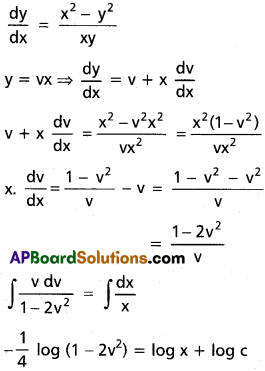
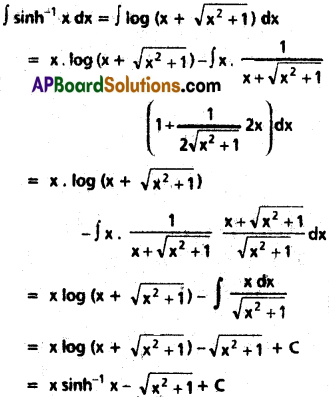
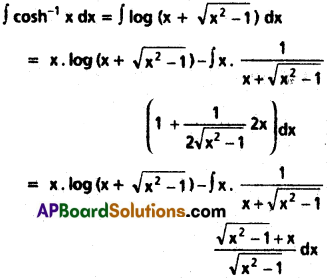
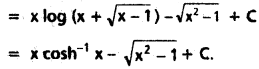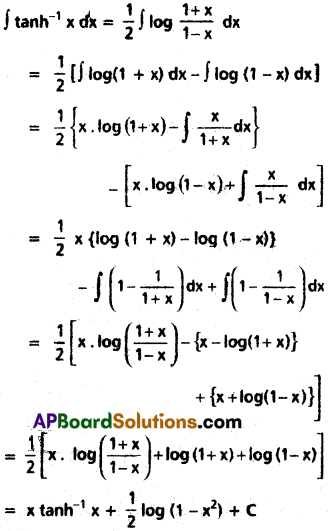SCERT AP 7th Class Science Study Material Pdf 11th Lesson Soil and Water Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Science 12th Lesson Questions and Answers Soil and Water
7th Class Science 12th Lesson Soil and Water Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
I. Fill in the blanks.
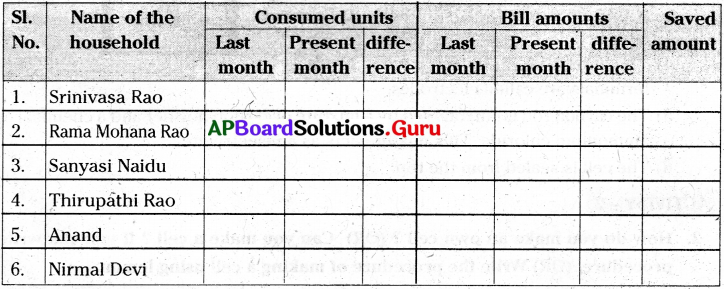
1. Wastewater released from houses is called _______.
2. The Science dealing with the formation of soil is called _______.
3. In modern water purifiers _______ are used instead of chlorine to kill the germs.
Answer:
1. Sewage
2. Pedology
3. Ultraviolet rays
II. Choose the correct answer.
1. In addition to the soil particles, the soil also has
a) air and water
b) water and plants
c) minerals, organic matter, air and water
d) water, air and plants
Answer:
c) minerals, organic matter, air and water
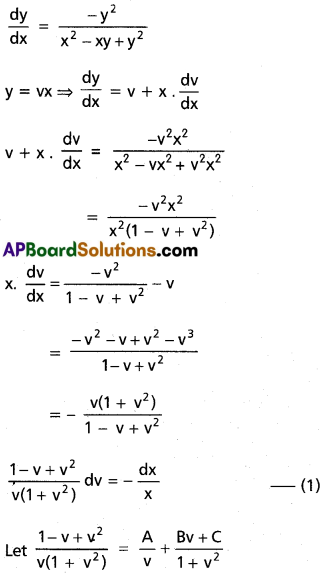
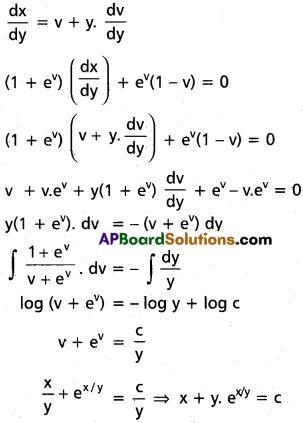
2. The water holding capacity is the highest in
a) sandy soil
b) clayey soil
c) loamy soil
d) mixture of sand and loam
Answer:
b) clayey soil
![]()
3. Which among the following is not responsible for water shortage?
a) Industrial growth
b) Population growth
c) Heavy rainfall
d) Mismanagement of water resources
Answer:
c) Heavy rainfall
III. Matching.
| A) Weathering | 1. more water retaining capacity |
| B) Clay soil | 2. washing off the top soil |
| C) Soil erosion | 3. soil formation |
| D) Afforestation | 4. 1% |
| E) Fresh water | 5. growing trees |
| 6. 99% |
Answer:
| A) Weathering | 3. soil formation |
| B) Clay soil | 1. more water retaining capacity |
| C) Soil erosion | 2. washing off the top soil |
| D) Afforestation | 5. growing trees |
| E) Fresh water | 4. 1% |
IV. Answer the following questions
Question 1.
Explain briefly the terms.
i) Weathering ii) Aquifer iii) Percolation iv) Sewage
Answer:
i) Weathering :
- In nature due to the action of various natural agents such as wind, water, sun and climate the bigger rocks (parent rock) gradually breakdown and give small particles. These form the soil. This process is known as Weathering.
- It takes approximately 500 -1000 years for the formation of 1 inch of soil.
- Weathering helps in the formation of soil.
- The process of formation of soil from the parent rock by the process of weathering is called ‘Pedogenesis’.
ii) Aquifer :
- Ground water is stored between layers of hard rock below the water table. This is called aquifer.
- The wells, tube wells and hand pumps get water present in the aquifer.
iii) Percolation :
- The absorption and downward movement of water through the soil layer is called percolation.
- The rate of percolation various from soil to soil.
- Sandy soils are well aerated and they have high percolation rate.
iv) Sewage :
- All the waste water released by homes, industries, hospitals, offices and other users are collectively called sewage.
- Sewage is a liquid waste.
- Sewage contain water with dissolved and suspended impurities, disease causing bacteria and other microbes. These impurities are called contaminants.
- Discharge of untreated sewage into canals causes harm to aquatic life.
Question 2.
List the differences between clayey soil, loamy soil and sandy soil. How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Answer:
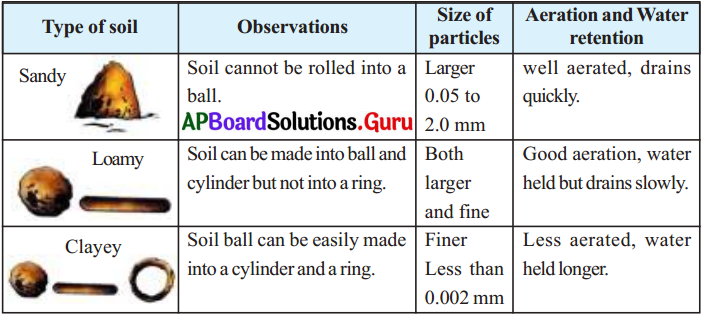
- Clayey soils are less aerated and their water holding capacity is higher.
- It has finer particles less than 0.002 mm. Hence, they retain the water for a longer period.
- Clayey soils are very suitable to grow crops like paddy. Sugarcane and cotton. Black soil with highest clay are suitable to grow crops like redgram. chillies etc.
Question 3.
Harshith observed that majority of the houses in his locality get water through bore well but no house has taken measures for rain water harvesting. Guess the long term effect on the water table.
Answer:
- Over use of ground water can cause wells to dry up.
- This leads to expensive and ultimately fertile attempts to keep up with the dropping water table by drilling deeper and deeper wells.
- People will have to travel for miles to get water for their daily use.
- People will migrate to longer distances in search of drinking water and villages would become barren.
![]()
Question 4.
If you get a chance to interview a soil scientist, what questions will you ask related to soil, its testing and conservation.
Answer:
I shall ask the following questions.
- How can you test the soil for its acidity?
- Is it possible to change the basic nature of the soil?
- How can the water holding capacity of the soil be increased at a low cost?
- Suggest methods to improve the fertility of the soil.
- What can be done with the black cotton soil when a building is to be constructed?
- As black cotton soil yields, and the building cracks, suggest preventive measures for it.
Question 5.
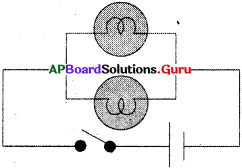
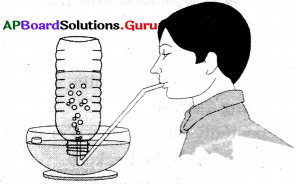
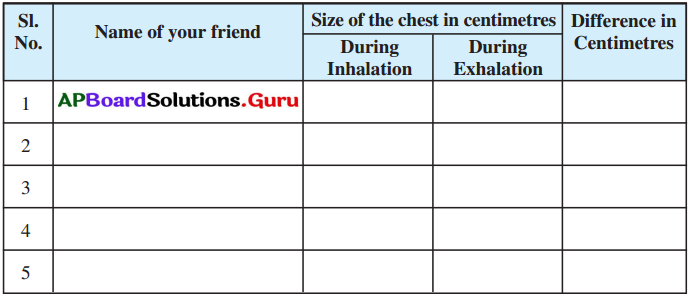
Your friends conducted an experiment in the field regarding the rate of percolation. They observed that it took 40 min for 200 ml of water to percolate through the soil. Calculate the rate of percolation. Also write the procedure to conduct the test.
Answer:


Procedure :
- Take a soil sample.
- Take a plastic funnel and place a filter paper in it as shown in the figure.
- Weigh 50 gms of dry soil and pour it into the funnel.
- Take 200 ml of water in a measuring cylinder.
- Then pour the water on the soil drop by drop.
- Pour the water all over the surface of the soil until it starts dripping out of the funnel. Calculate the time taken for the last water drop passes down the soil.
Question 6.
We call earth as “Bhoomatha -The Mother Earth”. How do you express your appreciation and gratitude to her?
Answer:
- Soil is one of the most important natural resources. It supports the existence of living organisms.
- We use soil for different purpose in our daily life. Almost all living things in our surroundings directly or indirectly depend on soil.
- The soil supports all plants, animals and micro organisms.
- We grow our food components in this soil.
- Soil is the birth place of all minerals, everything we get from this soil. Hence, we consider the earth as “Bhoomatha – The Mother Earth”.
![]()
Question 7.
Poorvika wants to maintain a garden,- what suggestions can you give her to minimize the use of water and also to improve the soil quality?
Answer:
- By using sprinklers and drip irrigation methods we can reduce the wastage of water in the garden.
- Construction of soaking pits in the garden enhances the percolation of raia water into the soil. It improves the ground water table.
- Rotting vegetation and animal remains make up the humus rich in fertility.
- They contain nutrients, natural manure, which give good support to the growth of ‘ plants.
- I also suggest Poorvika to grow big trees around the garden to stop winds.
- It is better to grow grass and other plants in the vacant portions of the garden. These grass plant roots hold the solid particles and prevent soil erosion during heavy rains.
7th Class Science 12th Lesson Soil and Water InText Questions and Answers
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 84
Question 1.
Where do animals and humans live?
Answer:
They live on the Earth.
Question 2.
What would happen if there is no soil on the Earth?
Answer:
Life on the earth would become impossible.
Question 3.
Why is woman in the picture using hand pump?
Answer:
For getting drinking water.
![]()
Question 4.
Why is soil an important resource?
Answer:
It is the important natural resources necessary for life on the earth. Human beings, plants and micro organisms depend on soil for their basic needs.
Question 5.
Where do plants get nutrients from?
Answer:
From soil.
Question 6.
Did you ever see earthworms and snails coming out of soil during rainy season?
Answer:
Yes, they live in the soil by making burrows.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 85
Question 7.
Is soil useful to us in any other way?
Answer:
Yes, soil is also needed.
- For agriculture
- For constructing buildings
- For making toys and idols
- For making utensils and pottery
- For making cosmetics (multani soil)
Question 8.
Did you observe stones of different sizes at the bank of a stream?
Answer:
Yes. I observed many stones with different sizes and shapes.
Question 9.
What happens when rocks get rubbed and scroll due to the flow of water?
Answer:
Weathering of rocks takes place.
![]()
Question 10.
You might have observed white coloured crinkles on the rocks at the bank of river. How do they appear?
Answer:
They appear like shining jewels. They are formed by the disintegration of rock due to the abarsion of water stream.
Question 11.
Have you observed the top soil in your surroundings? What is it made of?
Answer:
Yes. It is made of dead and decayed organic matter called Humus.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 86
Question 12.
What do you observe floating on the top?
Answer:
Humus.
Question 13.
What do you find at the bottom of the beaker?
Answer:
Inorganic matter of the soil.
Question 14.
Do you find any insects and plant parts in the beaker?
Answer:
Yes, they are floating. It is the organic matter of the soil.
Question 15.
What do you infer from your observation?
Answer:
We can infer that soil consists of water, air, organic matter, inorganic matter and organisms.
Question 16.
How many layers did you observe in the pit?
Answer:
Two layers can be observed in the pit.
![]()
Question 17.
Do all the layers have same colour, texture and depth?
Answer:
No, all the layers have different colour, texture and depth.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 87
Question 18.
How can you identify which soil is suitable for this purpose?
Answer:
Clayey soil is suitable for making Ganesh idol.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 88
Question 19.
Do all types of soils have same properties?
Answer:
No, they have different properties.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 89
Question 20.
What type of soils are generally seen in our state?
Answer:
Sandy soils, black soils, red soils, loamy soils are seen in our state.
Question 21.
Can we grow a crop in all types of soil?
Answer:
No, it is not possible.
Question 22.
What type of soil is required for growing paddy?
Answer:
Paddy is grown in clayey soil, which retains water for a longer period.
Question 23.
Is there any relationship between the crops and soil?
Answer:
Yes, all crops are not grown in all soils. Crops are soil specific. For example cashew is grown in sandy soils and cotton is grown in black soils.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 90
Question 24.
Why is soil testing done?
Answer:
It helps a farmer to make a soil suitable for growing crops.
Question 25.
How do the farmers benefit by soil testing?
Answer:
- Soil testing helps the farmer to know about the current health of the farm’s soil and how to improve it.
- It helps farmers to prevent the degradation of soil quality.
- It helps to minimize usage of fertilizers.
![]()
Question 26.
Did you observe that after heavy rain, the top soil get washed off?
Answer:
Yes. I observed it during rainy season.
Question 27.
What will happen if the top soil is washed off?
Answer:
The soil will loose its quality and fertility.
Question 28.
How can we prevent it?
Answer:
- By afforestation. Controlling the deforestation activities.
- Constructing checkdams and bunds
- Preventing over grazing of land by animals.
- By planting trees as shelter belt to stop winds. .
- By planned agricultural practices we can prevent soil erosion successfully.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 91
Question 29.
What are the other causes of soil erosion?
Answer:
- Unplanned and excessive usage of agro chemicals
- Over grazing of land
- Deforestation
- Digging the earth for construction and mining
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 92
Question 30.
Is water from seas and oceans useful for drinking and agriculture?
Answer:
No, the sea water is not useful for drinking and agriculture. But by desalinating the sea water we can use them for consumption.
Question 31.
Where is fresh water available from?
Answer:
From rivers, lakes, streams and ravines.
Question 32.
How much percentage of fresh water is available?
Answer:
only 1%.
Question 33.
How does the water reach the ground?
Answer:
The water reach the ground by infiltration.
Question 34.
Is the water table level same at all places?
Answer:
No, it is always vary in different places.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 93
Question 35.
Why do wells dry up?
Answer:
Decrease in ground water table leads to dry up of wells.
Question 36.
What will happen if the ground water table go down?
Answer:
All the wells and bore wells will dry up.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 94
Question 37.
Why is it essential to manage the water?
Answer:
To resolve the prevailing water scarcity in the society, proper water management of water resources is very essential.
Think & Respond
Question 1.
You may come across some people breaking large rocks into smaller ones to make road. Is it also the weathering of rocks? Why?
Answer:
- In natural weathering process, the parent rock is gradually breakdown into small particles by the action of air, water, sun heat, and climate. It takes 500 to 1000 years times. This helps in formation of soil.
- The break do\yn of rocks for the purpose of constructing roads and buildings also comes under weathering.
Here, the big rocks are blown down by using dynamites. In very short time, the bigger rocks become small gravel. It is artificial weathering or man made weathering. But this will not help in the formation of soil. This leads to the rapid depletion of natural resources like hills and mounds. The natural weathering factors like wind, water, sun have no role in this artificial weathering.
![]()
Question 2.
There is huge amount of water on earth, then why is water called a precious resource?
Answer:
- About 97% of water is present in seas and oceans which is not useful for drinking and agriculture.
- 2% of water is present in the form of rain, snow, sleet and precipitated water which is not available for consumption.
- Hence only 1% of fresh water is available in the form of surface and ground water sources. This 1% of water is useful for drinking, domestic usage and agriculture.
- Hence, we have to use this 1% of fresh water wisely and judiciously. This water is basis of life and human civilization. So, water is life. Save water save lives.
- So, we considered water as a precious resource.
Activities and Projects
Question 1.
Under the guidance of your teacher collect the wet waste from Mid Day Meal preparation and make Vermi compost for your school garden.
Answer:

- With the help of my science teacher, we constructed 10 × 1 × 1/2 meters Vermi Compost beds in sheds which protect these beds from direct sunlight and rain.
- We collected coconut, banana and sugarcane leaves. We made them into 3- 4 inches layer. This inner layer was wet with water.
- We collected the wet waste from Mid Day Meal to fill the bed. We were careful to avoid glass, polythlene, rubber and metal objects in the bed.
- After two weeks of making bed we kept thousand earth worms per square meter and covered the bed with Gunny bags to maintain 30 to 40% of moisture.
- After 60 days we collected the first manure. Second time we got the manure with in 40 – 50 days.
- By using this Vermi Compost we can reduce the investments on chemical fertilizers and other pesticides. The quality of the soil and agricultural produce increased.
Question 2.
Prepare a model of representing various horizons in the soil profile using a disposed plastic bottle, stones and soil.
Answer:

- Take soil from your surroundings, clean d: posable plastic bottle and home made paper funnel.
- Pour the soil into the funnel putting it on the plastic bottle.
- Now pour some water into the bottle upto its neck. Close the end of the bottle and shake it well. The heavier particles like gravel and sand settle to the bottom of the bottle, wait for a day to get all the soil particles to settle down in the bottle.
- After one day, you may observe that heavier particles like gravel settle at the bottom of the bottle. Above that you may find sand particles. Just above the sand particles, you may find very finer particles on the top of the bottle you will find humus floating on the surface of the water.
- From the top, first you find humus, the plant and animal organic matter which helps the growth of plants.
- Just below the hurhus, you find clay. Clay traps the water in the soil for the roots to absorb them.
- Below the clay, sand and gravel, they help to drain the water quickly so that the roots don’t rot.
- Basing on the percentage of each individual component loam soils may be classified into sandy loam, silty loam and clay loam.
- Here, the soil taken for this project is sandy loam. Like this way, we can determine the type of soils in our surroundings.
Activities
Activity – 1
Question 1.
How do you observe the plants and small living organisms in a given soil? Write your observations in a table.
Answer:
- I visited my school garden and the kitchen garden yesterday to observe the plants and small living things in those places.
- I marked an area of 30 cm × 30 cm. 1 dug the soil to a depth of 4 to 6 cm in the marked area.
- I carefully sorted out the soil and observed the presence of plants and small living organisms with the help of a hand lens.
I noted down the things 1 found in the given table.
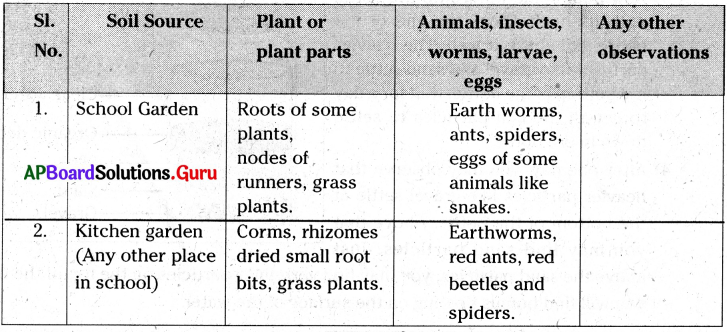
Inference :
- We can infer that soil consists various plants and dried plant parts etc.
- It is a good habitat for many small organisms.
Activity – 2
Question 2.
How do you observe the different components of the soil?
Answer:
Aim : To observe the different components of the soil.
Materials required : Soil, beaker, water, polythene bag.
Procedure :
- Collect a handful of soil sample in a transparent polythene bag and close it tightly.
- Leave it under the sun for 2 hours we can observe some droplets of water on the inner side of the bag.
- Fill a beaker with this handful of soil, pour water into it slowly and carefully. Fill the beaker with water and stir well the soil and water.
- Leave it for undisturbed for some time.
Observations :
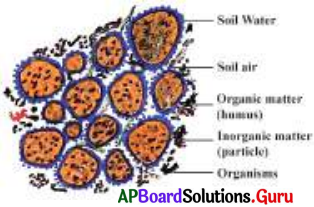
Organic substances, dry rotten leaves and roots float on water. Dead and decayed organic matter that mixes with soil is called humus.
My observations and inferences are shown in the table.
| Observation | Inference |
| Droplets of water in the bag | Presence of water in soil |
| Bubbles from soil when water is poured | Presence of air in soil |
| Floating of dry plant parts | Presence of organic matter in soil |
| Particles at the bottom | Presence of inorganic matter in soil |
| Insects and plant parts | Presence of organisms in soil |
Inference :
Soil consists of water, air, organic matter, inorganic matter and organisms.
Activity – 3
Question 3.
How do you identify the type of soil in your science lab?
Answer:
- We can identify the different types of soils in the line diagram given below.
- We can determine the soil on the basis of following chart.
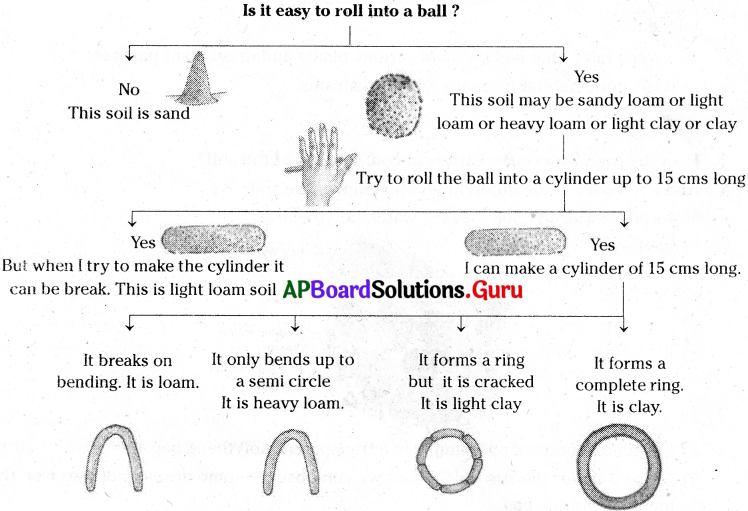
Activity – 4
Question 4.
How do you know about soil erosion?
Answer:
Aim : To know about soil erosion.

Procedure :
- Cut three disposable bottles sidewise and fill with soil as shown in the figure.
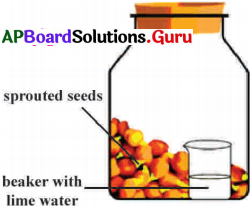
- Put some sprouts of green gram or any other seeds in one bottle and water regularly.
- Cover the second bottle with dry leaves and leave the third bottle without sowing anything.
- After a week, the sprouts in the first bottle will grow more.
- Now, make arrangements to collect the drained water from each bottle by arranging small vessels.
- Now blow air and pour water slowly in each bottle.
Observation :
In the first bottle containing sprouts, less soil is blown out by air and washed off by water.
Inference :
We can infer that the top soil is washed off by water and blown out by air. Plants help to prevent soil erosion.
![]()
Activity – 5
Question 5.
What are the differences in the water table in your locality due to increase in the construction and industries nearby?
Answer:
- The water levels in the wells are rapidly decreased.
- Many borewells are not working due to depletion in the water table.
- People are drilling deeper and deeper borewells to keep up with the dropping water table. It is an expensive task. Hence, they are facing financial troubles.
- People are facing drinking water shortage in the village.
- People have to walk for miles to get water for their usage.
- Many people migrated to different places due to scarcity of drinking water in the village.
- Population explosion, industrial growth, enhanced agriculture activities, deforestation, decrease in the effective area for seepage and drop in rainfall are other main reasons for the rapid decrease of water table on the earth.