Use these Inter 1st Year Maths 1A Formulas PDF Chapter 9 Hyperbolic Functions to solve questions creatively.
Intermediate 1st Year Maths 1A Hyperbolic Functions Formulas
→ ex = 1 + \(\frac{x}{1 !}+\frac{x^{2}}{2 !}+\frac{x^{3}}{3 !}+\ldots+\frac{x^{n}}{n !}\)+ … ∞
→ sinhx = \(\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{2}\)
and coshx = \(\frac{e^{x}+e^{-x}}{2}\)
→ tanh x = \(\frac{\sinh x}{\cosh x}\),
→ coth x = \(\frac{1}{\tanh x}\),
→ sech x = \(\frac{1}{\cosh x}\)
→ cosech x = \(\frac{1}{\sinh x}\), if x ≠ 0
![]()
→ cosh2x – sinh2x – 1, sech2x – 1 – tanh2x, cosech2x = coth2x – 1
| Function y = f(x) | Domain (x) | Range (y) |
| sinh x | R | R |
| cosh x | R | (1, ∞) |
| tanh x | R | (1, 1) |
| coth x | R- {0} | (-∞, -1) ∪ (1, ∞) |
| sech x | R | (0, 1] |
| cosech x | R – {0} | R – {0} |
→ sinh-1x = loge [x + \(\sqrt{x^{2}+1}\) ] for all x ∈ R
→ cosh-1x = loge [x + \(\sqrt{x^{2}-1}\)] for all x ∈ (1, ∞)
→ tanh-1x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{1+x}{1-x}\right)\), |x| < 1 (i.e) for all x ∈ (-1, -1)
→ coth-1x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{1+x}{1-x}\right)\), |x| > 1 (i.e) for all x ∈ (-∞, -1) (1, ∞)
→ sech-1x = loge\(\left(\frac{1+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}{x}\right)\) for all x ∈ (0, 1)
→ cosech-1x = loge\(\left(\frac{1-\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}{x}\right)\), if x < 0 (i.e,) x ∈ (-∞, 0) and
= loge\(\left(\frac{1+\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}{x}\right)\), if x > 0 (i.e,) x ∈ (0, ∞)
→ sinh (x + y) = sinh x cosh y + cosh x sinh y
→ cosh (x + y)= cosh x cosh y + sinh x sinh y
→ sinh (x – y) = sinh x cosh y – cosh x sinh y
→ cosh (x – y) = cosh x cosh y – sinh x sinh y
→ tanh (x + y) = \(\frac{\tanh x+\tanh y}{1+\tanh x \tanh y}\)
→ tanh (x – y) = \(\frac{\tanh x-\tanh y}{1-\tanh x \tanh y}\)
→ sinh 2x = 2 sinh x cosh x = \(\frac{2 \tanh x}{1-\tanh ^{2} x}\)
![]()
→ cosh 2x = cosh2x + sinh2x
= 2 cosh2x – 1 = 1 + 2 sinh2 x = \(\frac{1+\tanh ^{2} x}{1-\tanh ^{2} x}\)
→ tanh 2x = \(\frac{2 \tanh x}{1+\tanh ^{2} x}\)
→ sinh 3x = 3sinh x + 4sinh3 x
→ cosh 3x = 4cosh3 x – 3cosh x
→ tanh 3x = \frac{3 \tanh x+\tanh ^{3} x}{1+3 \tanh ^{2} x}
→ Inverse hyperbolic functions:
| Function y = f(x) | Domain (x) | Range (y) |
| (i) sinh-1(x) | IR | IR |
| (ii) cosh-1(x) | [1, ∞) | [0, ∞) |
| (iii) tanh-1(x) | (-1, 1) | IR |
| (iv) coth-1(x) | R –[-1, 1] | R- {0} |
| (v) sech-1(x) | (0, 1] | [0, ∞) |
| (vi) cosech-1(x) | R- {0} | R – {0} |
→ sin hx = \(\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{2}\)
→ cos hx = \(\frac{e^{x}+e^{-x}}{2}\)
→ tan hx = \(\frac{e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}\)
→ cosec hx = \(\frac{2}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}\)
→ sec hx = \(\frac{2}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}\)
→ cot hx = \(\frac{e^{x}+e^{-x}}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}\)
→ cos h2x – sinh2x = 1
→ 1 – tanh2x = sech2x
→ cot h2x – 1 = cosech2x
![]()
→ Prove that sinh-1x = log{x + \(\sqrt{x^{2}+1}\)}
Proof:
Let sinh-1x = y ⇒ x = sinh y
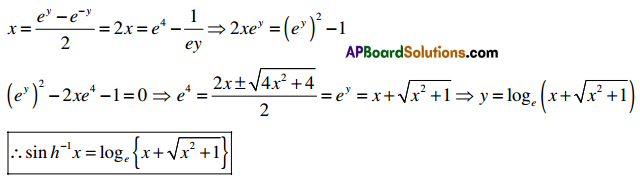
→ Prove that cosh-1x = loge(x – \(\sqrt{x^{2}-1}\)
proof:
Let cosh-1x = y ⇒ x = cosh y
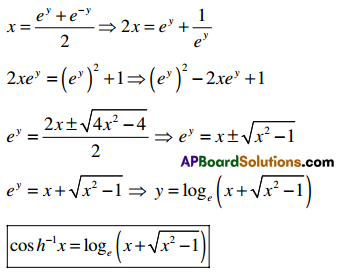
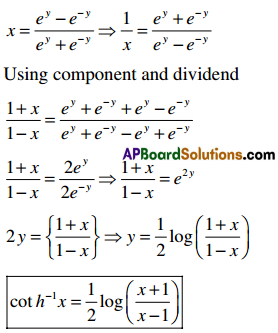
→ Prove that Tan-1x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)loge\(\left(\frac{4 x}{1-x}\right)\)
proof:
Let tanh-1x = y ⇒ x = tanh y
→ sech-1x = log\(\left\{\frac{1+\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}{x}\right\}\)
→ cosech-1x = log\(\left(\frac{1-\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}{x}\right)\) x < 0 = log\(\left\{\frac{1-\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}{x}\right\}\) x > 0
→ sin h(x + y) = sin hx cos hy + cos hx sin hy
→ sinh(x – y) = sin hx cos hy + cos hx sin hy
→ cosh(x + y) = cos hx cos hy + sin hx sin hv
→ cosh(x – y) = cos hx cos hy – sin hx sin hy
→ sin h2x = 2 sin hx cos hx = \(\)
→ cos h2x = cosh2x + sinh2x = 2cosh2x – 1 = 1 + 2sinh2x = \(\frac{1+{Tanh}^{2} x}{1-{Tanh}^{2} x}\)
→ Tanh(x + y) = \(\frac{\text { Tanhx+Tanhy }}{1-\text { TanhxTanhy }}\)
→ Tanh(x – y) = \(\frac{\text { Tanhx-Tanhy }}{1+\text { TanhxTanhy }}\)
→ coth(x + y) = \(\frac{\cot h x \cot h y+1}{\cot h y+\cot h x}\)
→ coth(x – y) = \(\frac{\cot h x \cot h y-1}{\cot h y-\cot h x}\)
→ Tanh2x = \(\frac{2 \tan h x}{1+\tanh ^{2} x}\)
→ cot h2x = \(\frac{\operatorname{coth}^{2} x+1}{2 \cot h x}\)