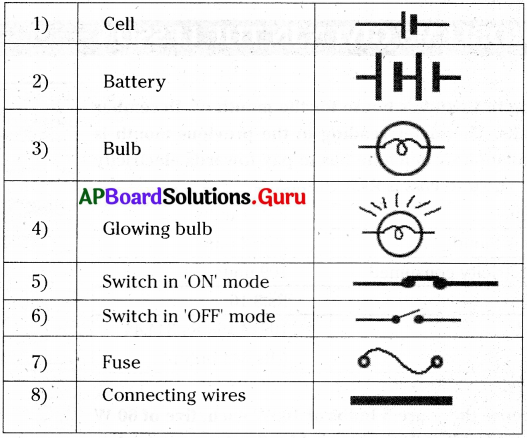
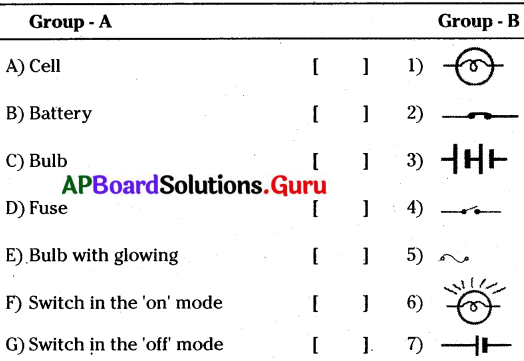
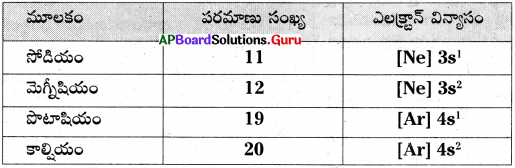
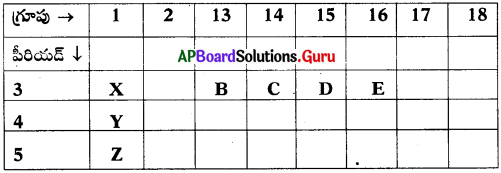
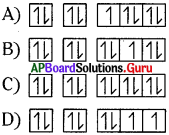
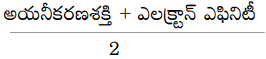These AP 8th Class Biology Important Questions 3rd Lesson సూక్ష్మజీవుల ప్రపంచం 2 will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 8th Class Biology 3rd Lesson Important Questions and Answers సూక్ష్మజీవుల ప్రపంచం 2
ప్రశ్న 1.
మైదాపిండికి ఈస్టు ఎందుకు కలుపుతారు ?
జవాబు:
- బ్రెడ్ ను తయారుచేయటానికి మైదాపిండికి ఈస్ట్ ను కలుపుతారు.
- ఈస్ట్ కిణ్వనం ద్వారా ఇథైల్ ఆల్కహాలు, కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ లను ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
- ఈ వాయువు మైదాపిండిలో చేరటం వల్ల దీని పరిమాణం పెరిగి స్పాంజి లాగా అవుతుంది.
- దీనివల్ల బ్రెడ్ / కేక్ అతి మెత్తగా వుంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 2.
సూక్ష్మజీవుల వల్ల ఉపయోగాలు తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- ఈ సూక్ష్మజీవుల వల్ల మనకు అనేక ఉపయోగాలు వున్నాయి.
- ఈస్ట్ అనే బాక్టీరియా చక్కెరను ఆల్కహాలుగా మారుస్తుంది.
- పెన్సిలిన్, టెట్రామైసిన్, ఎరిత్రోమైసిన్ లాంటి సూక్ష్మజీవ నాశకాలను మనం వీటితో తయారుచేయవచ్చు.
- వీటితో కుక్కలలో, జంతువులలో వచ్చు వ్యాధులను నివారించవచ్చును.
- ఇవి నత్రజని స్థాపనకు ఉపయోగపడతాయి. దీనివల్ల మృత్తిక ఆరోగ్యంగా వుండి అధిక దిగుబడులను ఇస్తుంది.
- ఇవి నేల సారాన్ని పెంచుతాయి.
- వ్యర్థ పదార్థాలను కుళ్ళింపచేసి నేలలో కలసిపోయేట్లు చేస్తాయి.
- జంతు మృత కళేబరాలను కుళ్ళింపచేస్తాయి.
- పర్యావరణాన్ని పరిశుభ్రంగా వుంచటంలో సహాయపడతాయి.
- ఆహారం, పాలు, వైన్ మొదలగు వాటిని నిల్వచేయటానికి సహాయపడతాయి.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 3.
సూక్ష్మ జీవనాశకాలు ఫ్లో చార్టును గీయండి.
జవాబు:
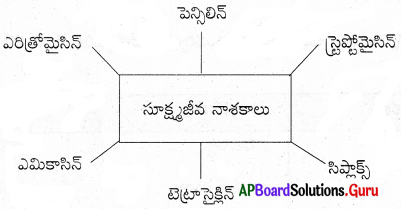
ప్రశ్న 4.
‘పెన్సిలిన్ ఆవిష్కరణ’ గురించి క్లుప్తంగా వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
- మొదటి ప్రపంచ యుద్ధకాలంలో అలెగ్జాండర్ ఫ్లెమింగ్ సైన్యంలో డాక్టరుగా పనిచేసేవాడు.
- యుద్ధంలో గాయపడిన సైనికులు బాక్టీరియా ఇన్ ఫెక్షన్ బారినపడి చనిపోవడం చూశాడు.
- దీనికి గల కారణాలను అన్వేషించటానికి ఆయన తన ప్రయోగశాలలో పరిశోధనలు చేయసాగాడు.
- దీనిలో భాగంలో ఫ్లెమింగ్, బాక్టీరియా సమూహాలను పెట్టాడిలో పెంచాడు.
- ఒక రోజు ఒక పెట్రెడిష్ లో ఒక రకమైన శిలీంధ్రం (బూజు) దానిలో వున్న బాక్టీరియా పెరుగుదలను నిరోధించటం గమనించాడు.
- ఆ శిలీంధ్రం ‘పెన్సీలియం నోటాటం’ అని గుర్తించాడు.
- ఇది ఉత్పత్తి చేసిన పదార్థం ‘పెన్సిలిన్’ అని నామకరణం చేశాడు.
- 1945లో దీనికి గౌరవంగా ఫ్లెమింగ్ కు నోబెల్ బహుమతి ఇచ్చారు.
ప్రశ్న 5.
‘సహజీవనం’ అంటే ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
- రైజోబియం బాక్టీరియా చిక్కుడు జాతి వేర్ల బొడిపెలలో వుంటాయి.
- ఇది వాతావరణంలోని నత్రజనిని, నత్రితాల రూపంలోకి మార్చి వేర్లతో నిల్వ చేస్తాయి.
- మొక్కలు బాక్టీరియాకు ఆవాసం ఇస్తే, బాక్టీరియా మొక్కకు నత్రితాలను తయారుచేయటంలో సాయపడింది.
- దీనినే Symboisis లేదా ‘సహజీవనం’ అంటారు.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 6.
అంటువ్యాధులు అంటే ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
ఒకరి నుండి మరొకరికి సంక్రమించే వ్యాధులను అంటువ్యాధులు అంటారు.
ఉదా : జలుబు, కండ్ల కలక, మశూచి, స్వైన్ ఫ్లూ, క్షయ, చికున్ గున్యా మొ॥నవి.
ప్రశ్న 7.
వాహకాలు అనగానేమి ?
జవాబు:
వ్యాధికారక సూక్ష్మజీవులను ఒక చోటి నుండి మరొక చోటికి తీసుకువెళ్ళే జంతువులను, కీటకాలను వాహకాలు అంటారు.
ఉదా : దోమలు (జ్వరాలు), ఈగలు (కలరా), మానవుడు (ఎయిడ్స్)
ప్రశ్న 8.
సూక్ష్మజీవులు మొక్కలలో కలుగచేసే వ్యాధుల వివరాలు పట్టిక రూపంలో రాయండి.
జవాబు:
| మొక్కలలో వచ్చే వ్యాధి | వ్యాధిని కలుగచేసే సూక్ష్మజీవి |
| సిట్రస్ కాంకర్ | బాక్టీరియా |
| చెరకు ఎర్రకుళ్ళు తెగులు | శిలీంధ్రం |
| వేరుశెనగలో తిక్కా తెగులు | శిలీంధ్రం |
| పొగాకులో ముసాయిక్ వ్యాధి | వైరస్ |
| వరిలో స్మట్ తెగులు | శిలీంధ్రం |
ప్రశ్న 9.
ఆహార పదార్థాలను సరైన విధానంలో నిల్వచేసి ప్యాకింగ్ చేయటం వల్ల ఉపయోగాలు ఉన్నాయా ? ఉంటే అవి ఏవి ?
జవాబు:
ఆహార పదార్థాలను నిల్వ లేదా ప్యాకింగ్ చేయటం ద్వారా
- ఆహారం పాడవకుండా నిరోధించవచ్చు.
- ఆహారాన్ని ఎక్కువ కాలం నిల్వచేయవచ్చు.
- నాణ్యతను ఎక్కువ కాలం కాపాడవచ్చు.
- దూర ప్రాంతాలకు ఎగుమతి చేయవచ్చు.
- అన్ని కాలాలలో అన్ని కాయలు, పండ్లు, పాలను అందుబాటులో ఉంచవచ్చు.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 10.
యాంటిబయాటిక్స్ విచక్షణా రహితంగా వాడటం వలన వచ్చే నష్టము ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
యాంటిబయాటిక్స్ ఎప్పుడంటే అప్పుడు ఇష్టం వచ్చినట్లు ఉపయోగించరాదు. అర్హత కలిగిన డాక్టరు ఇచ్చిన సూచనల ప్రకారమే ఉపయోగించాలి. లేకపోతే వాటివల్ల మనకు హాని కలగవచ్చు. అవసరం లేకుండా, ఎక్కువ మోతాదులో యాంటిబయాటిక్స్ ఉపయోగించటం వల్ల జీర్ణ వ్యవస్థలో మేలు చేసే బాక్టీరియా నశించిపోతుంది మరియు రోగకారక బాక్టీరియా నిరోధకతను (Resistance power) పెంచుకుంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 11.
ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్ టీకాను కనుగొన్న విధానం తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్ ఒక గ్రామీణ వైద్యుడు.
- ఇతని వద్దకు మశూచి సోకిన వారితోపాటు కౌపాక్స్ సోకిన రైతులు కూడా వచ్చేవారు.
- ఎవరికైతే కౌపాక్స్ సోకుతుందో వారికి మశూచి (smallpox) సోకకపోవడాన్ని ఆయన గమనించాడు.
- అంటే కౌపాక్స్ సోకిన వారిలో వ్యాధి నిరోధకశక్తి (immunity) అభివృద్ధి చెంది అది వారిలో మశూచి వ్యాధి రాకుండా కాపాడుతోందని గుర్తించాడు.
- 1796లో ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్ పాల డెయిరీలో పనిచేసే కౌపాక్స్ సోకిన వ్యక్తి శరీరం మీద ఉన్న బొబ్బ నుండి స్రావాన్ని (రసి) తీసి ఆరోగ్యంగా ఉన్న 8 సంవత్సరాల బాలునికి ఇచ్చాడు.
- ఆరు వారాల తరువాత ఆ బాలుడిని మశూచికి గురి చేశాడు.
- కానీ ఆ బాలునిలో ఎటువంటి మశూచి లక్షణాలూ కనపడలేదు.
- అంటే కౌపాక్స్ బొబ్బ స్రావంలో ఉండే పదార్థం మశూచి వ్యాధి రాకుండా వాక్సిన్ గా పనిచేసిందన్నమాట.
- ఈ మశూచి వాక్సిన్ లక్షలాది మందిని ఈ భయంకరమైన రోగం నుండి కాపాడింది.
ప్రశ్న 12.
ఈ క్రింది పదాలు నిర్వచించండి.
ఎ) వ్యాధి జనకాలు
బి) వ్యాధి వ్యాప్తి
సి) వాహకాలు
డి) అంటువ్యాధులు
జవాబు:
ఎ) వ్యాధి జనకాలు : వ్యాధిని కలిగించే సూక్ష్మజీవులను వ్యాధి జనకాలు అంటారు.
బి) వ్యాధి వ్యాప్తి : వ్యాధి ఒక వ్యక్తి నుండి మరొక వ్యక్తికి విస్తరించటాన్ని వ్యాధి వ్యాప్తి అంటారు.
సి) వాహకాలు : వ్యాధి జనకాలను మోసుకెళ్ళే జంతువులను వాహకాలు అంటారు.
డి) అంటువ్యాధులు : ఒకరి నుండి ఒకరికి సంక్రమించే వ్యాధులను అంటువ్యాధులు అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 13.
ఒకవేళ మన పరిసరాలలో సూక్ష్మజీవులు లేకపోతే ఏమి జరుగుతుందో ఊహించండి.
జవాబు:
- సూక్ష్మజీవులు మనచుట్టూ ఉండే పరిసరాలను శుభ్రం చేయుట ద్వారా మనకు సహాయం చేస్తాయి.
- మన పరిసరాలలో సూక్ష్మజీవులు లేకపోతే పరిసరాలు పరిశుభ్రంగా ఉండవు.
- మనచుట్టూ ఉన్న పరిసరాలు వృక్ష, జంతు వ్యర్థాలతో నిండిపోతాయి.
- చనిపోయిన కళేబరాలు భూమిలో కుళ్ళిపోవు. .
- అందువలన భూమిమీద నివసించటానికి స్థలం కొరవడుతుంది.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 14.
పాశ్చరైజేషన్ విధానం కనిపెట్టకపోతే ఏమి జరిగి ఉండేదో ఆలోచించండి.
జవాబు:
- పాశ్చరైజేషన్ పద్ధతిలో పాలను నిల్వ చేస్తాము.
- దీనివలన పాలను ఎక్కువకాలం ఉంచి దూరప్రాంతాలకు రవాణా చేయగలుగుతున్నాము.
- అన్ని ప్రాంతాలవారికి పాలు అందించగలుగుతున్నాము.
- పాశ్చరైజేషన్ విధానం లేకపోతే మనకు తీవ్రమైన పాల కొరత ఏర్పడేది.
- మనకు ఇన్ని రకాల పాల ఉత్పత్తులు లభించేవి కావు.
- ఎదిగే పిల్లలు పోషకాహార లోపంతో బాధపడేవారు.
ప్రశ్న 15.
మానవునిలో సూక్ష్మజీవుల వలన కలిగే సాధారణ వ్యాధులు, వాటి నివారణ పద్ధతులను సేకరించి పట్టిక రూపొందించండి.
జవాబు:
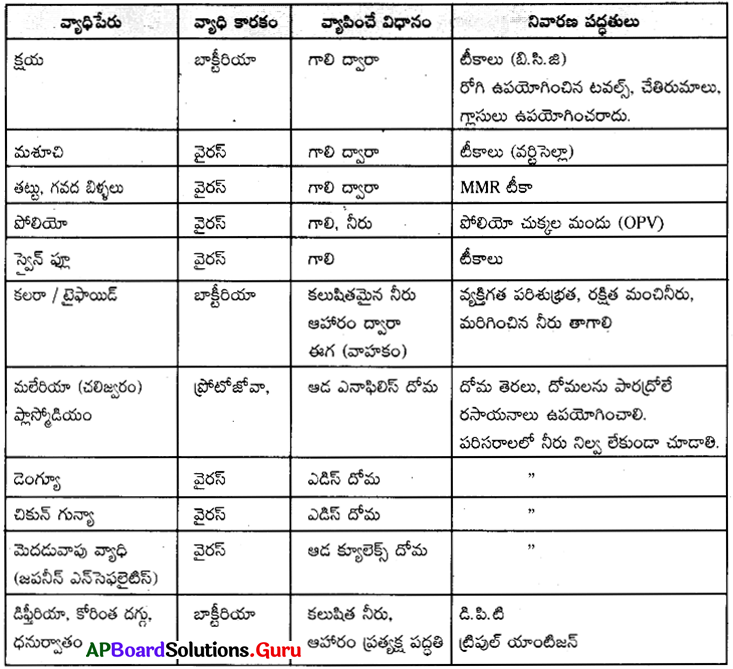
ప్రశ్న 16.
నాస్టాక్, అనబినా బొమ్మలు గీయండి.
జవాబు:
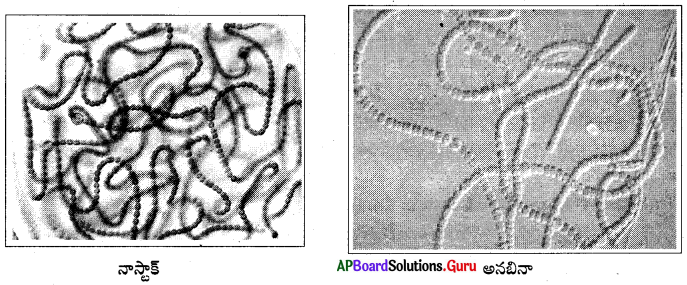
ప్రశ్న 17.
ఒక కాలనీలో అనేకమంది కలరాతో బాధపడుతున్నారు. కారణమేమైవుంటుందో ఊహించండి.
జవాబు:
- కలరా వ్యాధి కారక క్రిములు కలుషిత నీరు, కలుషిత ఆహారాన్ని స్వీకరించడం వలన వ్యాపిస్తాయి.
- అందువలన, కాలనీలోని ప్రజలు బహుశా కలుషిత నీటిని, ఆహారాన్ని సేవించడం వలన కలరా వ్యాధికి గురి అయి ఉండవచ్చు.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 18.
చేపలను నిల్వ చేసే ఏవైనా రెండు పద్ధతులను సూచించండి.
జవాబు:
- ఎండబెట్టడం
- పొగపెట్టడం
- క్యానింగ్
- శీతలీకరించడం
ప్రశ్న 19.
సహజీవనం అంటే ఏమిటి ? రెండు ఉదాహరణలివ్వండి.
జవాబు:
- రైజోబియం బాక్టీరియా చిక్కుడు జాతి వేర్ల బొడిపెలలో వుంటాయి.
- ఇది వాతావరణంలోని నత్రజనిని, నత్రితాల రూపంలోకి మార్చి వేర్లతో నిల్వ చేస్తాయి.
- మొక్కలు బాక్టీరియాకు ఆవాసం ఇస్తే, బాక్టీరియా మొక్కకు నత్రితాలను తయారుచేయటంలో సాయపడింది.
- దీనినే Symboisis లేదా ‘సహజీవనం’ అంటారు.
ఉదాహరణ 1 : లెగ్యుమినేసి మొక్కల వేర్ల బుడిపెలలో సహజీవనం చేయు రైజోబియం బ్యా క్టీరియా
ఉదాహరణ 2 : శైవలాలు, శిలీంధ్రాలు లైకెన్లలో జరుపు సహజీవనం.
ప్రశ్న 20.
చేపలను నిల్వ చేసే ఏవైనా రెండు పద్ధతులను సూచించండి.
జవాబు:
- ఎండబెట్టడం
- పొగపెట్టడం
- క్యానింగ్
- శీతలీకరించడం
ప్రశ్న 21.
ఒక ప్రయోగంలో బాసిల్లస్ రహిత వాతావరణంలో దోశపిండిని ఉంచారనుకుందాం. ఒక రోజు తరువాత పిండిలో ఏమి మార్పు జరుగుతుందో రాయండి ?
జవాబు:
- దోశపిండి పులియదు.
- దోశపిండి పరిమాణంలో ఎటువంటి మార్పు ఉండదు.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 22.
క్రింది ఇవ్వబడిన సూక్ష్మజీవులను ఉపయోగకరమైన మరియు హానికరమైన సూక్ష్మజీవులుగా వర్గీకరించండి.
ప్లాస్మోడియం, లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్, రైజోబియం, పెన్సీలియం, ఈస్ట్, వైరస్
జవాబు:
ఉపయోగకరమైన సూక్ష్మజీవులు :
- లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్రై
- జోబియం
- పెన్సీలియం
- ఈస్ట్
హానికర సూక్షజీవులు :
- ప్లాస్మోడియం
- వైరస్
ప్రశ్న 23.
చల్లటి పాలకు మజ్జిగ కలిపితే ఏమౌతుంది ?
జవాబు:
పాలు పెరుగుగా మారవు. ఎందుకంటే చల్లని పాలలో లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్ బాక్టీరియా ఉండదు.
ప్రశ్న 24.
సూక్ష్మజీవులను గూర్చి మీ పాఠశాలలో క్విజ్ నిర్వహించడానికి నీవు ఎలాంటి ప్రశ్నలు తయారుచేస్తావు ?
జవాబు:
- “పెన్సిలిన్” ను కనిపెట్టిన శాస్త్రవేత్త ఎవరు ?
- పాలను పెరుగుగా మార్చు బాక్టీరియా ఏది ?
- పాశ్చరైజేషన్ ప్రక్రియ ద్వారా నిలువ చేయబడు ఆహార పదార్థాలు ఏవి ?
- ఆల్కహాల్ తయారీలో ఉపయోగపడు సూక్ష్మజీవి ఏది ?
ప్రశ్న 25.
వేరు బుడిపెల్లో నత్రజని స్థాపనకు ఉపయోగపడే బాక్టీరియాల పేరేమిటి ?
జవాబు:
రైజోబియం
ప్రశ్న 26.
వ్యాధులు రాకుండా నీవెలాంటి జాగ్రత్తలు తీసుకుంటావు ?
జవాబు:
- పరిశుభ్రమైన నీటిని, ఆహారాన్ని తీసుకుంటాను.
- పరిసరాలను పరిశుభ్రంగా ఉంచుకుంటారు.
- వ్యాధులకు గురికాకుండా వ్యాక్సిన్లు వేయించుకుంటాను.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 27.
ఆరుబయట మలవిసర్జన వ్యాధికారక క్రిములు సులభంగా వ్యాపించడానికి మార్గం. దీని నుంచి రక్షించుకోవడానికి మనం ఏం చేయాలో తెలుపుతూ ర్యా లీ నిర్వహించడానికి మీరు కొన్ని నినాదాలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- పరిసరాల పరిశుభ్రత – మనందరి బాధ్యత
- మరుగుదొడ్డిని ఉపయోగిద్దాం – వ్యాధుల నుండి సురక్షితంగా ఉందాం.
- మరుగుదొడ్డిని వాడదాం – స్వఛ్ భారత్ ను సాధిద్దాం.
- మరుగుదొడ్డి వాడకం – జాతి భవిత నిర్దేశకం.
ప్రశ్న 28.
కింది సమాచారం చదివి సూక్ష్మజీవులు, అవి కలిగించే వ్యాధులను పట్టిక రూపంలో రాయండి.
సూక్ష్మజీవులు : వైరలు, బ్యాక్టీరియాలు, ప్రొటోజోవాలు, ఆరోపొడాలు
వ్యాధులు : గజ్జి, మలేరియా, కండ్లకలక, టైఫాయిడ్
జవాబు:
| సూక్ష్మజీవి | వ్యాధులు |
| వైరస్ | కండ్లకలక |
| బాక్టీరియా | టైఫాయిడ్ |
| ప్రొటోజోవా | మలేరియా |
| ఆర్థ్రోపోడా | గజ్జి |
1 మార్కు ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 1.
ప్రతిరక్షకాలు అంటే ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
వ్యాధిని కలిగించే సూక్ష్మజీవులు మన శరీరంలోకి ప్రవేశిస్తే వాటి నుండి మనల్ని రక్షించేందుకు మన శరీరం కొన్ని రక్షకాలను ఉత్పత్తి చేస్తుంది. వీటినే ప్రతిరక్షకాలు అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 2.
పాశ్చరైజేషన్ అంటే ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
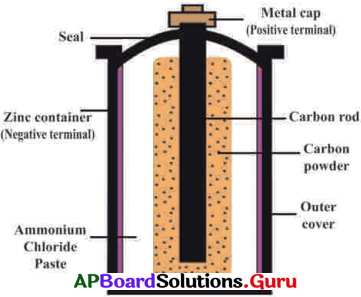
పాశ్చరైజేషన్ : ఆహార పదార్థాలను వేడి చేయటం ద్వారా సూక్ష్మజీవులను తొలగించి వాటిని ఎక్కువ సమయం నిల్వ చేయటాన్ని పాశ్చరైజేషన్ అంటారు. దీనిని లూయీపాశ్చర్ కనిపెట్టారు.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 3.
లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్ బాక్టీరియా పాలను పెరుగుగా మారుస్తుందని నీవు ఎలా చెప్పగలవు ?
జవాబు:
పెరుగులో లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్ బాక్టీరియా ఉంటుంది. ఈ పెరుగు గోరువెచ్చని పాలలో కలిపినప్పుడు ఈ బాక్టీరియా పాలలో పెరిగి, పాలను పెరుగుగా మారుస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 4.
అంటువ్యాధులు అంటే ఏమిటి ?
జవాబు:
ఒకరి నుండి మరొకరికి సంక్రమించే వ్యాధులను అంటువ్యాధులు అంటారు.
ఉదా : జలుబు, కండ్ల కలక, మశూచి, స్వైన్ ఫ్లూ, క్షయ, చికున్ గున్యా మొ॥నవి.
ప్రశ్న 5.
వాహకాలు అనగానేమి ?
జవాబు:
వ్యాధికారక సూక్ష్మజీవులను ఒక చోటి నుండి మరొక చోటికి తీసుకువెళ్ళే జంతువులను, కీటకాలను వాహకాలు అంటారు.
ఉదా : దోమలు (జ్వరాలు), ఈగలు (కలరా), మానవుడు (ఎయిడ్స్)
ప్రశ్న 6.
వ్యాధి జనకాలు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
వ్యాధి జనకాలు : వ్యాధిని కలిగించే సూక్ష్మజీవులను వ్యాధి జనకాలు అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 7.
వ్యాధి వ్యాప్తి అంటే ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
వ్యాధి వ్యాప్తి : వ్యాధి ఒక వ్యక్తి నుండి మరొక వ్యక్తికి విస్తరించటాన్ని వ్యాధి వ్యాప్తి అంటారు.
![]()
లక్ష్యాత్మక నియోజనము
సరియైన సమాధానమును గుర్తించుము.
ప్రశ్న 1.
…………… అనే ప్రక్రియ ఎసిటిక్ ఆమ్ల తయారీలో వాడతారు.
ఎ) శ్వాసక్రియ
బి) కర్బన స్థాపన
సి) కిణ్వనం
డి) జీర్ణక్రియ
జవాబు:
సి) కిణ్వనం
ప్రశ్న 2.
ఇది ప్రత్యుత్పత్తి వ్యవస్థలకు వచ్చే వ్యాధి.
ఎ) గనేరియా
బి) కలరా
సి) మశూచి
డి) క్షయ
జవాబు:
ఎ) గనేరియా
ప్రశ్న 3.
ఈస్ట్ కలిపిన చక్కెర …………. వాసన వస్తుంది.
ఎ) చేదు
బి) తీపి
సి) వగరు
డి) ఆల్కహాల్
జవాబు:
డి) ఆల్కహాల్
ప్రశ్న 4.
‘తాకడం’ ద్వారా వచ్చే వ్యా ధి …………..
ఎ) మలేరియా
బి) టైఫాయిడ్
సి) ఎయిడ్స్
డి) మెదడు వాపు
జవాబు:
సి) ఎయిడ్స్
ప్రశ్న 5.
ఈగల ద్వారా వ్యాప్తి చెందే వ్యాధి ………..
ఎ) కలరా
బి) ఎయిడ్స్
సి) గట్టి
డి) మలేరియా
జవాబు:
ఎ) కలరా
![]()
ప్రశ్న 6.
తట్టు, గవదబిళ్ళలకు ఇచ్చే టీకా …………
ఎ) చుక్కల మందు
బి) ట్రిపుల్ యాంటిజెన్
సి) MMR టీకా
డి) D.J.P
జవాబు:
సి) MMR టీకా
ప్రశ్న 7.
B.C.G. అనే టీకా మందు ఈ వ్యాధి రాకుండా ఇస్తారు.
ఎ) మశూచి
బి) క్షయ
సి) ఎయిడ్స్
డి) ఫ్లూ
జవాబు:
బి) క్షయ
ప్రశ్న 8.
వరిలో స్మట్ తెగులు ……… సూక్ష్మజీవి వల్ల వస్తుంది.
ఎ) వైరస్
బి) బాక్టీరియా
సి) శిలీంధ్రం
డి) ఆర్థోడ్
జవాబు:
సి) శిలీంధ్రం
ప్రశ్న 9.
పండ్లు, శీతల పానీయాలు, పాలు డబ్బాలలో వుంచి ఎక్కువ కాలం నిల్వ చేయవచ్చు.
ఎ) రేకు
బి) అల్యూమినియం
సి) గాలి తగలని
డి) అట్టపెట్టెలో
జవాబు:
సి) గాలి తగలని
ప్రశ్న 10.
చేపలకు ………… కలిపి ఎండబెట్టటం ద్వారా ఎక్కువ రోజులు నిల్వ చేస్తారు.
ఎ) ఉప్పు
బి) ఆమ్లం
సి) క్షారం
డి) ఆల్కహాల్
జవాబు:
ఎ) ఉప్పు
![]()
ప్రశ్న 11.
పాలు పెరుగుగా మారడానికి కారణం
ఎ) ఈస్ట్
బి) లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్
సి) ఆస్పర్జిల్లస్
డి) పెన్సీలియం
జవాబు:
బి) లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్
ప్రశ్న 12.
కిణ్వన ప్రక్రియలో విడుదలయ్యే వాయువు
ఎ) ఈథేన్
బి) మీథేన్
సి) కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
డి) ఆక్సిజన్
జవాబు:
సి) కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
ప్రశ్న 13.
మొలాసిస్ ద్రావణానికి ఈస్ట్ ని కలిపి దీనిని తయారు చేస్తారు.
ఎ) చక్కెర
బి) ఇథైల్ ఆల్కహాల్
సి) మిథైల్ ఆల్కహాల్
డి) రొట్టెలు
జవాబు:
బి) ఇథైల్ ఆల్కహాల్
ప్రశ్న 14.
బాక్టీరియాను చంపివేయటానికి ఉపయోగపడే సూక్ష్మజీవ నాశకాలను దీని నుండి తయారుచేస్తారు.
ఎ) బాక్టీరియా
బి) శైవలాలు
సి) శిలీంధ్రాలు
డి) ప్రోటోజోవన్లు
జవాబు:
సి) శిలీంధ్రాలు
ప్రశ్న 15.
సూక్ష్మజీవనాశకాలు దీనిని నిరోధించటానికి ఉపయోగిస్తారు.
ఎ) గనేరియా
బి) డయేరియా
సి) సెప్టిసీమియా
డి) పైవన్నీ
జవాబు:
డి) పైవన్నీ
![]()
ప్రశ్న 16.
పెన్సిలినను కనుగొన్నది
ఎ) జోనస్సక్
బి) ఎల్లాప్రగడ సుబ్బారావు
సి) అలెగ్జాండర్ ఫ్లెమింగ్
డి) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
జవాబు:
సి) అలెగ్జాండర్ ఫ్లెమింగ్
ప్రశ్న 17.
టెట్రాసైక్లినను కనిపెట్టినది
ఎ) జోనస్సీక్
బి) ఎల్లాప్రగడ సుబ్బారావు
సి) అలెగ్జాండర్ ఫ్లెమింగ్
డి) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
జవాబు:
బి) ఎల్లాప్రగడ సుబ్బారావు
ప్రశ్న 18.
పోలియో వ్యాధికి టీకాను కనుగొన్నది
ఎ) ఆల్బర్ట్ సాబిన్
బి) జోనస్సక్
సి) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
డి) అలెగ్జాండర్ ఫ్లెమింగ్
జవాబు:
బి) జోనస్సక్
ప్రశ్న 19.
పోలియో వ్యాధికి చుక్కలమందును కనుగొన్నది
ఎ) ఆల్బర్ట్ సాబిన్
బి) జోనస్సక్
సి) ఫ్లెమింగ్
డి) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
జవాబు:
ఎ) ఆల్బర్ట్ సాబిన్
ప్రశ్న 20.
ఏదైనా వ్యాధిని కల్గించే సూక్ష్మజీవులు శరీరంలోకి ప్రవేశిస్తే
ఎ) మన శరీరం ప్రతిజనకాలనుత్పత్తి చేస్తుంది.
బి) మన శరీరం ప్రతిరక్షకాలనుత్పత్తి చేస్తుంది.
సి) మనకు జ్వరం వస్తుంది.
డి) బి మరియు సి
జవాబు:
డి) బి మరియు సి
![]()
ప్రశ్న 21.
వ్యాక్సినేషన్ అనగా
ఎ) ప్రతిరక్షకాలను శరీరంలోకి ప్రవేశపెట్టడం
బి) వ్యాధిని కల్గించే నిర్జీవ సూక్ష్మజీవులను మన శరీరంలోకి ప్రవేశపెట్టడం
సి) వ్యాధిని తగ్గించే రసాయనాలను శరీరంలోకి ప్రవేశపెట్టడం
డి) వ్యాధిని తగ్గించే శిలీంధ్రాలను శరీరంలోనికి ప్రవేశపెట్టడం
జవాబు:
బి) వ్యాధిని కల్గించే నిర్జీవ సూక్ష్మజీవులను మన శరీరంలోకి ప్రవేశపెట్టడం
ప్రశ్న 22.
ఈ క్రింది వానిలో టీకాలేని వ్యా ధి
ఎ) గవదబిళ్ళలు
బి) తట్టు
సి) అమ్మవారు
డి) మలేరియా
జవాబు:
డి) మలేరియా
ప్రశ్న 23.
రేబిస్ వ్యాధికి వ్యాక్సినను కనుగొన్నది
ఎ) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
బి) లూయపాశ్చర్
సి) జోన్స క్
డి) ఆల్బర్ట్ సాబిన్
జవాబు:
బి) లూయపాశ్చర్
ప్రశ్న 24.
మశూచి వ్యాధికి వ్యాక్సినను కనుగొన్నది
ఎ) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
బి) లూయిపాశ్చర్
సి) జోనస్సక్
డి) ఆల్బర్ట్ సాబిన్
జవాబు:
ఎ) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
ప్రశ్న 25.
లాటిన్ భాషలో వాకా అనగా
ఎ) ఆవు
బి) కుక్క
సి) పిల్లి
డి) గేదె
జవాబు:
ఎ) ఆవు
![]()
ప్రశ్న 26.
గాలిలో నత్రజని శాతం
ఎ) 72%
బి) 75%
సి) 78%
డి) 82%
జవాబు:
సి) 78%
ప్రశ్న 27.
క్రింది వానిలో నత్రజని స్థాపన చేయనిది
ఎ) రైజోపస్
బి) రైజోబియం
సి) అనబిన
డి) నాస్టాక్
జవాబు:
ఎ) రైజోపస్
ప్రశ్న 28.
వేరుశనగ మొక్కలో రైజోబియం బాక్టీరియం ఎక్కడ ఉంటుంది?
ఎ) వేరుశనగకాయ
బి) ఆకులు
సి) కాండం
డి) వేర్లు
జవాబు:
డి) వేర్లు
ప్రశ్న 29.
క్రింది వానిలో లెగ్యుమినేసి కుటుంబానికి చెందని మొక్క
ఎ) చిక్కుడు
బి) బఠాణి
సి) పిల్లి పెసర
డి) బార్లీ
జవాబు:
డి) బార్లీ
ప్రశ్న 30.
B.T. అనగా
ఎ) బాక్టీరియం థురెంజెనిసిస్
బి) బాసిల్లస్ థురెంజెనిసిస్
సి) బాక్టీరియం ట్యూబర్క్యులోసిస్
డి) బాసిల్లస్ ట్యూబర్క్యులోసిస్
జవాబు:
బి) బాసిల్లస్ థురెంజెనిసిస్
![]()
ప్రశ్న 31.
సముద్రంలో ఓడల నుండి ప్రమాదవశాత్తూ ఒలికిపోయిన నూనె తెట్టును తొలగించడానికి దేనినుపయోగిస్తారు?
ఎ) సముద్ర శైవలాలు
బి) ప్రోటోజోవన్లు
సి) బాక్టీరియా
డి) శిలీంధ్రాలు
జవాబు:
సి) బాక్టీరియా
ప్రశ్న 32.
ఈ క్రింది వానిలో అంటువ్యాధి కానిది
ఎ) మలేరియా
బి) క్షయ
సి) జలుబు
డి) మశూచి
జవాబు:
ఎ) మలేరియా
ప్రశ్న 33.
మలేరియా వ్యాధిని కలుగచేసే ప్లాస్మోడియం అనే సూక్ష్మజీవికి వాహకం
ఎ) మగ ఎనాఫిలిస్ దోమ
బి) ఆడ ఎనాఫిలిస్ దోమ
సి) మగ క్యూలెక్స్ దోమ
డి) ఆడ క్యూలెక్స్ దోమ
జవాబు:
బి) ఆడ ఎనాఫిలిస్ దోమ
ప్రశ్న 34.
అంటువ్యాధులు దేనిద్వారా వ్యాప్తి చెందుతాయి ?
ఎ) గాలి
బి) నీరు
సి) ఆహారం
డి) పైవన్నీ
జవాబు:
డి) పైవన్నీ
ప్రశ్న 35.
ప్లాస్మోడియం ఆడ ఎనాఫిలిస్ దోమ ద్వారా వ్యాప్తి చెందుతుంది అని కనిపెట్టింది
ఎ) లూయిపాశ్చర్
బి) స్పాల్లాంజెనీ
సి) రొనాల్డ్రాస్
డి) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్
జవాబు:
సి) రొనాల్డ్రాస్
![]()
ప్రశ్న 36.
ఈగల వలన రాని వ్యాధి
ఎ) మలేరియా
బి) టైఫాయిడ్
సి) డయేరియా
డి) కలరా
జవాబు:
ఎ) మలేరియా
ప్రశ్న 37.
కలుషితమైన నీటి ద్వారా వచ్చే వ్యా ధి
ఎ) డెంగ్యూ
బి) చికున్ గున్యా
సి) స్వైన్ ఫ్లూ
డి) కలరా
జవాబు:
డి) కలరా
ప్రశ్న 38.
ఈ క్రింది వానిలో దోమల ద్వారా వ్యాపించని వ్యాధి
ఎ) స్వైన్ ఫ్లూ
బి) డెంగ్యూ
సి) చికున్ గున్యా
డి) మెదడువాపు వ్యాధి
జవాబు:
ఎ) స్వైన్ ఫ్లూ
ప్రశ్న 39.
గాలి ద్వారా వ్యాపించే వ్యాధి
ఎ) స్వైన్ ఫ్లూ
బి) పోలియో
సి) మశూచి
డి) పైవన్నీ
జవాబు:
డి) పైవన్నీ
ప్రశ్న 40.
ఈ క్రింది వానిలో శిలీంధ్రం ద్వారా రాని వ్యాధి ఏది?
ఎ) వరిలో కాటుక తెగులు
బి) వేరుశనగలో టిక్కా తెగులు
సి) చెరకులో ఎర్రకుళ్ళు తెగులు
డి) నిమ్మలో కాంకర తెగులు
జవాబు:
డి) నిమ్మలో కాంకర తెగులు
![]()
ప్రశ్న 41.
పొగాకులో మొజాయిక్ వ్యాధిని కల్గించేది
ఎ) బాక్టీరియా
బి) శిలీంధ్రం
సి) వైరస్
డి) కీటకాలు
జవాబు:
సి) వైరస్
ప్రశ్న 42.
ఆహారం విషతుల్యం అవడానికి కారణం అయ్యే బాక్టీరియం
ఎ) క్లాస్టీడియం బొట్యులినం
బి) సాల్లోనెల్లా టైఫోసా
సి) విబ్రియోకామా
డి) మైకో బాక్టీరియం
జవాబు:
ఎ) క్లాస్టీడియం బొట్యులినం
ప్రశ్న 43.
ఆంధ్రాక్స్ వ్యాధి వేటికి సోకుతుంది ?
ఎ) గొర్రెలు
బి) మేకలు
సి) మానవులు
డి) పై వాటన్నిటికీ
జవాబు:
డి) పై వాటన్నిటికీ
ప్రశ్న 44.
దీనిని కలపడం ద్వారా సూక్ష్మజీవుల పెరుగుదలను నివారించలేము.
ఎ) ఉప్పు
బి) పసుపు
సి) నూనె
డి) మసాల
జవాబు:
డి) మసాల
ప్రశ్న 45.
సూక్ష్మజీవులు ఇక్కడ వృద్ధి చెందవు.
ఎ) అతి ఎక్కువ ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద
బి) అతి తక్కువ ఉష్ణోగ్రత వద్ద
సి) ఎ మరియు బి
డి) పైవేవీ కావు
జవాబు:
సి) ఎ మరియు బి
![]()
ప్రశ్న 46.
పాశ్చరైజేషన్ లో పాలను ఎంత వరకు వేడిచేస్తారు ?
ఎ) 70°C
బి) 80°C
సి) 100°C
డి) 90°C
జవాబు:
ఎ) 70°C
ప్రశ్న 47.
మరిగించడం ద్వారా సూక్ష్మజీవులను చంపవచ్చని నిరూపించినది
ఎ) పాశ్చర్
బి) స్పాల్లాంజని
సి) జెన్నర్
డి) జోనస్నక్
జవాబు:
బి) స్పాల్లాంజని
ప్రశ్న 48.
క్రిమి సిద్ధాంతాన్ని ప్రతిపాదించినది
ఎ) పాశ్చర్
బి) స్పాల్లాంజని
సి) జెన్నర్
డి) జోనస్సక్
జవాబు:
ఎ) పాశ్చర్
ప్రశ్న 49.
ప్రపంచ మలేరియా దినం
ఎ) జూన్ 20
బి) జులై 20
సి) ఆగస్టు 20
డి) సెప్టెంబరు 20
జవాబు:
సి) ఆగస్టు 20
![]()
ప్రశ్న 50.
దీనిని ఉపయోగించుట ద్వారా వ్యాధి జనక జీవులను ప్రత్యక్షంగా సంహరించవచ్చు.
ఎ) ఆంటిసెప్టిక్స్
బి) ఆంటి బయోటిక్స్
సి) విటమిన్ సప్లిమెంట్స్
డి) పెరుగు
జవాబు:
బి) ఆంటి బయోటిక్స్
ప్రశ్న 51.
కిణ్వన ప్రక్రియలో వెలువడే వాయువు
ఎ) O2
బి) H2
సి) N2
డి) CO2
జవాబు:
డి) CO2
ప్రశ్న 52.
కింది వాటిలో ఏ వ్యాధి ప్రధానంగా గాలి ద్వారా వ్యాప్తి చెందుతుంది ?
ఎ) ట్యూబర్ క్యులోసిస్
బి) ఎయిడ్స్
సి) టైఫాయిడ్
డి) మలేరియా
జవాబు:
ఎ) ట్యూబర్ క్యులోసిస్
ప్రశ్న 53.
తప్పుగా జతచేసిన వాటిని గుర్తించండి.
ఎ) వేరుబుడిపెలు-రైజోబియం
బి) మలేరియా-వైరస్
సి) సిట్రస్ క్యాంకర్-వైరస్
డి) చెరుకులో రెడ్ ట్-ఫంగై (శిలీంధ్రం)
జవాబు:
బి) మలేరియా-వైరస్
ప్రశ్న 54.
టైఫాయిడ్, కలరా, డయేరియా, విరేచనాలు మరియు కామెర్లు అనే వ్యాధులు
ఎ) నీటి ద్వారా వచ్చే వ్యాధులు
బి) గాలి ద్వారా వచ్చే వ్యాధులు
సి) ఎ మరియు బి
డి) పైవేవీ కావు
జవాబు:
ఎ) నీటి ద్వారా వచ్చే వ్యాధులు
ప్రశ్న 55.
రిత్విక్ చక్కెర ద్రావణంకు ఈస్ట్ పౌడర్ కలిపి ఒక రోజంతా ఉంచాడు
ఎ) ద్రావణం ఉప్పగా మారి, వాసనలేకుండా ఉండడం
బి) ద్రావణం నీలినలుపు రంగులోకి మారడం
సి) ద్రావణంలో ఏ మార్పు కన్పించదు
డి) ద్రావణం ఆల్కహాల్ వాసన కల్గి ఉంటుంది.
ద్రావణంపైన బుడగలు కన్పిస్తాయి
జవాబు:
డి) ద్రావణం ఆల్కహాల్ వాసన కల్గి ఉంటుంది.
![]()
ప్రశ్న 56.
చిత్రంలో మొసాయిక్ వ్యాధిని గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:

ప్రశ్న 57.
ఇడ్లీ పిండికి ఈస్టు కలిపితే జరిగే పర్యవసానంలో సరియైనది
1) ఉష్ణోగ్రత తగ్గిపోతుంది
2) పిండి యొక్క పరిమాణం పెరుగుతుంది
3) ఈస్ట్ కణాలు నీటిని ఉత్పత్తి చేస్తాయి
4) కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ వాయువు విడుదలగును
ఎ) 1, 2 మాత్రమే
బి) 2, 3 మాత్రమే
సి) 2, 4 మాత్రమే
డి) 4 మాత్రమే
జవాబు:
సి) 2, 4 మాత్రమే
ప్రశ్న 58.
రైతులకు ఉపయోగపడే సూక్ష్మజీవి
ఎ) రైజోబియం
బి) లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్
సి) పెన్సిలిన్
డి) అమీబా
జవాబు:
ఎ) రైజోబియం
ప్రశ్న 59.
మొట్టమొదటిసారిగా టీకాలను కనుగొన్నది
ఎ) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్-1696
బి) రోనాల్డ్ రాస్-1796
సి) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్-1796
డి) లూయీ పాశ్చర్-1696
జవాబు:
సి) ఎడ్వర్డ్ జెన్నర్-1796
ప్రశ్న 60.
కింది వానిలో వైరస్ ద్వారా వచ్చే వ్యాధులు
ఎ) టైఫాయిడ్, డయేరియా
బి) మలేరియా, అమీబియాసిస్
సి) కండ్లకలక, అమ్మవారు
డి) గుండె జబ్బు
జవాబు:
సి) కండ్లకలక, అమ్మవారు
![]()
ప్రశ్న 61.
గేదె గిట్టలకు వ్యాధి వచ్చి అది సక్రమముగా నడవ లేకున్నది. ఇది ఏ వ్యాధి అయి వుండవచ్చును.
ఎ) ఆంథ్రాక్స్
బి) మశూచి
సి) రాబిస్
డి) గాలికుంటు
జవాబు:
డి) గాలికుంటు
ప్రశ్న 62.
టీకాల పనితీరును ప్రశ్నించేందుకు డాక్టరును అడగాల్సిన సరైన ప్రశ్న
ఎ) టీకాలు వేయించుకోవడం వల్ల ఆరోగ్యంగా వుంటామా ?
బి) టీకాల కంటే ఏంటిబయాటిక్స్ బాగా పనిచేస్తాయా?
సి) టీకాలు మన శరీరంలో ఎలా పనిచేస్తాయి ?
డి) టీకాలు వేయించుకోవడం వల్ల జ్వరం వస్తుందా?
జవాబు:
సి) టీకాలు మన శరీరంలో ఎలా పనిచేస్తాయి ?
ప్రశ్న 63.
జతపరచండి.
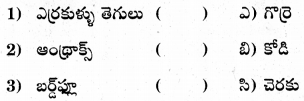
ఎ) 1 – ఎ, 2 – బి, 3 – సి
బి) 1 – బి, 2 – ఎ, 3 – సి
సి) 1 – సి, 2 – ఎ, 3 – బి
డి) 1 – బి, 2 – సి, 3 – ఎ
జవాబు:
సి) 1 – సి, 2 – ఎ, 3 – బి
ప్రశ్న 64.
రేబిస్ వ్యాధి దీనివల్ల కలుగుతుంది
ఎ) దోమలు కుట్టడం
బి) కుక్క కాటు
సి) దెబ్బలు తగలడం
డి) కలుషిత ఆహారం
జవాబు:
బి) కుక్క కాటు
ప్రశ్న 65.
కింది వాక్యాలు చదవండి. జవాబును గుర్తించండి.
1) జ్వరం వచ్చినపుడు వాక్సినను వేయించుకోవాలి
2) పోలియో రాకుండా ఏంటిబయాటికన్ను తీసుకోవాలి
ఎ) 1వది తప్పు 2వది సరైనది
బి) 1, 2 సరైనవే
సి) 1, 2 సరైనవి కావు
డి) 1 సరైనదే 2వది తప్పు
జవాబు:
బి) 1, 2 సరైనవే
![]()
ప్రశ్న 66.
వ్యాధుల నుండి దూరంగా వుండడానికి నీవు పాటించే అంశం
ఎ) కాచి చల్చార్చిన నీటిని తాగుతాను
బి) ఆహార పదార్థాలను వేడిగా వున్నప్పుడే భుజిస్తాను
సి) పరిసరాలను శుభ్రంగా వుంచుకొంటాను
డి) పైవన్నియు
జవాబు:
డి) పైవన్నియు
ప్రశ్న 67.
కింది సూక్ష్మజీవి బేకరీల్లో కేక్ తయారీలో ఉపయోగపడుతుంది
ఎ) ఈస్ట్
బి) లాక్టోబాసిల్లస్
సి) వైరస్
డి) రైజోఫస్
జవాబు:
ఎ) ఈస్ట్
ప్రశ్న 68.
నీ ఆరోగ్యాన్ని సంరక్షించుకొనేందుకు కింది వానిలో ఏది సరైన చర్య
ఎ) వాటర్ బాటిళ్ళలో నిల్వ చేసిన నీటిని తాగడం
బి) కుళాయి నీటిని తాగడం
సి) బావి నీటిని తేరు పట్టి తాగడం
డి) కాచి చల్లార్చిన నీటిని తాగడం
జవాబు:
డి) కాచి చల్లార్చిన నీటిని తాగడం

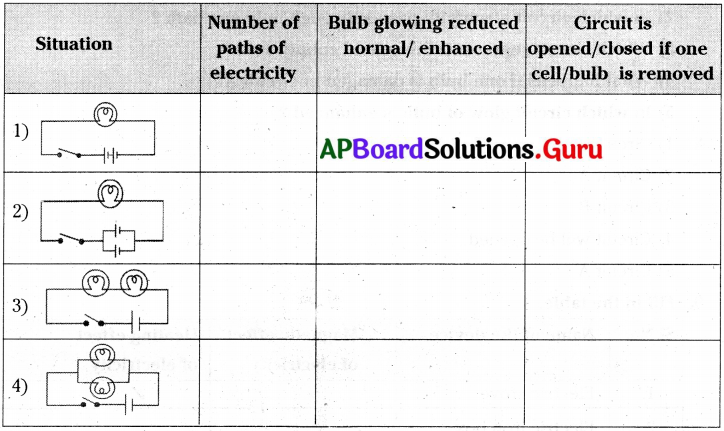
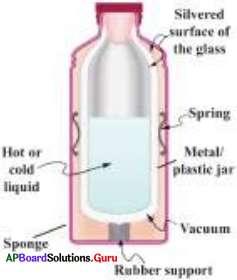
 The process in the picture is
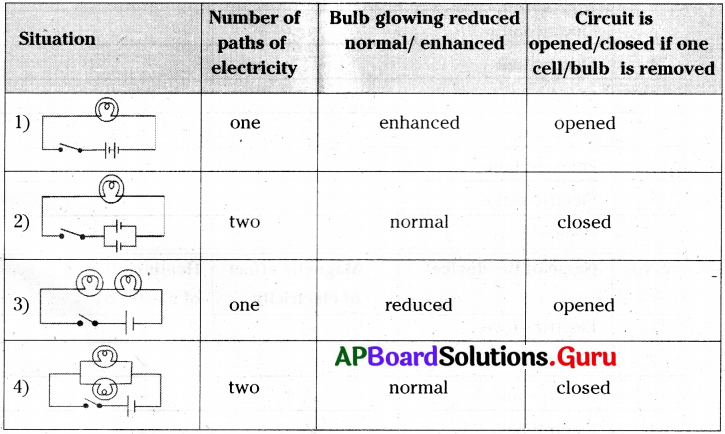
The process in the picture is The equipment show in the figure is
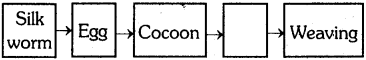
The equipment show in the figure is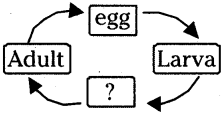
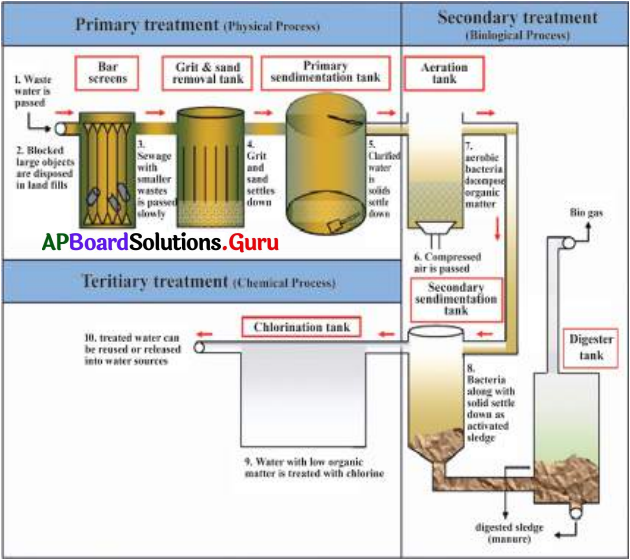





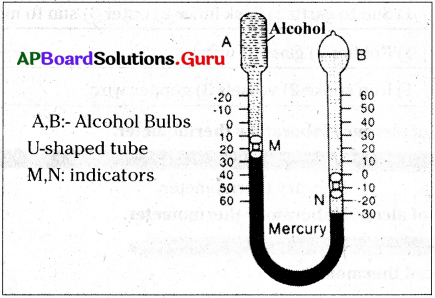
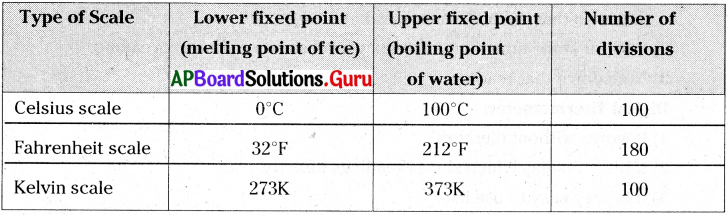
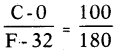
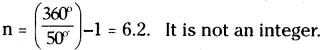

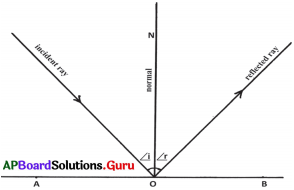
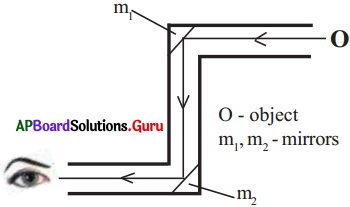

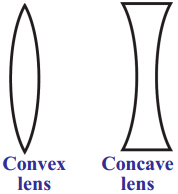




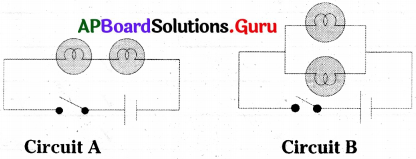
 This diagram indicates
This diagram indicates