SCERT AP 7th Class Science Study Material Pdf 11th Lesson దారాలు – దుస్తులు Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Science 11th Lesson Questions and Answers దారాలు – దుస్తులు
7th Class Science 11th Lesson దారాలు – దుస్తులు Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning (అభ్యసనాన్ని మెరుగుపరచుకుందాం)
I. ఖాళీలను పూరింపుము.
1. పొట్టిగా ఉన్న ఉన్ని వెంట్రుకలను తొలగించడం కోసం దువ్వెన వంటి యంత్రం దంతాల మధ్య నుండి వాటిని లాగడాన్ని ……………. అంటారు . (కూంబింగ్)
2. పట్టు దారాల కోసం పట్టుపురుగులను పెంచే ప్రక్రియను …………………… అంటారు. (పట్టు సంవర్ధనం)
3. పట్టువలె కనిపించే కృత్రిమ దారం …………. (రేయాన్)
4. పట్టులో ఉండే ప్రోటీన్ ……………….. (ఫైబ్రాయిన్)
5. ఊలుని ఇచ్చే జంతువుల మృదువైన పొట్టి శ్రేష్ఠమైన వెంట్రుకలు గల లోపలి పొరను ………….. అంటారు. (ఉన్ని)
II. సరైన జవాబు సూచించు అక్షరమును బ్రాకెట్లో రాయండి.
1. ఈ క్రింది వానిలో ఊలుని ఇచ్చే జంతువు కానిది ఏది?
a) జడల బర్రె
b) మేక
c) మోత్
d) ఒంటె
జవాబు:
c) మోత్
2. పట్టు పురుగు ………………..
a) ప్యూపా
b) కకూన్
c) డింభకము
d) ప్రౌఢ దశ
జవాబు:
c) డింభకము
3. షీరింగ్ అనగా………………
a) నాణ్యత ఆధారంగా ఉన్నిని ఎంపిక చేయడం
b) ఉన్నికి రంగు వేయడం
c) సన్నని చర్మపు పొరతో పాటుగా ఉన్నిని కత్తిరించడం
d) వేడి నీటిలో ఫైబర్లను శుభ్రపరచడం
జవాబు:
c) సన్నని చర్మపు పొరతో పాటుగా ఉన్నిని కత్తిరించడం

4. పట్టుదారం తయారీ ఈ మొక్కల సాగుతో ముడిపడి ఉన్నది ……………
a) ఓక్ చెట్లు
b) సాల్ చెట్లు
c) తెల్ల మద్ది వృక్షం
d) మల్బరీ చెట్టు
జవాబు:
d) మల్బరీ చెట్టు
5. భారతదేశంలో ఎక్కువగా తయారయ్యే పట్టు రకము ……….
a) ఈరీ
b) టసర్
c) మల్బరీ
d) మూగా
జవాబు:
c) మల్బరీ
III. జతపరచండి.
| గ్రూపు – A | గ్రూపు – B |
| A) ప్యూపా | 1) ఊలు |
| B) పట్టు మోత్ | 2) మేక |
| C) జంతు దారాలు | 3) కకూన్ |
| D) అంగోరా | 4) వన్య పట్టు |
| E) టసర్ | 5) బాంబిక్స్ మోరీ |
| 6) రేయాన్ |
జవాబు:
| గ్రూపు – A | గ్రూపు – B |
| A) ప్యూపా | 3) కకూన్ |
| B) పట్టు మోత్ | 5) బాంబిక్స్ మోరీ |
| C) జంతు దారాలు | 1) ఊలు |
| D) అంగోరా | 2) మేక |
| E) టసర్ | 4) వన్య పట్టు |
IV. ఈ క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు జవాబులు రాయండి.
ప్రశ్న 1.
స్టిప్లింగ్ ఎలా చేస్తారో తెలపండి. కకూన్లను సిప్లింగ్ చేయడం వలన కలిగే ప్రయోజనం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
స్టింగ్ : కకూన్ లోపలి గొంగళి పురుగును చంపే ప్రక్రియను స్టిప్లింగ్ అంటారు.
ఆవశ్యకతలు :
- 1. కకూన్లను స్టిఫ్టింగ్ చేయకపోతే, కకూన్ లోపలి మోత్, కకూనను పగలగొట్టుకొని వెలుపలికి వస్తుంది. పగిలిపోయిన కకూన్ల నుండి పొడవాటి దారాలను ఉత్పత్తి చేయలేము. ఇది పట్టువస్త్రాల నాణ్యతను తగ్గిస్తుంది.
- స్టిఫ్టింగ్ చేసిన కకూన్లను ఎక్కువకాలం పాటు నిలువచేసి అవసరమైనప్పుడు సరైన ధరకు మార్కెట్లో అమ్ముకోవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 2.
జంతు దారాలకు, మొక్కల నుండి లభించే దారాలకు భేదాలను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
| జంతు దారాలు | మొక్కల దారాలు |
| 1. జంతుదారాలు ప్రోటీన్ కల్గి ఉంటాయి. | 1. మొక్కల దారాలు సెల్యులోజ్ కల్గి ఉంటాయి. |
| 2. ఇవి నెమ్మదిగా మండుతాయి. | 2. ఇవి వేగంగా మండుతాయి. |
| 3. కాల్చినపుడు మాంసం వాసనతో కూడిన పొగలు వస్తాయి. | 3. కాల్చినపుడు పొగ ఘాటైన వాసన వస్తుంది. |
| 4. బూడిద పూసవలె ఉండి ముట్టుకుంటే పొడిగా మారుతుంది. | 4. బూడిద నల్లగా మసివలె ఉంటుంది. |
ప్రశ్న 3.
కృత్రిమ దారాల వినియోగంలో ఉండే ప్రయోజనాలను, నష్టాలను విశ్లేషించండి. ఏ రకమైన దుస్తులను ధరించేందుకు నీవు ఇష్టపడతావు?
జవాబు:
కృత్రిమ దారాల ప్రయోజనాలు:
- తక్కువ ధరకు లభిస్తాయి.
- తేలికగా ఉంటాయి.
- ఎక్కువ కాలం మన్నుతాయి.
- దృఢంగా ఉంటాయి.
- తక్కువ నీటిని పీల్చుకుంటాయి.
- త్వరగా ఆరిపోతాయి.
- శుభ్రం చేయటం సులభం.
కృత్రిమ దారాల నషాలు:
- ఇవన్ని పూర్తిగా రసాయనాలతో తయారౌతాయి.
- వీటి ఉత్పత్తి పర్యావరణ కాలుష్యానికి దారి తీస్తుంది.
- కొన్ని సంవత్సరాల పాటు నేలలో కలవవు.
- విచ్ఛిన్నం అయినపుడు విషపదార్థాలను విడుదల చేస్తాయి.
- చర్మానికి ఎలర్జీ కలిగించవచ్చు.
కావున నేను సహజ దారాలతో తయారైన దుస్తులు ధరించటానికి ప్రాధాన్యత ఇస్తాను. ఇది వ్యవసాయరంగానికి, కుటీర పరిశ్రమలకు చేయూతనివ్వటంతోపాటు పర్యావరణానికి హాని చేయదు.

ప్రశ్న 4.
కకూన్లను స్టిప్లింగ్ చేయకపోతే ఏమి జరుగుతుంది?
జవాబు:
- కకూన్ లోపలి గొంగళి పురుగును చంపే ప్రక్రియను స్టిఫ్లింగ్ అంటారు.
- కకూన్లను స్టింగ్ చేయకపోతే, లోపలి మోతా, కకూనను పగలగొట్టుకొని వెలుపలికి వస్తుంది.
- పగిలిపోయిన కకూన్ల నుండి పొడవైన పట్టుదారాలను తీయలేము.
- ఇది పట్టువస్త్రాల నాణ్యత తగ్గటానికి కారణమౌతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 5.
పట్టు పురుగు జీవిత చక్రము పటము గీసి, భాగములను గుర్తించండి. జీవిత చక్రంలో ఏ దశ పట్టు ఉత్పత్తిలో ముఖ్యమైనది? ఎందువలన?
జవాబు:
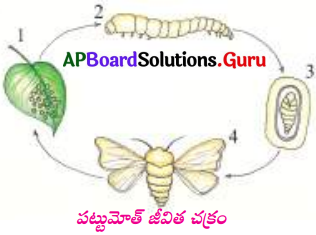
- పట్టుపురుగు జీవిత చక్రంలో కకూన్ లేదా పట్టుకాయ అనేది కీలకమైనది. దీని నుండి పట్టు తీస్తారు.
- కకూన్ దశలో గొంగళి పురుగు తన చుట్టు ఒక గుళికను -ఏర్పర్చుకొంటుంది. ఈ నిర్మాణాన్నే పట్టుకాయ అంటారు.
- పట్టుకాయనే సిప్లింగ్ చేసి, రీలింగ్ యూనిట్ కి పంపుతారు.
- రీలింగ్ యూనిట్లో పట్టుకాయ నుండి పట్టుదారము తీస్తారు.
ప్రశ్న 6.
జంతువుల ఉన్ని కోసం షీరింగ్ చేసే సమయంలో జంతువును బాధించకుండా ఉండటం కోసం షీరింగ్ చేసే వారు ఎటువంటి జాగ్రత్తలు తీసుకోవాలో సూచించండి.
జవాబు:
- జంతువుల చర్మంపై రెండు రకాల రోమాలు ఉంటాయి. మొదటి రకం బిరుసుగా, గట్టిగా ఉండగా రెండవ రకం మెత్తగా, మృదువుగా ఉంటుంది. దీనినే ఉన్ని లేదా ప్లీస్ అంటారు.
- జంతు చర్మం నుండి ఉన్ని లేదా ప్లీస్ ను తొలగించడాన్ని షీరింగ్ అంటారు.
- పదునైన కత్తెర వంటి సాధనాన్ని షీరింగ్ కి వాడతారు.
- ప్రస్తుత కాలంలో గన్ వంటి పరికరాలు వాడుతున్నారు.
జాగ్రత్తలు:
- షీరింగ్ సమయంలో చర్మం దెబ్బతినకుండా నూనె లేదా గ్రీజు వంటి పదార్థం పూస్తారు.
- శీతాకాలంలో జీవులకు ఉన్ని అవసరం. కావున, ఈ నెలలో షీరింగ్ చేయరు.
- వేసవికాలంలో జంతువులకు ఉన్ని అవసరం ఉండదు. కావున, వేసవికి ముందు వచ్చే వసంత కాలంలో సీరింగ్ చేస్తారు.
- షీరింగ్ తరువాత గొర్రెలకు ఆహారం బాగా అందించటం వలన అవి త్వరగా కోలుకొని ఉన్నిని ఉత్పత్తి చేసుకుంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 7.
పట్టు దారాలు కోసం కకూన్లలోని డింభకాలను చంపటంపై మీ అభిప్రాయాలను తెలియజేయండి. పట్టు మోత్ పట్ల ఇటువంటి నిర్ధయాపూరితమైన చర్యలను నివారించటం కోసం నీవు ఎటువంటి చర్యలను సూచిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
- పట్టుదారాల కోసం కకూన్లను చంపటం నాకు చాలా బాధగా అనిపించింది.
- నిజంగా ఇది నిర్దయకరమైన చర్య.
- దీనికి ప్రత్యామ్నాయంగా మోతలు జీవించగలిగే ప్రక్రియకు ప్రాధాన్యత ఇవ్వాలి.
- అహింసా పట్టు అహింసా మార్గంలో పట్టు సంవర్ధనం ద్వారా ఉత్పత్తి చేసే పట్టు.
- ఈ పద్దతిలో పట్టుపురుగును కకూన్ నుండి వెలుపలికి రానిచ్చి తరువాత మిగిలిన పట్టుకాయల నుండి పట్టు దారం తీస్తారు.
- ఈ పద్ధతిని, ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ చేనేత పరిశ్రమ శాఖలో పని చేసిన చేనేత నిపుణులు శ్రీ కుసుమ రాజయ్య పరిచయం చేశారు.
- అయితే ఈ విధానంలో పట్టు ఉత్పత్తి ఎక్కువ ఖర్చుతో కూడుకున్నది.
7th Class Science 11th Lesson దారాలు – దుస్తులు InText Questions and Answers
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 137
ప్రశ్న 1.
ప్రజలు చలి ప్రదేశములలో నివసిస్తున్నప్పుడు ఏఏ దుస్తులను ధరిస్తారు?
జవాబు:
చలి ప్రదేశాలలో నివసించే ప్రజలు ఉన్ని దుస్తులు ధరిస్తారు.

ప్రశ్న 2.
ఈ దుస్తులు ఏ వస్త్రంతో తయారవుతాయి?
జవాబు:
ఉన్ని దుస్తులు జంతువుల నుండి తీసిన రోమాలతో తయారవుతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 3.
సంక్రాంతి వంటి ముఖ్య వేడుకలలో ఏ వస్త్రంతో తయారయిన దుస్తులను నీవు ధరిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
సంక్రాంతి వంటి ప్రత్యేక సందర్భములలో నేను పట్టు దుస్తులు ధరిస్తాను.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 139
ప్రశ్న 4.
మన పరిసరాలలో గొర్రెలు, మేకలను ఎందుకని ఎక్కువ మొత్తంలో పెంచుతారు?
జవాబు:
ఉన్ని మరియు మాంసం కోసం గొర్రెలను, మేకలను పెంచుతారు.
7th Class Science Textbook Page, No. 143
ప్రశ్న 5.
మనకు రంగు రంగుల ఉన్ని దుస్తులు ఎలా లభిస్తున్నాయి?
జవాబు:
గొర్రెల ఉన్ని నలుపు, గోధుమ, తెలుపు రంగులలో ఉంటుంది. రంగు వేయటం ద్వారా, ప్లీస్ మొదట దానిలోని రంగు తొలగించబడటం కోసం బ్లీచింగ్ చేయబడి, తరువాత వేరు వేరు రంగులలో ముంచబడుతుంది.
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 157
ప్రశ్న 6.
మనం దుస్తులు ఎందుకు శుభ్రపరుస్తాము?
జవాబు:
చర్మ వ్యాధులు రాకుండా ఉండటం కోసం మనం ధరించిన దుస్తులు శుభ్రం చేయటం అవసరం.
ఆలోచించండి – ప్రతిస్పందించండి
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 157
ప్రశ్న 1.
పూర్వం పారాచూట్ తాళ్ళను పట్టుతో తయారుచేసేవారు. దీనికి ఉన్న బలం, సాగే గుణము, గాలిలో ఎగురుతున్నప్పుడు వ్యక్తి బరువును తట్టుకునే విధంగా ఉంటుంది. పట్టుకి ఉన్న ఈ సద్గుణాలతో పాటుగా నీటిని నిరోధించే గుణం కారణంగా పారాచూట్ తాళ్ళ తయారీదారులు నైలాన్ వైపుకు మొగ్గు చూపడం జరిగింది. నూలు లేదా ఊలును ఈ అవసరం కోసం ఉపయోగిస్తే ఏమి జరుగుతుంది?
జవాబు:
- పారాచూట్ తయారీకి పట్టు లేదా నైలాన్ దారాలు వాడటం మంచిది.
- వాటి స్థానంలో నూలు లేదా ఉన్ని ఉపయోగిస్తే గట్టిదనం తగ్గిపోతుంది.
- మనిషి బరువు మోయటంలో పారాచూట్ సామర్థ్యం తగ్గిపోతుంది.
- నూలు లేదా ఉన్నికి నీటిని పీల్చుకొనే స్వభావం వలన తేమ వాతావరణంలో ఉపయోగించలేము.
- ఈ దారాలు నీటిని పీల్చుకోవటం వలన పారాచూట్ బరువు పెరుగుతుంది.
- వాటిని వాడటం ప్రమాదకరం.
ప్రాజెక్ట్ పనులు
7th Class Science Textbook Page No. 165
ప్రశ్న 1.
భారతదేశ పటమును తీసుకుని, దేశంలోని వివిధ ప్రదేశాలలో ఉన్నిని ఇచ్చే జంతువులు జీవించే ప్రదేశాలను గుర్తించి, ఆయా ప్రదేశాలలో లభ్యమయ్యే ఆ జంతువుల పేర్లను నమోదు చేయండి.
జవాబు:
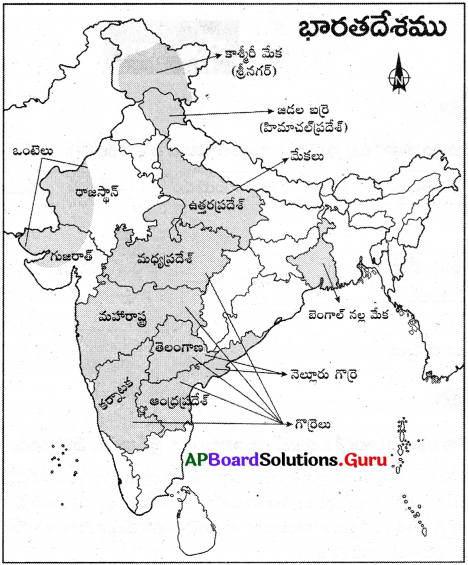
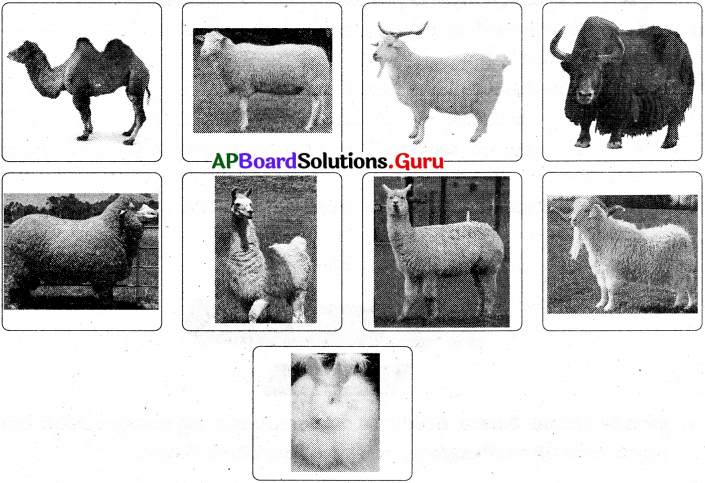
ప్రశ్న 2.
వివిధ రకములైన ఊలుని ఇచ్చే జంతువుల బొమ్మలతో ఒక స్క్రాప్బుక్ తయారు చేయండి.
జవాబు:

కృత్యాలు
కృత్యం – 1
ప్రశ్న 1.
“ఉన్ని నుండి వస్త్రం దాకా” ఉన్ని దుస్తుల తయారీలో ఇమిడి ఉన్న దశలతో ఒక ఫ్లో చార్ట్ ను తయారు చేయండి.
జవాబు:
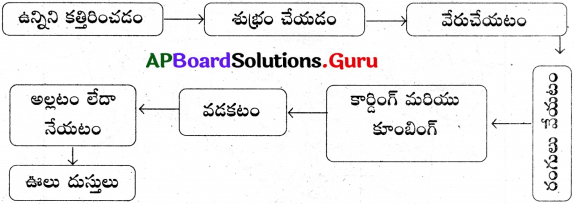
కృత్యం – 2
ప్రశ్న 2.
ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని వివిధ జిల్లాలలో సెరికల్చర్ యూనిట్లు ఉన్న ప్రదేశాలను పేర్కొనండి.
జవాబు:
ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని అనంతపురం జిల్లా ధర్మవరం, కర్ణాటకలోని రామనగర, గుజరాత్ లోని సూరత్, మధ్యప్రదేశ్ లోని చందేరీ, తమిళనాడులోని కాంచీపురం, తెలంగాణలోని పోచంపల్లి, ఉత్తరప్రదేశ్ లోని వారణాసిలు అధిక నాణ్యత గల పట్టు ఉత్పత్తి, నేత పరిశ్రమల కారణంగా భారతదేశంలో పట్టునగరాలుగా పేరుగాంచాయి. ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ అంతటా పట్టు పరిశ్రమ నెలకొని ఉంది.
| జిల్లా పేరు | పట్టు సంవర్ధన యూనిట్లు ఉన్న ప్రదేశాలు |
| 1. శ్రీకాకుళం | లావేరు, ఎట్చెర్ల |
| 2. విజయనగరం | నెలిమెర్ల |
| 3. విశాఖపట్టణం | పాడేరు |
| 4. పశ్చిమ గోదావరి | విజయ్ రాయ్ |
| 5. తూర్పు గోదావరి | కాకినాడ, చేబ్రోలు, గొల్లప్రోలు |
| 6. కృష్ణా | ఘంటసాల |
| 7. గుంటూరు | పెద కాకాని, బొల్లాపల్లి, తాడికొండ |
| 8. ప్రకాశం | గిద్దలూరు, కంభం |
| 9. నెల్లూరు | మర్రిపాడు, కలిగిరి, రాపూరు |
| 10. చిత్తూరు | పలమనేరు, మదనపల్లి, కుప్పం |
| 11. కడప | చెన్నూరు |
| 12. కర్నూలు | ఆత్మకూరు, కొత్తపల్లి, పత్తికొండ, నంద్యాల |
| 13. అనంతపురం | హిందూపూర్, కదిరి, పెనుగొండ |

ప్రశ్న 3.
టైలర్ లేదా బట్టల దుకాణం నుండి ఊలు, పట్టు, నూలు మరియు మరికొన్ని దారాలను సేకరించండి. ఒకదాని తరువాత ఒకటి క్రొవ్వొత్తి మంటలో మండించండి..అవి ఎలా మండుతున్నాయో మరియు ఎటువంటి పొగలను ఉత్పత్తి చేస్తున్నాయో పరిశీలించండి. పట్టికలో నమోదు చేయండి.
జవాబు:
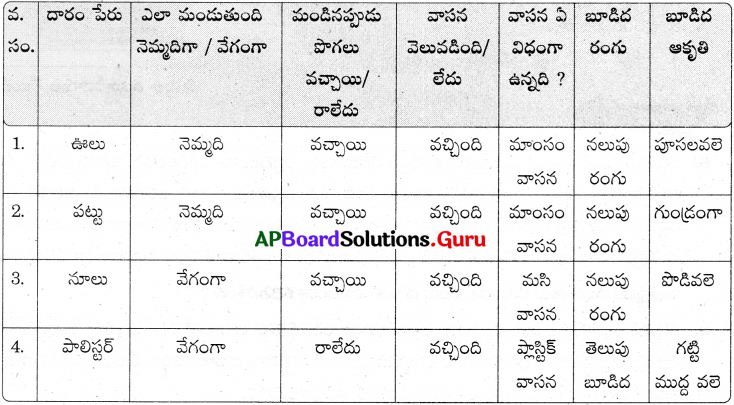
కృత్యం – 4
ప్రశ్న 4.
జంతు దారాల స్వచ్ఛతను ఎలా పరీక్షిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
ఉద్దేశం : జంతు దారాల స్వచ్ఛతను పరీక్షించుట.
పరికరాలు : రెండు బీకర్లు, సోడియం హైపోక్లోరైట్.

విధానం :
టాయిలెట్ క్లీనర్ లో ఉంచిన పట్టు దారాలు
- రెండు బీకర్లు తీసుకొని, వాటిలో కొంచెం సోడియం హైపోక్లోరైట్ ద్రావణం తీసుకోవాలి.
- రెండు బీకరులలో ఒకదానిలో ఉన్ని దారాన్ని మరొకదానిలో పట్టు దారాన్ని ఉంచాలి.
- 20 నిముషాలు ఆగి మార్పులు పరిశీలించాలి.
పరిశీలన :
రెండు దారాలు హైపోక్లోరైట్ ద్రావణంలో కరిగిపోయాయి.
వివరణ :
జంతు దారాలు ప్రోటీన్లతో తయారవుతాయి. ఇవి హైపోక్లోరైట్ వంటి బ్లీచింగ్ ద్రావణాలలో కరుగుతాయి.
నిర్ధారణ :
మంచి జంతు దారాలు, హైపోక్లోరైట్ ద్రావణాలలో కరుగుతాయి.
కృత్యం – 5
ప్రశ్న 5.
ఇవ్వబడిన పటంలోని దుస్తుల తయారీదారుల లేబుల్ ని పరిశీలించి క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
1) ఈ దుస్తులు ఏ వస్త్రంతో తయారయ్యాయి?
జవాబు:
ఈ దుస్తులు పాలిస్టర్ మరియు కాటన్లతో తయారైనవి.
2) ఈ దుస్తులను ఏ రకంగా ఉతకవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
ముదురు రంగు ఉన్న దుస్తులను వేరుచేసి ఉతకాలి.
3) దుస్తుల దీర్ఘకాల మన్నిక కొరకు ఎటువంటి జాగ్రత్తలు తీసుకోవాలి?
జవాబు:
- డిటర్జంట్ ను తక్కువగా వాడాలి.
- తక్కువ ఉష్ణోగ్రతలో ఆరవేయాలి.
- బ్లీచింగ్ వాడరాదు.
- తక్కువ వేడితో ఇస్త్రీ చేయాలి.

కృత్యం – 6
ప్రశ్న 6.
దర్జీ వద్ద నుండి రిబ్బను వెడల్పుతో, పొడవైన రెండు పట్టు వస్త్రములను సేకరించండి. వాటిని నీటిలో ముంచి తీసి, వాటిపై ఏర్పడిన ముడుతలను పరిశీలించండి. ఒక వస్త్రమును అలాగే ఆరవేయండి మరియు రెండవ వస్త్రమును ఒక కర్ర బొంగుకు కానీ, లోహపు కడ్డీకి కానీ బిగుతుగా, ముడుతలు లేకుండా లాగి, చుట్టివేయండి. ఈ వస్త్రమును అలాగే గాలికి ఆరనివ్వండి. రెండు మూడు గంటల తరువాత రెండు వస్త్రములను పరిశీలించండి.
ఏ వస్త్రము ముడుతలు లేకుండా, ముడుచుకుని పోకుండా కనిపిస్తోంది?
జవాబు:
చుట్టబడి ఆరబెట్టిన వస్త్రము ముడుతలు లేకుండా ఉంటుంది. కృత్రిమ దారాలతో చేసిన వస్త్రములను నిర్వహించడం సులభం కాబట్టి వాటిని ధరించేందుకు ఎక్కువ ఇష్టపడతాము. సహజ దారాలు జీవుల నుండి లభించే పదార్థాలతో తయారవుతాయి. అందువలన అవి మన చర్మానికి అనుకూలమైనవి.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()































