Students get through AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions 13th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
AP Inter 2nd Year Chemistry Important Questions 13th Lesson Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis exclusively forms primary amines only. Explain.
Answer:
Gabriel Phthalimide synthesis exclusively forms primary amines only.
Reason: In this reaction primary amines are formed without the traces of 2° (or) 3° amines.
Questions 2.
Write equations for carbylamine reaction of any one aliphatic amine.
Answer:
When Ethyl amine (1° – amine) reacts with chloroform in presence of alkali to form ethyl isocyanide.
CH3 – CH2 – NH2 + CHCl3 + 3KOH A ![]() CH3 – CH2 – NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
CH3 – CH2 – NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
![]()
Question 3.
Why aniline does not undergo Friedel — Crafts reaction?
Answer:
Aniline is a lewis base and AlCl3 is a Lewis acid. In Friedel.Craft’s reaction both of these combined to form a complex.
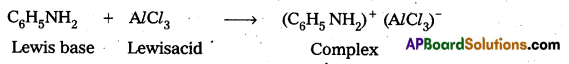
Due to formation of complex the electrophilic substitution tendency decreases in aniline and it does not undergo this reaction.
Question 4.
Give structures of A, B and C in the following reactIons. [T.S. Mar. 17] [A.P. & T.S. Mar. 16]
![]()
Answer:
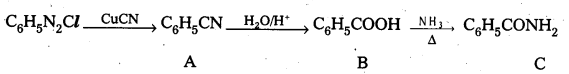
A – Phenyl Cyanide B – Benzoic acid C – Benzarnide
Question 5.
Why cannot aromatic primary amines be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis?
Answer:
Aromatic 1° – amines cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalinide synthesis because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with an ion formed by phthalinide.
Question 6.
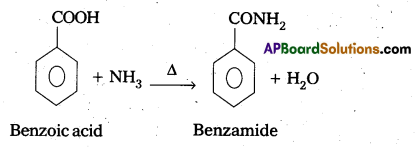
Accomplish the following conversions. [Mar. 14]
i) Benzolc acid to benzamide
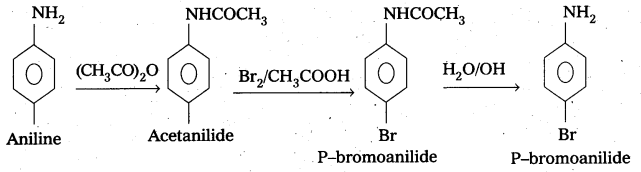
ii) Aniline to p – bromoanlline.
Ans:
Conversion of benzoic acid to benzamide
ii) Conversion of Aniline to p – bromoanlline.
Question 7.
How are Amines prepared by Hoffmann bromamide degradation method.
Answer:
Hoffmann bromamide degradation method: In this method amides are directly converted into amines. When amides are treated with Br5 in NaOH gives amine.
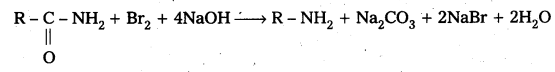
![]()
Question 8.
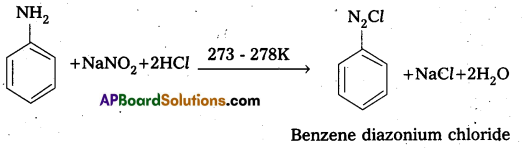
What is Diazotisation reaction ? Give equation. [IPE 16, 14 (T.S.)]
Answer:
Diazotisation reaction: Aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid at low temperatures to form diazonium salts.
Question 9.
What is sulphonation ? Give equation.
Answer:
Sulphonation : Aniline reacts with cone H2SO4 and forms anilinium hydrogen sulphate which on heating gives P – amino benzene sulphonic acid (sulphanilic acid) which exists as Zwitter ion.
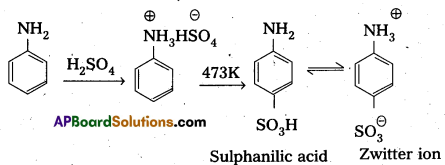
Aniline does not undergo Friedel crafts reactiondue to salt formation with AlCl3.
Question 10.
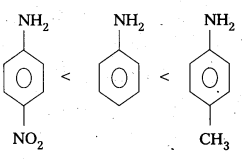
Arrange the following bases in increasing order of their basic strength. Aniline, P – nitroaniline and P – toluidine.
Answer:
The increasing order of basic strength of given compounds is
P – nitroaniline < aniline < P – toluidine
![]()
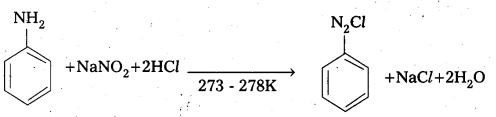
Question 11.
How is benz ene diazonium chloride prepared? Give equation.
Answer:
Preparation: Benzene diazomum chloride is prepared by the reaction of aniline with nitrous acid at 273 – 278K. The conversion of primary aromatic amine into diazonium chloride is called Diazotisation.
Question 12.
Arrange the following bases in decreasing order of pHb, values. C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3, (C2H5)2 NH and C6H5NH2.
Answer:
The decreasing order of pKb values of given amines is
C6H5NH2 > C6H5NHCH3 > C6H5NH2 > (C2H5)2 NH
Question 13.
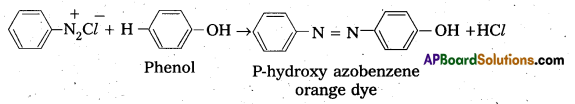
What is a coupling reaction ? Give equation. .
Answer:
Coupling reactions : The azoproducts obtained when diazonium slats react with aromatic compounds have extended conjugated system through N = N. This reaction is called coupling reaction and the prodocuts formed are coloured.
a) Reaction with Phenol
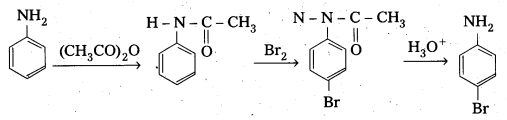
Question 14.
How do you convert aniline to parabromo aniline. [IPE 2014]
Answer:
Aniline is first acylated to give acetaniiyde which on bromination gives parabromo derivative. This bromo derivative on hydrolysis gives parabromo aniline.
Question 15.
How is Aniline prepared. [IPE 2016 (TS)]
Answer:
Aniline is prepared by reduction of nitro benzene in acid medium.
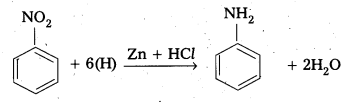
![]()
Question 16.
Explain why ethylamine is more soluble in water where as aniline is not soluble.
Answer:
Ethyl amine is a primary amine, due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding with water molecules it is soluble in water. Though Aniline has – NH2 group, due to hydrophobic aryl group it is not soluble in water.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain with a suitable example how benzene sulphonylchloride can distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Answer:
Benzene sulphonyl chloride is called Hinsberg’s reagent. This is used to distinguish the 1°, 2°, 3° – amines.
- with 1° – amine : Benzene sulphonyl chloride reacts with 1° – amine and produce N – Alkyl benzene sulphonamide which is soluble in alkali.
- with 2° – amine : Benzene sulphonyl chloride reacts with 2° – amine and produce N, N – Dialkyl benzene sulphonamide which is insoluble in alkali.
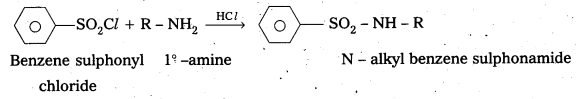
- with 2° – amine: Benzene suiphonyl chloride reacts with 2° – amine and produce N, N – Dialkyl benzene sulphonamide which is insoluble in alkali.
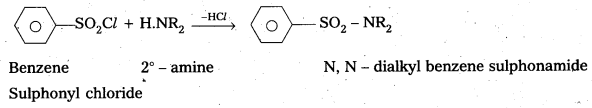
- with 3° – amine : Benzene sulphonyl chloride does not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride.
Question 2.
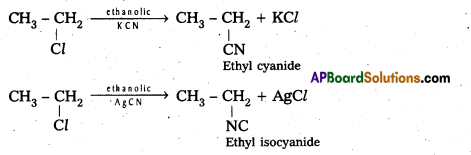
How do you prepare Ethyl cyanide and Ethyl isocyanide from a common alkylhalide ? [IPE 2014]
Answer:
Preparation of ethyl cyanide : Ethyl chloride reacts with aq. Ethanolic KCN to form Ethyl cyanide as a major product.
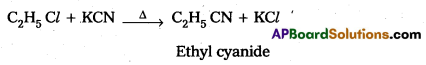
Preparation of Ethyl isocyanide : Ethyl chloride reacts with aq. Ethanolic AgCN to form Ethyl iso cyanide as a major product.

Question 3.
How do you distinguish cyanides and isocyanides by hydrolysis and reducation.
Answer:
i) Hydrolysis : Cyanides on hydrolysis give carboxylic acids and ammmonia where as isocynanides on hydrolysis give primary amines and formic acid:
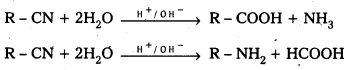
ii) Reduction: Reducation of nitriles give primary amines where as reduction of isocyanides yield secondary amines.
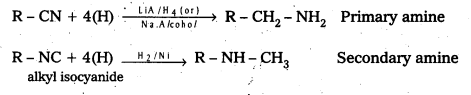
![]()
Question 4.
How do you carryout the following conversions? .
i) N – Ethylamine to N, N – Diethyl propanamine
ii) Aniline to Benzene suiphonamide
Answer:
Conversion of
i) N – Ethyl amine to N, N – Diethyl propanamine : Ethyl amine reads with ethyl chloride and propyl chloride to from N, N – Di ethyl propanamine.

ii) Conversion of Aniline to Benzene sulphonamide : Aniline reacts with benzene sulphonyl chloride to form N – Phenyl benzene sulphonamide.
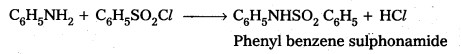
Question 5.
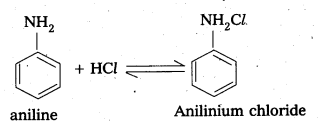
Explain the basic character of different Amines.
Answer:
Basic Character of Amines : Aniline reacts with acid and form salts.
Structure qnd Basicity : Alkyl amines are more basic than ammonia. The alkyl group pushes the electrons towards nitrogen by + I effect. Thus line pair of electrons on nitrogen are more available for sharing with the proton of acid. Hence the basic nature of alkylamines increases with increase in number of alkyl groups. Thus in gaseous phase the basicity order of amines is in the order 36 amine > 2° amine >1° amine > ammonia.
In the aqueous phase the substituted ammonium cations get stabilised by +1 effect and also by solvation with water molecules. Greater the size of the ion, lesser will be the solvation and less stabilised is the ion. The order of stability is.
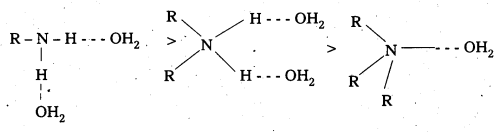
Greater the stability of the ammonium cation, stronger is the basic nature of amine. The order of basicity of aliphatic amines is primary > secondary > tertiary. The – CH3 group Creates less steric hindrance to hydrogen bortding than C2H5 group, thus the change of alkyl group changes the basic strength. The basic strength of methyl substituted and ethly substituted amines in aqueous soltuion is in the order.
(C2H5)2 NH > (C2H5)3 N > C2H5 – NH2 > NH3
(CH3 NH)2 > CH3 – NH2 > (CH3)3N >NH3
Aromatic amines are less basic than ammonia. The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen is in conjugation with benzene ring.
![]()
Question 6.
Write two methods each for the preparation of alkyl cyanide and alkyl isocyanide.
Answer:
Preparation
a) From Alkyl Halides : Alkyl halides with ethanolic potassium cyanide gives cyanides where as with silver cyanide gives alkyl isocyanide.
b) From amides and aldoximes : The dehydration of amides (or) oximes with dehydrating agents like P2O5 (or) with benzene suiphonyl chloride yeild cyanides.
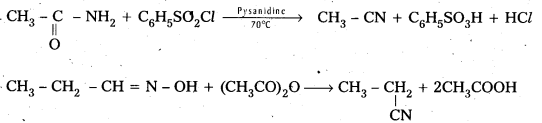
c) Isocyanides from amines: (Carbyl amine reaction)
![]()
![]()
Question 7.
Give one chemical test to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.
i) Methylamine and dimethylamine
ii) Aniline and N.Methylanhline
iii) Ethylamine and aniline
Answer:
i) Methyl amine (1° – amine) and dimethyl amine (2° – amine) are distinguished by iso cyanide test (or) Carbylamine test. Methyl amine responds to carbylamine reaction to produce methyl isocyanide where as dimethyl amine does not respond to the iso cyanide test.
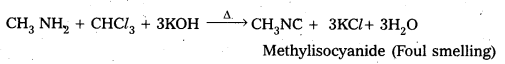
ii) Anjiine (1° – amine) and N.methyl (2° – amine) aniline are distinguished by carbylamine test (or) isocyanide test. Aniline responds to carbyl amine test to give foul smelling phenyl iso cyanide where as N – methyl aniline does not responds to carbyl amine Test.
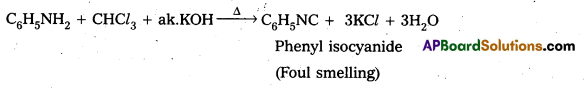
iü) Ethyl amine (1° – aliphatic amine) and aniline (1° – aromatic amine) are distinguished by Diazotisation reaction. Aniline undergo diazotisafion reaction to form benzene diazonium salt where as ethyl amine form highly unstable alkyl diazonium salt.
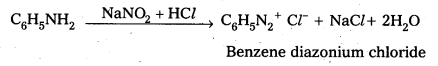
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the following name reactions: [T.S. Mar. 17] [IPE -2015, B.M.P 2016 (TS), (AP)]
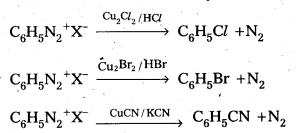
i) Sandmeyer reaction
ii) Gatterman reaction
Answer:
i) Sandmeyer reaction: Formation of chiorobenzene, Bromo benzene (or) cyano benzene from benzene diazonium salts with reagents Cu2Cl2/HCl, Cu2Br2/HBr, CuCN/KCN is called sandmyeres reaction.
ii) Gatterman reaction : Formation of chioro benzene, Bromobenzene from benzene diazonium salts with reagents Cu/HCl, Cu/HBr is referred as gatterman reaction.
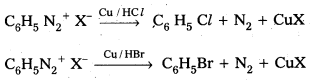
Question 2.
Complete the following conversions.
i) CH3NC + HgO →
ii) ? + 2H2O → CH2NH2 + HCOOH
iii) CH3CN + C2H5MgBr → ? ![]()
iv) CH3CH2NH2 + CHCl3 + KOH ![]()
v) ![]()
Answer:
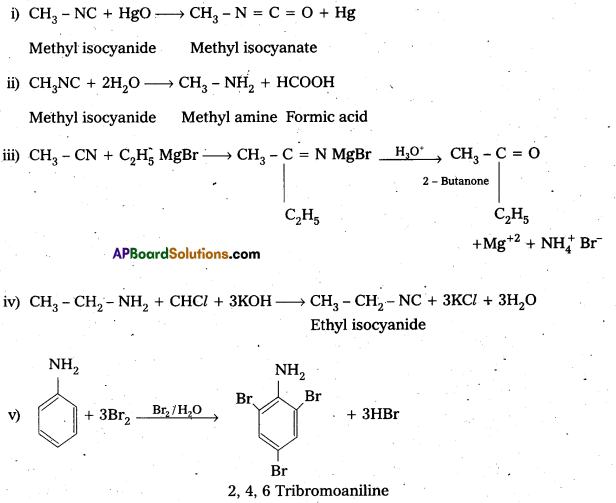
![]()
Question 3.
Explain why aniline in strong acidic medium gives a mixture Of Nitro anilines and what steps need to be taken to prepare selectively P – nitro aniline.
Answer:
In strong acidic medium anline undergo nitration to form mixture of nitro anilines. In strongly acidic medium aniline is protonated to form the anilinium ion which is metadirecting. So besides the ortho and para derivatives meta derivative also formed. .
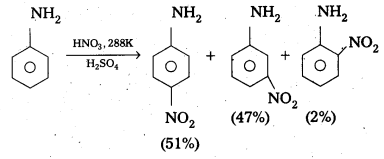
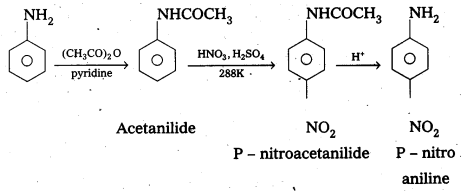
By protecting – NH2 group by acetylation reaction with acetic anhydride the nitration reaction can be controlled and the – P nitro derivative can be formed as major product.
Question 4.
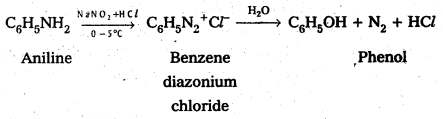
Complete the following conversions : Aniline to
i) Fluorobenzene
ii) Cyanobenzene
iii) Benzene and
iv) Phenol
Answer:
i) Aniline to Fluorobenzene
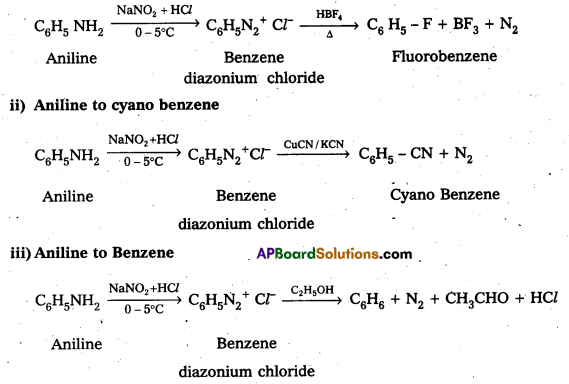
iv) Aniline to phenol
![]()
Question 5.
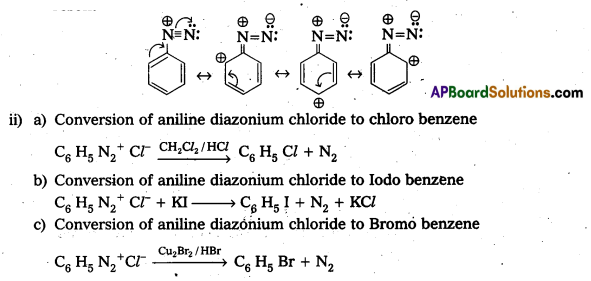
i) Account for the stability of aromatic diazonium ions when compared to aliphatic diazonium ions.
ii) Write the equations showing the conversion of aniline diazoniumchloride to
a) chlorobenzene,
b) Iodobenzene and
c) Bromobenzene
Answer:
i) Aliphatic diazonium salts which are formed from 1° -aliphatic amines are highly unstable and liberate nitrogen gas and alcohols.
Aromatic diazonium salts formed from 1° – aromatic amines are stable for a short time in solution at low temperatures (0 – 5°C). The stability of arene diazonium ion is explained on the basis of resonance.
Question 6.
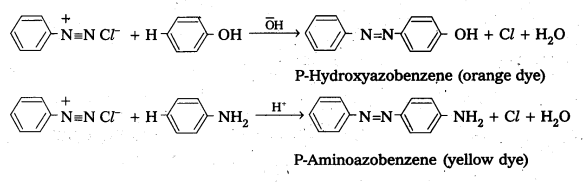
Write the steps involved in the coupling of Benzene diazonium chloride with aniline and phenol.
Answer:
Benzene diazonium chloride reacts with phenol in which the phenol molecule at its para position is coupled with the diazonium salt to form P-hydroxyazobenzene. This type of reactions is known as coupling reactions. Similarly the reaction o£ diazonium salt with aniline yields P – amino azobenzene.