Andhra Pradesh BIEAP AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 6th Lesson Tertiary Sector Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP Inter 2nd Year Economics Study Material 6th Lesson Tertiary Sector
Essay Questions
Question 1.
Define tertiary sector. Explain the importance of tertiary sector in Indian economy.
Answer:
The tertiary sector activities include all other activities like transport communication, banking, insurance and trade. Tertiary sector with its sub-sectors act as complementary sector to the development of primary and secondary sectors. Economists argue that the development of the economy is associated with high proportion of grass domestic product and working population employed in tertiary sector. The importance of the tertiary sector can be illustrated by the following indices.
1) Share in the gross domestic product: A review of the sectoral contribution to the gross domestic product reveals that the contribution of service sector has been increasing from 1950, its share was 27.5 percent of the GDP in 1950 – 51 and increased to around 56.0 percent in 2007 – 2008. The share of services sector in India is continuously increasing. It was only 27.5 percent in 1950 – 51 and increased to 40.59 percent in 1990 – 91 and further to 55.73 percent in 2007 – 08. In 2013 it was 57.0%.
2) Workers employed : Generally there is a tendency for the tertiary sector to expand more rapidly than secondary sector activities as a consequency the percentage of labour force engaged in this sector also registers an increase.
The workers engaged in tertiary sector has increased from 178.56 lakhs (1991) to 182.65 lakhs in 2008. Though 189.60 lakh workers were employed in tertiary sector during 2001 there was a decline in the number of workers employed to 182.65 lakhs in 2008. This was mainly due to the decline in the employment of workers in public sector.
It is evident form the data that 54.1 percent of the workers employed in tertiaiy sector are in rural areas and the proportion of urban areas was 45.9 percent.
3) Exports of services: India has been recording high growth in the export of services during the last few years. Exports of services was US $ 460 billion in 2004 – 05, increased to US $ 61.4 billion in 2005 – 06 and to US $ 90.1 billion in 2007 – 08 growth of exports was particularly repaid in the miscellaneous services which comprise software services, business services, financial services and communication services India’s export of services is expected to touch US $ 310.9 billion powered by the booming software consultancy, engineering and tourism sectors by 2011 -12.
![]()
Question 2.
Infrastructure contributes to the economic development of a country. Explain.
Answer:
“Infrastructure” is an umbrella term for many service activities referred to as social overhead. Capital by many development economists infrastructure facilities are also referred to as economic and social overhead often they have also referred to urban and rural infrastructure. Adequate infrastructural facilities help to determine a country’s success and another failure. They diversity production, expand trade, reduce poverty and improve the environmental conditions.
Generally infrastructure is categorised into two groups. They are :
- Economic infrastructure
- Social infrastructure
The services and facilities that are used in the economic production and by households is called as Economic infrastructure.
Engineering structures, equipment, power, gas, telecommunications, water supply, sanitation public works for irrigation, roads and railways, urban transport ports, waterways, air ports etc., are grouped as “economic infrastructure”.
Social infrastructure includes education, healthcare, family welfare housing, labour welfare etc. Both economic and social infrastructural serve as the true “engine of growth” and provides the needed impetus to the economy. The services associated with the use of infrastructure are called as infrastructural services, act as wheels of the economic activity. The availability on infrastructure improves the per capita GDP and has the following effects:
- Raises the productivity of the production process.
- Increases access to markets.
- Leads to agricultural expansion.
- Brings higher yields in agriculture.
- Lowers the cost of doing business.
- Provides ability to complete in the international trade, even in traditional commodities.
- Provides employment opportunities.
- Achieves cost – saving in inventory and working capital.
- Delivers the product just-in-time particularly in exports.
- Facilitates diversification of trade.
- Leads to modernisation and diversification of production.
- Provides ability to repond to changes in demand and prices.
- Facilitates employment intensive growth.
- Defines welfare and ensures growth with poverty reduction.
- Helps to identify the poor.
- Improves the quality of life.
- Offers non-farm employment opportunities.
- Encourages the modification of physical surroundings as environment friendly surroundings.
- Promotes environment sustainability of human settlements.
- Removes and disposes the liquid and solid wastes.
- Protects public health and provides health benefits.
Keeping in view all these beneficial impacts of infrastructural services, the Government of India has decided to invest ₹ 4,35,349 crore, to spend exclusively on the improvement of rural infrastructure. This amount is allocated for the development of electricity, roads, telecommunications, irrigation, water supply and sanitation.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the contribution of GDP in service sector.
Answer:
Service sector has become very prominent in world’s economies. The importance may be highlighted in terms of its contribution to GDP, employment and exports.
The share of GDP is high in many countries. The following table shows that the contribution of services sector to the overall GDP those countries is very high in the tuble U.K has highest share of service sector followed by U.S.A, France. In India the share of service sector increase between 2001 and 2013.
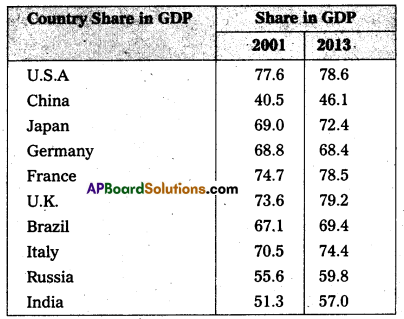
![]()
Question 2.
What are the activities considered under the India’s Services Sector ?
Answer:
Services in India are emerging as a prominent sector in terms of contribution of national and State incomes, trade flows, foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows and employment. The following activities can be considered to form the part of the service sector.
- Trade.
- Hotels and Restaurants.
- Transport (Including Railways and transport by other means)
- Storage.
- Communication.
- Banking and Insurance.
- Real Estate and Business Services.
- Public administration and defence.
- Construction.
- Other services including education, medical and health, religious and other community services, legal services, recreation services.
Question 3.
What are the advantages of Roadways? [A.P. Mar. 18, 17, 16]
Answer:
The principle mode of connectivity between places in roadways. India has one of the largest road networks in the world, spread over 48.65 lakh k.m. district and villages road constitutive 95.2% of the total road network in our country.
Advantages of Roadways :
- Road transport connects all the villages and regions and finally it connects to the railways.
- Road transport does not required heavy capital expenditure.
- The chances of delay, damages are less in case of road transport.
- Road transport provides transports the goods to the railway station.
- Road transport help the farmers particularly easily and quickly to transport to mandis and towns.
- Road transport is more flexible when compared to other means of transport. It can provide door to door service.
- Enables to defence forces to move areas inaccessible by railways in emergencies.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the importance of Railways.
Answer:
Railways provide the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers. They are the great integrating force for the past 150 years and helping in acclerating the development of industry and agriculture railways made a very modest beginning in 1853. With a route length of 34 kms. Indian railways have grown into a vast network of 7,183 stations spread over a route length of 53,332 kilometers. They have a flat of 8025 locomotives, 44090 passenger service vehicles, 5990 other loading vehicles and 2,07,176 wagons. The Indian railways is the world’s third largest rail network under a single management. Better resource management rational pricing policy have led to a significant improvement in the performance of the railways. In India the development of agriculture and industrial sectors has generated higher level of demand for rail transport. Coal, pig iron, iron ore, cement, food grains, fertilizers sugar, salt, steel, petroleum products and other essential commodities are transported by railways.
Question 5.
What is tourism ? Explain its importance in Indian economy.
Answer:
Tourism is the sub – sector of tertiary sector in general and services industry in particular.
W.T.O defined Tourism as “the activities of persons travelling and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more then one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes”.
Importance:
- Tourism provides revenue to the government.
- Tourism creates employment facilities for women.
- It provides regional development.
- It is a source of foreign exchange earnings.
- Tourism sells indirectly the environmental resources.
- It can be used as a means of reducing poverty.
- It builds partnership with private sector.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the banking system in India.
Answer:
A well – developed banking system is necessary pro -requisite for achievement of economic development. Banks play an important role in mobilization of savings and investments. Banks are the efficient agents of capital formation in the economy and give access to use the resources in a productive way.
Banking system in India has been playing a very important role in the process of economic development. Depending upon the nature of the activity performed by them, banking system in India may be classified into the following categories. They are :
a) Commercial Banks
b) Cooperative Banks
c) Central Bank (Reserve Bank of India)
a) Commercial Banks : The commercial banks were nationalized in phased manner in 1969 and 1980. They are classified as public sector (nationalized) banks and private sector banks. The State Bank of India and its associates along with another 20 banks are the public sector banks. The Indian scheduled banks, which are not nationalized and branches of foreign banks operating in India are called as private sector banks.
b) Cooperative Banks: Under Cooperative Banking System State Cooperative Banks, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCB) and primary to short term credit. State Cooperative Agriculture and Rural Development Banks and Primary Agriculture and Rural Development Bank provide long term credit.
c) Reserve Bank of India (RBI) : The RBI is India’s Central Bank was established on 1st April 1935 was nationalized on 1st January 1949. RBI is Supreme Monetary Authority in the country. It keeps the reserves of all scheduled banks, which were included in 2nd schedule of RBI and which were not included is called as ‘Non-schedule Banks’.
Question 7.
What are the major constituents of insurance industry in India ?
Answer:
A Health and Development Insurance Sector of vital importance to every modem economy. It encourages the savings habits provides a safety net to rural and urban enterprises and individuals and generates long term funds for infrastructure development. Development and insurance is therefore, necessary to support continued economic growth social security and person reforms also benefit from a mature insurance industry.
There are two major constituents of Insurance :
- Life Insurance
- Non Life Insurance (General)
1) Life Insurance : LIC offers schemes, policies and plans to investors. Particularly the main objective of UC is giving protecting against risk of death and channalizing the funds for the benefits and the economy in the socially oriented sectors during 2013 -14.
Life Insurance under wrote first – year premium of ₹ 1,19,641 crore as against ₹ 1,07,361 crore during 2012-13 registering a growth of 11.44 percent.
2) Non Life Insurance (General): The general insurance companies deal with non life insurance. The GIC was approved as the Indian Reinsurer on 3rd November 2000. It offers fire, marine, motor, health and other insurance. During 2013-14, non-life insurance including stand lone health insurance and specialize insurance (Export Credit Guarantee Scheme) and Agriculture Insurance Company (AIQ underwrote premium worth ₹ 77,584 crore as against ₹ 69,089 crore during 2012 -13 registering a growth of 12.23 percent.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Service sector [A.P. Mar 17]
Answer:
Service sector is also known as tertiary sector. Service sector is the life, line for the social and economic growth of a country. The service sector activities include trade, transport, communications, banking, insurance, education, health, energy, marketing etc., all these facilities and services constitutes collectively the tertiary sector.
![]()
Question 2.
Infrastructure
Answer:
An umbrella term for service activities in the economy. Infrastructure is categorized into two groups. They are economic infrastructure and social infrastructure.
Question 3.
Transport
Answer:
Transport means conveyance of people or property from one place to another. These services provide a link between production distribution and consumption activities. Road ways, railways, airways, waterways are the important means of transport.
Question 4.
Water Transport
Answer:
Water Transport is the another important means of transport. Shipping is an important indicator of both commodity and service trade of any country. Water transport in India is of two types. They are the land water transport and International water transport (Shipping).
Question 5.
Civil Aviation
Answer:
Air transport has a vital role in the economic development of the country. It is the modem and quickest transport. In India the first commercial flight started on February 18th, 19.11. The real progress in civil aviation started in 1920.
Question 6.
Tourism [A.P. Mar. 17, 16]
Answer:
Tourism is the sub-sector of tertiary sector in general and services industry in particular. Tourism as “the activities of persons travelling and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes.
![]()
Question 7.
LIC [A.P. Mar. 18, 16]
Answer:
Life Insurance Corporation of India was set up in 1956. UC has its central office at Mumbai with 7 Zonal offices, 101 divisional offices and 2,048 branch offices. It mobilise savings of the public to invest in the industrial securities.
Question 8.
GIC
Answer:
General Insurance Industry in India was nationalized in 1972 and a government company known as General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC) was established. There are four GIC companies.
- National Insurance Company Limited
- New India Assurance Company Limited
- Oriental Insurance Company Limited
- United India Insurance Company Limited. The GIC deal with non-life insurance.
Question 9.
Micro – Insurance [A.P. Mar. 18]
Answer:
A system that blends insurance with savings and credit practices. The member of self help groups, farmers, migrant workers and tribals are the target groups for this micro finance. This insurance offers both individuals and group insurance services.
Question 10.
Communication
Answer:
The communication system is an integral part of the development process. Communication means the transmission of information. By providing necessary information about markets and supply of goods. It consists of posts of telegraphs, telecommunications broadcasting, television etc.
![]()
Question 11.
Science and Technology
Answer:
Science and technology are ideas and means with which man seeks to change his environment. Science represents accumulation of knowledge, while technology represents ‘refinement in tools. These two have helped to improve the quality of human life.
Question 12.
Performance of software industry
Answer:
The software industry is the main component of the information technology in India. India’s pool of young-aged man power is the key behind this success story. Presently there are more then 500 software forms in the country. Global software gaints like Microsoft, Oracle etc.