Students get through Maths 1B Important Questions Inter 1st Year Maths 1B Differentiation Important Questions which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
Intermediate 1st Year Maths 1B Differentiation Important Questions
Question 1.
If f(x) = x2 (x ∈ R), prove that f is differentiable on R and find its derivative.
Solution:
Given that f(x) = x2
for x, h ∈ R, f(x + h) – f(x)(x + h)2 – x2
= x2 + h2 + 2hx – x2
= 2hx + h2 = h(2x + h)
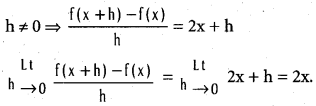
∴ f is differentiable on R and f'(x) = 2x for each x ∈ R
![]()
Question 2.
Suppose f(x) = \(\sqrt{x}\) (x > 0). Prove that f is differentiable on (0, ∞) and find f(x).
Solution:
Let x ∈ (0, ∞) h ≠ 0 and |h| < 0
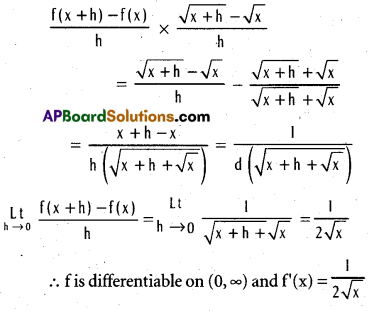
Question 3.
If f(x) = \(\frac{1}{x^{2}+1}\) (x ∈ R), prove that f is differentiable on R and find f'(x).
Solution:
Let x ∈ R and h ≠ 0
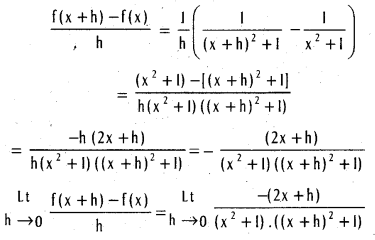
= –\(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)^{2}}\)
∴ f is differentiable and f'(x) = –\(\frac{2 x}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)^{2}}\) for each x ∈ R .
Question 4.
If f(x) = sin x (x ∈ R), then show that f is differentiable on R and f'(x) = cosx.
Solution:
Let x ∈ R and h ≠ 0
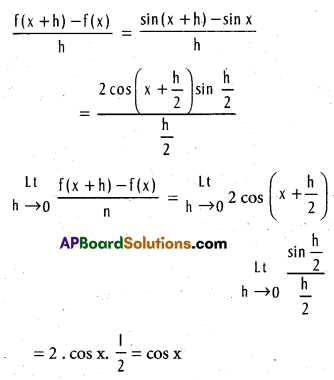
∴ f is differentiable on R and f'(x) = cos x for each x ∈ R.
![]()
Question 5.
Show that f(x) = |x| (x ∈ R) is not differentiable at zero and is differentiable at any x ≠ 0.
Solution:
Given f(x) = |x|
∴ f(x) = x if x ≥ 0
if h ≠ 0
\(\frac{f(0+h)-f(0)}{h}\) = \(\frac{f(h)}{h}\) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{r}
1 \text { if } h>0 \\
-1 \text { if } h<0
\end{array}\right.\)
f'(0+) = 1, f'(0–) = -1
∴ is not differentiable at zero it can be easily proved that f is differentiable at any x ≠ 0 and that f'(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
1 \quad \text { if } x>0 \\
-1 \text { if } x<0
\end{array}\right.\)
Question 6.
Check whether the following function is differentiable at zero f(x) = \(\left\{\begin{array}{l}
3+x \text { if } x \geq 0 \\
3-x \text { if } x<0
\end{array}\right.\)
Solution:

f has the left hand derivative at zero and f'(0–) = -1
∴ f'(0+) ≠ f'(0–)
f(x) is not differentiable at zero.
![]()
Question 7.
Show that the derivative of a constant function on an interval is zero.
Solution:
let f be a constant function on an interval I.
f(x) = C ∀ x ∈ I for some constant.
Let a ∈ I, for h ≠ 0 \(\frac{f(a+h)-f(a)}{h}\) = \(\frac{c-c}{h}\) = 0
for sufficiently small (h)
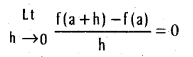
∴ f is differentiable 0 and f'(0).
Question 8.
Suppose for all x, y ∈ R f(x + y) = f(x). f(y) and f'(0) exists. Then show that f(x) exists and equals to f(x) f'(0)for all x ∈ R.
Solution:
Let x ∈ R, for h ≠ 0, we have
\(\frac{f(x+h)-f(x)}{h}\) = \(\frac{f(x) f(h)-f(x)}{h}\)
= f(x) \(\frac{[f(h)-1]}{h}\) ………………….. (1)
f(0) = f(0 + 0) = f(0) f(0) ⇒ f(0) (1 —f(0)) = 0
∴ f(0) = 0 or f(0) = 1
Case (1) : Suppose f(0) = 0
f(x) = f(x + 0) = f(x) f(0) = 0 ∀ x ∈ R
∴ f(x) is a constant function = f'(x) = 0 for all x ∈ R
∴ f'(x) = 0 = f(x) . f'(0)
Case (ii): Suppose f(0) = 1
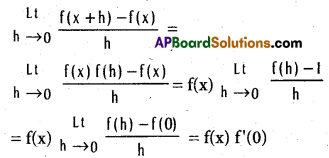
∴ f is differentiable and f'(x) = f'(x) f'(0).
Question 9.
If f(x) = (ax + b)n, (x > –\(\frac{b}{a}\)), then find f'(x).
Sol:
Let u = ax + b so that y = un
f'(x) = \(\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) (un) \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= n.un-1a.
= an(ax+b)n – 1
Question 10.
Find the derivative of f(x) = ex (x2 + 1)
Solution:
Let u = ex, V = x2 + 1
\(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = ex, \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 2x
f'(x) = u(x) v'(x) + u'(x) . v(x)
= ex2x + (x2 + 1) ex
= ex(2x + x2 + 1)
= ex(x + 1)2
![]()
Question 11.
If y = \(\frac{a-x}{a+x}\) (x ≠ -a), find \(\frac{\mathrm{d} y}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Let u = a – x and v = a + x so that y = \(\frac{\mathrm{u}}{\mathrm{v}}\)
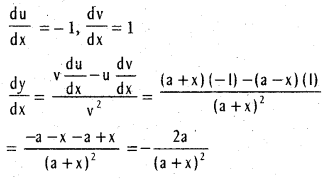
Question 12.
If f(x) = e2x . log x (x > 0), then find f'(x).
Solution:
Let u = e2x, v = log x so that
\(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 2 . e2x , \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 1
f(x) = u.v
f'(x) = u . \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) + y . \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= e2x . \(\frac{1}{x}\) + log x (2e2x)
= e2x (\(\frac{1}{x}\) + 2 logx)
Question 13.
If f(x) = \(\sqrt{\frac{1+x^{2}}{1-x^{2}}}\) (|x| < 1), then find f'(x)
Solution:
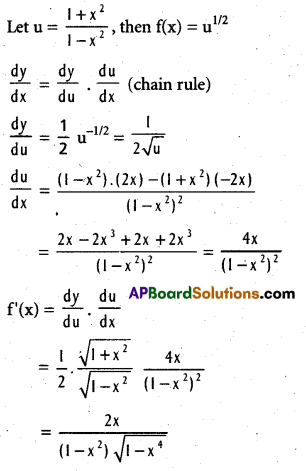
Question 14.
If f(x) = x2, 2x log x (x > 0), find f'(x).
Solution:
u = x2, v = 2x, w = logx
\(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 2x, \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 2x . log2, \(\frac{\mathrm{dw}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{x}\)
f'(x) = uv . \(\frac{\mathrm{dw}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) + vw . \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) + uw . \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= x22x . \(\frac{1}{x}\) + 2x . logx(2x) + x2 . logx . 2x log2
= x . 2x (logx2 + xlogx (log 2) + 1)
![]()
Question 15.
If y = \(\left|\begin{array}{l}
f(x) g(x) \\
\phi(x) \psi(x)
\end{array}\right|\) then show that \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\left|\begin{array}{l}
f^{\prime}(x) g^{\prime}(x) \\
\phi(x) \psi(x)
\end{array}\right|\) + \(\left|\begin{array}{l}
f(x) g \backslash(x) \\
\phi^{\prime}(x) \Psi(x)
\end{array}\right|\)
Solution:
Given y = \(\left|\begin{array}{l}
f(x) g(x) \\
\phi(x) \psi(x)
\end{array}\right|\)
= f(x) ψ(x) – Φ(x) g(x)
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = f(x) ψ'(x) + ψ(x) f'(x) – [Φ(x). g'(x) + g(x). Φ'(x)]
= [f(x) ψ'(x) – g(x) Φ’x)] + [f'(x) ψ(x) – Φ(x).g'(x)]
= \(\left|\begin{array}{l}
f(x) g(x) \\
\phi^{\prime}(x) \psi^{\prime}(x)
\end{array}\right|\) + \(\left|\begin{array}{cc}
f^{\prime}(x) & g^{\prime}(x) \\
\phi(x) & \psi(x)
\end{array}\right|\)
Question 16.
If f(x) = 7x2+3x (x > 0), then find f'(x).
Solution:
Let u = x3 + 3x ⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 3x2 + 3 = 3(x2 + 1)
f(X) = 7u
f'(x) = \(\frac{d f}{d u}\) . \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) (7u . l0g 7) [3(x2 + 1)]
= 3(x2 + 1) 7x2+3x log 7
Question 17.
If f(x) = x ex sin x, then find f(x).
Solution:
Let u = x ,v = ex, w = sin x
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 1, \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = ex . \(\frac{\mathrm{dw}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = cos x
f(x) = u.v.w
f'(x) = uv . \(\frac{\mathrm{dw}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) + uw \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) + vw \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= xex cos x + x . sinx ex + ex sin x.
![]()
Question 18.
If f(x) = sin (log x), (x > 0), find f'(x).
Solution:
Let u = logx, y = f(x) so that y = sin u
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{d y}{d u}\) . \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = cos u, \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{x}\)
f'(x) = \(\frac{1}{x}\) . cos u = \(\frac{1}{x}\) cos (log x)
Question 19.
If f(x) =(x3 + 6x2 + 12x – 13)100; find f'(x).
Solution:
u = x3 + 6x2 + 12x – 13
⇒ \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 3x2 + 12x + 12
= 3(x2 + 4x + 4)
= 3(x + 2)2
f(x) = u100
f'(x) = 100 . u99 . \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= 100 (x3 + 6x2 + 12x – 13)99 . 3(x + 2)2
= 300 (x + 2)2 (x3 + 6x2 + 12x – 13)99
Question 20.
Find the derivative of f(x) = \(\frac{x \cos x}{\sqrt{1+x^{2}}}\)
Solution:
Let u = x cos x, and v = \(\sqrt{1+x^{2}}\) so that
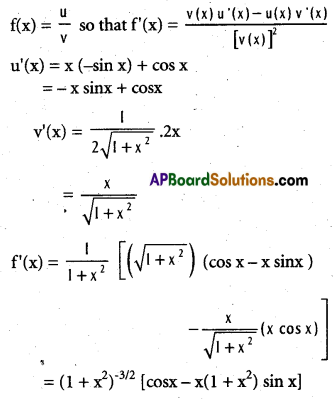
Question 21.
li f(x) = log (secx + tan x), find f'(x). [Mar 14, May 11]
Solution:
Let u = sec x + tan x and y = log u
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{u}\), \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = sec x. tan x + sec2 x
= sec x (sec x + tan x)
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) . \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= \(\frac{1}{\sec x+\tan x}\) . sec x(sec x + tan x) = sec x
![]()
Question 22.
If y = sin-1\(\sqrt{x}\), find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
Solution:
u = \(\sqrt{x}\), y = sin-1 x.
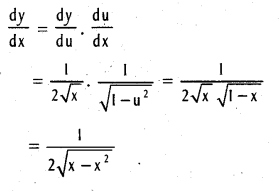
Question 23.
If y = sec (\(\sqrt{\tan x}\)), find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
u = \(\sqrt{\tan x}\), v = tanx
Then y = sec u, u = \(\sqrt{\mathrm{v}}\), v = tan x
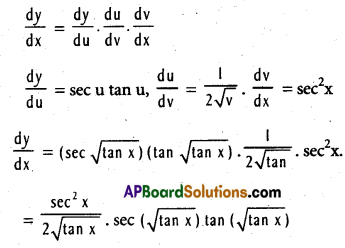
Question 24.
If y = \(\frac{x \sin ^{-1} x}{\sqrt{1-x^{2}}}\), find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Let u = x sin-1x, v = \(\sqrt{1-x^{2}}\)
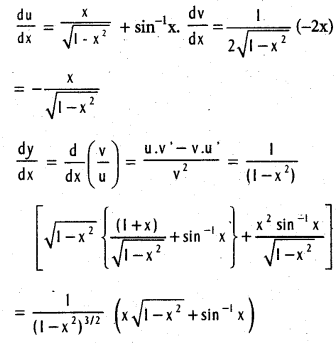
![]()
Question 25.
If y = log (cosh 2x), find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Let u = cosh 2x, so that y = log u
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{u}\); \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 2 sin h2x
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{d y}{d u}\) . \(\frac{\mathrm{du}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= 2 sin h 2x . \(\cosh 2 x\) = 2 tan h 2x
Question 26.
If y = log (sin (log x)), find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Let v = log x, u = sin v so that y = log u.
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{u}\); \(\frac{d u}{d v}\) = cos u; \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{x}\)
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{d y}{d u}\) . \(\frac{d u}{d v}\) . \(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
= \(\frac{1}{\sin (\log x)}\) . cos (logx) \(\frac{1}{x}\) = \(\frac{\cot (\log x)}{x}\)
Question 27.
If y = (cot-1x3)2, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
u = cot-1x3, u = x3, y = u2
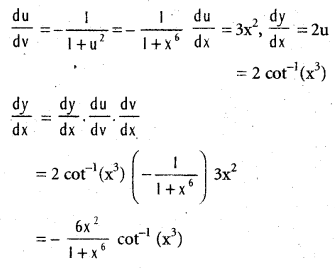
![]()
Question 28.
If y = cosec-1(e2x+1), find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
u = e2x+1, y = cosec-1u
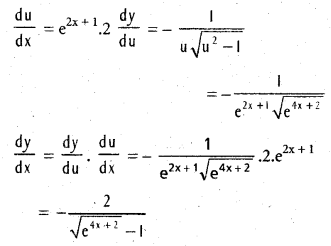
Question 29.
If y = tan-1 (cos \(\sqrt{x}\)), find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
v = \(\sqrt{x}\) and u = cos v, y = tan-1u
\(\frac{\mathrm{dv}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{x}}\), \(\frac{d u}{d v}\) = – sin u; \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{1}{1+u^{2}}\)
= – sin \(\sqrt{x}\) = \(\frac{1}{1+\cos ^{2}(\sqrt{x})}\)
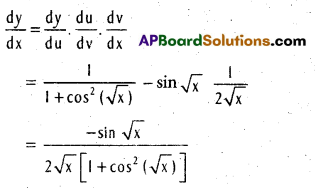
Question 30.
If y = Tan-1 \(\sqrt{42}\) for 0 < |x| < 1, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\). [May, Mar 12]
Solution:
Put x2 = cos 2θ
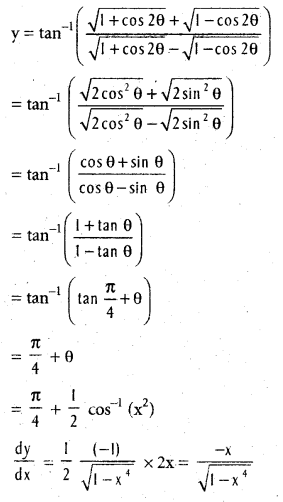
![]()
Question 31.
If y = x2exsin x, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
log y = log x2. ex. sin x
= log x2 + log ex + log sin x
= 2 log x + log ex + log sin x
Differentiating w.r.to by sin x
\(\frac{1}{y}\) . \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{2}{x}\) + 1 + \(\frac{1}{sin x}\) . cos x
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = y(\(\frac{2}{x}\) + 1 + cot x)
Question 32.
If y = xtanx + (sin x)cos x, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) [Mar. 14, 11]
Solution:
Let u = xtanx and v = (sin x)cos x
log u logx tanx = (tan x) log x
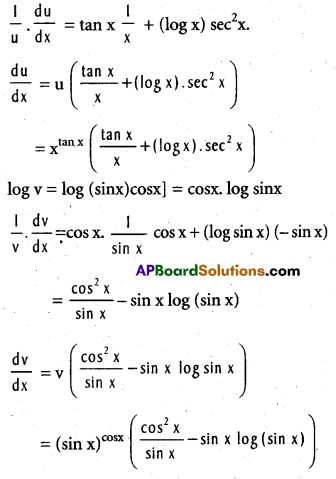
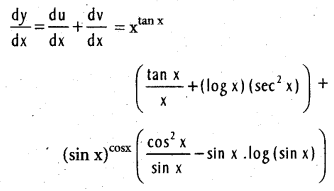
Question 33.
If x = a(cos t + log tan (\(\frac{t}{2}\))), y = a sin t, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
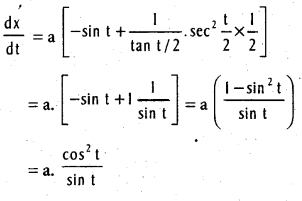
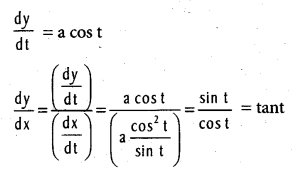
![]()
Question 34.
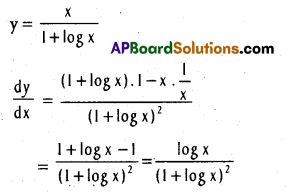
If xy = ex-y, than show that \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{\log x}{(1+\log x)^{2}}\) [May 07]
Solution:
xy = ex-y
log xy = log ex-y
y log x = (x – y) (log e = 1)
y(1 + log x) = x
Question 35.
If siny = x sin (a + y), then show that \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{\sin ^{2}(a+y)}{\sin a}\) (a is not a multiple of π)
Solution:
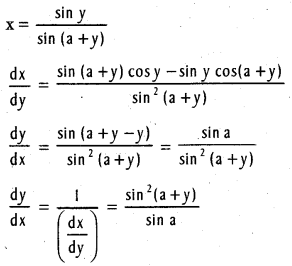
Question 36.
If y = x4 + tan x, then find y”.
Solution:
y = x4 + tan x
\(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 4x3 + sec2 x
\(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}\) = 12x2 + 2 sec x (sec x tan x)
= 12x2 + 2 sec2x . tan x
![]()
Question 37.
If f(x) = sinx, sin 2x sin 3x, find f”(x).
Solution:
f(x) = \(\frac{1}{2}\) sin 2x(2 sin 3x sin x)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) (sin 2x) (cos 2x – cos4x)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) (2 sin 2x cos 2x – 2 sin 2x cos 4x)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\) (sin2x + sin4x – sin6x)
Therefore,
f'(x)= \(\frac{1}{4}\)[2 cos 2x+ 4cos 4x – 6cos 6x]
Hence,
f”(x) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) (-4 sin 2x – 16 sin 4x + 36 sin 6x)
= 9 sin 6x – 4 sin 4x – sin 2x.
Question 38.
Show that y = x + tan x satisfies cos2x \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}\) + 2x = 2y.
Solution:
y = x + tan x implies that y’ = 1 + sec2 x
That is, y’ cos2x = 1 + cos2x.
Differentiating both sides of the above equation we get
y” cos2x + y’ . 2 cos x (-sin x) = 2 cos x (- sin x)
∴ y” cos2 x = 2(y’ – 1) sin x cos x
= 2 sec2x sin x cos x = 2 tan x = 2(y – x)
This proves the result.
Question 39.
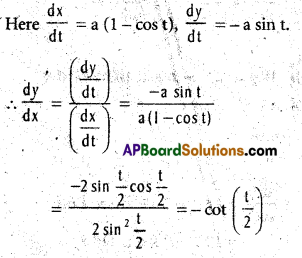
If x = a(t – sin t),y = a(1 + cost), find \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}\).
Solution:
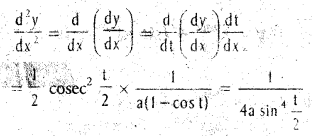
![]()
Question 40.
Find the second order derivative of y = tan-1(\(\frac{2 x}{1-x^{2}}\))
Solution:
Put x = tan θ, Then
y = tan-1 (\(\frac{2 \tan \theta}{1-\tan ^{2} \theta}\))
= tan-1 (tan 2θ)
= 2θ = 2 tan-1x
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{2}{1+x^{2}}\) and \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}\) = \(\frac{-4 x}{\left(1+x^{2}\right)^{2}}\).
Question 41.
If y = sin (sin x), show that y” + (tan x) y’ + y cos2x = 0.
Solution:
y = sin (sin x) implies that .
y’ = cos x . cos (sin x) and
y” = -cos2x sin (sin x) – sin x cos (sin x)
= – y cos2x – sin x (\(\frac{y^{\prime}}{\cos x}\))
= -y cos2x – y’ tan x
∴ y” + (tan x)y’ + y cos2 x = 0.
Question 42.
If f(x) = ex(x ∈ R), then show that f(x) = ex by first principle.
Solution:
From f(x) = ex we have for h ≠ 0
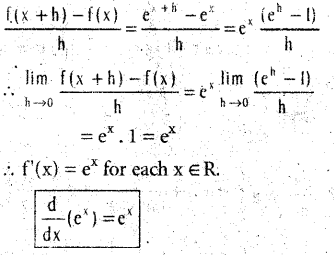
![]()
Question 43.
If f(x) = log x (x > 0), then show that f(x) = \(\frac{1}{x}\) by first principle.
Solution:
Now for h ≠ 0
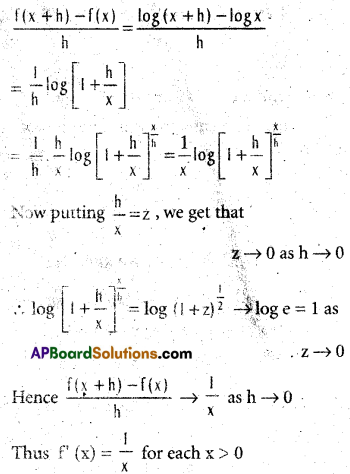
\(\frac{d}{dx}\) (log x) = \(\frac{1}{x}\)
Question 44.
If 1(x) = ax (x ∈ R) (a > 0), then show that f'(x) = ax log a by first principle.
Solution:
For h ≠ 0
\(\frac{f(x+h)-f(x)}{h}\) = \(\frac{a^{x+h}-a^{x}}{h}\) = ax [latex]\frac{a^{h}-1}{h}[/latex]
We know that \(\frac{a^{h}-1}{h}\) → log a as h → 0
Hence f'(x) = ax . log a.
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) = (ax) = ax log a
Question 45.
If y = Tan-1 \(\sqrt{\frac{1-x}{1+x}}\) (|x| < 1), we shall find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Substituting x cos u (u ∈ (0, π)) in y, we get
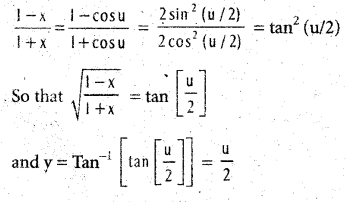
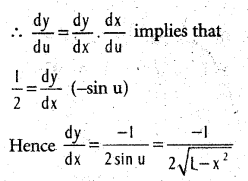
observe that Tan-1x, \(\sqrt{\frac{1-x}{1+x}}\) and cos u are the functions that stand for f(x), g(x) and h(u) respectively, mentioned in the method.
![]()
Question 46.
If y = Tan-1[latex]\frac{2 x}{1-x^{2}}[/latex] (|x| < 1) then we shall \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Substituting x = tan u
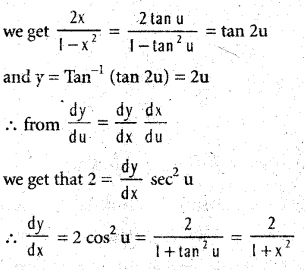
Question 47.
If x = a cos3t, y = a sin3t, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Here \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = 3a cos2t (-sin t) and
\(\frac{d y}{d t}\) = 3a sin2t. cost.
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dt}}}{\frac{\mathrm{dx}}{\mathrm{dt}}}\) = -tan t
Question 48.
If y = et +cost, x = log t + sin t find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\)
Solution:
Here \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = et – sin t and \(\frac{d x}{d t}\) = \(\frac{1}{t}\) + cos t
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{t\left(e^{t}-\sin t\right)}{(1+t \cos t)}\)
![]()
Question 49.
To find the derivative of f(x) = x\(\sin ^{\frac{1}{x}}\) with respect to g(x) = sin-1x, we have to compute \(\frac{d f}{d g}\)
Solution:
Now f(x) = x\(\sin ^{\frac{1}{x}}\) implies that
log f(x) = sin-1x . log x so that
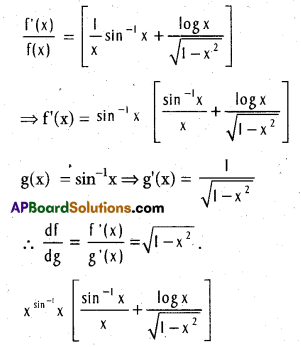
Question 50.
If x3 + y3 – 3axy = 0, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Let the given equation define the function.
y = 1(x) that is x3 + (f(x))3 – 3axf(x) = 0
Differentiating both sides of this equation with respect to x, we get
3x2 + 3 (f(x))2 f'(x) – [3a. f(x) + 3axf'(x)] = 0
Hence 3x2 + 3y2 f'(x) – [3ay + 3ax f'(x)] = 0
∴ f'(x) = \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = \(\frac{a y-x^{2}}{y^{2}-a x}\)
Question 51.
If 2x2 – 3xy + y2 + x + 2y – 8 = 0, find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Treating y as a function of x and then differentiating with respect to x,
we get 4x – 3y – 3xy’ + 2yy’ + 1 + 2y’ = 0
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = y’ = \(\frac{3 y-4 x-1}{2 y-3 x+2}\)
![]()
Question 52.
If y = xx (x > 0), we shall find \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Taking logarithms on both the sides of
y = xx we obtain log y = x log x
Differentiating with respect to x,
We get \(\frac{y^{\prime}}{y}\) = x . \(\frac{1}{x}\) + log x = 1 + log x
∴ \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = y’ = y(1 + log x) = xx (1 + log x)
Question 53.
If y = (tan x)sin x [o < x < \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) ] compute \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\).
Solution:
Taking logarthms on both sides of
y= (tan x)sin x, we get
log y = sin x . log (tan x)
Differentiating with respect to x, we get
\(\frac{y^{\prime}}{y}\) = \(\frac{\sin x}{\tan x}\) . sec2x + cosx . log (tan x)
= sec x + cos x . log (tan x)
Hence \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\) = (tan x)sin x [sec x + cos x log (tan x)]