :
The first step of conducting the elections can be described as the delimitation of constituencies which is done by a Delimitation Commission appointed after every census by the President. This happens for every 10 years. Generally, a constituency which elects a member of the Lok Sabha consists of six or seven State Legislative Assembly constituencies. The decisions of the Delimitation commission are final and cannot be challenged in any court.
2. Recognition of Political Parties :
Political parties have to be registered with the Election Commission. According to certain criteria, set by the Election Commission regarding the length of political activity and success in elections, parties are categorized by the Commission as National or State parties, or simply declared registered-unrecognized parties. National parties are given a symbol that is for their use only, throughout the country. State parties have the sole use of a symbol in the state in which they are recognized as such Registered- unrecognized parties can choose a symbol from a selection of ‘free’ symbols.
3. Photo Identity Cards :
In an attempt to improve the accuracy of the electoral roll and prevent electoral fraud, the Election Commission ordered the making of photo identity cards for all voters in the country in Aug, 1993. To take advantage of latest technological innovations, the Commission issued revised guidelines for Election Photo Identity Card (EPIC) Program in May 2000.
4. Electoral Rolls :
An important step in the conduct of elections is to get prepared constituency-wise electoral rolls which record the names of the eligible voters. The electoral rolls are revised after each census, before every election or after regular intervals.
5. Notification and Appointment of Returning Officers :
When general elections are to be held, the President of India sends a communication to the Election Commission and the latter, after consulting Central and State Governments, announces the poll calendar, i.e., the dates for filing the nomination papers, scrutiny of nomination papers and withdrawal of nominations by the candidates. The Election Commission then appoints Returning Officers for various constituencies. The Regional Election Commissioners help the Election Commission in the smooth conduct of elections.
6. Filing of Nomination Papers :
The candidates who wish to contest in the elections have to file their nomination papers with the Returning Officer in their respective I constituencies. Such candidates must submit their nominations in a given formats prescribed by the Election Commission. If the contestant is a party candidate, the name has to be proposed by a voter and seconded by another voter. In the case of non-party contestant, the candidate has to be subscribed by 10 registered electors of the constituency as proposers.
7. Scrutiny of Nominations :
After the last date for the filing of the nominations, all the nomination papers are duly scrutinized by the Returning Officers in the presence of the candidates or his nominee. The scrutiny is conducted for determining whether the nomination papers have been filed properly, the candidates possess the required qualifications, and they have complied with all rules and regulations. Later, the Returning Officer decides all cases and notifies the names of those candidates whose nomination papers are found in order.
8. Withdraw of Nominations:
After scrutiny, the candidates are allowed to voluntarily withdraw their nominations within a fixed date and time as fixed by the Election Commission. For this purpose a candidate has to apply in writing to the Returning Officers.
9. Election Campaign :
The next stage in the electoral process involves the election campaign. The contestants and parties get engaged in the election campaign. Each party issues an Election manifesto which states its policies, programmes and promises.
10. Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) :
An electronic voting machine is a simple electronic device used to record votes in place of ballot papers and boxes which were used earlier in conventional voting system. The advantages of the EVM over the traditional ballot paper system are given here.
a) It eliminates the possibility of invalid and doubtful votes.
b) It makes the process of counting of votes much faster than the conventional system.
c) It reduces to a great extent the quantity of paper used, thus saving a large number of trees.
d) It reduces cost printing as only one sheet of Ijallot papers required for each polling station.
11. Polling of Votes:
Polling personnel are appointed and polling booths are set up in different localities. Each polling booth, on an average caters to about a more than thousand voters. The voting is a secret one.
12. Supervising Elections by Observers :
The Election Commission appoints a.lafge number of Election Observers to ensure that the campaign is conducted fairly, and that people are free to vote as they choose. Election Observers keep a check on the amount that each candidate and party spends on the election.
13. Media Coverage:
In order to bring as much transparency as possible to the electoral process, the media are encouraged and provided with facilities to cover the election.
14. Counting of votes and Declaration of Results :
After the process of polling of votes, on a fixed day and time, the Returning Officer and his staff members open the voting machines in the presence of the agents. Then each candidate verifies his votes polled recorded in the EVM. A candidate who gets more valid votes than the other contesting candidate in very constituency is declared elected. These results declared on the basis of relative majority of vote victory system. The Returning Officer makes an announcement of the results in this regard.
15. Election Petitions :
Any elector or candidate can file an election petition if he or she thinks there has been malpractice during the election. An election petition is not an ordinary civil suit, but treated as a contest in which the whole constituency is involved. Election petitions are tried by the High Court of the state concerned and if upheld can even lead to the restaging of the election in that constituency.
Question 3.
Write a short note on composition and Functions of Election Commission. [(AP. Mar. 16) Mar. 18]
Answer:
Composition :
The Election Commission of India consists of the Chief Election Commissioner and two other commissioners. They are appointed by the President of India.
Functions of Election Commission :
- It prepares all periodically revised electoral rolls.
- It makes every effort to ensure that the voters’ list is free of errors like non-existence of names of registered voters or existence of names of that non-eligible or non-existent.
- It notifies the dates and schedules of election and scrutinizes nomination papers.
- During this entire process, the Election Commission has the power to take decisions to ensure a free and fair poll.
- It can postpone or cancel the election in the entire country or a specific State or constituency on the grounds that the atmosphere is vitiated and therefore, a free and fair election may not be possible.
- The Commission also implements a model code of conduct for parties and candidates. It can order a re-poll in a specific constituency.
- It can also order a recount- of votes when it feels that the counting process has not been fully fair and just.
- The Election Commission accords recognition to political parties and allots symbols to each of them.
- It advices the President whether elections can be held in a state under President’s rule in order to extent the period of emergency after one year.
- It advices the Governor on matters relating to the disqualifications of the members of State Legislature.
Question 4.
What is Representation? What do you know about Territorial Repre-sentation.
Answer:
Representation:
In democracy, people elect members to the Legislatures. The elected members are the representatives of the people. They represent the people in the Legislature. This process is called representation.
Territorial Representation :
In the territorial or geographical representation system, the total electorate of the country is divided into territorial units called constituencies which elect one or more representatives. The constituencies are more or less equal in size and population. All voters living in a particular Constituency take part in the election of representatives. Where one representative is elected from a constituency it is known as a single-member constituency. Where more than one representative is elected, it is known as multi-member constituency. Most of the modem states, including India, have followed single¬members constituencies for the elections to the lower houses of the legislature.
Question 5.
Estimate the pros and cons of FPTP system in India.
Answer:
In our country we have been following a special method of elections. The entire country is dividend into 550 constituencies, each constituency elects one representative and the candidate who secures the highest number of votes in that constituency is declared elected. It is important to note that in this system whoever has more votes than all other candidates is declared elected.
The winning candidate need not secure a majority of votes. This method is called the First Past the Post system (FPTP). In the election race, the candidate who is ahead of others, who crosses the Wining post first of all, is the winner. This method is also- called the Plural System. This is the method of election prescribed by the Constitution.
In India this FPTP System is popular and successful because of its simplicity. The entire election system is extremely simple to understand even for common voters who may have no specialized knowledge about politics and elections. There is also a clear choice presented to the voters at the time of elections. Voters may either give greater importance to the party or the candidate or balance the two.
The FPTP system generally gives the largest party or coalition some extra bonus seats, more than their share of votes would allow. Thus, this system makes it possible for parliamentary government to function smoothly and effectively by facilitating the formation of a stable government. Finally, the FPTP System encourages voters from different social groups to come together to win an election in a locality. Above all, the FPTP System has proved to be simple and familiar to the ordinary voters. It has helped larger parties to win clear majorities at the centre and state levels.
Question 6.
Write a Note on the Electoral Reforms. [Mar. 17]
Answer:
The Electoral Reforms will ensure the free and fair elections in the country. The successful functioning of Indian democracy depends on the electoral reforms.
Some Electoral Reform proposed :
- The donation of companies to the political parties should be strictly banned.
- The accounts of the political parties are to be audited by the Election commission periodically.
- The number of members of the Election commission shall be raised.
- The limit on election expenditure of the candidates must be proper, practical and realistic.
- The announcement of new policies, projects and programmes by the party in power during elections should be banned.
- The membersof the election commission should be appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister, leader of the opposition in the Lok Sabha and the chief justice of India.
- The government should meet the election expenditure of the candidates.
- The election commission should be authorised to invalidate the election of a candidate if it was proved that he had used government machinery during elections.
- Notification should be issued to the voters and electronic voting machines should be introduced after fool-proof arrangements.
- The candidate who secure 51 percent of the polled votes shall be declared as winner.
Question 7.
What is meant by proportional representation system.
Answer:
Under this system each party gets representation strictly in accordance with its voting strength. It means majority of electors would have majority of the representatives, but a minority of electors would have minority of representatives.
There are two methods in proportional representation. These are
A) Single Transperable Vote System :
The election of President, Vice President and members of Rajya Sabha etc in India is based on this system.
The main features of this system are.
- Each voter will have only one vote.
- But the voter has to distribute this vote according to his preference (First preference, second preference etc.).
- The candidate to be declared elected should secure the required QUOTA of votes.
- Provision for transper of votes.
QUOTA :
Under this system as stated above, A candidate in order to be declared elected need not secure majority votes. But he requires only quota of votes. For determining quota, two methods are followed :
A) Hare and Andrae method fixing Quota :
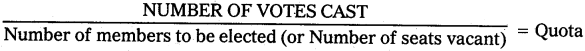
Ex:
Number of votes Cast = 14000
Number of seats-vacant =14
Quota = 1400 votes
B) Drop method :
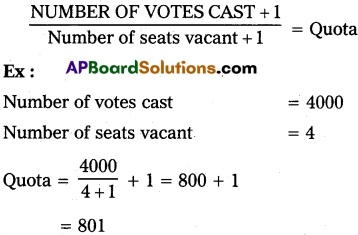
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Relations between democracy and elections.
Answer:
Elections are the Central institution of democratic representative governments. In democracy, elections are periodic. Elected officials are accountable to the people, and they must return to the voters at prescribed intervals to seek their mandate to cantinue in office. This means that officials .in a democracy must accept the risk of being voted out of office. In democratic system the elections are also indusive.
The definition of citizen and voter must be large enough to include a large proportion of the adult population. Democratic elections are definitive. They determine the leadership of the government. Subject to the laws and constitution of the country, popularly elected representatives hold the reins of power.
Question 2.
Electronic voting machines. [Mar. 18, 16]
Answer:
An Electronic voting machine is a simple electronic device used to record votes in place of ballot papers and boxes which were used earlier in conventional voting system. The advantages of the EVM over the traditional ballot paper system are give below.
- It eliminates the possibility of invalid and doubtful votes.
- It makes the process of counting of votes much faster that the conventional system.
- It reduces to a great extent the quantity of paper used, thus saving a large number of trees.
- It reduces cost printing as only one sheet of ballot papers required for each polling station.

Question 3.
Territorial Representation.
Answer:
In the territorial or geographical representation system, the total electorate of the Country is divided into territorial units called constituencies which elect one or more representatives. The constituencies are more or less equal in size and populatiqn. All voters living in a particular constituency take, part in the election of representatives. Where one representative is elected from a constituency it is known as a single-member constituency.
Where more than one representative is elected, it is known as multi-member constituency. Most of the modem states, including India, have followed single. Members constituencies for the elections to the lower houses of the legislature.
Question 4.
Functional Representation. [Mar. 17]
Answer:
It is based on occupation. People engaged in the same kind of occupation have more things in common than people living in the same locality. Doctors, farmers, industrial workers, traders, journalists, lawyers, teachers etc., have more in common than those who live as neighbours. One man cannot represent all traders, Hence, representation should be on functional basis. A legislature representing such different occupational groups would be a proper forum where different interests would be projected and pleaded for. But it is not possible to provide representation to each and every occupation which are innumerable in number and the classification of profession is a touch task.
Question 5.
Composition of Election commission of India.
Answer:
Article 324 of the constitution has made the following provisions with regard to the composition of election Commission. Since its inception 1950 and till 15th Oct, 1989, the election commission functioned as a single member body consisting of the Chief Election Commissioner. On 16th October, 1989 the President of India appointed two more election Commissioners to cope up with the increased work of the Election Commission. Thereafter, the Election Commission started functioning as a multimember body consisting of 3 Election Commissioners.
Question 6.
Electoral Reforms.
Answer:
The various commitees and commissions have recommended various reforms that have to be introduced in our electoral system, election machinery and election process. These can be mentioned briefly here under.
- Lowering of voting age
- Deputation to Election commission
- Electronic voting machines
- Prohibition on the sale of liquor
- Number of proposers
Question 7.
Election offences.
Answer:
Some of the electoral offences as given below.
- Promoting enmity between classes or grounds of religion, race, community or language.
- Convening, holding or attending any public meeting during 48 hours before the end of poll.
- Causing disturbance at election meetings.
- Printing of election pamphlets, posters etc., without printers / publishers names and addresses.
- Violation of maintenance of secrecy of vote.
- Influencing of voting by officials connected with conduct of elections and police personnel.
- Disorderly conduct and disturbance in or near a polling station, indulging use of loud speakers etc.
- Canvassing within 100 meters of a polling station on the day of poll.
- Misconduct at the polling station or failure to obey the lawful direction of the presiding officer.
- Illegal hiring or procuring of vehicles for conveying voters to and from polling stations.
- Unlawful removal of ballot papers / EVMs from the polling stations.
- Booth capturing.
Question 8.
Corrupt practices in elections.
Answer:
Following are some important corrupt practices during the elections. They are.
- Briling a person to induce him/her to stand or not to stand as a candidate.
- Interference with free exercise of anybody’s electoral right.
- Threat with injury of any kind, including social ostracism, excommunication, divine displeasure or spiritual censure.
- Appeal on grounds of religion, caste, community or Language or the use of religious or national symbols.
- Publication of false statement about personal character and conduct of any
- Hiring or procuring of vehicles for free conveyance of voters.
- Incurring of election expenditure by a candidate in excess of the prescribed limit.
- Booth capturing.
Question 9.
Role of the Election Commission in India. [Mar. 17]
Answer:
Over the years, the Election Commission of India has emerged as an independent authority which has asserted its powers to ensure fairness in the election process. It has acted in an importial and unbaised manner in order to protect the sancity of the electoral process. The record of EC also shows that every improvement in the functioning of institutions does not require legal or constitutional change.
It is widely agreed that the Election Commission is more independent and assertive now than it was till twenty five years ago. This is not because the powers and constitutional protection of the Election commission have increased. The Election Commission has started using more effectively the powers it always had in the constitution.
In the past sixty five years, sixteen Lok Sabha Elections have been held. Many more state assembly elections and bye-elections have been conducted by the Election Commis-sion.

Question 10.
Representation.
Answer:
In democracy people elect members to the legislatures. The elected members are the representatives of the people. They represent the people in the legislature. This process is called representation.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()