Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions Lesson 6(d) Group-18 Elements which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions Lesson 6(d) Group-18 Elements
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
List out the uses of Neon.
Answer:
Uses of Ne:
- Ne is used in discharge tubes and fluorescent bulbs for advertisement display purposes.
- ‘Ne’ – bulbs are used in botanical gardens and in greenhouses.
Question 2.
Write any two uses of argon.
Answer:
Uses of Ar:
- ‘Ar’ is used to create an inert atmosphere in a high-temperature metallurgical process.
- ‘Ar’ is used in filling electric bulbs.
![]()
Question 3.
In modern diving apparatus, a mixture of He ánd O2 is used – Why? (IPE 2016 (AP))
Answer:
In modem diving apparatus, a mixture of He and O2 is used because He is very low soluble in blood.
Question 4.
Helium is heavier than hydrogen. Yet helium is used (instead of H2) in filling balloons for meteorological observations – Why?
Answer:
‘He’ is a non—inflammable and light gas. Hence it is used in filling balloons for meterological observations.
Question 5.
How is XeO3 prepared? (IPE May – 2015(AP), 2014)
Answer:
XeF6 on hydrolysis produce XeO3.
XeF6 + 3H2O → XeO3 + 6HF
Question 6.
Give the preparation of
a) XeOF4 and
b) XeO2F2. (TS Mar. 17; IPE 2014)
Answer:
Partial hydrolysis of XeF6 gives oxy fluorides XeOF4 and XeO2F2
XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
XeF6 + 2H2O → XeO2F2 + 4HF
Question 7.
Explain the structure of XeO3. (TS Mar. 17; IPE 16, 15’ 14 (TS))
Answer:
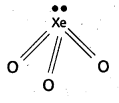
Structure of XeO3:
- Central atom is Xe’.
- ‘Xe undergoes sp3 hybridisation in 3rd excited state.
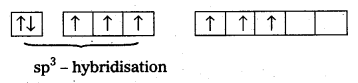
- ‘Xe’ forms 3σ-bonds and 3π-bonds with three oxygens.
- Shape of molecule is pyramidal with bond angle 103°.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the shape of XeF4 on the basis of VSEPR theory.
Answer:
Shape of XeF4:
- Central atom in XeF4 is
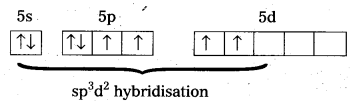
- Xe undergoes sp3d2 hybridisation in its 2nd excited state.
- Shape of the molecule is squãre planar with bond angle 90° and bond length 1.95A
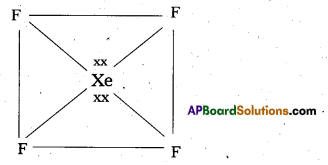
- Xe – forms four σ-bonds by the overlap of sp3d2 – 2pz(F) orbitals.
Question 9.
Which noble gas is radio active ? How is it formed?
Answer:
Radon (Rn) is radio active noble gas. Radon is obtained as decay product of 86R226.
86Ra226 → 86Rn222 + 2He4
Question 10.
How are XeF2, XeF4, XeF6 prepared? Give equation.
Answer:
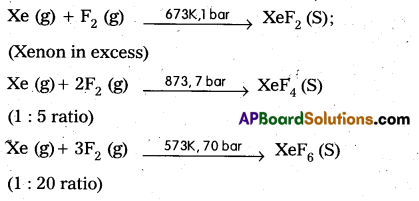
Question 11.
Noble gases are inert – explain.
Answer:
Noble gases are chemically inert:
- Noble gases have stable electronic configuration octet configuration except He.
- Noble gases have high Ionisation energy values and have large positive values of electron gain enthalpy.
Question 12.
Write the name and formula of the first noble gas compound prepared by Bertlett.
Answer:
The first noble gas compound prepared by Bertlett is XePtF6. Name of the compound is xenon hexa fluoro platinate.
Question 13.
Why do noble gases form compounds with fluorine and oxygen only?
Answer:
Noble gases form compounds with flourine and oxygen only.
Reason: Oxygen and Fluorine are most electronegative elements.
![]()
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the structures of
a) XeF2 and
b) XeF4. (AP Mar. ‘17, IPE 16, 15, ‘14 (TS)) (TS Mar. ’14)
Answer:
Xenon forms the binary fluorides XeF2, XeF4, XeF6 as follows. These are formed by direct combination of Xe and F2.
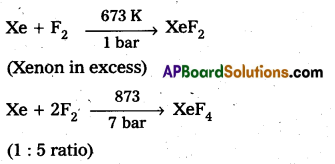
Structure of XeF2:
- In XeF2 central atom is ‘Xe’.
- ‘Xe’ undergoes sp3d hybridisation in its 1st excited state.
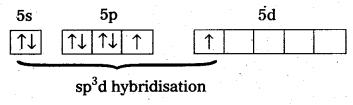
- Shape of molecule is linear.
- Xe form two σ-bonds with two fluorines.
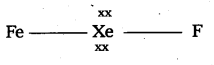
b) Structure of XeF4:
- Central atom in XeF4 is ‘Xe’.
- Xe undergoes sp3d2 hybridisation in it’s 2nd excited state.
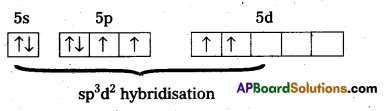
- Shape of the molecule is square planar with bond angle 90° and bond length 1.95A
- Xe forms four σ-bonds by the overlap of sp3d2 – 2pz (F) orbitals.
Question 2.
Explain the structures of
a) XeF6 and
b) XeOF4 (IPE Mar & May – 2015, 14)
Answer:
Structure òf XeF6 is ‘Xe’.
- Central atom in XeF6 is ‘Xe’.
- Xe undergoes sp3d3 hybridisation in it’s 3rd excited state.
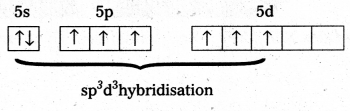
- Shape of molecule is distorted octahedral.
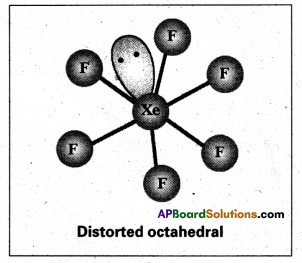
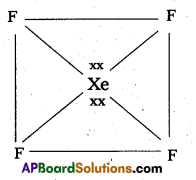
b) Structure of XeOF4:
- In XeOF4 molecule ‘Xe’ undergoes sp3d2 hybridisation.
- Shape of the molecule is square pyramid.
- There is one Xe-O double bond containing.
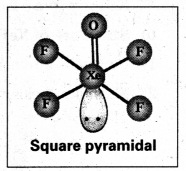
pπ = dπ overlapping.
Partial hydrolysis of XeF6 gives XeOF4
XeF6 + H2O → XeOF4 + 2HF
XeOF4 is a colourless volatile liquid. It has a square pyramidal shape.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the structure of
a) XeO3 and
b) XeO4 (T.S. Mar. ‘16)
Answer:
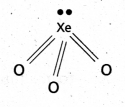
a) Structure of XeO3:
- Central atom is ‘Xe’
- ‘Xe’ undergoes sp3 hybridisation in 3rd excited state.
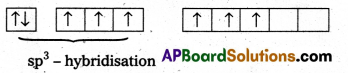
- ‘Xe forms 3σ-bonds and 3π-bonds with three oxygens.
- Shape of molecule is pyramidal with bond angle 103°.
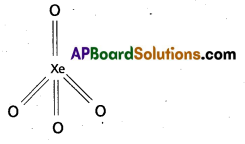
b) Structure of XeO4:
Xe is in sp3 hybridisation four singma bonds and four dπ – pπ bonds. Shape of XeO4 is tetrahedral.
Question 4.
Write the preparations of Xenon flourides.
Answer:
Xenon flourides : Xenon forms three binary fluorides, Xe F2, XeF4, and XeF6 by the direct reaction of Xenon with fluorine under suitable conditions.
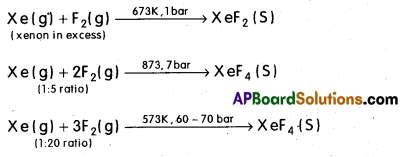
XeF6 can also be prepared by the interaction of XeF4 and O2F2 at 143 K.
XeF4 + O2F2 → XeF6 + O2
Question 5.
Write the preparations of Xenon Oxides.
Answer:
Xenon Oxides: Xenon forms two oxides XeO3 and XeO4 with oxygen.
These oxides are formed by the hydrolysis of xenon fluorides.
6XeF4 + 12 H2O → 4 Xe + 2 XeO3 + 24 HF + 3O2
XeF6 + 3 H2O → XeO3 + 6 HF
Question 6.
Give the formulae and describe the structures of a noble gas species, isostructural with
a) \(\mathrm{ICl}_4^{-}\)
b) \(\mathbf{I B r}_2^{-}\)
c) \(\mathrm{BrO}_3^{-}\)
Answer:
a) \(\mathrm{ICl}_4^{-}\) is also structural with XeF4 and it has square planar shape.
b) \(\mathbf{I B r}_2^{-}\) is also structural with XeF2 and it has linear shape.
c) \(\mathrm{BrO}_3^{-}\) is iso-structural with XeO4 and it has tetrahedral šhape.
![]()
Question 7.
Write any two uses of Helium.
Answer:
Uses of Helium:
- It is non inflammable and very light gas. Hence it is used in the balloons of Meteorological observations.
- It is used in gas cooled nuclear reactors and used as cryogenic agent.
- It is used as diluent for oxygen in modern diving apparatus.