Students get through Maths 2A Important Questions Inter 2nd Year Maths 2A Partial Fractions Important Questions which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
Intermediate 2nd Year Maths 2A Partial Fractions Important Questions
Question 1.
\(\frac{x+4}{\left(x^{2}-4\right)(x+1)}\) (Mar. 14)
Solution:
\(\frac{x+4}{\left(x^{2}-4\right)(x+1)}\) = \(\frac{A}{x+1}\) + \(\frac{B}{x+2}\) + \(\frac{c}{x-2}\)
Multiplying with (x2 – 4) (x + 1)
x + 4 = A(x2 – 4) + B(x + 1) (x – 2) + C (x + 1) (x + 2)
x = -1 ⇒ 3 = A(1 – 4) = -3A ⇒ A = -1
x = -2 ⇒ 2 = B(-2 + 1) (-2 – 2)
= 4B ⇒ B = + \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
x = 2 ⇒ 6 = C(2 + 1)(2 + 2)
= 12C ⇒ C = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Question 2.
\(\frac{x^{2}-x+1}{(x+1)(x-1)^{2}}\) (TS Mar. 15)
Solution:
Let \(\frac{x^{2}-x+1}{(x+1)(x-1)^{2}}\) = \(\frac{A}{x+1}\) + \(\frac{B}{x-1}\) + \(\frac{C}{(x-1)^{2}}\)
Multiplying with (x + 1) (x – 1)2
x2 – x + 1 = A(x – 1)2 + B(x + 1) (x – 1) + C(x + 1)
Put x = -1, 1 + 1 + 1 = A(4)
⇒ A = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Put x = 1, 1 – 1 + 1 = C(2)
⇒ C = + \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Equating the coefficients of x2,
A + B = 1
⇒ B = 1 – A = 1 – \(\frac{3}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
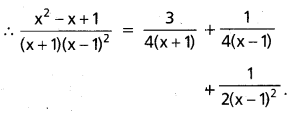
![]()
Question 3.
Resolve the \(\frac{2 x^{2}+3 x+4}{(x-1)\left(x^{2}+2\right)}\) into partial fractions. (AP Mar. ’15, ’11; May ’11) (TS Mar. ’17)
Solution:
Let \(\frac{2 x^{2}+3 x+4}{(x-1)\left(x^{2}+2\right)}\) = \(\frac{A}{x-1}\) + \(\frac{\mathrm{Bx}+\mathrm{C}}{\mathrm{x}^{2}+2}\)
Multiplying with (x – 1) (x2 + 2)
2x2 + 3x + 4 = A(x2 + 2) + (Bx + C)(x – 1)
x = 1 ⇒ 2 + 3 + 4 = A(1 + 2)
9 = 3A ⇒ A = 3
Equating the coefficients of x2
2 = A + B ⇒ B = 2 – A = 2 – 3 = -1
Equating constants
4 = 2A – C ⇒ C = 2A – 4 = 6 – 4 = 2
\(\frac{2 x^{2}+3 x+4}{(x-1)\left(x^{2}+2\right)}\) = \(\frac{3}{x-1}\) + \(\frac{-x+2}{x^{2}+2}\)
Question 4.
Resolve \(\frac{x^{4}}{(x-1)(x-2)}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
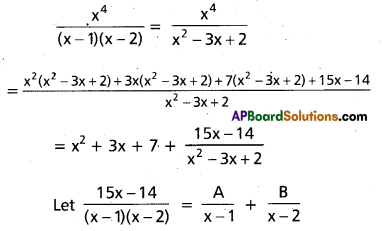
Equating the coefficients of (x – 1) (x – 2),
15x – 14 = A(x – 2) + B(x – 1)
Put x = 1, 15 – 14 ⇒ A(-1) = A = -1
Put x = 2, 30 – 14 = B(1) ⇒ B = 16
∴ \(\frac{x^{4}}{(x-1)(x-2)}\) = x2 + 3x + 7 – \(\frac{1}{x-1}\) + \(\frac{16}{x-2}\)
Question 5.
Resolve \(\frac{x^{2}-3}{(x+2)\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) into partial fractions. (AP Mar. ’17, ’16)
Solution:
Let \(\frac{x^{2}-3}{(x+2)\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) = \(\frac{A}{x+2}\) + \(\frac{B x+C}{x^{2}+1}\)
Multiplying with (x + 2) (x2 + 1)
x2 – 3 = A(x2 + 1) + (Bx + C)(x + 2)
x = -2 ⇒ 4 – 3 = A(4 + 1)
1 = 5A ⇒ A = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Equating the coefficients of x2
1 = A + B ⇒ B = 1 – A
= 1 – \(\frac{1}{5}\) = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Equating the constants – 3 = A + 2C
2C = -3 – A = -3 – \(\frac{1}{5}\) = – \(\frac{16}{5}\)
C = –\(\frac{8}{5}\)
\(\frac{x^{2}-3}{(x+2)\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\) = \(\frac{1}{5(x+2)}\) + \(\frac{4 x-8}{5\left(x^{2}+1\right)}\)
![]()
Question 6.
Resolve \(\frac{1}{(x-1)^{2}(x-2)}\) into partial fractions. (May ’13)
Solution:
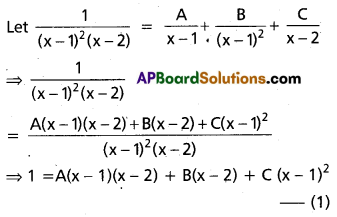
Put x = 1 in (1)
1 = A(0) + B(1 – 2) + C(0)
⇒ -B = 1 ⇒ B = -1
Put x = 2 in (1)
⇒ 1 = A(0) + B(0) + C (2 – 1)2
⇒ C = 1
Equating the coefficients of x2 in (1)
0 = A + C ⇒ A = -C = -1
A = -1
∴ \(\frac{1}{(x-1)^{2}(x-2)}\) = \(\frac{-1}{x-1}\) – \(\frac{1}{(x-1)^{2}}\) + \(\frac{1}{x-2}\)
Question 7.
Resolve \(\frac{5 x+1}{(x+2)(x-1)}\) into Partial fractions.
Solution:
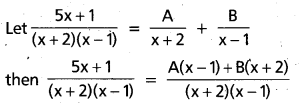
⇒ 5x + 1 = A(x – 1) + B(x + 2) —– (1)
Put x = 1 in(1)
5(1) + 1,= A(0) + B(1 + 2)
⇒ 3B = 6 ⇒ B = 2
Put x = -2 in (1)
5(-2) + 1 = A (-2 – 1) + B(0)
⇒ -9 = -3A ⇒ A = 3
∴ \(\frac{5 x+1}{(x+2)(x-1)}\) = \(\frac{3}{x+2}\) + \(\frac{2}{x-1}\)
![]()
Question 8.
Resolve \(\frac{2 x+3}{5(x+2)(2 x+1)}\) into Partial fractions.
Solution:
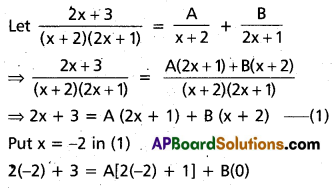
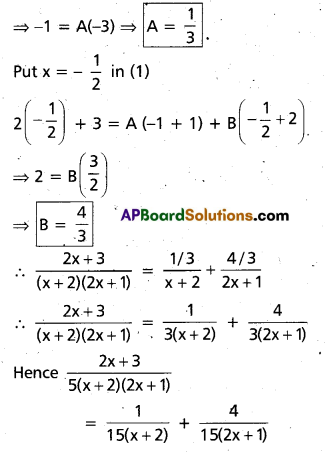
Question 9.
Resolve \(\frac{13 x+43}{2 x^{2}+17 x+30}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
2x2 + 17x + 30 = 2x2 + 12x + 5x + 30
= 2x(x + 6) + 5(x + 6)
= (x + 6) (2x + 5)
Let \(\frac{13 x+43}{(x+6)(2 x+5)}\) = \(\frac{A}{x+6}\) + \(\frac{B}{2x+5}\)
∴ 13x + 43 = A(2x + 5) + B(x + 6)
putting x = -6
-78 + 43 = A(-12 + 5)
-35 = -7A
⇒ A = 5
Putting x = \(\frac{-5}{2}\)
13\(\left(\frac{-5}{2}\right)\) + 43 = \(B\left(\frac{-5}{2}+6\right)\)
⇒ -65 + 86 = B(—5 + 12)
⇒ 21 = 7B
⇒ B = 3
∴ \(\frac{13 x+43}{2 x^{2}+17 x+30}\) = \(\frac{5}{x+6}\) + \(\frac{3}{2 x+5}\)
Question 10.
Resolve \(\frac{x^{2}+5 x+7}{(x-3)^{3}}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
Let x – 3 = y ⇒ x = y + 3
\(\frac{x^{2}+5 x+7}{(x-3)^{3}}\) = \(\frac{(y+3)^{2}+5(y+3)+7}{y^{3}}\)
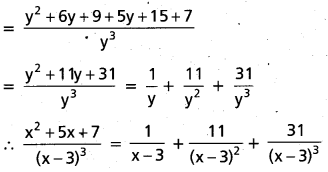
Question 11.
Resolve \(\frac{x^{2}+13 x+15}{(2 x+3)(x+3)^{2}}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
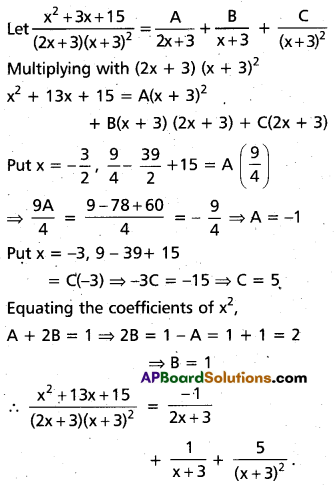
Question 12.
Resolve \(\frac{1}{(x-1)^{2}(x-2)}\) into Partial fractions.
Solution:
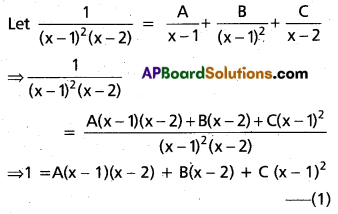
Put x = 1 in (1)
1 = A (0) + B(1 – 2) + C(0)
⇒ -B = 1 ⇒ B = -1
Put x = 2 in (1)
1 = A(0) + B(0) + C(2 – 1)2
⇒ C = 1
Equating the coefficients of x2 in (1)
0 = A + C ⇒ A = -C = -1
A = -1
∴ \(\frac{1}{(x-1)^{2}(x-2)}\) = \(\frac{-1}{x-1}\) – \(\frac{1}{(x-1)^{2}}\) + \(\frac{1}{x-2}\)
![]()
Question 13.
Resolve \(\frac{3 x-18}{x^{3}(x+3)}\) into Partial fractions.
Solution:
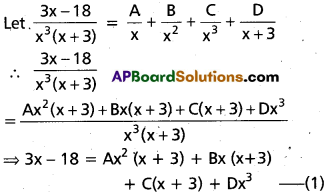
Put x = -3 in(1)
3(-3) – 18 = A(0) + B(0) + C(O) + D (-3)3
⇒ -27D = -27 ⇒ D = 1
Put x = 0 in (1)
3(0) – 18 = A (0) + B(0) + C(0 + 3) + D(0)
⇒ 3C = -18 ⇒ C = -6
Equating the coefficients of x3 in (1)
0 = A + D
⇒ A = -D = -1 ⇒ A = -1
Equating the coefficients of x2 in (1)
0 = 3A + B
⇒ B = -3A = -3(-1) = 3 ⇒ B = 31
∴ \(\frac{3 x-18}{x^{3}(x+3)}\) = \(\frac{-1}{x}\) + \(\frac{3}{x^{2}}\) – \(\frac{6}{x^{3}}\) + \(\frac{1}{x+3}\)
Question 14.
Resolve \(\frac{x-1}{(x+1)(x-2)^{2}}\) into Partial fractions.
Solution:
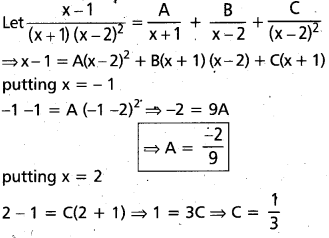
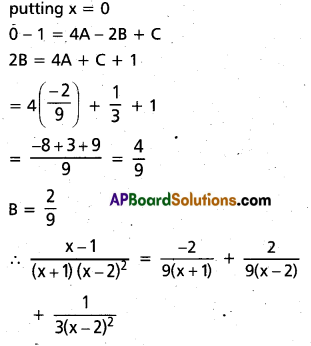
Question 15.
Resolve \(\frac{2 x^{2}+1}{x^{3}-1}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
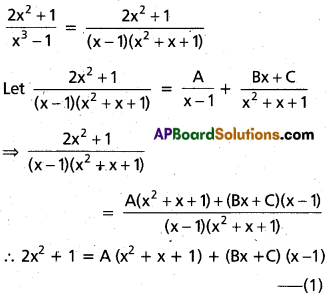
Put x = 1 in (1)
2(1) + 1 = A(1 + 1 + 1) + (B + C)(0)
⇒ 3A = 3 ⇒ A = 1
Put x = 0 in (1)
0 + 1 = A(1) + (0 + C)(0 – 1)
⇒ 1 = A – C
⇒ 1 = 1 – C ⇒ C = 0
Equating the coefficients of x2 in (1)
2 = A + B
⇒ 2 = 1 + B ⇒ B = 1
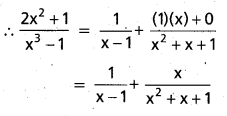
Question 16.
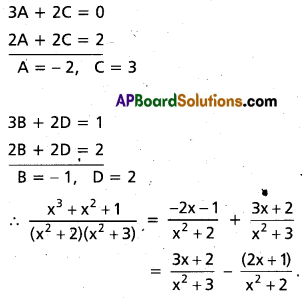
Resolve \(\frac{x^{3}+x^{2}+1}{\left(x^{2}+2\right)\left(x^{2}+3\right)}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
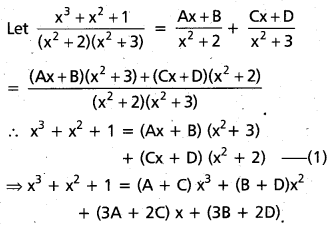
Comparing the coefficients of x3, x2, x and constant terms
A + C = 1, B + D = 1, 3A + 2C = 0, 3B + 2D = 1
Solve
Question 17.
Resolve \(\frac{3 x^{3}-2 x^{2}-1}{x^{4}+x^{2}+1}\) into Partial fractions.
Solution:

A – B + C + D = 0 —— (3)
B + D = -1 ——- (4) D = -1 – B
Substitute C, D in (2)
-A + B + 3 – A – 1 – B = -2
⇒ -2A = -4 ⇒ A = 2
Substitute C, D in (3)
A – B + 3 – A – 1 – B = 0 ⇒ 2 = 2B ⇒ B = 1
∴ C = 3 – 2 = 1, D = -1 – 1 = -2
Ax + B = 2x + 1, Cx + D = x – 2
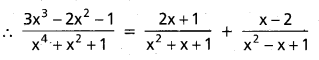
![]()
Question 18.
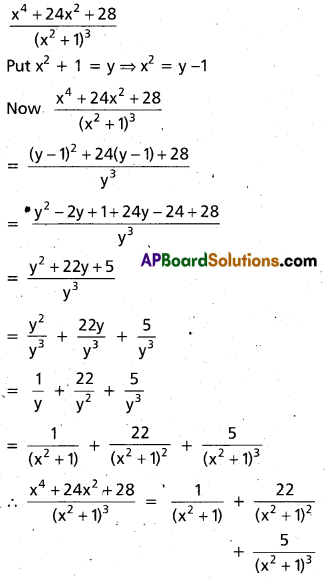
Resolve \(\frac{x^{4}+24 x^{2}+28}{\left(x^{2}+1\right)^{3}}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
Question 19.
Resolve \(\frac{x+3}{(1-x)^{2}\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
Let \(\frac{x+3}{(1-x)^{2}\left(1+x^{2}\right)}\)
= \(\frac{\mathrm{A}}{1-x}\) + \(\frac{B}{(1-x)^{2}}\) + \(\frac{C x+D}{1+x^{2}}\)
= x + 3 = A(1 – x) (1 – x2) + B(1 + x2) + (Cx + D)(1 – x2)
Comparing the coefficients of like powers of x, we get
A + B + D = 3 → (1)
-A + C – 2D = 1 → (2)
A + B – 2C + D = 0 → (3)
-A + C = 0 → (4)
Solving these equations, we get
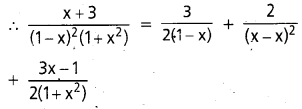
Question 20.
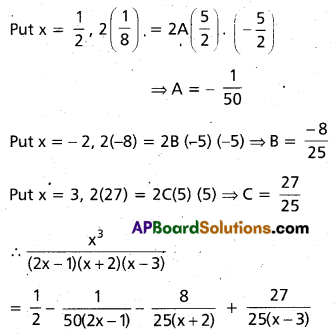
Resolve \(\frac{x^{3}}{(2 x-1)(x+2)(x-3)}\) into partial fractions.
Solution:
\(\frac{x^{3}}{(2 x-1)(x+2)(x-3)}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) + \(\frac{A}{2 x-1}\) + \(\frac{B}{x+2}\) + \(\frac{c}{x-3}\)
Multiplying with 2(2x – 1) (x + 2) (x – 3)
2x3 = (2x – 1) (x + 2) (x – 3) + 2A(x + 2)
(x – 3) + 2B (2x – 1) (x – 3) + 2C (2x -1) (x + 2)
Question 21.
Resolve \(\frac{x^{4}}{(x-1)(x-2)}\) into partial fractions. (T.S. Mar. ’16, March – 2013)
Solution:
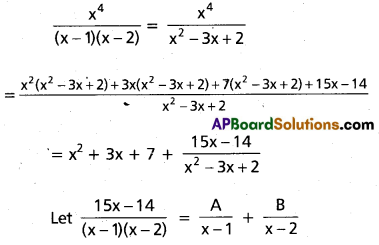
Equating the coefficients of (x – 1) (x – 2),
15x – 14 = A(x – 2) + B(x – 1)
Put x = 1, 15 – 14 = A(-1) ⇒ A = -1
Put x = 2, 30 – 14 = B(1) ⇒ B = 16
∴ \(\frac{x^{4}}{(x-1)(x-2)}\) = x2 + 3x + 7 – \(\frac{1}{x-1}\) + \(\frac{16}{x-2}\)
Question 22.
Find the coefficient of x4 in the expansion of \(\frac{3 x}{(x-2)(x+1)}\) in powers of x specifying the interval in which the expansion is valid.
Solution:
\(\frac{3 x}{(x-2)(x+1)}\) = \(\frac{A}{x-2}\) + \(\frac{B}{x+1}\)
Multiplying with (x – 2) (x + 1)
3x = A(x + 1) + B(x – 2)
Put x = -1, -3 = B(-3) ⇒ B = 1
Put x = 2, 6 = A(3) ⇒ A = 2
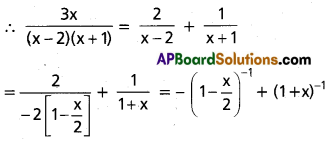
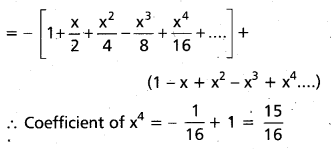
![]()
Question 23.
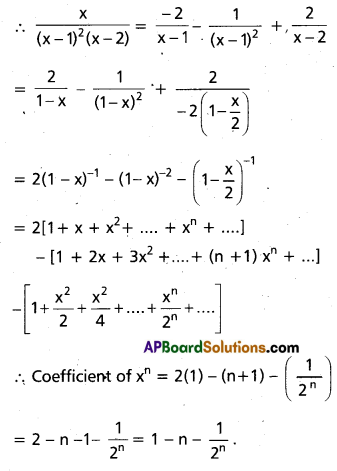
Find the coefficient of xn in the power series expansion of \(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x-2)}\) specifying the region in which the expansion is valid.
Solution:
\(\frac{x}{(x-1)^{2}(x-2)}\) = \(\frac{A}{x-1}\) + \(\frac{B}{(x-1)^{2}}\) + \(\frac{C}{x-2}\)
Multiplying with (x – 1)2 (x – 2)
x = A(x – 1) (x – 2) + B(x – 2) + C(x – 1)2
Put x = 1, 1 = B(-1) ⇒ B = -1
Put x = 2, 2 = C(1) ⇒ C = 2
Put x = 0, 0 = 2A – 2B + C ⇒ 2A = 2B – C
= -2 – 2 = -4 ⇒ A = -2