These AP 10th Class Biology Important Questions 10th lesson సహజ వనరులు will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 10th Class Biology 10th lesson Important Questions and Answers సహజ వనరులు
10th Class Biology 10th lesson సహజ వనరులు 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
ప్రశ్న 1.
మృత్తికక్షయాన్ని అరికట్టుటకు మీరు ఇచ్చే ఏవైనా రెండు సలహాలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- అడవులను పెంచటం
- చెక్ డ్యామ్ లు నిర్మించటం
- ఖాళీ నేలలో గడ్డి పెంచటం మొదలైన వాటి వలన క్రమక్షయం నివారించవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 2.
మీ ప్రాంతములో “నీటి సంరక్షణ” పై చైతన్యము కల్గించడానికి ఏ నినాదమును సూచిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
- నీటిని పొదుపుగా వాడాలి
- నీటిని వృథా చేయవద్దు
- జలమే జీవం
ప్రశ్న 3.
 గుర్తు దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది? దాని అర్థం ఏమిటి?
గుర్తు దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది? దాని అర్థం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
పటంలోని గుర్తు పునఃవినియోగాన్ని సూచిస్తుంది. ఇది వాడిన వస్తువులను తిరిగి వాడటం గురించి తెలుపుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 4.
అడవుల విస్తీర్ణం బాగా తగ్గితే ఏం జరుగుతుంది?
జవాబు:
- వన్యజీవుల ఆవాసాల విధ్వంసం జరుగును.
- నేల క్రమక్షయం జరుగును.
- గ్రీన్హౌస్ వాయువుల పెరుగుదల చేత భూతాపము పెరుగుతుంది.
- అడవులపై ఆధారపడి నివసించేవారు జీవనోపాధి కోల్పోతారు.
- అడవుల విస్తీర్ణం బాగా తగ్గితే వర్షపాతం తగ్గుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 5.
విద్యుత్ పొదుపుకు మీరు చేస్తున్న రెండు పనులను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- విద్యుత్ దీపాలు, పరికరాలు, ఫ్యాన్స్ వాడనప్పుడు స్వి ను ఆపివేయవలెను.
- విద్యుత్ను ఆదా చేసే పరికరాలైన LEDS మరియు CFL బలను ఉపయోగించవలెను.
- సాంప్రదాయేతర ఇంధన వనరులైన సౌరశక్తి మరియు పవనశక్తిని ఉపయోగించాలి.

ప్రశ్న 6.
సహజవనరులను పునరుద్ధరించడానికి మీరు ఏఏ చర్యలు తీసుకొంటారు?
జవాబు:
- ప్రజలు నీటిని సంరక్షించుకునే విధంగా ప్రేరేపించాలి.
- నీటిని వీలైనంత వరకు సృధా చేయకూడదు.
- ఖాళీ ప్రదేశాలలో మొక్కలు నాటాలి
- నీటి వినియోగంపై రైతులకు అవగాహన కల్పించాలి.
- వీలైనంత వరకు నీటిని పునర్వినియోగించుకునేటట్లు చేయూలి.
ప్రశ్న 7.
తక్కువ నీటి సౌకర్యాలు ఉన్న ప్రాంతాలలో రైతులు అనుసరించదగిన ఏవైనా రెండు విధానాలు రాయుము.
జవాబు:
- ఇంకుడు గుంతలు త్రవ్వుట,
- బిందు సేద్యం మరియు స్ప్రింక్లర్స్ తో సూక్ష్మ నీటిపారుదల పద్ధతి.
ప్రశ్న 8.
మన రాష్ట్రంలో ఇటీవల ప్రకటించిన “వనం-మనం” అను కార్యక్రమమును ప్రజల్లోకి తీసుకెళ్ళడానికి మీరు ఏవైనా రెండు నినాదాలు తయారుచేయండి.
(లేదా)
మీ పాఠశాల ర్యాలిలో ప్రదర్శించడానికి “వనం-మనం” కార్యక్రమం గురించి కొన్ని నినాదాలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- మొక్కలు నాటుదాము – స్వచ్ఛమైన గాలిని పొందుదాము.
- మొక్కలు పెంచు – కాలుష్యం తగ్గించు.
- మొక్కలు పెంచుదాము – భౌగోళిక వెచ్చదనాన్ని తగ్గిద్దాము.
- చెట్లను నరికితే – జీవుల ప్రాణం తీసినట్లే.
- వృక్షోరక్షతి రక్షితః
- చెట్లను పెంచుదాం దండిగా – పరిసరాలను ఉంచుదాం పచ్చగా.
ప్రశ్న 9.
“పునరుద్దరింపబడని వనరుల సంరక్షణ” పై రెండు నినాదాలు తయారుచేయండి.
జవాబు:
- జీవ ఇంధనాలను వాడదాం – శిలాజ ఇంధనాలను తగ్గిదాం.
- ప్రత్యామ్నాయ ఇంధనాలను వాడదాం – పర్యావరణాన్ని కాపాడదాం.
ప్రశ్న 10.
అడవులను ఎందుకు సంరక్షించుకోవాలో రెండు కారణాలు తెల్పండి.
జవాబు:
అడవులను సంరక్షించుకోవటానికి గల కారణాలు :
- అడవులు వాతావరణంలో పెరుగుతున్న కార్బన్ డయాక్సెడ్ ను గ్రహించి భౌగోళిక వెచ్చదనాన్ని తగ్గిస్తాయి.
- అడవుల నుండి విలువైన వనరులు అనగా ఔషధాలు, కలప, లక్క తేనె మొదలైన వాటిని పొందుతున్నాము.
- అడవులు వర్షాలుపడటంలో ప్రముఖ పాత్ర వహిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 11.
పునరుద్దరింపలేని వనరులకు రెండు ఉదాహరణలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
1. బొగ్గు 2. పెట్రోల్ 3. సహజ వాయువు 4. ఆయిల్ (నూనె)
ప్రశ్న 12.
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు ఎలా ఉత్పత్తి అవుతాయి?
జవాబు:
బొగ్గు, పెట్రోలియం, సహజవాయువు వంటి శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు వేల సంవత్సరాల క్రిందట భూగర్భంలో పాతుకుపోయిన వృక్ష, జంతు కళేబరాల నుండి ఉత్పత్తి అవుతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 13.
వనరులు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
అధిక మోతాదులో లభిస్తూ, భవిష్యత్ లో వాడకానికి వీలుగా ఉన్న పదార్థాలను “వనరులు” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 14.
సహజ వనరులు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
సహజ వనరులు :
పకృతిలో సహజంగా లభించే వనరులను సహజ వనరులు అంటారు.
ఉదా : గాలి, నీరు.

ప్రశ్న 15.
సహజ వనరులు ఎన్ని రకాలు? అవి ఏవి?
జవాబు:
సహజ వనరులు రెండు రకాలు
- పునరుద్ధరింపబడేవి
- పునరుద్ధరింపబడనివి.
ప్రశ్న 16.
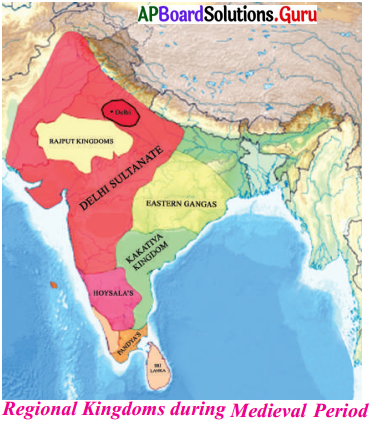
శ్రీరాం సాగర్ ప్రాజెక్టు ఏ జిల్లాల అవసరాలు తీర్చుతుంది?
జవాబు:
కరీంనగర్, వరంగల్, ఆదిలాబాద్, నల్గొండ, ఖమ్మం జిల్లావాసుల అవసరాలను శ్రీరాం సాగర్ ప్రాజెక్టు తీర్చుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 17.
శ్రీరాం సాగర్ ప్రాజెక్టు నీటి నిల్వ సామర్థ్యం ఎంత?
జవాబు:
శ్రీరాం సాగర్ ప్రాజెక్టు నీటి నిల్వ సామర్థ్యం 80.66. టి.ఎమ్.సి.లు.
ప్రశ్న 18.
ఇంకుడు చెరువు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
ఇంకుడు చెరువు :
నీటి ప్రవాహాలకు అడ్డంగా రాళ్లు, మట్టితో అడ్డుకట్టలు కట్టి ఏర్పాటు చేసే నీటి నిల్వలను “ఇంకుడు చెరువులు” (Percolation tanks) అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 19.
సెంటర్ ఫర్ వరల్డ్ సాలిడారిటీ సంస్థ ఎక్కడ ఉంది?
జవాబు:
సెంటర్ ఫర్ వరల్డ్ సాలిడారిటీ సంస్థ ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని సికింద్రాబాద్ లో ఉంది.
ప్రశ్న 20.
మైక్రో ఇరిగేషన్ అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
మైక్రో ఇరిగేషన్ :
డ్రిప్ మరియు స్ప్రింక్లర్లతో, తక్కువ నీటితో వ్యవసాయం చేసే పద్ధతిని “మైక్రో ఇరిగేషన్” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 21.
నేల వనరు సద్వినియోగానికి ఉపయోగపడే రైతు ఆధారిత విధానాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
వెడల్పు చాళ్లు తియ్యడం, తక్కువ ఎత్తు పెరిగే పంటలు పెంచడం, కాంటూర్ సేద్యం చేయటం వంటి పద్ధతుల ద్వారా నేలను సద్వినియోగం చేయవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 22.
నేలలో నైట్రోజన్ నిల్వలు ఎలా పెంచవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
గట్ల మీద గెరిసీడియా మొక్కలను, లెగ్యుమినేసి పంటలను పండించటం వలన నేలలో నైట్రోజన్ నిల్వలు పెంచవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 23.
‘సుస్థిరాభివృద్ధి’ అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
సుస్థిరాభివృద్ధి :
అభివృద్ధికి, సంరక్షణకు రెండింటికి ప్రాధాన్యమిస్తూ భావితరాలకు అవసరమయ్యే సహజ వనరులను అందుబాటులో ఉండే విధంగా పర్యావరణాన్ని ఉపయోగించుకోవడాన్ని “సుస్థిరాభివృద్ధి” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 24.
సుస్థిర అటవీ పద్ధతులు కొన్ని తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
చెట్లు తక్కువగా నరకటం, చెట్లు తిరిగి ఎదగడానికి అవకాశం ఇవ్వటం, ఎత్తైన చెట్లను, పెద్దచెట్లను నరకకుండా చూడటం వలన అటవీ వనరులను కాపాడుకోవచ్చు. వీటినే “సుస్థిర అటవీ పద్దతులు” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 25.
కాంటూర్ పట్టీ పంటలు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
కాంటూర్ పట్టీ పంటలు: ఏటవాలు ప్రాంతాలలో నేల వాలుకు అడ్డంగా గాలి వీచే దిశకు అడ్డంగా నేలను దున్ని ఒక్కొక్క వరుసలో ఒక్కొక్క పంటను పండించే పద్ధతిని “కాంటూర్ పట్టి పంటలు” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 26.
జీవవైవిధ్య వినాశనానికి దారితీసే ప్రక్రియలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
వేటాడడం, కాలుష్యం, ఆవాసాలు విధ్వంసం వంటి కార్యకలాపాలు జీవవైవిధ్య వినాశనానికి దారితీస్తున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 27.
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు :
బొగ్గు, పెట్రోలియం, సహజవాయువు వంటి శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు వేల సంవత్సరాల క్రిందట భూగర్భంలో పాతుకు పోయిన వృక్ష జంతు కళేబరాల నుండి ఉత్పత్తి అవుతాయి. వీటిని “శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 28.
జీవ ఇంధనాలు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
జీవ ఇంధనాలు :
శక్తిని ఇచ్చే జీవ ద్రవ్యరాశిని “జీవ ఇంధనాలు” అంటారు.
ఉదా : బయోడీజిల్.

ప్రశ్న 29.
బయోడీజిల్ ఉత్పత్తికి అనువైన మొక్కలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
జట్రోపా (అడవి ఆముదం) కర్కాస్ మొక్కలు విత్తనాల నుండి బయోడీజిల్ తయారుచేస్తారు.
ప్రశ్న 30.
4R సూత్రం అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
పర్యావరణ పరిరక్షణకు, వనరుల సద్వినియోగానికి 4R సూత్రం పాటించాలి. అవి:
- Reduce:తగ్గించటం
- Reuse :తిరిగివాడటం
- Recycle: పునఃచక్రీయం
- Recover : తిరిగి ఏర్పరచడం
ప్రశ్న 31.
ఈ క్రింది పటం దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది?

జవాబు:
ఇది పునఃచక్రీయానికి గుర్తు.
ప్రశ్న 32.
IUCN అనగా నేమి?
జవాబు:
‘ఇంటర్నేషనల్ యూనియన్ ఫర్ ద కన్సర్వేషన్ ఆఫ్ నేచర్’ ను సంక్షిప్తంగా IUCN అంటారు. 1980లో ఇది ప్రపంచ సంరక్షణ విధానాన్ని ప్రతిపాదించింది.
ప్రశ్న 33.
తరగని వనరులు తరిగిపోయే వనరులుగా మారే అవకాశం ఉందా?
జవాబు:
విచక్షణారహిత వినియోగం వలన తరగని వనరులు తరిగిపోయే వనరులుగా మారే ప్రమాదం ఉంది.
ప్రశ్న 34.
భూగర్భజలాలు తగ్గటానికి కారణాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ఋతుపవనాల రాకడలో మార్పులు, లోతైన గొట్టపు బావులు, భూగర్భ జల వినియోగంలో విచక్షణా రాహిత్యం మొదలయిన వాటి వలన భూగర్భజలాలు తగ్గుతున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 35.
ICRISAT పూర్తి పేరు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
“ఇంటర్ నేషనల్ క్రాప్ రీసెర్చి ఇన్స్టిట్యూట్ ఫర్ సెమి-ఎండ్ ట్రాపిక్స్” ను ఇక్రిసాట్ అంటారు. ఇది సికింద్రాబాదులో ఉంది.
10th Class Biology 10th lesson సహజ వనరులు 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
ప్రశ్న 1.
“అడవి ఒక ప్రధాన పునరుద్ధరింపదగిన వనరు” – దీనిని నీవు ఎలా సమర్థిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
“అడవి ఒక ప్రధాన పునరుద్దరింపదగిన ప్రధాన వనరు.” దీనిని నేను సమర్థిస్తాను.
ఉదాహరణలు:
- చెట్లను నరికివేస్తే తిరిగి పెరుగుతాయి. వాటంతట అవే పెరుగుతాయి.
- అటవీ పదార్థాలు వాడిన కొద్ది తిరిగి ఏర్పడుతాయి.
- మొక్కలు పెంచటం, సామాజిక అడవుల అభివృద్ధి వంటి కార్యక్రమాల ద్వారా అడవులు పునరుద్ధరించబడతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 2.
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు పొదుపుగా ఎందుకు వాడాలి?
జవాబు:
- శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు తరిగిపోయే ఇంధనాలు.
- ఇవి తిరిగి ఏర్పడటానికి లక్షల సంవత్సరాలు పడుతుంది.
- విచక్షణా రహితంగా వీటిని వాడినట్లయితే మనకు ఇంధన కొరత వస్తుంది.
- భవిష్యత్ అవసరాలకు ఇంధన పరిరక్షణ కొరకు వీటిని పొదుపుగా వాడాలి.
ప్రశ్న 3.
భూగర్భ జలాల సంరక్షణ గురించి అవగాహన కలిగించుటకు మీరిచ్చే రెండు సలహాలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
భూగర్భ జలాల సంరక్షణ :
- ఇంకుడు గుంతలు త్రవ్వడం, చెక్ డ్యాం నిర్మించడం ద్వారా వర్షపు నీటిని నిల్వ చేయడం.
- ర్యాలీలు నిర్వహించడం, కరపత్రాలు, గోడ పత్రికల ద్వారా ప్రచారం చేయడం ద్వారా భూగర్భ జల సంరక్షణపై అవగాహన కల్పించడం.
- తక్కువ నీటితో వ్యవసాయ పద్ధతులను ప్రోత్సహించడం మొదలగునవి.
ప్రశ్న 4.
భూమి వేడెక్కుటలో గ్రీన్హౌస్ వాయువుల పాత్రను వివరించుము.
జవాబు:
- CO2, CFC’s, NO2, హైడ్రోకార్బన్లు మరియు మిథేన్ వంటి వాయువులను గ్రీన్హౌస్ వాయువులంటారు. ఇవి భూమిని వెచ్చగా ఉంచుతాయి.
- గ్రీన్హౌస్ వాయువుల గాఢత పెరుగుట వలన భూమి యొక్క ఉష్ణోగ్రత కూడా పెరుగుతుంది.
- గ్రీన్హౌస్ వాయువులు భూమి నుండి ఉద్గారమయ్యే వేడిమిని గ్రహించి భౌగోళిక వెచ్చదనానికి కారణమవుతున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 5.
సహజ వనరులను సద్వినియోగం చేసుకోవడమే దేశానికి మనం చేసే సేవ అని చెప్పవచ్చు. దీనిని నీవు సమర్థిస్తావా? ఎందుకు?
జవాబు:
- ఒక దేశపు సహజ వనరులు ఆ దేశం యొక్క ఆర్థిక, సామాజిక పురోభివృద్ధిని నిర్ణయిస్తాయి.
- సహజ వనరులు ప్రకృతిలో సహజంగా లభిస్తూ మానవ కార్యకలాపాలకు, మనుగడకు ఉపయోగపడతాయి.
- సహజ వనరులు తయారుకావడానికి చాలాకాలం పడుతుంది.
- వీటిని విచక్షణారహితంగా వాడినపుడు పూర్తిగా అంతరించిపోతాయి.
- కావున సహజ వనరులను భవిష్యత్ తరాలకు అందుబాటులో ఉండే విధంగా సద్వినియోగం చేసుకోవడమే దేశానికి మనం చేసే సేవ.

ప్రశ్న 6.
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలను సంరక్షించుటకు మీరు పాటించే నాలుగు పద్ధతులు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- ప్రత్యామ్నాయ ఇంధనాలను ఉపయోగించాలి.
- శిలాజ ఇంధనాల వాడకాన్ని తగ్గించాలి.
- కార్లవంటి సొంత వాహనాలలో కాకుండా బస్సులు, రైళ్ళ వంటి ప్రజారవాణా వ్యవస్థలను ఉపయోగించాలి.
- వీలైనప్పుడు నడవడం, సైకిలను ఉపయోగించాలి.
- విద్యుత్ ఆదా చేసే పరికరాలను ఉపయోగించాలి.
ప్రశ్న 7.
మానవులమైన మనము ప్రకృతి ప్రసాదించిన వనరులను విచక్షణా రహితంగా వినియోగిస్తున్నాము. ఫలితంగా ప్రకృతి వనరులు చాలా వేగంగా తరిగిపోతున్నాయి. దీనివల్ల భవిష్యత్ లో జరుగబోవు పరిణామాలను ఊహించి వ్రాయుము. జ. సహజ వనరులను విచక్షణారహితంగా వాడటం వలన ఈ క్రింది దుష్పరిణామాలు సంభవిస్తాయి.
జవాబు:
- వర్షపాతంలో తగ్గుదల.
- కరువు సంభవించుట.
- వాతావరణ ఉష్ణోగ్రతలలో పెరుగుదల.
- అరుదైన జాతులు అంతరించిపోయే ప్రమాదం గలదు.
ప్రశ్న 8.
సంవత్సరం నుండి మరో సంవత్సరానికి వాతావరణ ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు పెరుగుతున్నాయి కదా ! ఇలానే ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు పెరుగుతూ పోతే జరిగే పరిణామాలను ఊహించి వ్రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు పెరిగే కొలది ధృవప్రాంతాలలో మంచు కరిగి, సముద్రాలలో నీటిమట్టం పెరుగుతుంది.
- సముద్రాలలో నీటిమట్టం పెరుగుట వల్ల చిన్న చిన్న దీవులు మునిగిపోతాయి.
- ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు పెరుగుట వల్ల వర్షాలు తగ్గి కరువులు ఏర్పడతాయి.
- ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు ఎక్కువ పెరిగినప్పుడు కొన్ని జీవజాతులు అంతరించవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 9.
స్వచ్ఛ భారత్ సాధనలో 4R’s ప్రాముఖ్యతను తెలియచేయండి.
జవాబు:
- చెత్తను ఉత్పత్తి చేయటాన్ని తగ్గించటము. .
- చెత్తను తిరిగి వాడుటము ద్వారా ఎరువులను, కరెంట్ ను ఉత్పత్తి చేయవచ్చును.
- చెత్తను పారవేసేముందు తడిచెత్త, పొడి చెత్తలను వేరు చేయటము ద్వారా పునఃచక్రీయం చేయవచ్చు.
- చెట్లను నరికివేసినప్పుడు ప్రత్యామ్నాయంగా మరో చోట చెట్లను పెంచడం.
ప్రశ్న 10.
ఇంకుడు చెరువులు అనగానేమి? వీటిని ఎలా నిర్మిస్తావు?
జవాబు:

నీటి ప్రవాహాలకు అడ్డంగా ‘ రాళ్లు, మట్టితో అడ్డుకట్టలు కట్టి ఏర్పాటు చేసే నీటి నిల్వలను ఇంకుడు చెరువులు (Percolation tanks) అంటారు. బంకమట్టి, ఇసుక, కంకర, గులకరాళ్లు మొదలైన వాటిని బాగా కలిపి ఒకదానిపైన ఒకటి వచ్చేటట్లుగా పొరలపొరలుగా చెరువు నేలను, అంచుల వెంబడి కప్పుతారు. తరువాత దీనిని గట్టిగా కుదురుకునేలా చేస్తారు. వ్యవసాయం కోసం నీటిని సరఫరా చేయడానికి మట్టికట్టకు తూము ఏర్పాటు చేస్తారు. పూర్తి నీటి నిల్వ మట్టానికి, అడుగు మట్టానికి మధ్య నాలుగోవంతు ఎత్తులో తూమును ఏర్పాటు చేస్తారు. అందువల్ల తగినంత నీటిని విడుదల చేసుకోవడానికి వీలుకలుగుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 11.
కేడీ నిర్వహించిన వనపర్తి, వట్టిచెర్ల గ్రామాల మధ్యగల పోలికలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
వృత్తులు, పంట విధానాలు, భౌగోళిక స్థితిగతులు, మౌలిక సదుపాయాలు, సామాజిక సేవలు వంటి అంశాల దృష్ట్యా వనపర్తి, వడ్డిచెర్ల గ్రామాలు ఒకే విధంగా ఉన్నాయి. రెండు గ్రామాలలో చిన్న రైతులు చాలా ఎక్కువ సంఖ్యలో ఉన్నారు. సరాసరి కుటుంబ ఆదాయం వనపర్తిలో ఎక్కువ. ఈ రెండు గ్రామాల్లో వ్యవసాయమే జీవనాధారం. బావులే నీటిపారుదలకు మూలం. కుటుంబ ఆదాయం, భూగర్భజలం యొక్క స్థాయిపైనే ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది. కుటుంబ ఆదాయాన్ని ప్రభావితం చేసే పంటల క్రమం ఈ గ్రామాల్లో వేరు వేరుగా ఉంది.
ప్రశ్న 12.
భూగర్భజలం ఇటీవలి కాలంలో తగ్గటానికి గల కారణాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
గత కొన్ని సంవత్సరాల నుండి ఋతుపవనాల రాకడలో మార్పులు సంభవించడం వలన, భూగర్భజలాల వినియోగంపై ఒత్తిడి పెరిగింది. డ్రిల్లింగ్, లోతైన గొట్టపుబావులు, బోరుబావులను తవ్వడం వంటి చర్యల వలన, విచక్షణారహితంగా రాష్ట్రంలోని భూగర్భజలాన్ని వాడడం వలన ఈ వనరు బాగా తరిగిపోతున్నది. మన రాష్ట్రంలో 1998-2002 మధ్యకాలంలో సరాసరిగా నీటి స్థాయి 3 మీటర్ల దాక తగ్గింది.
ప్రశ్న 13.
భూగర్భ జల సంరక్షణకు సెంటర్ ఫర్ వరల్డ్ సాలిడారిటీ సంస్థ చేపట్టిన చర్యలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
సెంటర్ ఫర్ వరల్డ్ సాలిడారిటీ (సికింద్రాబాదు, ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్), గ్రామాలలో ఎండిపోతున్న బావులలో నీరు చేరుకునేలా, భూగర్భజలాలపై సుస్థిరత్వంపై దృష్టి కేంద్రీకరించింది. రైతులందరూ సమష్టిగా నీటిని పంచుకొని వాడుకునే విధంగా ప్రోత్సహించారు. ఒకే నీటి వనరును ఉపయోగించుకునే విధంగా, రైతులు చిన్న, పెద్ద గ్రూపులుగా ఏర్పడ్డారు. డ్రిప్ మరియు స్ప్రింక్లర్లతో సూక్ష్మ నీటిపారుదల (మైక్రో ఇరిగేషన్) పద్ధతులను అనుసరించేలా రైతులు స్ఫూర్తిని పొందారు. వర్షపు నీటి సంరక్షణకై ఇంకుడు గుంటలు తవ్వారు.
ప్రశ్న 14.
నీటిని విచక్షణాయుతంగా వాడవలసిన అవసరం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
భూమిపై ఉన్న మొత్తం నీటిలో సముద్రాలు, మహాసముద్రాలు, భూగర్భ జలాలలో ఉన్న నీటిలో 97 శాతం ఉప్పు నీరే. 2.5-2.75% మాత్రమే మంచినీరు. దీనిలో 1.75-2% (మూడింట రెండు వంతులు) నీరు గ్లేషియర్లు, మంచు, హిమపాతం రూపంలో గడ్డకట్టి ఉంటుంది. 0.7-0.8% మంచినీరు భూగర్భజలంగా, నేలలో నీటి ఆవిరి రూపంలో ఉంటుంది. 0.01%’ కంటే తక్కువ పరిమాణంలో మంచినీరు ఉపరితల జలం రూపంలో సరస్సులు, నదులలో ఉంటుంది. మంచినీరు చాలా తక్కువ ఉన్నప్పటికీ విచక్షణతో ఉపయోగించాలి.

ప్రశ్న 15.
పూర్వకాలంలో గ్రామ సరిహద్దులను ఎలా నిర్ణయించేవారు?
జవాబు:
పూర్వం వాటర్ షెడ్ (రెండు నదులు లేదా కాలువల మధ్యగల భూ ప్రాంతం) ఆధారంగా, నిపుణులైన రైతులు గ్రామ సరిహద్దులను నిర్ణయించేవారు. రెండు గ్రామాల మధ్యగల మురుగు నీటిపారుదల వ్యవస్థ ఆధారంగా ఈ హద్దులు నిర్ణయించబడేవి. వ్యవస్థలోని సభ్యులందరూ వీటిని సామాజికంగా అంగీకరించేవారు.
ప్రశ్న 16.
సర్వే నిర్వహణకు ముందు కొత్తపల్లి గ్రామ ప్రజల పరిస్థితులు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కొత్తపల్లి గ్రామంలో సర్వేకు పూర్వపరిస్థితులు:
1. సాగుభూమి కన్నా బీడు భూములు విస్తృతంగా ఉండేవి; 2. తక్కువ అక్షరాస్యత ; 3. శ్రామికులు తక్కువగా ఉండేవారు; 4. చిన్న కమతాలలో లేదా పొలాలలో క్రిమిసంహారకాలు లేదా ఎరువులు ఎక్కువగా వాడేవారు ; 5. పంట దిగుబడి తక్కువగా ఉండేది ; 6. గ్రామంలో నీటి సంరక్షణ నిర్మాణం ఒక్కటి కూడా లేదు. ఉత్పాదకత, ఆదాయాన్ని పెంపొందించే విధానాలు లేవు.
ప్రశ్న 17.
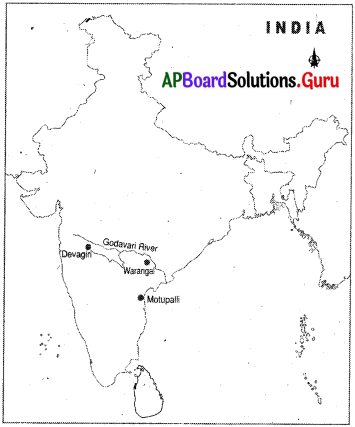
శ్రీరాం సాగర్ ప్రాజెక్ట్ గురించి రాయండి.
జవాబు:

శ్రీరాం సాగర్ ప్రాజెక్టు పోచంపాడు ప్రాజెక్టు అని కూడా అంటారు. ఇది గోదావరి నదిపై ఉన్న ప్రాజెక్టు, తెలంగాణా ప్రాంతంలో అధిక భాగానికి ఇది జీవనాధారం. కరీంనగర్, వరంగల్, ఆదిలాబాద్, నల్లగొండ, ఖమ్మం జిల్లా వాసుల అవసరాలను ఈ ప్రాజెక్టు తీరుస్తుంది. గోదావరి నదిపై, ఇతర రాష్ట్రంలో ఆనకట్ట నిర్మించడం వలన, ఎక్కువ శాతం నీరు ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ కు చేరకుండానే పై రాష్ట్రాలలో నిలువ చేయబడుతోంది. ఆగస్టు 2013 గణాంకాల ప్రకారం ఈ ప్రాజెక్టు యొక్క అంచనా వేయబడిన నీటి నిలువ సామర్థ్యం 80, 66 టి.ఎం.సి.లు.
ప్రశ్న 18.
బీడు భూములను ఎలా అభివృద్ధి పర్చవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
రోడ్ల వెంబడి, పొలాలు, కాలువల గట్ల వెంబడి ఉపయోగకరమైన జాతుల మొక్కలను పెంచడం ద్వారా బీడు భూములు అభివృద్ధి చేయవచ్చు. ఇందుకుగాను రైతులు అనేకచోట్ల 0.3 మీటర్ల ఎత్తు కట్టలను కట్టి, 10 మీటర్ల దూరానికి ఒకటి చొప్పున కాంటూర్ కందకాలను ఏర్పాటు చేశారు. సీతాఫలం మొక్కలతో పాటు అనేక ఉపయోగకరమైన జాతుల మొక్కలను, గెరిసీడియా మొక్కలను వారు పెంచడం మొదలు పెట్టారు. 2500 పండ్ల చెట్లు, టేకు చెట్లను నాటారు. ఇదే విధంగా బీడు భూములను అభివృద్ధి చేయవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 19.
పునరుద్దరించదగిన వనరులు (Reneuuable resources) అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
మనం జీవించడానికి అవసరమయ్యే ఆహారం, నీరు, గాలి, నివాసం అన్నీ సహజ వనరుల నుండి లభిస్తాయి. కొన్ని సహజ వనరులు ఉపయోగించిన తరువాత, తిరిగి ఉత్పత్తి చేయబడుతాయి. వీటిని పునరుద్ధరింపదగిన వనరులు (Renewable resources) అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 20.
పునరుద్దరింపలేని వనరులు (Non-reneuable resources) అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు వంటి వనరులను పునరుద్దరింపలేము. ఒకసారి వీటిని పూర్తిగా వాడుకున్నట్లయితే, అవి ఎప్పటికీ తరిగిపోయినట్లే. అతి తక్కువ కాలం ఇవి వినియోగించబడతాయి. కానీ, ఇవి తయారవ్వాలంటే చాలా కాలం పడుతుంది. వీటినే పునరుద్ధరింపలేని వనరులు (Non-renewable resources) అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 21.
అదవులు చాలా ప్రాముఖ్యత గలవని అనుకోవటానికి కారణాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
అడవులు చాలా ప్రాముఖ్యత కలిగినవి. ఎందుకంటే అంటార్కిటికా తప్ప మిగిలిన ఖండాలన్నింటిలోనూ అడవులు ఉన్నాయి. మొక్కలకు, జంతువులకు ఒక గొప్ప ఆవాసంగా ఉన్నాయి. ప్రపంచానికి అడవులు ఊపిరితిత్తులు వంటివి మరియు కొత్త జీవితానికి పోషకాలనందించే ప్రముఖ స్థానం వంటివి లెక్కలేనన్ని ఉత్పత్తులు అడవుల నుండి లభిస్తున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 22.
అడవుల సంరక్షణలో రాజస్థానీయులు చూపిన చొరవ తెలపంది.
జవాబు:
రాజస్థాన్లో వైష్ణోయిలు చేసిన కార్యక్రమం మనకు మార్గదర్శకం. అమృతాదేవి, ఆమె కుమార్తెలు, వారి గ్రామస్తులందరూ కలిసి గ్రామ సమీపంలో ఉండే అడవుల్లోని వృక్షాలను కొట్టివేయకుండా కాపాడుకొన్నారు. ఇలాంటి అద్భుతమైన ఉద్యమాలు మనకు పర్యావరణాన్ని కాపాడుకోవడంలో స్ఫూర్తినిస్తాయి. అడవిని నరికి కలప సేకరించి రాజభవనం కట్టుకోవాలన్న రాజుగారికి వ్యతిరేకంగా పోరాటం చేసి అడవితో ప్రశాంతమైన సహసంబంధాన్ని గడపడానికి ప్రతిన పూనారు. ప్రకృతిని కాపాడేందుకు 29 నియమాలతో స్వయంచట్టం చేసుకున్నారు.
ప్రశ్న 23.
నేల ప్రాధాన్యత తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ఆహారోత్పత్తికి నేల చాలా ముఖ్యమైనది. మనకు అవసరమైన పంటలు పండించాలంటే బాగా సారవంతమైన నేల ఉండాలి. వన్యజాతి మొక్కలు పెరగాలన్నా నేల అవసరం. మొక్కలు, జంతువులు మరియు ఇతర వనరులను సంరక్షించుకోవడానికి మనం చేసే అన్ని ప్రయత్నాలు నేల సంరక్షణ పైనే ఆధారపడి ఉంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 24.
నేలకు నష్టాలు కలిగిస్తున్న కారకాలు తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ఒక పొలంలో ఒకే రకం పంటను పలుమార్లు పండించడం వంటి లోపభూయిష్టమైన వ్యవసాయ పద్ధతులు నేలలోని పోషకాలను తొలగిస్తాయి. కొండ ప్రాంతాలను దున్నడం వలన నీరు, గాలి ద్వారా నేలకోత చాలా ఎక్కువవుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 25.
జీవవైవిధ్యం అనగానేమి? దాని ప్రాముఖ్యత ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
భూమిపై నివసిస్తున్న జీవులలో గల వైవిధ్యమే జీవవైవిధ్యం. ప్రకృతి నుండి మనకు లభించే ఉత్పత్తులు మరియు లాభాలన్నీ జీవవైవిధ్యం నుండి పొందుతున్నవే. ఆహార పదార్థాలు, వాటి నిర్మాణాలకు ఉపయోగించే పదార్థాలు, ఔషధాలు లభించాలన్నా మరియు పరిశుభ్రమైన, ఉపయోగకరమైన నేల ఉండాలన్నా జీవవైవిధ్యం ఎంతో అవసరం.
ఆహార వనరులు వైవిధ్యంగా, సమృద్ధిగా ఉండే విధంగా మనం జీవవైవిధ్యాన్ని కాపాడుకోవలసిన అవసరం ఉంది. ఆహారం కన్నా జీవవైవిధ్యం గొప్పది. ఉదాహరణకు ప్రపంచంలో మొత్తంలో 50,000 నుండి 70,000 వృక్ష జాతులను ఔషధాల తయారీలో వినియోగిస్తున్నారు.

ప్రశ్న 26.
శిలాజ ఇంధనాల వినియోగం ఎలా తగ్గించవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలను జాగ్రత్తగా వినియోగిస్తూ, ప్రతి ఒక్కరూ వాటిని సంరక్షించాలి. విద్యుత్ దీపాలను, పరికరాలను వాడనప్పుడు స్వి ను ఆపివేయండి. విద్యుత్ను ఆదాచేసే పరికరాలను మాత్రమే కొనండి. వీలైనపుడు నడవడం, సైకిలను ఉపయోగించడం చేయాలి.
కార్ల వంటి సొంత వాహనాలలో కాకుండా బస్సులు, రైళ్లు వంటి ప్రజా రవాణా వ్యవస్థల ద్వారా ప్రయాణిస్తే లాభదాయకం. ఈ విధంగా చేస్తే సమాజానికి ఎంతో ఉపయోగం.
ప్రశ్న 27.
ఖనిజాల వినియోగం వలన భవిష్యత్ లో వచ్చే సమస్యలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
భూమిలో ఖనిజ వనరులు తగ్గిపోతాయి. కనుగొనబడిన, గుర్తించబడిన చాలా ఖనిజాలు తరిగిపోతాయి. అల్యూమినియం, ఇనుము యొక్క ఖనిజ నిలువలు లేదా ఖనిజ నిక్షేపాలు కనుమరుగైపోతుండడం వలన వాటి ధరలు చాలా పెరిగిపోయే అవకాశం ఉంది. ఈ మూలకాలతో తయారుచేసే పరికరాలు, యంత్రాల యొక్క ధరలు పెరిగి, వాటిని కొనడం మరియు వినియోగించడం కష్టమైపోతుంది.
10th Class Biology 10th lesson సహజ వనరులు 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
ప్రశ్న 1.
అడవి ఒక పునరుద్దరింపదగిన వనరు. కాని ప్రతి సంవత్సరం భూమిపై 36 మిలియన్ల ఎకరాల అడవులు నరికివేయబడుతున్న నేపథ్యంలో అవి పునరుద్ధరింపబడని వనరులుగా మారకుండుటకు నీవు ఎటువంటి సూచనలు చేస్తావు?
జవాబు:
ప్రపంచానికి అడవులు ఊపిరితిత్తులు వంటివి. అవి పునరుద్ధరింపబడని వనరుగా మారకుండా ఉండుటకు నేనిచ్చే సూచనలు :
- సుస్థిర అటవీ విధానాల ద్వారా భవిష్యత్ తరాలవారికి అందచేయగలం.
- చాలా తక్కువగా చెట్లను నరకడం.
- సహజంగా చెట్లు, తిరిగి ఎదగటానికి అవకాశం కల్గించే పద్ధతులు పాటించాలి.
- ఎత్తైన చెట్లు, పెద్ద చెట్లను నరికివేసే విధానాలను నిషేధించాలి.
- పునఃచక్రీయ పద్ధతులు అవలంబించడం.
- కలపకు బదులుగా ప్రత్యామ్నాయ వనరులను ఉపయోగించటం.
- అడవులను దహించకుండా చేయడం.
ప్రశ్న 2.
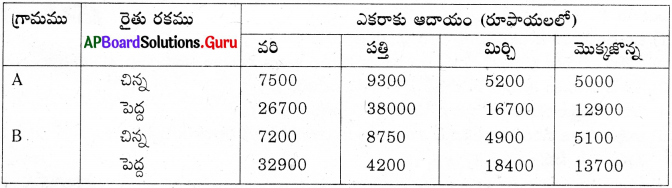
పై పట్టికను పరిశీలించి, క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు ఇవ్వండి.
1) రెండు గ్రామములలో చిన్న రైతులు పండించడానికి అనుకూలమైన పంట ఏది?
జవాబు:
మొక్కజొన్న, వరి.
2) నీవు ఒకవేళ పెద్ద రైతువైతే ఏ పంట పండిస్తావు ?
జవాబు:
మిర్చి, వరి
3) A మరియు B గ్రామముల మధ్య ఏమైన పోలికలను గమనించావా?
జవాబు:
A మరియు B గ్రామాలలో చిన్న పెద్ద రైతు ఒకే రకమైన పంటలు పండిస్తున్నారు. A మరియు B గ్రామాలలో చిన్నకారు రైతు కంటే పెద్దకారు రైతు ఎకరాకు వచ్చే ఆదాయం ఎక్కువగా ఉంది. రెండు గ్రామాలలో పెద్ద రైతు ఎక్కువ ఆదాయాన్ని వరి, మిర్చి, మొక్కజొన్న పంటలలో పొందుతున్నారు.
4) పై పట్టికలో తక్కువ ఆదాయాన్ని ఇచ్చే పంట ఏది?
జవాబు:
పత్తి
5) పంటకు, ఆదాయంనకు ఏమైన సంబంధం ఉన్నదా? వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఉంది. పంట దిగుబడి ఎక్కువగా ఉన్నప్పుడు ఆదాయం ఎక్కువగా ఉంటుంది. (లేదా)
ఉండకపోవచ్చు. మార్కెటు అవసరాన్ని బట్టి ఆదాయం ఉంటుంది. వాణిజ్య పంటలకు ఎక్కువ ఆదాయం వస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 3.
AR లు అనగానేమి? ఇవి పర్యావరణ సంరక్షణకు ఎలా ఉపయోగపడతాయి?
(లేదా)
పర్యావరణ సంరక్షణకు అవసరమయ్యే 4R సూత్రం వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
పర్యావరణ సంరక్షణకు నాలుగు నియమాలు పాటించాలి. అవి :
తగ్గించడం (Reduce) :
వనరులను తక్కువగా -వృథా చేయకుండా వినియోగించడం, కారుతున్న నల్లాలను, పంపులను సరిచేయడం, స్నానాల గదిలో షవర్ల వాడకం తగ్గించడం ద్వారా నీటి వినియోగాన్ని తగ్గించవచ్చు. అవసరం లేని సమయాల్లో విద్యుద్దీపాలను, ఫ్యాన్లను ఆపివేయడం వలన విద్యుచ్ఛక్తిని పొదుపు చేయవచ్చు.
తిరిగి వాడడం (Reuse) :
పారేయకుండా తిరిగి ఉపయోగించుకోవడం. కాగితాన్ని తిరిగి వాడడం వలన మొక్కలను కాపాడడమే కాకుండా కాలుష్యాన్ని తగ్గించినవారమవుతాము.

పునఃచక్రీయం (Recycle) :
ఇది అన్నిసార్లు సాధ్యం కాకపోవచ్చు. ఉదాహరణకు ప్లాస్టికను పునఃచక్రీయం చేయడమనేది చాలా క్లిష్టమైన, ప్రమాదకరమైన ప్రక్రియ. ప్లాస్టిక్కు గల సంక్లిష్టత వలన ఈ సమస్య ఉత్పన్నమవుతుంది. ప్లాస్టిక్ వలన ఎన్ని ఉపయోగాలు ఉన్నాయో అన్ని రకాల నష్టాలూ ఉన్నాయి. ఒక రకమైన ప్లాస్టికను అదే రకం నుండి పునఃచక్రీయం చేయాలి. కావున, వివిధ రకాల ప్లాస్టిక్ లను పునఃచక్రీయం చేయడానికి పునఃచక్రీయం ముందు వేరుచేయాలి. ఒక్కొక్క దానిని ఒక్కొక్క రకంగా రీసైకిల్ చేయాల్సి ఉంటుంది.
తిరిగి ఏర్పాటుచేయటం (Recover) :
మనం వాడుకొన్న వనరులను, తిరిగి నెలకొల్పటాన్ని తిరిగి ఏర్పాటు చేయటం అంటారు.
ఉదా : కర్మాగారాలు, రోడ్ల నిర్మాణం కోసం చెట్లను కొట్టివేసినపుడు, అడవులను నరికివేసినపుడు ప్రత్యామ్నాయంగా మరొకచోట చెట్లను పెంచటం అవసరం.
ప్రశ్న 4.
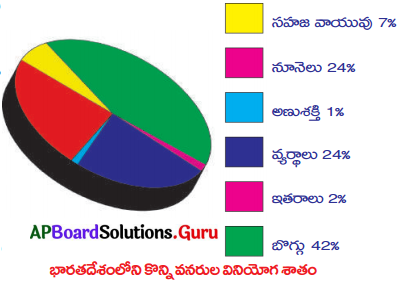
ఈ క్రింది పై (Ple) చార్టును విశ్లేషించి, దిగువనీయబడిన ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు వ్రాయుము.
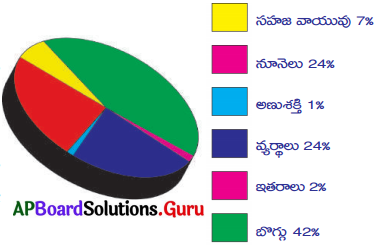
జవాబు:
i) వీటిలో శిలాజ ఇంధనాలను గుర్తించి రాయండి.
జవాబు:
బొగ్గు, సహజవాయువు, నూనెలు.
ii) వ్యర్థాలను ప్రధాన ఇంధన వనరులుగా భవిష్యత్తులో ఎందుకు అభివృద్ధి చేసుకోవాలి?
జవాబు:
భవిష్యత్ లో శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు తరిగిపోవచ్చు కనుక ప్రత్యామ్నాయ ఇంధనముగా వ్యర్థాలను భవిష్యత్తులో ఉపయోగించవచ్చును.
iii) శిలాజ ఇంధనాలపై దీర్ఘకాలం మనం ఎందుకు ఆధారపడలేము?
జవాబు:
శిలాజ ఇంధనాలు పునరుద్దరింపదగని వనరులు కనుక.
iv) శిలాజ ఇంధనాలకు ప్రత్యామ్నాయంగా ఉపయోగించగల ఇంధన వనరులు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
సౌరశక్తి, పవనశక్తి, తరంగశక్తి, అణుశక్తి, వ్యర్థాలు.

ప్రశ్న 5.
నీటి యాజమాన్యం కొరకు పాటించవలసిన సముదాయ ఆధారిత విధానాలు, రైతు ఆధారిత విధానాలను మరియు వాటి ప్రాధాన్యతను వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
సముదాయ ఆధారిత విధానాలు :
14 నీటిని నిలువ చేసే నిర్మాణాలు, 60 చిన్న ఇంకుడు గుంతలు, డైక్లు, 38 హెక్టార్ల పొలంగట్ల ద్వారా 28 ఎండిన బావులలోకి నీరు చేరేలా చేయడం జరిగింది. వర్షపు నీటిని నీటి వినియోగదారుల సంఘంగా ఏర్పడి సంరక్షించుకోగలిగారు. ఈ నిర్మాణాలలో నిలువ చేయబడిన నీరు భూగర్భజలాల నీటి మట్టాన్ని పెంచుటకు ఉపయోగించబడింది.
రైతు ఆధారిత విధానాలు :
వెడల్పు చాళ్ళు తీయడం, తక్కువ ఎత్తు పెరిగే పంటలను పెంచడం, కాంటూరు సేద్యం చేయడం, గట్ల మీద గెరిసిడియా చెట్లను పెంచడం, సూక్ష్మ సేద్య పద్ధతులు వంటివి వ్యక్తిగతంగా రైతులు వారి వారి పొలాలలో చేయడం జరిగింది. వీటి వలన నేల, వర్షపు నీరు, పోషకాలు దుర్వినియోగం కాకుండా కలుపు నివారణా పద్ధతులు పాటించడం, నైట్రోజన్ నిలువలను పెంచడం జరుగుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 6.
రైతు ఆధారిత విధానాల గూర్చి రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- రైతు ఆధారిత విధానాల ద్వారా నేల, నీటి సంరక్షణ కార్యక్రమాలను అమలు చేశారు. వెడల్పు చాళ్లు తియ్యడం, తక్కువ ఎత్తు పెరిగే పంటలు పెంచడం, కాంటూర్ సేద్యం చేయడం మొదలైన యాజమాన్య పద్ధతులు పాటిస్తూ నేల, నీరు, పోషకాలు దుర్వినియోగం కాకుండా కాపాడుతారు.
- కలుపు నివారణ పద్ధతులు పాటించడంతోబాటు 38 హెక్టార్ల పొలాల చుట్టూ దీర్ఘచతురస్రాకారంలో గట్ట కట్టడం, వాలులకు అడ్డంగా కాంటూర్ కందకాలు ఏర్పాటు చేయడం ద్వారా వర్షపు నీటిని సంరక్షించవచ్చు.
- గట్లు బలంగా ఉండేందుకు. నేలలో నైట్రోజన్ నిల్వలు పెరిగేందుకు గట్టమీద గ్లైరిసీడియా (లెగ్యూమ్ మొక్క) లను పెంచుతారు. రైతులు ఉమ్మడిగా నీటిని వినియోగించుకోడం, సూక్ష్మ సేద్యం పద్దతులు చేస్తారు.
- వెడల్పు చాళ్లు తీయడం, సూక్ష్మసేద్య పద్ధతులు పాటించడం వలన హెక్టారుకు 250 కిలోల పైగా జొన్నలు, 50 కిలోల పైగా మొక్కజొన్నలు అధిక దిగుబడి సాధించవచ్చు.
- బిందు సేద్యం అమలు చేయడం వలన 70% నీటిని పొదుపు చేయవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 7.
అడవుల నరికివేత వలన కలిగే నష్టాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
- కలప లేదా వ్యవసాయం లేదా అభివృద్ధి పేరిట ప్రజలు అడవులను నరుకుతున్నారు.
- ప్రతి సంవత్సరం భూమిపై 36 మిలియన్ల ఎకరాల అడవులు (ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని సగభాగం కన్నా ఎక్కువ భాగం) నరికివేయబడుతున్నాయి.
- అడవులను నరికివేయడం వలన వన్యజాతుల ఆవాసాలు నాశనమవుతాయి. నేలకోత ఎక్కువవుతుంది.
- హరిత గృహ వాయువులు (Green house gases) విడుదలై, భౌగోళిక వెచ్చదనానికి (Global warming) దారితీస్తాయి
- ప్రపంచంలో విడుదలయ్యే హరిత గృహ వాయువుల మొత్తంలో 15% వాయువులు అడవులను నరకడం వలననే విడుదలవుతున్నాయి.
- అటవీ ఉత్పత్తుల సేకరణ కోసం, వంటచెరకుకు మరియు జీవనోపాధి కోసం, మనుగడ కోసం అడవులపై ఆధారపడి జీవించే ప్రజలు అడవులు నరకడం వలన చాలా నష్టపోతున్నారు.
ప్రశ్న 8.
అడవుల సంరక్షణకు పాటించవలసిన సుస్థిర పద్ధతులు తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
అడవులను కాపాడుకోడానికి సుస్థిర అటవీ పద్దతులు కొన్ని పాటించాలి. ఉదాహరణకు చాలా తక్కువగా చెట్లు నరకడం, సహజంగా చెట్లు తిరిగి ఎదగడానికి అవకాశం కలిగించే పద్ధతులను పాటించడం, ఎత్తయిన చెట్లు, పెద్ద పెద్ద చెట్లను పెద్ద ఎత్తున నరికివేసే విధానాలను నిషేధించడం మొదలైనవి.
పునఃచక్రీయ వలన చెట్లను సంరక్షించవచ్చును. ఉదాహరణకు చైనా మరియు మెక్సికో దేశాల ప్రజలు రాయడానికి మరియు ఇతర అవసరాలకు వాడే కాగితాన్ని, కార్డుబోర్డును తిరిగి వాడడం ద్వారా అడవులను సంరక్షిస్తున్నారు. ప్రపంచంలోని కాగితంలో సగభాగం తిరిగి వాడడం జరిగితే, ప్రపంచంలోని కొత్త కాగితానికి ఉన్న అవసరం తీరడమే కాకుండా భూమి పైనున్న చెట్లను కాపాడినట్లవుతుంది. కొన్ని కలప వస్తువులకు బదులుగా వెదురు వాడవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 9.
నేల సంరక్షణ విధానాలు తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- నేలల సంరక్షణా విధానాలలో కాంటూర్ పట్టి పంటల (Contour strip cropping) పద్ధతి ఒకటి. ఈ విధానంలో నేలవాలుకు అడ్డంగా, గాలివీచే దిశకు అడ్డంగా దున్ని ఒక్కొక్క వరుసలో ఒక్కొక్క రకం పంటను వేస్తారు. ఉదాహరణకు ఒక వరుసలో మొక్కజొన్న, మరొక వరుసలో గోధుమ, ఇంకొక వరుసలో క్లోవర్ (పులిచింత) పంటలు పండించడం.
- వేరువేరు పంట మొక్కలు వేరువేరు రకాల వేరు వ్యవస్థలను, భిన్న పరిమాణంలో ఆకులను కలిగి ఉంటాయి. కాబట్టి నేలక్రమక్షయం జరగకుండా కాపాడుతాయి.
- అలాగే పంటకోసేటపుడు కూడా ఒక్కొక్క మొక్కను లేదా చిన్న గుంపును తీసివేయడం వంటి ఎంపిక వంట పద్దతులు (Selective harvesting) పాటించడం వల్ల మిగిలిన మొక్కలు నేల కొట్టుకుపోకుండా పట్టి ఉంచుతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 10.
వనరుల సంరక్షణకు అంతర్జాతీయ సంస్థలు చూపుతున్న శ్రద్ధను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
ఎన్నో అంతర్జాతీయ సంస్థలు వనరుల సంరక్షణ పట్ల శ్రద్ధ చూపుతున్నాయి. వర్షారణ్యాలను కాపాడడం, జంతువులు అంతరించిపోకుండా సంరక్షించడం మరియు గాలిని శుభ్రపరచడం వంటి కార్యకలాపాలను సంస్థ సభ్యులు బలపరుస్తున్నారు. 1948లో ప్రభుత్వ, ప్రైవేటు సమూహాల సమ్మేళనం ‘ద ఇంటర్నేషనల్ యూనియన్ ఫర్ ద కన్ఫర్వేషన్ ఆఫ్ నేచర్ (IUCN)’ ఏర్పడింది.
1980లో ఇది ప్రపంచ సంరక్షణా విధానాన్ని ప్రతిపాదించింది. ఎన్నో దేశాల ప్రభుత్వాలు వాటి సంరక్షణా పథకాలను అభివృద్ధి చేసుకోవడంలో IUCN విధానాలనే అనుసరించాయి. అంతేకాకుండా IUCN అనే సంస్థ ప్రమాదం అంచున ఉన్న వన్యజాతులను, జాతీయ ఉద్యానవనాలు, సంరక్షణా కేంద్రాలు, పర్యావరణానికి సంబంధించిన అంశాల స్థాయిని పరిశీలిస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 11.
మీ గ్రామంలో బావులు, చెరువులు ఎండిపోయాయి. భూగర్భజలాలు తగ్గిపోయాయి. ఇందుకు గల కారణాలను గుర్తించండి. మీ గ్రామంలోని రైతులందరూ కలిసి పనిచేస్తే నీటి కరవు తీరుతుందా?
జవాబు:
భూగర్భజలాలు తగ్గిపోవడానికి కారణాలు :
- ఈ మధ్యకాలములో ఋతుపవనములు సకాలములో రాకపోవడము, వచ్చినా సరిపోయిన మొత్తములో వర్షములు ఇవ్వకపోవడం ప్రధాన కారణంగా భావించవచ్చు.
- తక్కువ మొత్తంలో బోరుబావులు తవ్వి సాగునీటి అవసరాల కోసం విచక్షణారహితంగా వినియోగించడం. వీటి ద్వారా ఎక్కువ మొత్తంలో నీటిని ఉపయోగించటం వలన భూగర్భజల మట్టాలు పడిపోవడం జరిగినది.
- ఆహార పంటలు ఎక్కువగా పండించుట వలన కూడా నీటి వినియోగం ఎక్కువ కావటం భూగర్భజలమట్టాలు పడిపోవడం జరుగుతుంది.
- మా గ్రామంలోని రైతులందరూ ఉమ్మడిగా నీటిని వినియోగిస్తే పంటలకు నీటికొరత ఉండదు. మా ఊరిలో ఉన్న రైతులను నీటి సద్వినియోగం కొరకు ఉమ్మడిగా మరియు సూక్ష్మనీటిపారుదల పద్ధతులను అవలంబించవలసినదిగా సూచించడమైనది.
- సూక్ష్మసాగునీటి పద్ధతులయిన బిందుసేద్యం, స్ప్రింక్లర్లు మొదలైనవి వినియోగించడం వలన నీటిని పొదుపుగా వాడటమే కాకుండా ఎక్కువ మొత్తంలో దిగుబడులు సాధించడం జరిగింది.

ప్రశ్న 12.
మీ గ్రామంలో తాగునీటికి, సాగునీటికి తీవ్రమైన కొరత ఉంది అనుకుందాం. దానిని నివారించడానికి నీవు ఇచ్చే సలహాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
- నీటిని పొదుపుగా వాడుకోవలసిన అవసరాన్ని, సంరక్షించుకోవలసిన విధానాన్ని గురించి ప్రజలకు అవగాహన కల్పిస్తాను.
- నీటి వాడకంలో వృథాను అరికట్టే విధంగా ప్రజలను ప్రోత్సహిస్తాను.
- భూగర్భ జలమట్టాలను పెంచడానికి రీఛార్జి గుంటలను ఇళ్ళు మరియు పాఠశాల ఆవరణలో నిర్మించే విధంగా ప్రోత్సహిస్తాను.
- బీడు భూముల్లో విరివిగా మొక్కలు నాటే కార్యక్రమాన్ని చేపడతాను.
- రైతులు సూక్ష్మ నీటి సాగు పద్ధతులైన బిందుసేద్యం, స్ప్రింక్లర్స్ విధానాలను ఆచరించే విధంగా ప్రోత్సహిస్తాను.
- అందుబాటులో ఉన్న నీటి వనరులను సామూహికంగా వినియోగించుకునే విధంగా రైతులను ప్రోత్సహిస్తాను.
- ఇంకుడు గుంతలు మరియు చెరువులను తవ్వి వృథాగా పోయే వర్షపునీటిని పరిరక్షించి భూగర్భజలమట్టాలను పెంచడానికి ప్రయత్నిస్తాను.
- వాటర్ షెడ్ పథకాల అమలును పర్యవేక్షిస్తాను.
ప్రశ్న 13.
సహజ వనరుల సద్వినియోగం దేశ ఆర్థికాభివృద్ధిలో ఎంతో దోహదం చేస్తుందని నీవు ఎలా చెప్పగలవు?
జవాబు:
- గాలి, నీరు, నేల, ఖనిజాలు, ఇంధనాలు, మొక్కలు, జంతువులు భూమిపై ఉండే సహజ వనరులు.
- వర్తమానంలో మరియు భవిష్యత్తులో జీవులన్నీ లాభం పొందాలంటే సహజ వనరులు సంరక్షించబడాలి.
- ప్రజలు చాలా వరకు పునరుద్దరింపదగిన మరియు పునరుద్ధరింపలేని వనరులను నాశనం చేస్తుంటారు. మనుగడ కొనసాగించడమనేది, సహజ వనరులను విచక్షణతో ఉపయోగించడంపై ఆధారపడి ఉంటుంది.
- జంతువులు ఇతర ఆవాసాలకు తరలిపోయేలా వాటికి నష్టం చేకూరుస్తూ భవిష్యత్తులో ఉపయోగపడవలసిన వనరులను తరిగిపోయేలా చేస్తూ, నేడు అందుబాటులో ఉన్న వనరులన్నింటినీ నాశనం చేస్తూ మనం అభివృద్ధి యొక్క ప్రయోజనాలను లెక్కిస్తున్నాం.
- అభివృద్ధి, సంరక్షణ రెండింటికీ ప్రాధాన్యమిస్తూ మనుగడ సాగించవచ్చును.
- భావితరాలకు అవసరమయ్యే సహజవనరులను అందుబాటులో ఉండేవిధంగా మనం పర్యావరణాన్ని ఉపయోగించుకున్నట్లయితే అది సుస్థిరాభివృద్ధి అవుతుంది.
- సుస్థిరంగా జీవించాలంటే మనం ఎన్నో రకాల వనరులను జాగ్రత్తగా వినియోగిస్తూ సంరక్షించుకోవాలి.
ప్రశ్న 14.
రైతులకు వ్యవసాయం ఎంపిక విధానంపై అవగాహన కల్పించటానికి నీవు చేపట్టే కార్యక్రమాలేవి?
జవాబు:
- వ్యవసాయ సంబంధ మరియు అనుబంధ అంశాలపై రైతులకు అవగాహన కల్పించడానికి రైతు సదస్సులు ఏర్పాటు చేస్తాను.
- రసాయనిక ఎరువులు కలిగించే నషాన్ని రైతులకు వివరించి ఆరానిక్ ఎరువులను వాడే విధంగా ప్రోత్సహిసాను.
- మృత్తిక యొక్క సహజ స్వరూపాన్ని కాపాడవలసిన అవసరతను రైతులకు వివరిస్తాను. తద్వారా దిగుబడి ఎక్కువ సాధించుటకు రైతులను ప్రోత్సహిస్తాను.
- దిగుబడులను పెంచడానికి రైతులు అధిక దిగుబడినిచ్చే వంగడాలను వినియోగించే విధంగా ప్రోత్సహిస్తాను.
- మొక్కల సంఖ్యను అధికం చేయడానికి కణజాలవర్గన పద్ధతులను అవలంబించే విధంగా రైతులకు అవగాహన కలిగిస్తాను.
- నీటిని పొదుపుగా వాడటానికి సూక్ష్మ సేద్య సాగునీటి పద్దతులైన బిందుసేద్యం మరియు స్ప్రింక్లర్ విధానమును అవలంబించే విధంగా రైతులకు సూచనలిస్తాను.
- రెతులు సామూహికంగా నీటిని వినియోగించుకునే విధంగా ప్రణాళికలను రూపొందిస్తాను. తద్వారా పంట సాగుకు అతి తక్కువ మొత్తంలో నీరు వాడే విధంగా చూస్తాను.
- వర్షపు నీటిని ఆదాచేయడానికి ఇంకుడు గుంతలు, చెరువులు నిర్మించే విధంగా రైతులను ప్రోత్సహిస్తాను.
10th Class Biology 10th lesson సహజ వనరులు 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
ఉదాహరణలు ఇవ్వండి
1. బిందు సేద్యం అనేది ఒక రకమైన సూక్ష్మ నీటిపారుదల సాంకేతికత. మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
స్ప్రింక్లర్
2. భూగర్భ జలాలు లేదా ఎండిన బోర్లను బాగా రీఛార్జ్ చేయడానికి పెర్కొలేషన్ ట్యాంక్ ఉపయోగించబదుతుంది. మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
ఇంకుడు గుంటలు
3. రైతు ఆధారిత సేద్యానికి బ్రాడ్ బెడ్ ఫర్రో ల్యాండ్ ఫామ్ ఒక ఉదాహరణ. మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
ఆకృతి నాటడం
4. పొడి ప్రాంతాల్లో పెరగడానికి అనువుగా ఉండే లెగ్యుమినస్ మొక్కకు ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
గ్లైరిసిడియా
5. శిలాజ ఇంధనాలకు పెట్రోలియం మరియు సహజ వాయువు ఉదాహరణలు. మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
బొగ్గు
6. గోండు ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లో ఒక రకమైన గిరిజనులు. మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
చెంచు
7. జపాన్ ఆటోమొబైల్స్ తయారీలో రీసైకిల్ ముడి పదార్థాలను వాడుతున్న దేశం. ఇటువంటి దేశానికి మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
అమెరికా సంయుక్త రాష్ట్రాలు
8. సూర్యకాంతి విద్యుత్ ఉత్పత్తిలో ఉపయోగించే ప్రత్యామ్నాయ వనరు. మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
పవన శక్తి
9. అడవి అంటే మనం నిర్వహించాల్సిన మరియు పరిరక్షించాల్సిన వనరు. ఇటువంటి మరో ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
నేల / నీరు
10. గ్లైరిసిడియా మొక్కల నేలను సారవంతం చేయటానికి ఉపయోగిస్తారు. ఇటువంటి మొక్కలకు మరో ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
సీతాఫల మొక్కలు
11. కాంటూర్ సేద్యం అనేది నేల సంరక్షణకు ఒక పద్ధతి. మరొక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
పంట మార్పిడి.
విస్తరించుము
12. ICRISAT ని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఇంటర్నేషనల్ క్రాప్ రీసెర్చ్ ఇనిస్టిట్యూట్ ఫర్ సెమీ – అరిడ్ ట్రాపిక్స్
13. T.M.Cని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
వెయ్యి మిలియన్ క్యూబిక్ అడుగులు
14. B.B.F ని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
బ్రాడ్ బెడ్ ఫర్రో
15. MTRని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
మౌంటైన్ టాప్ రిమూవల్

16. 4Rని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
తగ్గించటం (Reduce), పునర్వినియోగం (Re-use), పునఃచక్రీయము (Recycle), తిరిగి పొందటం (Recover).
17. I.U.C.Nని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఇంటర్నేషనల్ యూనియన్ ఫర్ ది కన్జర్వేషన్ ఆఫ్
18. O.N.G.Cని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఆయిల్ అండ్ నేచురల్ గ్యాస్ కార్పొరేషన్
19. U.N.D.P ని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఐక్యరాజ్యసమితి అభివృద్ధి కార్యక్రమం
20. FAOని విస్తరించండి.
జవాబు:
ఆహార మరియు వ్యవసాయ సంస్థ
దోషాన్ని గుర్తించి, సరిచేసి రాయండి
21. ఉపరితల నీటి పారుదల పద్దతి నీటి వినియోగాన్ని 70% తగ్గిస్తుంది.
జవాబు:
బిందు సేద్యం పద్దతి నీటి వినియోగాన్ని 70% తగ్గిస్తుంది.
22. ప్రతి సంవత్సరం భూమి అటవీ నిర్మూలనకు సుమారు 63 మిలియన్ ఎకరాల అడవిని కోల్పోతుంది.
జవాబు:
ప్రతి సంవత్సరం భూమి అటవీ నిర్మూలనకు సుమారు 36 మిలియన్ ఎకరాల అడవిని కోల్పోతుంది.
23. పులులను రక్షించడానికి చిప్కో ఉద్యమం ముడిపడి ఉంది.
జవాబు:
చెట్లు రక్షించడానికి చిప్కో ఉద్యమం ముడిపడి ఉంది.
24. నదీ జలాల pH 7 పైన ఉంటే నదీ జలాలు ఆమ్ల వ్యర్థాలతో కలుషితమవుతాయని చెబుతారు.
జవాబు:
నదీ జలాల pH 7 పైన ఉంటే నదీ జలాలు క్షార వ్యర్థాలతో కలుషితమవుతాయని చెబుతారు.
ఖాళీలను పూరించండి
25. ఫ్లో చార్టులో ఖాళీని పూరించండి.
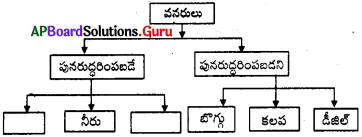
జవాబు:
గాలి, సూర్యరశ్మి
26. అటవీ నిర్మూలన వలన ప్రపంచంలోని గ్రీన్హౌస్ గ్యాస్ ఉద్గారాలలో ……….. వెలువడుతుంది.
జవాబు:
15%
27. భూమిపై మంచినీటి శాతం …………
జవాబు:
2.5 – 2.75%
నేను ఎవరు?
28. మేము రాజస్థాన్లో గిరిజనులం. ప్రకృతిని పరిరక్షించదానికి మాకు 29 నియమాల సమితి ఉంది. మేము ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
బిష్ణోలు
29. నా కుమార్తె, మా గ్రామస్తులు మరియు నేను అటవీ స్థలం కోసం రాజు సైనికుడిచే చెట్లను నరికివేయకుండా కాపాడాము. నేను ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
అమృతా దేవి

30. నేను హిమాలయ లోయలలో అటవీ నిర్మూలనకు వ్యతిరేకంగా పోరాడుతున్నాను. మరియు అటవీ నిర్మూలనకు వ్యతిరేకంగా నా ఉద్యమాన్ని చిప్కో ఉద్యమం అంటారు. నేను ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
సుందర్లాల్ బహుగుణ
31. నేను పర్యావరణవేత్తని. నేను నర్మదా నదికి అడ్డంగా అనేక ఆనకట్టలను నిర్మిస్తున్నాను. నేను ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
మేధా పాట్కర్
32. నేను ఒక మొక్కను. నా విత్తనాలను బయోడీజిల్ ఉత్పత్తికి ఉపయోగిస్తారు. నేను ఎవరు?
జవాబు:
జట్రోపా కర్కస్ (అడవి ఆముదం)
33. మీరు గది నుండి బయలుదేరినప్పుడు లైట్ మరియు ఫ్యాన్ ఆపివేయండి. ఇది ఏ రకమైన R?
జవాబు:
తగ్గింపు
జతపరచుట
34. సరిగ్గా సరిపోలినదాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
షవర్ బాత్ మానటం – తగ్గింపు
స్నేహితులతో పుస్తకాలను పంచుకోండి – రీసైకిల్ చేయడం
లీకైన కుళాయిలను రిపేర్ చేయండి – పునర్వినియోగం
జవాబు:
షవర్ బాత్ మానటం – తగ్గింపు
35. సరిగ్గా సరిపోలినదాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
వస్త్ర సంచులను వాడండి – పునర్వినియోగం
పునర్వినియోగపరచదగిన బ్యాటరీలను
ఉపయోగించండి – తగ్గించడం
పెన్ను రీఫిల్ చేయండి – రీసైకిల్ చేయడం
జవాబు:
పునర్వినియోగపరచదగిన బ్యాటరీలను ఉపయోగించండి – తగ్గించడం
36. సరిగ్గా సరిపోలినదాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
జట్రోపా – శిలాజ ఇంధనం
గ్లిరిసిడియా – లెగ్యుమినస్ మొక్క
కస్టర్డ్ ఆపిల్ – జీవ ఇంధన కర్మాగారం
జవాబు:
గ్లిరిసిడియా – లెగ్యుమినస్. మొక్క
37. సరిగ్గా సరిపోలనిదాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
బ్రాడ్ బెడ్ ఫర్రో – రైతు ఆధారిత సేద్యం
వర్షాధార ఆనకట్ట – సమాజ ఆధారిత సేద్యం
పునరుత్పాదక వనరు – బొగ్గు
జవాబు:
పునరుత్పాదక వనరు – బొగ్గు
నినాదాలు
38. ర్యాలీ నిర్వహించడానికి మీ పాఠశాలలో ఈ క్రింది నినాదాలు తయారుచేయబడ్డాయి. ఏ సందర్భంగా ర్యాలీ నిర్వహిస్తారు?
చెట్టును కత్తిరించవద్దు – జీవితాన్ని కత్తిరించవద్దు
చెట్టును పెంచండి – వరదకు దూరంగా ఉండండి.
జవాబు:
జూన్-6 – ప్రపంచ పర్యావరణ దినం.
39. ఈ క్రింది నినాదాల యొక్క ఉద్దేశ్యం ఏమిటి?
నీరు జీవితాధారం.
ప్రతి నీటి చుక్కను లెక్కింపు చేద్దాం.
ఒక చుక్కను దాచండి – భవిష్యత్తును కాపాడండి.
జవాబు:
నీటి పొదుపు

40. కింది నినాదాల యొక్క ప్రాథమిక భావన ఏమిటి?
నూనె కంటే నేల విలువైనది.
రోజుకు ఒక చెట్టును నాటండి మరియు నేల కోతను దూరంగా ఉంచండి.
జవాబు:
నేల పరిరక్షణ
41. ఓజోన్ యొక్క ప్రాముఖ్యత ఈ క్రింది నినాదాలలో ప్రస్తావించబడింది. ఇది ఏ రకమైన కిరణాల నుండి మనలను రక్షిస్తుంది?
ఓజోన్ లేదు, డెడ్ జోన్ మాత్రమే
ఓజోన్ ప్రకృతి స్వంత సన్
జవాబు:
అతినీలలోహిత కిరణాలు
బొమ్మలపై ప్రశ్నలు
42.

ఈ లోగో దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
సమగ్రాభివృద్ధి
43.

ఈ లోగో దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
పునఃచక్రీయము
44.

ఈ చిత్రం ఏ 4R ను సూచిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
తిరిగి వాడడం
10th Class Biology 10th lesson సహజ వనరులు 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
1. భూగర్భ జలాలు తగ్గటానికి కారణం ………..
A) వర్షం పడకపోవడం
B) అడవుల నరికివేత
C) బోర్ బావుల సంఖ్య ఎక్కువైపోవుట
D) పైవన్నీ
జవాబు:
D) పైవన్నీ
2. తక్కువ నీటి సౌకర్యాలు ఉన్న ప్రాంతాలలో రైతులు అనుసరించదగిన విధానం
i) స్వల్పకాలిక పంటలు పండించడం.
ii) వ్యాపార పంటలు పండించడం.
iii) బిందు సేద్యం చేయడం.
iv) పంట విరామం ప్రకటించడం.
A) (i), (ii)
B) (i), (ii), (iii)
C) (i), (iv)
D) (iii), (iv)
జవాబు:
B) (i), (ii), (iii)
3. ఒక రైతు తన పంటపొలంలో కీటకాలను నివారించేందుకు తొండలను ప్రవేశపెట్టాడు. ఇది ఒక …..
A) పర్యావరణ నైతికత పద్ధతి
B) జైవిక నియంత్రణ పద్ధతి
C) జైవిక వ్యవస్థాపనం
D) జైవిక వృద్ధీకరణము
జవాబు:
B) జైవిక నియంత్రణ పద్ధతి

4. క్రింది వానిలో పునరుద్ధరింపలేని వనరు
A) నీరు
B) సౌరశక్తి
C) బొగ్గు
D) మృత్తిక
జవాబు:
C) బొగ్గు
5. అడవులను అధికంగా నిర్మూలిస్తే జరిగే పరిణామాన్ని
A) అగ్నిపర్వతాలు బ్రద్దలగుట
B) భూకంపాలు వస్తాయి.
C) భౌగోళిక వెచ్చదనం కలుగును
D) సునామీలు వస్తాయి.
జవాబు:
C) భౌగోళిక వెచ్చదనం కలుగును
6. ఇంధనాన్ని ఆదా చేసే మార్గం ఇది కాదు.
A) సైకిలను ఉపయోగించడం
B) కారుకు బదులు రైలులో ప్రయాణించడం
C) సెల్ఫోన్ను వాడడం
D) బావి నుండి నీటిని తోడుకోవడం
జవాబు:
C) సెల్ఫోన్ను వాడడం
7. గాలిని కలుషితం చేసే రేణురూప కలుషితం
A) CO2
B) బూడిద
C) SO2
D) CO
జవాబు:
B) బూడిద
8. క్రింది వృత్త రేఖాచిత్రంలో “నీటి పారుదల సౌకర్యాలు – విస్తీర్ణం” వివరాలు చూపబడ్డాయి. అందు భూగర్భ జల వనరుల శాతం ……………..

A) 40%
B) 45%
C) 43%
D) 48%
జవాబు:
C) 43%
9. IUCN యొక్క ప్రధాన విధి
A) వన్య ప్రాణుల ఆవాసాల పరిరక్షణ
B) మెట్ట పంటల అధ్యయనం
C) వైరల్ వ్యాధుల అధ్యయనం
D) నీటి పంటలు (wet land) వ్యవసాయ అధ్యయనం
జవాబు:
A) వన్య ప్రాణుల ఆవాసాల పరిరక్షణ
10. ఇంకుడు గుంట వలన ఉపయోగము ……..
A) వర్షాకాలంలో వచ్చే వరదలను అరికట్టడము
B) వ్యవసాయానికి నీరు అందించుట
C) వర్షపు నీటిని నిల్వచేయడము ,
D) భూగర్భజల మట్టాలను పెంచడము
జవాబు:
C or D
11.  ఈ లోగో దీనిని సూచిస్తుంది ……. ఊహించండి.
ఈ లోగో దీనిని సూచిస్తుంది ……. ఊహించండి.
A) రియూజ్
B) రెడ్యూస్
C) రీసైకిల్
D) అన్నీ
జవాబు:
C) రీసైకిల్

12. తరిగిపోని ఇంధన వనరుకు ఉదాహరణ
A) సహజవాయువు
B) పెట్రోలు
C) సౌరశక్తి
D) వంటచెరకు
జవాబు:
C) సౌరశక్తి
13. భూగర్భ జల మట్టాలను పెంచాలంటే …………
A) బావులు తవ్వాలి
B) కాలువలు తవ్వాలి
C) రోడ్లను తవ్వాలి
D) ఇంకుడు గుంతలు తవ్వాలి
జవాబు:
D) ఇంకుడు గుంతలు తవ్వాలి
14. నేల సంరక్షణా పదతి
A) కాంటూర్ పద్ధతి
B) గడ్డి మొక్కల పెంపకం
C) పంటమార్పిడి పద్ధతి
D) పైవన్నీ
జవాబు:
D) పైవన్నీ
15. ఓజోన్ పొర వినాశనానికి కారణమైన వాయువు …………………
A) కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సెడ్
B) ఆక్సిజన్
C) క్లోరోఫ్లోరోకార్బన్స్
D) నైట్రోజన్ డై ఆక్సెడ్
జవాబు:
C) క్లోరోఫ్లోరోకార్బన్స్
16. UNDP అనగా……………….
A) United Nations Development Plan
B) United Nations Development Programme
C) United Nations Drought Programme
D) United Nations Dropout Programme
జవాబు:
B) United Nations Development Programme
17. ICRISAT ఉన్న ప్రదేశం
A) బెంగళూరు
B) హైదరాబాద్
C) చెన్నై
D) పుణె
జవాబు:
B) హైదరాబాద్
18. ఈ గుర్తు దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది?

A) UNDP
B) ఇంకుడు గుంతలు
C) సుస్థిర అభివృద్ధి
D) పునః చక్రీయం లోగో
జవాబు:
C) సుస్థిర అభివృద్ధి
19. క్రింది వాక్యా లలో సరియైనది.
a) అభివృద్ధి అవసరం
b) అభివృద్ధి పర్యావరణ స్నేహపూర్వకంగా ఉండాలి.
A) a సరియైనది, b తప్పు
B) a తప్పు, b సరియైనది.
C) a, b రెండూ తప్పు
D) a, b రెండూ సరియైనవి.
జవాబు:
D) a, b రెండూ సరియైనవి.

20. తక్కువ నీటి సౌకర్యాలు ఉన్న ప్రాంతాలలో రైతులు అనుసరించదగిన విధానం
1) స్వల్పకాలిక పంటలు పండించడం
2) వ్యాపార పంటలు పండించడం
3) బిందు సేద్యం చేయడం
4) పంట విరామం ప్రకటించడం
A) 1, 3
B) 2, 3
C) 1, 4
D) 3, 4
జవాబు:
A) 1, 3
21. దోమల జనాభా పెరుగుటకు కారణం
A) సముద్రపు నీరు
B) నదులలో ప్రవహించే నీరు
C) కాలువలలో ప్రవహించే నీరు
D) నిలకడగా ఉండే నీరు
జవాబు:
D) నిలకడగా ఉండే నీరు
22. సరి అయిన వాక్యాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
A) గ్యాసన్ను ఆదా చేయటానికి ప్రెషర్ కుక్కర్ వాడాలి.
B) ఉడికించటానికి ఎక్కువ నీరు వాడాలి.
C) వండే ముందు పదార్థాలను నానబెట్టకూడదు.
D) అన్ని అమర్చుకోకుండా స్టవ్ వెలిగించాలి.
జవాబు:
A) గ్యాసన్ను ఆదా చేయటానికి ప్రెషర్ కుక్కర్ వాడాలి.
23. అడవులు లేని ఖండం
A) ఆర్కిటిక్
B) ఆసియా
C) ఆస్ట్రేలియా
D) అంటార్కిటికా
జవాబు:
D) అంటార్కిటికా
24. మన ఇంట్లో గ్యాస్ పొదుపు చేసే మార్గం.
A) వంటలో ఎక్కువ నీరు వాడాలి.
B) వండే ముందు పదార్థాలు నానబెట్టాలి.
C) వండే ముందు పదార్థాలు ఫ్రిజ్ లో పెట్టాలి.
D) గ్యాస్పోయ్యికి పెద్ద బర్నర్ వాడాలి
జవాబు:
B) వండే ముందు పదార్థాలు నానబెట్టాలి.
25. ఈ మధ్య జరిపిన పరిశోధనలలో పొద్దుతిరుగుడు పంట దిగుబడి తగ్గడానికి కారణం ఏమని తెలిసింది?
A) పరాగ సంపర్కానికి తోడ్పడే కీటకాల సంఖ్య తగ్గిపోవడం
B) రసాయన ఎరువుల వాడకం వల్ల
C) కరువు పరిస్థితులు
D) పైవేవీ కాదు
జవాబు:
A) పరాగ సంపర్కానికి తోడ్పడే కీటకాల సంఖ్య తగ్గిపోవడం
26. భూగర్భ జలాలు పెంచుటకు చేయవలసినది
A) ఎక్కువ బోరుబావులు తవ్వడం
B) అడవుల నిర్మూలన
C) పట్టణీకరణ
D) ఇంకుడు గుంతల ఏర్పాటు
జవాబు:
D) ఇంకుడు గుంతల ఏర్పాటు

27. రైతులు గెరిసిడియా పెంచుటకు కారణం
A) కాలుష్యం తగ్గించుటకు
B) నేలలో నైట్రోజన్ నిల్వలు పెరిగేందుకు
C) కలుపు మొక్కల నియంత్రణకు
D) పశుగ్రాసం కొరకు
జవాబు:
B) నేలలో నైట్రోజన్ నిల్వలు పెరిగేందుకు
మీకు తెలుసా?

* నీటి ప్రవాహాలకు అడ్డంగా రాళ్ళ, మట్టితో అడ్డుకట్టలు కట్టి ఏర్పాటు చేసే నీటి నిల్వలను ఇంకుడు చెరువులు, (Percolation tanks) అంటారు. బంకమట్టి, ఇసుక, కంకర, గులకరాళ్ళు మొదలైన వాటిని బాగా కలిపి ఒకదానిపైన ఒకటి వచ్చేటట్లుగా పొరలు పొరలుగా చెరువు నేలను, అంచుల వెంబడి కప్పుతారు. తరువాత దీనిని గట్టిగా కుదురుకునేలా చేస్తారు. వ్యవసాయం కోసం నీటిని సరఫరా చేయడానికి మట్టికట్టకు తూము ఏర్పాటు చేస్తారు. పూర్తి నీటి నిల్వ మట్టానికి అడుగు మట్టానికి మధ్య నాలుగోవంతు ఎత్తులో తూమును ఇంకుడు చెరువు ఏర్పాటు చేస్తారు. అందువల్ల తగినంత నీటిని విడుదల చేసుకోడానికి వీలు కలుగుతుంది.
* గత కొన్ని సంవత్సరాల నుండి ఋతుపవనాల రాకడలో మార్పులు సంభవించడం వలన, భూగర్భజలాల వినియోగంపై ఒత్తిడి పెరిగింది. డ్రిల్లింగ్, లోతైన గొట్టపు బావులు, బోరు బావులను తవ్వడం వంటి చర్యల వలన విచక్షణారహితంగా రాష్ట్రంలోని భూగర్భజలాన్ని వాడడం వలన, ఈ వనరు బాగా తరిగిపోతున్నది. మన రాష్ట్రంలో 1998-2002 మధ్య కాలంలో సరాసరిగా నీటి స్థాయి 3 మీటర్ల దాక తగ్గింది.
* పూర్వం వాటర్షెడ్ (రెండు నదులు లేదా కాలువల మధ్య గల భూ ప్రాంతం) ఆధారంగా, నిపుణులైన రైతుల గ్రామ సరిహద్దులను నిర్ణయించేవారు. రెండు గ్రామాల మధ్య గల మురుగు నీటి పారుదల వ్యవస్థ ఆధారంగా, ఈ హద్దులు నిర్ణయించబడేవి. వ్యవస్థలోని సభ్యులందరూ వీటిని సామాజికంగా అంగీకరించేవారు.

* శ్రీరాంసాగర్ ప్రాజెక్టును పోచంపాడు ప్రాజెక్టు అని కూడా అంటారు. ఇది గోదావరి నదిపై ఉన్న ప్రాజెక్టు, తెలంగాణా ప్రాంతంలోని అధిక భాగానికి ఇది జీవనాధారం. కరీంనగర్, వరంగల్, ఆదిలాబాద్, నల్లగొండ, ఖమ్మం జిల్లావాసుల అవసరాలను ఈ ప్రాజెక్టు తీరుస్తుంది. గోదావరి నదిపై ఇతర రాష్ట్రంలో ఆనకట్ట నిర్మించడం వలన, ఎక్కువ శాతం నీరు ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ కు చేరకుండానే పై రాష్ట్రాలలో నిలువ చేయబడుతోంది. ఆగస్టు 2013 గణాంకాల ప్రకారం ఈ ప్రాజెక్టు యొక్క అంచనా వేయబడిన నీటి నిలువ సామర్థ్యం 80.66 టి.ఎం.సి.లు.
* ప్రపంచంలోని చాలా ప్రాంతాలలో నీటి వినియోగంపై నిషేధాలు ఉన్నాయి. ఆస్ట్రేలియాలో కరవు వల్ల సంభవించిన తీవ్రమైన నీటి కొరత వలన తోటలకు నీళ్ళు పెట్టడం, వాహనాలు కడగడం, ఈత కొలను నీటితో నింపడం వంటి కార్యకలాపాలు నిషేధించాలని ఉత్తర్వులు జారీ చేశారు. అందువల్ల ప్రజలలో నీటి వినియోగంపై అవగాహన కలిగింది. వృథాను అరికట్టగలిగారు.

* బయో డీజిల్ ఉత్పత్తికి జట్రోపా కర్కాస్ యొక్క విత్తనాలు వాడడం అనేది శక్తి సుస్లిరత్వాన్ని సాధించడంలో భారతదేశం యొక్క ప్రణాళికలో ముఖ్యమైన ఘట్టం. జట్రోపా మొక్కల పెంపకంపై ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ ప్రభుత్వం, రిలయన్స్ కంపెనీతో ఒక ఒప్పందాన్ని చేసుకుంది. జట్రోపా మొక్కలను పెంచి నాణ్యమైన బయో డీజిల్ ను ఉత్పత్తి చేయడానికి ఈ కంపెనీ కాకినాడ వద్ద 200 ఎకరాల స్థలాన్ని సేకరించింది. జీవ ఇంధనాలను తయారుచేసే పద్దతిని బయో ఎస్టరిఫికేషన్ అంటారు.
పునశ్చరణ

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


![]()

![]()
![]()

![]()






























































 గుర్తు దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది? దాని అర్థం ఏమిటి?
గుర్తు దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది? దాని అర్థం ఏమిటి?