These AP 7th Class Science Important Questions 10th Lesson Changes Around Us will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 7th Class Science 10th Lesson Important Questions and Answers Changes Around Us
Question 1.
What is a natural change?
Answer:
The change that is brought about by nature itself is called a natural change.
Question 2.
What are man made changes? Give two examples.
Answer:
- Changes which are taken place by the involvement of human beings are called man made changes.
- Examples for man made changes are cooking of rice, construction of buildings, preparation of laddu.
Question 3.
What are fast changes? Give examples.
Answer:
- Changes which occur in short duration of time are called fast changes.
- Burning of paper, cutting of piece of cake, firing of crackers, spinning of a top are the examples of fast changes.
Question 4.
What are the slow changes? Give examples.
Answer:
- Changes which take longer duration of time to happen are called slow changes.
- Examples for slow changes are growing of plant from seed to a tree, developmental changes in the child, rusting of iron, changes of season, formation of mountain etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What are reversible changes? Give examples.
Answer:
- The changes in which the formed substance can be converted into their original substance are called reversible changes.
- Example for reversible changes are melting of wax, magnetizing a needle using bar magnet etc.
Question 6.
What are irreversible changes? Give examples.
Answer:
- Changes in which we cannot get the original substance by reversing the experimental conditions are called irreversible changes.
- Examples are burning of wood, burning of diwali crackers, ripening of fruits, rusting of iron etc.
Question 7.
What are periodic changes? Give examples.
Answer:
- The changes which are repeating at regular intervals of time are called as periodic changes.
- Formation of the full moon and new moon, occurrence of seasons in every year at regular intervals, the heart beats of human beings are examples for periodic changes.
Question 8.
What are non-periodic changes? Give examples.
Answer:
- Changes which do not occur at regular intervals of time and which can not be predicted are called non-periodic changes.
- Examples are pattern of rainfall, storms in seas, volcanic erruptions etc.
Question 9.
“In a physical change, the chemical properties of a substance do not change.” Do you agree with this statement? How?
Answer:
- Yes, I agree with this statement.
- Why because, when a piece of gold is melted, it’s chemical composition remains the same in the solid form and also in the liquid form.
Question 10.
“A physical change is usually temporary and reversible in nature” – Do you agree with this statement? State the reason.
Answer:
- I absolutely agree with this statement.
- It is because, when water is heated, water vapours are formed. Once water vapours are cooled water can be obtained again.
![]()
Question 11.
“In a physical change, change in physical properties such as colour, shape and size of a substance may under go a change”. Do you support this statement? Why?
Answer:
- I support this statement.
- In cutting of vegetables changing physical properties, such as colour, shape and size of a substance.
Question 12.
What is galvanization?
Answer:
The process of deposition of a layer of zinc on iron is called “Galvanization.”
Question 13.
What is a chemical change? Give one example.
Answer:
- Changes that occur with the formation of new substance with different chemical composition or transformation of a substance into another substance with the evolution or absorption of heat or light energy are called as chemical changes.
- Example when Magnesium burns in the presence of oxygen, it forms magnesium oxide in the form of powdered ash.
Magnesium + oxygen → Magnesium oxide
Question 14.
What is rusting?
Answer:
- When ron reacts with atmospheric oxygen and moisture it forms a new substance called Iron oxide as rust on iron articles made of iron.
- This process is known as rusting.
Iron + oxygen (from air) + water → rust (iron oxide)
Question 15.
What are the reasons for global warming?
Answer:
- Global warming is due to drastic increase in the emission of carbondioxide by the burning of fossil fuels.
- Deforestation.
Question 16.
What are the reasons for acid rains?
Answer:
- When coal and oils are burnt, they release acidic gases like NO2 and SO2.
- They mix up with the water vapour and come down as acid rains.
Question 17.
The changes like chicks came out of eggs, blossoming flowers etc. are very pretty to see. List out such changes around you feel happy on observation.
Answer:
- Swarming of honeybees
- Rainbow formation
- Clouds passing across the mountains.
- Rows of birds flying in the sky.
Question 18.
Give examples for metals that do not rust.
Answer:
- Metals like gold, silver, zinc do not rust even though they are exposed to moist air.
- Zinc is used in Galvanization process to prevent rusting of iron articles.
Question 19.
How can you say that rusting is a chemical change?
Answer:
- When the metals are exposed to air, they form metal oxides.
- Hence, as new substances are formed, rusting is a chemical change.
![]()
Question 20.
Observe the following changes and decode weather they are physical or chemical changes? Mention the reason, a) Preparation of tea b) Making dough for roti.
Answer:
a) This is a chemical change. Water + Milk + Tea powder + Sugar → Tea Here tea is a new substance. Hence it is a chemical change,
b) Making dough for roti is a physical change as there is no formation of new substance.
Question 21.
How is an iron gate prevented from rusting?
Answer:
- Iron gate when exposed to moisture and air gets rusted.
- To prevent rusting of Iron gates it should be painted with a paint.
7th Class Science 10th Lesson Changes Around Us Short Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the examples for natural changes?
Answer:
- Formation of day and night
- Changes of weather.
- Developmental changes of a child into an adult. ‘
- rowth of a seed into a plant.
Question 2.
How can we prevent browning of cut fruits and vegetables?
Answer:
- By keeping the cut vegetables in cold water, we can prevent browning of them.
- Cold water prevents the outer surface of the potato and brinjal from colouring.
- Small quantities of acids like vinegar or lemon juice in water will also prevent browning of vegetables.
- We can also rub the surface of cut fruits with juices of citrus fruits like lemon to avoid from browning.
- Ascorbic acid can also be used to prevent browning.
Question 3.
What is the reason for browning of vegetables in our daily life?
Answer:
- Some fruits and vegetables like potato and brinjal, when they cut react with oxygen in air.
- The process of reaction with oxygen is called oxidation.
- Due to this oxidation process, brown layer is formed on the surface of fruits and vegetables.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the harmful physical and chemical changes in environment?
Answer:
- Plastic decomposition
- Acid rains
- Global warming
- Oil spills in seas and rivers
- Earthquakes and
- Floods are some of the harmful physical and chemical changes in environment.
Question 5.
What changes might have we noticed in our daily life?
Answer:
- The colour ,of tender leaf changing from red to green.
- Hard raw fruit becoming soft ripen fruit.
- Colour changes observed in slices of brinjal and apple after being cut.
- Change of milk into the curd.
- Ash produced on burning paper.
- Raw rice becoming soft after cooking etc.
Question 6.
What questions would you pose to your teacher about changes around us?
Answer:
- Why changes occur around us?
- Why would we depend on changes in the nature?
- What would happen if changes do not occur?
- How changes in the nature influence us?
Question 7.
![]()
What type of change is it? Is itreversible? If so, how?
Answer:
- Ice slowly melts and becomes water.
- On further heating water changes to steam.
- This is a physical change.
- No new substance is formed.
- The change is reversible. If we reduce the temperature the water vapour changes back to water when the temperature is further reduced, it changes to ice.
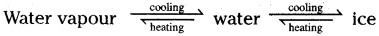
Question 8.
What are the characteristics of a physical change?
Answer:
- No new substances are formed.
- It is usually temporary and reversible in nature.
- The chemical properties of a substance do not change.
- Change in physical properties such as colour, shape and size of a substance may undergo a change.
Question 9.
What are the characteristics of a chemical change?
Answer:
- During chemical change new substance are formed.
- It is a permanent change and irreversible in nature.
- Chemical composition of the substances changes.
- Heat, light may be released or absorbed.
- A colour change may take place and sound may be produced.
Question 10.
Where do you see the iron pilar that is not rusted for thousands of years? What are the reasons for that?
Answer:

- We can see an iron pillar at the Qutub complex in Delhi which is not rusted. It is 1600 years old.
- It is made by 98% wrought iron, a special type of iron that has 1% of phosphorous.
- It don’t have Sulphur and Magnesium.
- More over, the pillar is covered by a thin layer of compound called Misawitea.
- So, rusting of this iron pillar is too slow and it will take thousands of years to get rusted.
Question 11.
What is so special about Lonar Lake?
Answer:
- The Lonar lake in Buldhana district of Maharashtra was created by plummeting meteor about 5200 years ago.

- The water of Lonar lake turned into pink colour recently due to Haloarchaea microbes present in the salty water.
- But the colour is not permanent.
- When the biomass of the microbes settled at the bottom, then the water again becomes transparent.
Questions 12.
Anurag appreciates the changes in ripe mango as “How nice its colour and taste are”? Give some examples of changes that makes you feel happy, or wonder.
Appreciate them in your own words.
Answer:
- When mango ripens, the contents present in the fruit gives good taste. The change in colour indicates that the fruit is ripend.
- Similar situations we experience with many fruits like banana, guava, papaya, pine apple … etc.
- In fact fruits are a gift to human beings as they give instantaneous energy when eaten.
- Nature is so kind to us to provide such ready made safe foods.
7th Class Science 10th Lesson Changes Around Us Long Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is rust and rusting? Why does iron rust? What type of a change is this?
Answer:
- When iron nails, iron gates, iron benches or pieces of iron are left is the open ground for a long time, we find a brown layer on the surface of iron articles.
- This is called rust’ and process of forming this layer is called rusting.
- When iron is exposed to air for a long time, the Oxygen present in air reacts with it in the presence of moist air and forms a new substance called iron oxide as rust on iron articles. This process is known as rusting.
Iron + Oxygen (from air) + Water → rust (Iron oxide) - As a new substance is formed in this change, we call it a chemical change.
![]()
Question 2.
Answer the following questions.
The gas we use in kitchen is in the form of liquid in the cylinder. When it comes out from the cylinder it becomes a gas (step-I), then it burns (step-II).
Choose the correct statement from the following.
a. Only step – I is a chemical change.
b. Only step – II is a chemical change.
c. Both steps – I & II are chemical changes.
d. Both steps – I & II are physical changes.
Answer:
a) Step -1 – is a physical change (not a chemical change)
b) Step – II – is a chemical change (It is correct)
c) Both steps I & II – are chemical changes.
This is not correct.
Step – I – Physical change and
Step – II – Chemical Change is correct.
d) Both steps I & II – are physical changes – This is not correct.
Step I – Physical change
Step II – Chemical change.
Question 3.
What are periodic changes? Explain briefly.
Answer:
| S.No. | Name of the Change |
| 1. | Change of day and night |
| 2. | Withering of leaves |
| 3. | Rising of the pole star |
| 4. | Change of Seasons |
| 5. | Change of Greenery in the fields of cultivation |
| 6. | Changes in lengths of shadows |
| 7. | Appearance of Full Moon |
- If we observe that every change mentioned is the table repeats after some period of time.
- Such changes are known as periodic changes.
- The events which repeat at regular intervals of time are called periodic events.
Question 4.
What is Galvanisation? Explain its importance.
Answer:
- Some articles made up of iron, don’t get rusted even they are exposed to air.
- To prevent iron articles from coming into contact with oxygen in air or water or both, we deposit a layer of a metal like Chromium or Zinc on them.
- This process of depositing a layer of zinc or Chromium on Iron is called Galvanisation.
- Generally we use Zinc for such type of coatings.
- We find in our house that water pipe lines are without rust on them.
- If we observe carefully, we notice that there is some metallic coating on these pipes to prevent rusting.
- They do not get rusted even after a long time since they are galvanized.
- The process of depositing one metal on another metal is called galvanisation.
Question 5.
Write the environmental issues due to physical and chemical changes.
Answer:
Physical and chemical changes occur all around us. These changes are essential parts of our daily lives. However a few of the physical and chemical changes that occur daily are harmful to the environment.
For example
- Plastic decomposition, global warming, effects of acid rain and oil spills, earthquakes, floods etc.
- Plastic waste is a widely recognised source of pollution. Most plastics are non- biodegradable. They take hundreds of years to decompose. Hence their disposal causes pollution.
- Global warming is due to drastic increase in the emission of carbon dioxide by the burning of fossil fuels. The climate change affects not only the atmosphere and living things on land but also creatures of ocean.
- Acidic gases are produced when fossil fuels such as coal and oil are burned in power station, factories and homes.
- Oil spills occur when liquid petroleum is released into the environment by human interference causing damage to creatures of ocean.
- Changes are quite common in nature. Human beings are misusing the natural re-sources for their needs.
- But we should take care that our needs should not bring drastic changes that causes harm to the nature and mankind.
AP Board 7th Class Science 10th Lesson 1 Mark Bits Questions and Answers Changes Around Us
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer and write its letters in the brackets.
1. Change in the shape of balloon is done by bibwing air into it. This is a……
A) manmade change
B) natural change
C) chemical change
D) periodic change.
Answer:
A) manmade change
2. Which of the following is not a man made-change?
A) preparation of bricks
B) making of paper
C) weaving of clothes
D) growing of nails
Answer:
D) growing of nails
![]()
3. Which of the following is not a fast change?
A) burning of paper
B) firing of crackers
C) making of a cake
D) spinning of a top
Answer:
C) making of a cake
4. The change happens in less time is.
A) slow change
B) fast change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change.
Answer:
B) fast change
5. Which of the following is not reversible?
A) Weight suspended from a spring
B) Water changed to water vapour
C) Inflating of a balloon
D) Burning of a coal
Answer:
D) Burning of a coal
6. On …………… ice converts to water
A) heating
B) cooling
C) freezing
D) evaporating
Answer:
A) heating
7. some changes we cannot regain the original substance, these are.
A) manmade change
B) natural change
C) irreversible change
D) reversible change
Answer:
C) irreversible change
8. Limewater
A) Calcium Hydroxide
B) Sodium hydroxide
C) Potassium hydroxide
D) Carbonic acid
Answer:
A) Calcium Hydroxide
9. Which of the following is an irreversible change?
A) burning of wood
B) burning of Diwali crackers
C) ripening of fruits
D) all
Answer:
D) all
10. Which gas is released when lemon juice reacts with baking soda?
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide
C) nitrogen
D)water vapour
Answer:
B) carbon dioxide
![]()
11. These changes are repeating at regular intervals of time.
A) slow change
B) fast change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change.
Answer:
C) periodic change
12. Changes which do not occur at regular intervals of time and which cannot be predicted are called
A) slow change
B) fast change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change
Answer:
D) non periodic change
13. Crystallization requires
A) heating
B) cooling
C) evaporating
D) A or C
Answer:
A) heating
14. In crystallization….
A) no new substances are formed.
B) new substances are formed.
C) no heating is required
D) none
Answer:
A) no new substances are formed.
15. Crystallization is
A) chemical change
B) physical change
C) periodic change
D) non periodic change
Answer:
B) physical change
16. Choose correct answer.
S: Crystallization is a Physical Change.
R: In crystallization no new substances are formed.
A) S and R are correct.
B) S and R are incorrect.
C) S is correct and R is incorrect.
D) S is incorrect and R is correct.
Answer:
A) S and R are correct.
17. Which change takes place when ice cube melts?
A) colour
B) phase
C) chemical
D) all
Answer:
B) phase
18. When a piece of gold is melted?
A) no new substances are formed.
B) new substances are formed.
C) chemical composition changes
D) none
Answer:
A) no new substances are formed.
![]()
19. When a piece of gold is melted, its chemical composition in the Solid form and also in the liquid form.
A) changes
B) varies
C) remains same
D) different
Answer:
C) remains same
20. In physical change ……….. changes.
A) shape
B) colour
C) size
D) all
Answer:
D) all
21. It is not a characteristic of a physical change…
A) No new substances are formed
B) Temporary and reversible in nature.
C) The chemical properties of a substance do not change.
D) It is a periodic change.
Answer:
D) It is a periodic change.
22. In curdling of milk is
A) a physical change
B) reversible change
C) chemical change
D) temporary change
Answer:
C) chemical change
23. When magnesium burns in the presence of oxygen, it forms magnesium oxide
A) magnesium oxide
B) magnesium chloride
C) carbon dioxide
D) none
Answer:
A) magnesium oxide
24. Magnesium Hydroxide is…..
A) an acid
B) a base
C) a neutral
D) none
Answer:
B) a base
![]()
25. Characteristic of a chemical change
A) During chemical change new substances are formed.
B) It is a permanent change and irreversible in nature.
C) Chemical composition of the substance changes.
D) All
Answer:
D) All
26. In chemical change which is not happens.
A) Heat, light may be released or absorbed.
B) A colour change may take place and sound may be produced.
C) Original substances may be formed on reversing the process
D) None
Answer:
C) Original substances may be formed on reversing the process
27. Rusting of iron requires
A) moisture
B) air
C) both
D) none
Answer:
C) both
28. Rust is…
A) iron oxide
B) calcium chloride
C) iron peroxide
D) above all
Answer:
A) iron oxide
29. Oxidization is observed in
A) iron articles
B) apples
C) brinjal
D) none
Answer:
D) none
30. Which of the following is used to prevent browning of the outer surface of the potato and brinjal?
A) cold water
B) lemon juice
C) ascorbic acid
D) above all
Answer:
D) above all
31. Which of the following is used in galvanizing?
A) zinc
B) chromium
C) A & C
D) none
Answer:
C) A & C
32. This process of deposition of a layer of zinc on iron is called
A) oxidation
B) galvanization
C) crystallization
D) none
Answer:
B) galvanization
33. Due to this process of brown layer is formed on the surface of fruits and vegetables.
A) oxidation
B) galvanization
C) crystallization
D) none
Answer:
A) oxidation
34. Which of the following is a useful change?
A) global warming
B) acid rain
C) plastic decomposition
D) fermentation
Answer:
D) fermentation
35. Which of the following occurs due to drastic increase in the emission of carbon dioxide by the burning of fossil fuels
A) global warming
B) floods
C) earth quakes
D) fermentation
Answer:
A) global warming
36. Ice converting to water, water converting to steam are ………. changes.
A) reversible
B) chemical
C) periodic
D) all
Answer:
A) reversible
37. Ripening of fruits is ………….. change.
A) reversible
B) physical
C) periodic
D) irreversible
Answer:
D) irreversible
38. The change occurs only in Size, colour and shape of the substance and no change in chemical composition are called ………….. changes
A) chemical
B) physical
C) periodic
D) irreversible
Answer:
B) physical
39. ………. change occurs with the formation of new substance in different chemical composition.
A) Reversible
B) Physical
C) Periodic
D) Chemical
Answer:
D) Chemical
![]()
40. The process of depositihg zinc on iron metals is called
A) oxidation
B) galvanization
C) rusting
D) crystallization
Answer:
B) galvanization
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. The changes which were taken place by the involvement of human beings are called ………………. change.
2. Changes which occur in ………………. duration of time are called fast changes.
3. Changes which takes longer duration of time to happen are called ………………. Change.
4. Changing of vegetable to curry : slow reaction:: changing of acid into vapour ………………. .
5. On ………………. water converts to ice.
6. The changes in which the formed substance can be converted into their ………………. are called reversible changes.
7. ………………. changes Limewater into milky white.
8. Vinegar + Baking Soda → Sodium acetate + ………………. + water
9. ………………. + Lime water → Calcium carbonate + water
10. Changes in which we cannot get the original substance by reversing the experimental conditions are called ………………. Changes.
11. ………………. changes are repeating at regular intervals of time .
12. The process of separating a soluble solid from the solution by heating or evaporating is called ………………. .
13. A ………………. is usually temporary and reversible in nature.
14. The substances which undergo change in colour or state or size or shape are ………………. .
15. When a Magnesium ribbon burns it gives ………………. light leaving a powdery substance behind.
16. ………………. + Water → Magnesium Hydroxide
17. Changes that occur with the formation of new substance with different chemical composition or transformation of a substance into another substance with the evolution or absorption of heat or light energy are termed as ………………. .
18. Iron + Oxygen (from air) + Water → ……………….
19. Apply a coat of paint or grease on iron articles. Prevents ………………. .
20. To prevent iron articles from coming contact with oxygen in air and water, a layer of another metal like ………………. is coated on them.
21. The process of deposition of a layer of zinc on iron is called ………………. .
22. Browning is not only observed on iron articles but also on cut fruits and ………………. .
23. Rubbing of the surface of cut fruits with ………………. to avoid from browning.
24. The process of reaction with ………………. is called oxidation.
25. ………………. waste is a widely recognized source of pollution.
26. ………………. gases are produced when fossil fuels such as coal and oil are burned in power station, factories and homes.
27. Oil spills occur when ………………. is released into the environment.
28. Formation of day and night, occurrence of seasons are ………………. changes.
29. Curding of milk : useful changes :: ………………. : harmful change.
Answer:
- 1. man-made
- short
- slow
- fast reaction
- cooling
- original substance
- Carbon dioxide
- carbon dioxide
- Carbon dioxide
- irreversible
- periodic changes
- crystallization
- physical change
- physical changes
- brilliant white dazzling
- Magnesium Oxide
- chemical change
- rust (Iron oxide)
- rusting of iron
- chromium or zinc
- Galvanization
- vegetables
- juices of citrus fruits
- oxygen
- Plastic
- Acidic
- liquid petroleum
- periodic
- global warming
III. Match the following.
1.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Ripening of fruit | a) physical change |
| 2) Burning of a dry leaf | b) chemical change |
| 3) Melting of ice | c) periodic change |
| 4) Day and nights | d) fast change |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Ripening of fruit | b) chemical change |
| 2) Burning of a dry leaf | d) fast change |
| 3) Melting of ice | a) physical change |
| 4) Day and nights | c) periodic change |
2.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Carbon dioxide | a) galvanizing |
| 2) Oxygen | b) crystallization |
| 3) Zinc | c) global warming |
| 4) sugar | d) oxidation |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Carbon dioxide | c) global warming |
| 2) Oxygen | d) oxidation |
| 3) Zinc | a) galvanizing |
| 4) sugar | b) crystallization |
3.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) browning of vegetables | a) vinegar |
| 2) browning of iron | b) dazzling light |
| 3) formation of crystal | c) galvanization |
| 4) burning of magnesium | d) crystallization |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) browning of vegetables | a) vinegar |
| 2) browning of iron | c) galvanization |
| 3) formation of crystal | d) crystallization |
| 4) burning of magnesium | b) dazzling light |
4.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) more time | a) physical change |
| 2) less time | b) chemical change |
| 3) time period | c) periodic change |
| 4) reversible | d) fast change |
| 5) new substances | e) slow change |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) more time | e) slow change |
| 2) less time | d) fast change |
| 3) time period | b) chemical change |
| 4) reversible | c) periodic change |
| 5) new substances | a) physical change |
5.
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Zinc | a) Chemical changes |
| 2) Formation of Magnesium oxide | b) Natural changes |
| 3) Belum Caves | c) Periodic changes |
| 4) Changes in seasons | d) Oxidation |
| 5) Photosynthesis | e) Galvanisation |
| f) Crystallization |
Answer:
| Group – A | Group – B |
| 1) Zinc | e) Galvanisation |
| 2) Formation of Magnesium oxide | d) Oxidation |
| 3) Belum Caves | b) Natural changes |
| 4) Changes in seasons | c) Periodic changes |
| 5) Photosynthesis | a) Chemical changes |
Do You Know?
→ Belum caves are naturally formed caves located near Kolimigundla mandal of Kurnool district. These are the second largest caves in Indian subcontinent after Meghalaya state caves. The name is derived from Bilum” Sanskrit word for caves. The caves reach its deepest point (120 feet from entrance level) at the point known as “Paathalaganga” only 1.5 km is open to tourists. In 1988 Andhra Pradesh Tourism , Development Corporation (APTDC) declared them protected and developed the caves as a tourist attraction in February 2002. Borra Caves are also famous natural caves located at Visakhapatnam District.
→ The Lonar lake in Buldhana district of Maharashtra was created by plummeting meteor about 5200 years ago. The water of Lonar lake turned into pink colour recently due to Haloarchaea microbes present in the salty water. But the colour is not permanent. When the biomass of the microbes settled at the bottom, then the water again becomes transparent.
![]()
→ The Iron pillar at Delhi :
Amazingly there is an iron that did not rust! There is an iron pillar at the Qutub complex in Delhi which is more than 1600 years old. Even after such a long period, the iron pillar kept in open space has hot rusted at all. Do you know how? It is made by wrought iron which contains more amounts of phosphorus than usual. The main reason for rust resistance is due to the formation of Iron hydrogen phosphate on its surface. So its takes more time to rest. That’s why still the iron pillar at Delhi did not get rust.