These AP 10th Class Biology Important Questions 1st Lesson పోషణ – ఆహార సరఫరా వ్యవస్థ will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 10th Class Biology 1st Lesson Important Questions and Answers పోషణ – ఆహార సరఫరా వ్యవస్థ
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson పోషణ – ఆహార సరఫరా వ్యవస్థ 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
ప్రశ్న 1.
డాక్టరు దగ్గర నుండి పౌష్టికాహార లోపం వలన కలుగు వ్యాధుల గురించి తెలుసుకొనుటకు కావలసిన పట్టికను వ్రాయండి.
జవాబు:
| వ్యాధి పేరు | లక్షణాలు | ఏ పోషకాహార లోపం వల్ల కలుగుతుంది |
| 1. క్యాషియార్కర్ | కాళ్ళు, చేతులు, ముఖం బాగా ఉబ్బుతాయి. | ప్రోటీన్ లోపం |
| 2. మెరాస్మస్ | నిస్సత్తువగా, బలహీనంగా ఉండటం; కీళ్ళవాపు, కండరాలలో పెరుగుదల లోపం | ప్రోటీన్లు, కేలరీల లోపం |
ప్రశ్న 2.
మానవుని ప్రేగులో నివసించే బ్యాక్టీరియా తయారుచేసే విటమిన్ ఏది?
జవాబు:
B12 విటమిన్ ప్రేగులో నివసించే బాక్టీరియాచే తయారుచేయబడును.
ప్రశ్న 3.
ఎంజైములు లేని జీర్ణరసం ఏది?
జవాబు:
ఎంజైములు లేని జీర్ణరసం ‘పైత్యరసం’.
ప్రశ్న 4.
ఒక విద్యార్థి అధిక కేలరీలు ఉన్న ఆహారాన్ని ఎక్కువగా తింటాడు. మరొక విద్యార్థి కేలరీలు తక్కువగా ఉన్న ఆహారాన్ని ఎక్కువగా తింటాడు. అయినా ఇద్దరూ వ్యాధులకు గురయ్యారు. వారికి ఏ వ్యాధులు వచ్చి ఉంటాయి?
జవాబు:
- అధిక కేలరీలు ఉన్న ఆహారాన్ని ఎక్కువగా తిన్న విద్యార్థి స్థూలకాయత్వం అనే వ్యాధికి గురయ్యాడు.
- కేలరీలు తక్కువగా ఉన్న ఆహారాన్ని ఎక్కువగా తిన్న విద్యార్థి మెగాస్మస్ అనే వ్యాధికి గురయ్యాడు.
ప్రశ్న 5.
ఆకులలో పిండి పదార్థం ఉనికిని తెలుసుకొనుటకు మీరు నిర్వహించిన ప్రయోగంలో ఉపయోగించిన రెండు రసాయనాల పేర్లు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- అయోడిన్ లేదా బెటాడిన్ లేదా టింక్చర్ అయోడిన్.
- ఆల్కహాల్ లేదా మిథైలేటెడ్ స్పిరిట్ లేదా స్పిరిట్

ప్రశ్న 6.
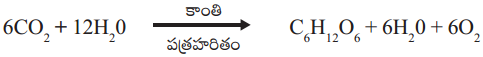
కిరణజన్య సంయోగ క్రియను నిర్వచించి, ఈ క్రియను సూచించేందుకు తుల్య సమీకరణం రాయండి.
జవాబు:
మొక్కలలో పత్రహరితం కలిగిన పత్రాలు కాంతిశక్తిని వనరుగా ఉపయోగించుకుంటూ, సరళ అకర్బన అణువులను (CO2, నీరు) సంక్లిష్ట కర్బన అణువులుగా మార్చు జీవ రసాయనిక ప్రక్రియను కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 7.
పోషకాహార లోపం గురించి తెల్సుకోవడానికి నీవు డాక్టర్ గారిని అడిగే ప్రశ్నలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- పోషక ఆహార లోపం అనగానేమి?
- పోషక ఆహారలోప రకాలు తెలపండి.
- పోషక ఆహారలోప కారణాలు ఏమిటి?
- పోషక ఆహార లోపాన్ని ఎలా నివారించవచ్చు?
ప్రశ్న 8.
మోల్స్ అర్ధ పత్ర ప్రయోగములో KOH ను ఎందుకు ఉపయోగిస్తారు?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు CO2 అవసరమని సూచించుట ఈ ప్రయోగ ఉద్దేశము. సీసాలోపల ఉన్న KOH సీసాలోని CO2 ను పీల్చుకుంటుంది. దాని వల్ల సీసాలోపల ఉన్న ఆకులో CO2 లేకపోవడం వల్ల పిండి పదార్థాలు ఏర్పడవు.
ప్రశ్న 9.
భూమిక “భూమిపైన ఆకుపచ్చని మొక్కలు లేకపోతే భూమిపైన జీవరాశి మనుగడ కష్టమవుతుందని” చెప్పింది. దీనిని నీవు ఎలా సమర్థిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
భూమిపై కల సమస్త జీవరాశులన్నీ ఆకుపచ్చని మొక్కలపై ప్రత్యక్షంగా కానీ, పరోక్షంగా కానీ ఆహారం మరియు ఆక్సిజన్ కోసం ఆధారపడతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 10.
వెంటవెంటనే గర్భం దాల్చడం వల్ల లేదా ఎక్కువ కాన్పులయిన తల్లికి పుట్టే పిల్లల్లో సంభవించే వ్యాధి ఏది?
జవాబు:
మర్మా స్
ప్రశ్న 11.
ట్రిప్సిన్ ఆహారంలోని ఏ అంశంపై చర్య జరిపి వేటిగా మారుస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
- ప్రోటీన్లపై చర్య జరుపును.
- పెన్షన్లుగా మార్చును.
ప్రశ్న 12.
పోషకాహార లోపం వల్ల కలిగే వ్యాధులకు రెండు ఉదాహరణలు వ్రాయండి.
జవాబు:
పోషకాహార లోపం వల్ల కలిగే వ్యాధులు :
1) క్వాషియార్కర్, 2) మెరాసమస్, 3) బెరిబెరి, 4) గ్లాసైటిస్, 5) పెల్లాగ్రా, 6) అనీమియా, 7) స్వర్వీ, 8) రికెట్స్.
ప్రశ్న 13.
మలబద్దకంతో బాధపడుతున్న మీ స్నేహితునికి ఎలాంటి సలహాలు ఇస్తావు?
జవాబు:
i) ప్రతిరోజూ తీసుకునే ఆహారం నందు పీచుపదార్థాలు తప్పక ఉండే విధంగా చూసుకోవాలి.
ii) ప్రతిరోజూ సరిపడినంత నీరు త్రాగాలి.
ప్రశ్న 14.
పోషకాహార లోపనివారణ ప్రచార కార్యక్రమానికి అవసరమయ్యే రెండు నినాదాలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- “సంతులిత ఆహారం తిందాం – ఆరోగ్యంగా ఉందాం.”
- “పోషకాహారాన్ని తీసుకో – వ్యాధులను దూరం చేసుకో”.
ప్రశ్న 15.
జీర్ణక్రియలో నాలుక పాత్ర ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
నాలుక ఆహారాన్ని మిశ్రమంగా చేయటానికి దంతాల మధ్యకు చేర్చుతుంది. ఆహారం నమిలిన తరువాత ఆహార వాహికలోనికి నెట్టటానికి తోడ్పడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 16.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ జరగడానికి కావలసిన ముడి పదార్థాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియకు కావలసిన ముడి పదార్థాలు:
- కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
- నీరు
- సూర్యరశ్మి
- పత్రహరితం
ప్రశ్న 17.
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో చిట్టచివరిగా ఏర్పడే ఉత్పన్నాలు ఏమై ఉంటాయి?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో ఏర్పడే అంత్య ఉత్పన్నాలు :
గ్లూకోజ్, నీటిఆవిరి మరియు కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్. గ్లూకోజ్ పిండి పదార్థంగా మార్చబడి నిల్వ చేయబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 18.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ ద్వారా కాంతిశక్తి రసాయనశక్తిగా మార్చబడుతుందని మీరు భావిస్తున్నారా?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియకు కావలసిన శక్తి సూర్యుని నుండి గ్రహించబడుతుంది. ఈ సౌరశక్తిని ఉపయోగించుకొని మొక్కలు ఆహార పదార్థాలను తయారుచేసుకొంటాయి. ఆహార పదార్థాలలో శక్తి రసాయనిక బంధాల రూపంలో నిల్వ చేయబడుతుంది. కావున కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ ద్వారా కాంతిశక్తి రసాయనశక్తిగా మార్చబడుతుందని భావిస్తున్నాను.

ప్రశ్న 19.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలోని ప్రధాన సోపానాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో ప్రధానంగా రెండు దశలు కలవు.
- కాంతిచర్యలు : గ్రానాలో జరుగుతాయి.
- నిష్కాంతి చర్యలు : అవర్ణికలో జరుగుతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 20.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలోని దశలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ ప్రధానంగా రెండు దశలలో జరుగుతుంది. అవి:
1. కాంతి చర్య :
కాంతి సమక్షంలో జరిగే కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ మొదటి దశ ఇది. ఈ దశలో కాంతిశక్తి గ్రహించబడి, పత్రహరితం ఆక్సీకరణం చెందుతుంది. ఇది పత్రహరితంలోని గ్రానాలో జరుగుతుంది.
2. నిష్కాంతి చర్య :
ఇది కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలోని రెండవదశ. హరితరేణువులోని సోమాలో జరుగుతుంది. కాంతి శక్తితో పనిలేదు. కానీ కాంతి చర్యలో ఏర్పడిన శక్తిగ్రాహకాలు అవసరం.
ప్రశ్న 21.
జీర్ణక్రియ అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
జీర్ణక్రియ :
ఎంజైమ్ ల సహాయంతో సంక్లిష్ట పదార్థాలు సరళపదార్థాలుగా విడగొట్టి, శరీరం శోషించుకోవడానికి అనువుగా మార్చే విధానాన్ని “జీర్ణక్రియ” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 22.
సంతులిత ఆహారం అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
సంతులిత ఆహారం :
అన్ని రకాల పోషకాలు సరిపడిన స్థాయిలో ఉన్న ఆహారాన్ని సంతులిత ఆహారం అంటారు. సంతులిత ఆహారం వలన అన్ని రకాల పోషకాలు శరీరానికి అంది జీవక్రియలు సక్రమంగా జరుగుతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 23.
పోషకాహార లోపం అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
ఒకటి లేదా అంతకంటే ఎక్కువ పోషకాలు లోపించిన ఆహారం తీసుకోవటం వలన కలిగే దుష్ఫలితాలను పోషకాహారలోపం అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 24.
పోషకాహార లోపాన్ని ఎన్ని రకాలుగా విభజించవచ్చు? అవి ఏవి?
జవాబు:
పోషకాహార లోపాన్ని 3 రకాలుగా విభజించవచ్చు. అవి :
- కేలరీ పరమైన పోషకాహార లోపం
- ప్రొటీన్ల సంబంధిత పోషకాహార లోపం
- పోషక విలువలు లేని ఆహారం తీసుకోవటం.
ప్రశ్న 25.
‘రెటినాల్’ లోప ఫలితం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
విటమిన్ ‘ఎ’ ను రెటినాల్ అంటారు. దీని లోపం వలన రేచీకటి, అంధత్వం , కంటి సమస్యలు వస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 26.
మొక్కలలోని పోషణ విధానం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
మొక్కలు కాంతి స్వయంపోషణను అవలంబిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 27.
పత్రహరితం అనగానేమి? దాని ప్రత్యేకత ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
మొక్కలలో ఆకుపచ్చ రంగుని కలిగించే వర్ణ పదార్థాన్ని పత్రహరితం అంటారు. ఇది సౌరశక్తిని గ్రహించి రసాయన శక్తిగా మార్చుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 28.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ అంత్య పదార్థాలు తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
పిండిపదార్థం, నీటి ఆవిరి, ఆక్సిజన్, కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో ఏర్పడతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 29.
ఆకు నుండి పత్రహరితం తొలగించటానికి ఏమి చేయాలి?
జవాబు:
ఆకును మీథైలేట్ స్పిరిట్లో ఉంచి, వేడి చేయుట ద్వారా పత్రహరితం తొలగించవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 30.
పిండి పదార్థాన్ని ఎలా నిర్ధారిస్తావు?
జవాబు:
పిండి పదార్థ నిర్ధారణ :
అయోడిన్ పరీక్ష ద్వారా పిండి పదార్థాన్ని నిర్ధారించవచ్చు. అయోడిన్ సమక్షంలో పిండి పదార్థం నీలి నల్లరంగుకు మారుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 31.
CO2 ను పీల్చుకొనే రసాయన పదార్థం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
పొటాషియం హైడ్రాక్సైడ్ (KOH) CO2, ను పీల్చుకొనే స్వభావం కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 32.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో వెలువడే వాయువు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో వెలువడే వాయువు ఆక్సిజన్.
ప్రశ్న 33.
హరితరేణువులు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
హరితరేణువులు :
పత్రహరితం కలిగి ఉన్న కణాంగాలను “హరితరేణువులు” అంటారు. ఇవి పత్రాంతర కణాలలో 40 నుండి 100 వరకు ఉంటాయి.

ప్రశ్న 34.
గ్రానా అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
గ్రానా :
హరితరేణువులో థైలకాయిడ్ త్వచముల దొంతరలను “గ్రానా” అంటారు. దొంతరల మధ్య ఉన్న ద్రవభాగాన్ని “సోమా” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 35.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ వర్ణదాలు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
హరితరేణువులో కాంతిని శోషించే పదార్థాలను కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ వర్ణదాలు అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 36.
పత్రహరిత వర్ణద్రవ్యాలు ఎక్కడ ఉంటాయి? అవి ఏవి?
జవాబు:
హరితరేణువుల్లోని థైలకాయిడ్ దొంతరలో రెండు ప్రధాన రకాలైన పత్రహరిత వర్ణద్రవ్యాలు ఉంటాయి. క్లోరోఫిల్ – ‘ఎ’ నీలి ఆకుపచ్చ వర్ణదం కాగా, క్లోరోఫిల్ ‘బి’ పసుపు ఆకుపచ్చగా ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 37.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలోని దశలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ రెండు దశలలో జరుగుతుంది. అవి
- కాంతిచర్య
- నిష్కాంతి చర్య
ప్రశ్న 38.
ఫోటాలసిస్ అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
ఫోటాలసిస్ :
కాంతి రేణువులోని శక్తిని వినియోగించుకొని నీటి అణువు విచ్ఛిన్నం చెందడాన్ని కాంతి నీటి విశ్లేషణ లేదా ‘ఫోటాలసిస్’ అంటారు.
H2O → H+ + OH–
ప్రశ్న 39.
కాంతి చర్య అంత్య ఉత్పన్నాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ATP, NADPH లు కాంతి చర్య అంత్య పదార్థాలుగా ఏర్పడతాయి. వీటిని ‘శక్తి గ్రాహకాలు’ అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 40.
నిష్కాంతి చర్యలోని మధ్యస్థ పదార్థం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
నిష్కాంతి చర్యలోని మధ్యస్థ పదార్థం ‘రిబ్యులోజ్ బై ఫాస్ఫేట్’. ఇది అనేక ఎంజైమ్స్ లను ఉపయోగించుకొంటూ, చివరిగా గ్లూకోజ్ ను ఏర్పరుస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 41.
శిలీంధ్రాలలోని పోషణ విధానము ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
శిలీంధ్రాలు పూతికాహారపోషణ విధానాన్ని ప్రదర్శిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 42.
పెరిస్టాల్టిక్ చలనం అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
పెరిస్టాల్టిక్ చలనం:
పదార్థాల కదలిక కోసం అవయవాలలో ఏర్పడే అలల తరంగం వంటి ఏకాంతర చలనాన్ని “పెరిస్టాలిక్ చలనం” అంటారు. దీనిని ఆహార వాహికలో స్పష్టంగా గమనించవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 43.
ఎమల్సీకరణం అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
ఎమల్సీకరణం :
కాలేయం ద్వారా విడుదలయ్యే పైత్యరసం, కొవ్వు పదార్థాలను జీర్ణంచేసి చిన్న చిన్న రేణువులుగా మార్చుతుంది. ఈ విధానాన్ని “ఎమల్సీకరణం” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 44.
క్లోమరసంలోని ఎంజైమ్స్ ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
క్లోమరసంలో ఉండే ట్రిప్సిన్ అనే ఎంజైమ్ ప్రోటీన్లను జీర్ణం చేయడానికి అదే విధంగా లైపేజ్ కొవ్వులను జీర్ణం చేయటానికి ఉపయోగపడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 45.
చిన్న ప్రేగులలోని జీర్ణరసం ఏమిటి? దాని ప్రయోజనం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
చిన్నప్రేగుల గోడలు ఆంత్రరసాన్ని స్రవిస్తాయి. ఈ స్రావాలు ప్రోటీన్లు మరియు కొవ్వులను మరింత చిన్న చిన్న అణువులుగా శోషించడానికి వీలుగా మార్పు చెందిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 46.
కైమ్ అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
క్రైమ్ :
ఆహారంలో ఉండే ప్రోటీన్లు మరియు కార్బోహైడ్రేట్ అణువులు చిన్న చిన్న ముక్కలుగా విడగొట్టబడి మెత్తగా చిక్కటి రూపంలోనికి మారుతుంది. దీనిని “కైమ్” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 47.
జఠర సంవరణీకండర ప్రయోజనం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయం చివరి భాగంలో సంవరణీ కండరం ఉంటుంది. దీనిని జఠర సంవరణీకండరం అంటారు. ఇది ఆంత్రమూలంలోనికి ప్రవేశించే ఆహారాన్ని నియంత్రిస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 48.
ఎంజైమ్స్ లేని జీర్ణరసం ఏది? జీర్ణక్రియలో దాని పాత్ర ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ఎంజైమ్స్ లేని జీర్ణరసం పైత్యరసం. ఇది కాలేయంచే స్రవించబడుతుంది. ఈ జీర్ణరసం కొవ్వుల ఎమల్సీకరణకు తోడ్పడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 49.
శోషణ అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
శోషణ :
జీర్ణమైన అంత్యపదార్థాలు ప్రేగు నుండి రక్తంలోనికి రవాణా కావడాన్ని “శోషణ” అంటారు. ఇది చిన్న ప్రేగులో జరుగుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 50.
ఆంత్రచూషకాలు అనగానేమి? దాని ప్రయోజనం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ఆంత్రచూషకాలు :
చిన్నప్రేగు లోపలి ఉపరితలం మడతలు పడి, వ్రేళ్ళ వంటి నిర్మాణాన్ని ఏర్పరుస్తాయి. వీటిని “ఆంత్రచూషకాలు” అంటారు. శోషణాతల వైశాల్యం పెంచటానికి ఇవి తోడ్పడతాయి.

ప్రశ్న 51.
పెద్దప్రేగు యొక్క పని ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
జీర్ణంకాని వ్యర్థ పదార్థాల నుండి నీటిని, లవణాలను తిరిగి పీల్చుకోవటం పెద్ద ప్రేగు ప్రధాన విధి.
ప్రశ్న 52.
మలవిసర్జన అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
మలవిసర్జన :
జీర్ణంకాని వ్యర్థ పదార్థాలు పెద్ద ప్రేగులో మలంగా మారుతుంది. ఈ మలం పాయువు ద్వారా విసర్జింపబడుతుంది. ఈ ప్రక్రియను “మలవిసర్జన” అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 53.
వాంతి అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయం నుండి అనవసరమైన పదార్థాలు కానీ, హానికరమైన పదార్థాలను కానీ బయటకు పంపే ప్రక్రియను వాంతి అంటారు. ఈ ప్రక్రియను ఆహార వాహికలో వ్యతిరేక “పెరిస్టాల్ సిస్” జరగటం వలన ఆహారం జీర్ణాశయం నుండి నోటి ద్వారా బయటకు వస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 54.
న్యూనతా వ్యాధులు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
న్యూనతా వ్యాధులు :
పోషకాహార లోపం వలన కలిగే వ్యాధులను న్యూనతా వ్యాధులు అంటారు. ఉదా : క్వాషియార్కర్, మెరాస్మస్.
ప్రశ్న 55.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ ప్రయోగాలలో మొక్కను మొదట చీకటిలో ఉంచి, తరువాత వెలుతురులో ఉంచటానికి కారణం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియను పిండిపదార్థ ఉనికి ద్వారా నిర్ధారిస్తారు. ఆకును నేరుగా పిండిపదార్ధ పరీక్ష చేస్తే, ఆకులో నిల్వ ఉన్న పిండిపదార్ధము వలన పరీక్షా ఫలితాలు తప్పుగా వస్తాయి. కావున ఆకులో నిల్వ ఉన్న ఆహారాన్ని తొలగించటానికి మొక్కను చీకటిలో ఉంచుతారు. తరువాత ప్రయోగ పరిస్థితులలో కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ జరగటానికి మొక్కను వెలుతురులో ఉంచుతారు.
ప్రశ్న 56.
క్వాషియార్కర్ వ్యాధి కారణము ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
క్వాషియార్కర్ ప్రోటీన్స్ లోపం వలన కలిగే న్యూనతా వ్యాధి.
ప్రశ్న 57.
మెగాస్మస్ వ్యాధి కారణం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ప్రోటీన్స్ మరియు కేలరీ పోషకాహారం లోపం వలన మెరాస్మస్ వ్యాధి కలుగును.
ప్రశ్న 58.
దాదాపుగా సజీవ ప్రపంచానికంతటికి కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియను మౌలిక శక్తివనరు అని చెప్పగలరా?
జవాబు:
భూమి మీద ఉన్న అన్ని జీవరాశులు మొక్కల పై ప్రత్యక్షంగానో, పరోక్షంగానో ఆధారపడి జీవిస్తున్నాయి. కావున సజీవ ప్రపంచానికి కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియను మౌలిక శక్తి వనరుగా చెప్పవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 59.
స్వయంపోషకాలకు కావలసిన శక్తి ఎక్కడ నుండి లభిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
స్వయంపోషకాలకు కావలసిన శక్తి సూర్యుని నుండి లభిస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 60.
ఎక్కువ రోజుల పాటు కొవ్వుతో కూడిన ఆహార పదార్థాలు తిన్నప్పుడు కలిగే ఫలితం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
మనం ఎక్కువ రోజుల పాటు కొవ్వుతో కూడిన ఆహార పదార్థాలను తిన్నప్పుడు, సాధారణంగా పైత్యంతో, పసరుతో కూడిన వాంతులతో బాధపడుతుంటాము. ఎక్కువగా కొవ్వు పదార్థాలను తిన్నప్పుడు, కాలేయం కొవ్వును తట్టుకొనే శక్తిని కోల్పోతుంది. అప్పుడు మనం తలనొప్పి, వాంతులతో బాధపడతాం.
ప్రశ్న 61.
సిట్రస్ ఫలాలలో లభించే విటమిన్ ఏది?
జవాబు:
విటమిన్ ‘సి’ సిట్రస్ ఫలాలలో లభిస్తుంది. ఇది గాయాలు మాన్పటంలో తోడ్పడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 62.
అన్ని విటమిన్లు ఆహారం ద్వారా లభిస్తాయా?
జవాబు:
లేదు. కొన్ని విటమిన్స్ ఆహారం ద్వారా లభిస్తే మరికొన్ని విటమిన్లు శరీరంలోని బాక్టీరియాచే తయారుచేయబడతాయి.
ఉదా : B12, విటమిన్ K.

ప్రశ్న 63.
గోధుమలు, జొన్నలు, బియ్యం వంటి వాటిని నోటిలో నమిలితే కాసేపటికి తియ్యగా ఉన్నట్లు అనిపిస్తుంది. ఎందుకు?
జవాబు:
గోధుమలు, జొన్నలు, బియ్యం వంటి వాటిని నోటిలో నమిలినపుడు లాలాజలము నందలి ఎంజైమ్ ఎమైలేజ్ పై వాటినందు ఉండు సంక్లిష్ట పిండిపదార్థ అణువులను మాత్రసు అనే చక్కెరగా ‘మారుస్తుంది. అందువలన మనకు ఆహార పదార్ధములు తియ్యగా అనిపిస్తాయి.
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson పోషణ – ఆహార సరఫరా వ్యవస్థ 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
ప్రశ్న 1.
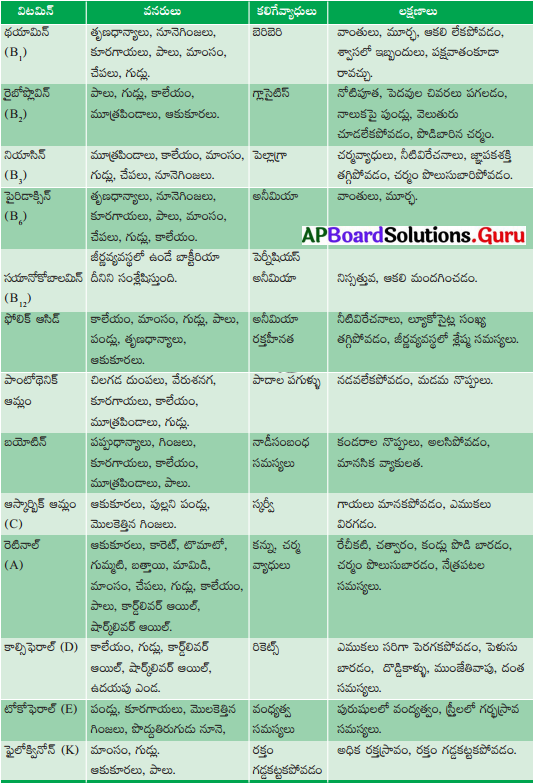
A, D, E, K విటమిన్స్ క్రొవ్వులలో కరుగుతాయి. వీటి లోపం వల్ల మనం ఎటువంటి వ్యాధులకు గురి అవుతాము. ఈ విటమినుల కొరకు ఏ ఏ వనరులు మనకు అవసరము పట్టిక రూపంలో వ్రాయండి.
జవాబు:
| విటమిన్లు | కలిగే వ్యాధులు | వనరులు |
| విటమిన్ A | రేచీకటి, చత్వారం, కండ్లు పొడిబారడం, చర్మం పొలుసులు బారడం | ఆకుకూరలు, క్యారట్, టమాటా, గుమ్మడికాయ, చేపలు, గుడ్లు, కాలేయం, కాడ్ లివర్ ఆయిల్, షార్క్ లివర్ ఆయిల్, పాలు |
| విటమిన్ D | రికెట్స్ | కాలేయం, గుడ్లు, వెన్న, ఉదయపు ఎండ |
| విటమిన్ E | వంధ్యత్వ సమస్యలు | పండ్లు, కూరగాయలు, మొలకెత్తిన గింజలు, మాంసం, గుడ్లు, పొద్దుతిరుగుడు నూనె |
| విటమిన్ K | రక్తం గడ్డకట్టకపోవడం | మాంసం, గుడ్లు, ఆకు కూరలు, పాలు |
ప్రశ్న 2.
లాలాజల గ్రంథుల నాళాలు మూసుకొనిపోతే ఏమవుతుంది?
జవాబు:
- లాలాజల గ్రంథులు లాలాజలాన్ని స్రవిస్తాయి. లాలాజలం మ్యూసిన్ మరియు టయలిన్ లేదా, అమైలేజ్ ను కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
- మ్యూసిన్ ఆహారానికి జారుడు స్వభావాన్ని కలుగజేసి సులువుగా మింగడానికి ఉపయోగపడుతుంది.
- టయలిన్ లేదా అమైలేజ్ సంక్లిష్ట పిండిపదార్థాలను సరళ చక్కెరలుగా జీర్ణం చేస్తుంది.
- లాలాజల గ్రంథుల నాళాలు మూసుకుపోతే పై ప్రక్రియలన్నీ జరగక ఆహారం సరిగా జీర్ణం కాదు.
ప్రశ్న 3.
స్థూలకాయత్వం, దాని పర్యవసానాల గూర్చి తెలుసుకోవడానికి మీ ఉపాధ్యాయుడిని అడిగే ప్రశ్నలు నాలుగింటిని రాయండి.
జవాబు:
ఉపాధ్యాయుని స్థూలకాయం గురించి మరింత తెలుసుకోవడానికి కింది ప్రశ్నలు అడుగుతాను. TS June 2017
- స్థూలకాయత్వానికి కారణాలు ఏమిటి?
- ప్రణాళికాబద్ధంగా శరీర బరువును ఎలా తగ్గించాలి?
- స్థూలకాయత్వం వల్ల కలిగే దుష్పరిణామాలు ఏవి?
- స్థూలకాయత్వంతో బాధపడేవారు ఏ రకమైన ఆహారం తీసుకోవాలి?
ప్రశ్న 4.
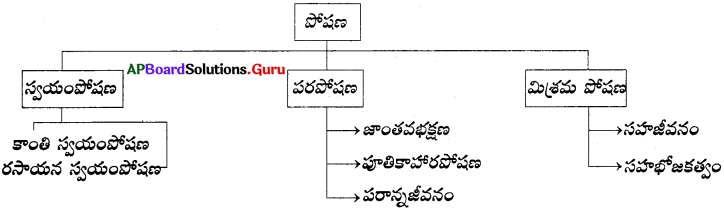
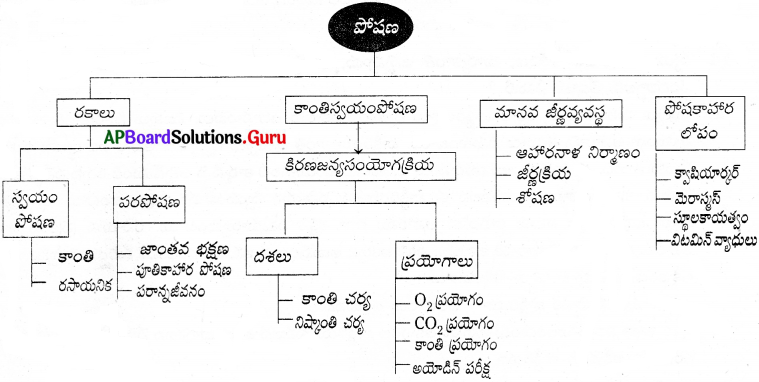
పోషణ అనగానేమి? అందలి రకాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
పోషణ :
జీవి శరీరంలోనికి పోషకాలను గ్రహించటాన్ని పోషణ అంటారు. ఇది ప్రధానంగా మూడు రకాలు. అవి :
- స్వయంపోషణ
- పరపోషణ
- మిశ్రమపోషణ
ప్రశ్న 5.
స్వయంపోషణ గురించి రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- స్వయంపోషకాలు కాంతిశక్తిని ఉపయోగించుకుని రసాయనిక సమ్మేళనాలు తయారుచేసుకుంటాయి.
- అవి నేలలోని నీటిని మరియు ఖనిజ లవణాలతో పాటుగా గాలిలోని కొన్ని వాయువులను కూడా వినియోగించుకుంటాయి.
- ఈ సరళ పదార్థాలను ఉపయోగించి పిండిపదార్థాలు, మాంసకృత్తులు, కొవ్వుల వంటి సంక్లిష్ట పదార్థాలను ఉత్పత్తి చేస్తాయి.
- స్వయం పోషకాలైన మొక్కల ద్వారా ఉత్పత్తి అయ్యే’ ఈ కార్బోహైడ్రేట్ మానవులతో బాటు అత్యధిక శాతం జీవరాశులకు శక్తినివ్వడానికి ఉపయోగపడుతున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 6.
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
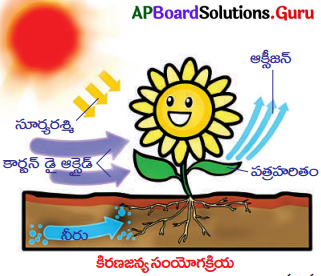
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ:
కాంతిని ఒక వనరుగా ఉపయోగించుకుంటూ, అంత్య ఉత్పత్తిగా కార్బోహైడ్రేట్సును తయారుచేస్తూ, ఆకుపచ్చ మొక్కలలో జరిగే సంక్లిష్ట రసాయనిక చర్యలను కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ అంటారు.
(లేదా)
ఆకుపచ్చ మొక్కలలో వుండే హరిత రేణువులు సూర్యకాంతిలో కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్, నీరు ఉపయోగించి, కార్బోహైడ్రేట్సను తయారుచేసే కాంతి రసాయన చర్యను కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ అంటారు.

ప్రశ్న 7.
శోషణ సముదాయం లేదా కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ ప్రమాణాలు అనగానేమి?
జవాబు:
పత్రంలోని హరితరేణువుల్లోని థెలకాయిడ్ దొంతరలలో రెండు ప్రధాన రకాలైన పత్రహరిత వర్షకాలుంటాయి. క్లోరోఫిల్ ‘ఏ’ నీలి-ఆకుపచ్చ వర్ణదం కాగా క్లోరోఫిల్ ‘బి’ పసుపు-ఆకుపచ్చగా ఉంటుంది. ప్రతి గ్రానాలోనూ దాదాపు 250 నుండి 400 వర్ణద అణువులు కలిసి కాంతి శోషణ సముదాయం (Light Harvesting Complex) గా ఏర్పడతాయి. వీటిని కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ ప్రమాణాలు అంటారు. ఆకుపచ్చని మొక్కల క్లోరోప్లాస్లో అధిక సంఖ్యలో ఉండే ఈ క్రియా ప్రమాణాలు అన్నీ కలిసి కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియను సంయుక్తంగా నిర్వహిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 8.
పూతికాహారులు అనగానేమి? ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
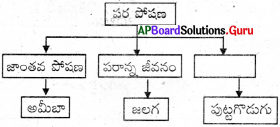
కొన్ని ఈస్టు, కుక్కగొడుగులు, రొట్టె బూజులు వంటి జీవులు ఆహారాన్ని శరీరం వెలుపల చిన్న చిన్న అణువులుగా విడగొట్టి శోషిస్తాయి. వీటిని పూతికాహారులు అంటారు. ఇంకొన్ని రకాల జీవులు అతిథేయ జీవిపై ఆధారపడి దానిని చంపకుండా పరాన్న జీవన విధానంలో ఆహారాన్ని సేకరిస్తాయి. ఉదాహరణకు కస్కుట, పేను, జలగ, బద్దెపురుగు మొదలైన జీవులు పరాన్న పోషణను పాటిస్తాయి.
ప్రశ్న 9.
పారామీషియంలో పోషణ విధానం తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
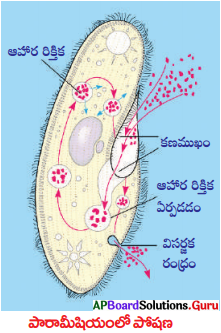
ఏకకణ జీవి అయిన పారామీషియంకి నిర్దిష్టమైన ఆకారం ఉంటుంది. ఒక ప్రత్యేకస్థానం నుండి ఆహారం గ్రహించబడుతుంది. శరీరం అంతా వ్యాపించి ఏర్పడటం ఉన్న శైలికల కదలిక వలన ఆహారం ఆ ప్రత్యేక స్థానాన్ని చేరుకుంటుంది. అక్కడ నుండి శరీరం లోపలికి వెళ్తుంది. ఆ భాగాన్ని కణముఖం (Cytostome) అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 10.
బంగారు తీగ (డాడర్)లో పోషణ విధానం తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
బంగారు తీగ లేదా డాడర్ అని పిలువబడే ఈ మొక్కలో పత్రహరితం ఉండదు. కస్కుటా రిఫ్లెక్సాలో చాలా తక్కువ మొత్తంలో పత్రహరితం ఉంటుంది. ఇది చూషకాలు (Haustoria) ద్వారా ఆహారాన్ని సేకరిస్తుంది. హాస్టోరియాలు వేళ్ళమాదిరిగా ఉండి అతిథేయి కణజాలంలో చొచ్చుకొనిపోతాయి. ఒక్కొక్కసారి అతిథేయిని చంపేస్తాయి కూడా.
ప్రశ్న 11.
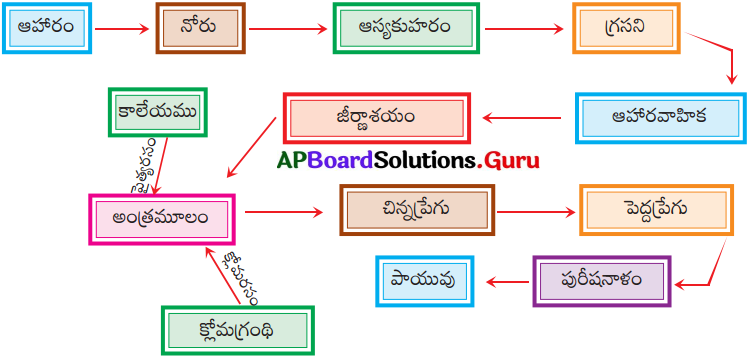
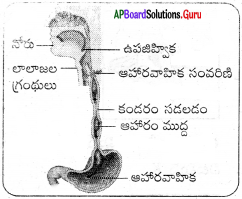
జీర్ణవ్యవస్థలోని భాగాలను వాటిలో ఆహార ప్రయాణ మార్గాన్ని సూచిస్తూ ఫ్లోచార్టు గీయండి.
జవాబు:
ప్రశ్న 12.
నోటిలో జరిగే జీర్ణక్రియను వర్ణించండి.
జవాబు:
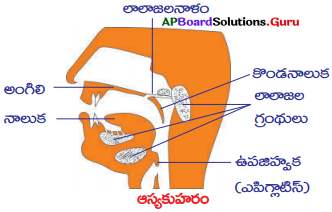
- మనం తీసుకున్న ఆహారం నోటిలో దంతాల ద్వారా ముక్కలుగా లాలాజలనాళం చేయబడి నోటిలోని లాలాజలంతో కలుస్తుంది. ఫలితంగా ఆహారం తడిగా, మెత్తగా జారుడు స్వభావాన్ని పొందుతుంది. దీనినే ముద్దగా అంగిలి – చేయడం (Mastication) అంటాం.
- ఇటువంటి మెత్తగా జారుడు స్వభావం కలిగిన ఆహారం ఆహారవాహిక ఉపజిహ్వక (Oesophagus) గుండా జీర్ణాశయంలోకి వెళ్ళడానికి అనువుగా ఉంటుంది.
- ఆస్యకుహరంలో ఉండే 3 జతల లాలాజల గ్రంథుల ద్వారా లాలాజలం స్రవించబడుతుంది.
- రెండు జతల లాలాజల గ్రంథులు దవడల ప్రక్కన మరియు నాలుక కింద అమరి ఉంటాయి. ఒక జత గ్రంథులు అంగిలిలో అమరి ఉంటాయి.
- లాలాజలంలో అమైలేజ్ (టయలిన్) అనే ఎంజైమ్ ఉంటుంది. అమైలేజ్ ఎంజైమ్ సంక్లిష్ట కార్బోహైడ్రేట్లను సరళమైన పదార్థాలుగా మారుస్తుంది.

ప్రశ్న 13.
ఆరోగ్యంగా ఉన్న వ్యక్తి అజీర్తి కలగకుండా తీసుకోవలసిన జాగ్రత్తలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
మనం తీసుకున్న ఆహారం జీర్ణంకానప్పుడు అజీర్తితో బాధపడుతుంటాం. ఆరోగ్యంగా ఉన్న వ్యక్తి అజీర్తి కలగకుండా ఈ కింది జాగ్రత్తలు పాటించాలి.
- సాధారణమైన సమతుల ఆహారాన్ని తీసుకోవడం
- మెల్లగా, ప్రశాంతంగా తినడం
- ఆహారాన్ని బాగా నమిలి తినడం
- తిన్న వెంటనే వ్యాయామం వంటి పనులు చేయకపోవడం.

ప్రశ్న 14.
అల్సరకు గల కారణాలు ఏమిటి? నివారణ మార్గాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయం ఆంత్రమూలంలో ఏర్పడిన పుండ్లు (Ulcers) అజీర్తికి ప్రధాన కారణం. ఈ పరిస్థితిని ఎక్కువగా ఎల్లప్పుడు చికాకు, ఆందోళనతో ఉండే వారిలో చూస్తాం. విశ్రాంతి లేకుండా పనిచేయడం, హడావిడిగా భోజనం చేయడం అజీర్తికి కారణాలు. పని ఒత్తిడి ఎక్కువగా ఉండే డాక్టర్లు, ఉపాధ్యాయులు, రాజకీయవేత్తలు, స్టాక్ బ్రోకర్లు, వ్యాపారస్తులు మొదలైనవారు ఎక్కువగా అల్సర్లకు గురవుతుంటారు. ఎవరైతే ప్రశాంతంగా ఎటువంటి ఒత్తిడి లేకుండా ఉంటారో వారికి జీర్ణాశయంలో పుండ్లు వచ్చే అవకాశం చాలా తక్కువ. ఈ మధ్యకాలంలో జీర్ణాశయ అల్సర్లకు బాక్టీరియా కారణం అవుతోంది.
ప్రశ్న 15.
మలబద్దకం యొక్క నష్టాలు ఏమిటి? దానిని ఎలా నివారించవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
ఆరోగ్యంగా ఉండాలంటే మలబద్దకం లేకుండా ప్రతిరోజు మన జీర్ణాశయాన్ని ఖాళీ చేయాలి. జీర్ణంకాని ఆహారం పెద్ద ప్రేగులో చాలా రోజుల వరకు అలాగే నిల్వ ఉంటే అందులో పెరిగే బ్యాక్టీరియా విడుదల చేసే హానికరమైన పదార్థాలు రక్తంలోకి శోషించబడతాయి. అందువల్ల అనేక ఇతర రకాల వ్యాధులు కూడా వచ్చే అవకాశం ఉంది. మన ఆహారంలో పీచుపదార్థాలు ఎక్కువగా తినటం వలన మలబద్దకాన్ని నివారించవచ్చు.
ప్రశ్న 16.
క్వాషియార్కర్ గురించి రాయండి.
జవాబు:

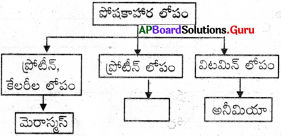
క్వాషియార్కర్ (Kwashiorkor)
ఇది ప్రోటీన్ లోపం వలన కలిగే వ్యాధి. శరీరంలోని కణాంతరావకాశాలలో నీరు చేరి శరీరమంతా ఉబ్బినట్లుగా కనిపిస్తుంది. కండరాల పెరుగుదల చాలా నెమ్మదిగా ఉంటుంది. కాళ్ళు, చేతులు, ముఖం బాగా ఉబ్బి ఉంటాయి. పొడిబారిన చర్మం, విరేచనాలతో బాధపడుతూ ఉంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 17.
మెరాస్మస్ గురించి రాయండి.
జవాబు:

మెరాస్మస్ (Marasmus)
ఈ వ్యాధి ప్రోటీన్లు, కేలరీలు రెండింటి లోపం వల్ల కలుగుతుంది. సాధారణంగా ఈ వ్యాధి వెంటవెంటనే గర్భం దాల్చడం వల్ల పుట్టే పిల్లల్లో లేదా ఎక్కువ కాన్పులయిన తల్లికి పుట్టే పిల్లల్లో సంభవిస్తుంది. ఈ వ్యాధిగ్రస్తులలో నిస్సత్తువగా, బలహీనంగా ఉండడం, కీళ్ళవాపు కండరాలలో పెరుగుదల లోపం, పొడిబారిన చర్మం, విరేచనాలు మొదలైన లక్షణాలుంటాయి.
ప్రశ్న 18.
స్థూలకాయత్వం గురించి రాయండి.
జవాబు:

స్థూలకాయత్వం (Obesity)
అధిక కేలరీలు ఉండే ఆహారాన్ని ఎక్కువగా తినడం వల్ల ఈ వ్యాధి కలుగుతుంది. ఈ మధ్యకాలంలో ఇది ఒక పెద్ద ఆరోగ్యసమస్యగా మారింది. స్థూలకాయంతో బాధపడుతుండే పిల్లలు భవిష్యత్తులో డయాబెటిస్, గుండె సంబంధిత సమస్యలు, జీర్ణ సంబంధిత సమస్యలకు తొందరగా గురయ్యే ప్రమాదం ఉంది. స్థూలకాయతకు దారితీస్తున్న ఇతర జంక్ ఫుడ్స్, అనారోగ్యకర ఆహార అలవాట్ల గురించి మీ తరగతిలో చర్చించండి.
ప్రశ్న 19.
విటమిన్లు అనగానేమి? అందలి రకాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
విటమిన్లు :
జీవక్రియలలో కీలకపాత్ర వహించే కర్బన పోషక పదార్థాలను విటమిన్లు అంటారు. ఇది సూక్ష్మ పరిమాణంలో ఉంటూ, జీవక్రియలను నియంత్రిస్తాయి.
లభ్యత :
శరీరం విటమిన్లు పొందటానికి రెండు రకాల వనరులను కలిగి ఉంది. ఒకటి మనం తినే ఆహారం ద్వారా విటమిన్ల లభ్యత, రెండవది జీర్ణవ్యవస్థలో బాక్టీరియా విటమిన్లను సంశ్లేషించి శరీరానికి అందిస్తుంది.
రకాలు :
విటమిన్లు కరిగే స్వభావాన్ని బట్టి రెండు రకాలు. అవి:
- నీటిలో కరిగేవి : బి కాంప్లెక్స్, విటమిన్ సి
- కొవ్వులలో కరిగేవి : విటమిన్ ఎ, డి, ఇ మరియు కె
ప్రశ్న 20.
జ్వరం వచ్చినపుడు డాక్టర్లు నూనెలో వేయించిన వేపుళ్ళు తినకూడదంటారు. ఎందుకో కారణాలు తెల్పండి.
జవాబు:
జ్వరముగా ఉన్నప్పుడు రోగులకు తేలికపాటి ఆహారమును తీసుకోవాలని సూచిస్తారు. జ్వరంగా ఉన్నప్పుడు జీర్ణవ్యవస్థ ఎక్కువ పోషక విలువలు కలిగిన మాంసం, చేపలు తదితరములైన వేయించిన పదార్థములను తేలికగా జీర్ణం చేసుకోలేదు. వేపుడు పదార్థములు జీర్ణ వాహికపై అదనపు శ్రమను కలుగజేసే లక్షణములు కలిగి ఉంటాయి. అందువలన డాక్టర్లు వేపుళ్ళు తినకూడదని అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 21.
స్వయంపోషణ జరగడానికి కావలసిన పరిస్థితుల గురించి వివరించండి. ఈ చర్యలో ఏర్పడే ఉత్పన్నాలు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
- స్వయంపోషణలో ప్రధానమైనది కాంతి స్వయంపోషణ. ఈ ప్రక్రియను కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ అంటారు.
- ఈ క్రియ జరగటానికి మొదటిగా పత్రహరితం అవసరం. దీనితోపాటుగా, నీరు, CO2, సూర్యరశ్మి తప్పనిసరి. ఈ నాలుగు కారకాలు లేకుండా స్వయంపోషణ జరగదు.
- స్వయంపోషణలో చివరిగా పిండి పదార్థం, నీటిఆవిరి మరియు ఆక్సిజన్ ఏర్పడతాయి.
ప్రశ్న 22.
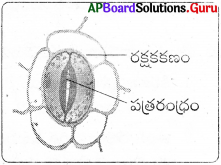
పత్రరంధ్రం పటం గీయండి. కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో దీని పాత్రను తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
- కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో CO2 గ్రహించబడి ఆక్సిజన్ వెలువడుతుంది.
- ఈ వాయు వినిమయం పత్రరంధ్రాల ద్వారా జరుగుతుంది.
- పత్ర రంధ్రాలు మొక్కకు ముక్కువంటివి. ఇవి శ్వాసించటానికి మరియు రక్షకకణం కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో వాయు వినిమయానికి ఉపయోగపడతాయి.
- కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో గ్రహించబడే కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ పత్రరంధ్రాలచే పత్రరంధ్రం నియంత్రించబడుతుంది.
- రక్షక కణాల సడలింపు వ్యాకోచం వలన పత్రరంధ్ర పరిమాణం మారుతూ, వాయు వినిమయాన్ని నియంత్రిస్తుంది.
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson పోషణ – ఆహార సరఫరా వ్యవస్థ 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
ప్రశ్న 1.
ప్రక్క పటంలోని ప్రయోగమును పరిశీలించి ప్రశ్నలకు జవాబులీయండి.

ఎ) ఈ ప్రయోగం ద్వారా ఏ విషయాన్ని నిరూపిస్తావు?
బి) ప్రయోగమునకు ఉపయోగించిన పరికరాలేమిటి?
సి) ప్రయోగమును నీడలో ఉంచి జరిపితే ఫలితాలు ఎలా ఉంటాయి?
డి) ప్రయోగ ఫలితాన్ని రాబట్టుటకు నీవేమి చేస్తావు?
జవాబు:
ఎ) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో ఆక్సిజన్ విడుదలగునని నిరూపించుట.
బి) 1. బీకరు, 2. పరీక్షనాళిక, 3 గరాటు, 4. హైడ్రిల్లా మొక్కలు
సి) పరీక్ష నాళిక నీటిమట్టంలో ఎటువంటి మార్పు ఉండదు. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరగదు / గాలిబుడగలు ఏర్పడవు.
డి) మండుతున్న అగ్గిపుల్లను పరీక్షనాళిక మూతి వద్ద ఉంచినట్లయితే ప్రకాశవంతంగా మండును.
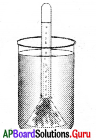
ప్రశ్న 2.
పటంలోని ప్రయోగంను పరిశీలించి ప్రశ్నలకు జవాబులు ఇవ్వండి.
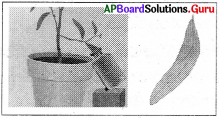
A) ఈ ప్రయోగం ద్వారా ఏ విషయాన్ని నిరూపిస్తావు?
B) ఈ ప్రయోగానికి ఉపయోగించిన పరికరాలు ఏవి?
C) ఈ ప్రయోగానికి KOH ద్రావణాన్ని ఎందుకు ఉపయోగించారు?
D) ఈ ప్రయోగంలో రెండు ఆకులు ఎందుకు పరీక్షించాలి?
జవాబు:
A) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సెడ్ అవసరం అని నిరూపించడం.
B) వెడల్పు మూత గల గాజు సీసా, చీల్చబడిన రబ్బరు కార్కు: KOH ద్రావణం, కుండీలో పెరుగుతున్న మొక్క అయోడిన్.
C) సీసాలో ఉన్న గాలిలోని CO2 ను పీల్చివేయడానికి
D) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు CO2 అవసరం అని నిరూపించే ప్రయోగం కాబట్టి CO2 లభించిన ఒక పత్రంను మరియు CO2 లభించని మరొక పత్రంను పరీక్షించాలి.
ప్రశ్న 3.
కింది సమాచారాన్ని విశ్లేషించండి. ఇచ్చిన ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
| విటమిన్ | వనరులు | విటమిన్ లోపంతో కనిపించే వ్యాధి లక్షణాలు |
| థయామిన్ | తృణ ధాన్యాలు, నూనె గింజలు, కూరగాయలు, పాలు, మాంసం, చేపలు, గుడ్లు | వాంతులు, మూర్చ, ఆకలి లేకపోవడం, శ్వాస సమస్యలు, పక్షవాతం |
| ఆస్కార్బిక్ ఆమ్లం | మొలకెత్తిన గింజలు, క్యారెట్, ఆకుకూరలు, టమాట | గాయాలు మానకపోవడం, ఎముకలు విరగడం |
| రెటినాల్ | ఆకుకూరలు, క్యారెట్, టమాట, గుమ్మడి, బొప్పాయి, మామిడి, మాంసం, చేపలు, గుడ్లు, కాలేయం, పాలు, కార్డ్ లివర్ ఆయిల్, షార్క్ లివర్ ఆయిల్ | రేచీకటి, చత్వారం, కంటి నుండి నీరు కారడం, చర్మం పొలుసుబారుట, నేత్ర పటల సమస్యలు |
| కాల్సిఫెరాల్ | కాలేయం, గుడ్లు, కార్డ్ లివర్ ఆయిల్, షార్క్ లివర్ ఆయిల్ | ఎముకలు సరిగ్గా పెరగకపోవడం, పెళుసు బారడం, దొడ్డికాళ్ళు, ముంజేతి వాపు, దంత సమస్యలు |
| టోకోఫెరాల్ | పండ్లు, కూరగాయలు, మొలకెత్తిన గింజలు, పొద్దు తిరుగుడు నూనె | పురుషులలో వంధ్యత్వం, స్త్రీలలో గర్భస్రావం |
| ఫైలో క్వినైన్ | మాంసం, గుడ్లు, ఆకుకూరలు, పాలు | అధిక రక్తస్రావం, రక్తం గడ్డ కట్టకపోవడం |
(i) ఎముకల సంబంధ వ్యాధులు ఏ విటమిన్ల లోపం వల్ల వస్తాయి?
(ii) పండ్లను తినడం వల్ల ఏ విటమిన్లు లభిస్తాయి?
(iii) పక్షవాతం ఏ విటమిన్ లోపం వల్ల వస్తుంది? ఇది రాకుండా ఉండాలంటే ఏ ఆహార పదార్థాలు తినాలి?
(iv) ఏ ఆహార పదార్థాలు తింటే విటమిన్ల లోపం వల్ల వచ్చే వ్యాధులు రావు?
జవాబు:
i) కాల్సిఫెరాల్ / విటమిన్ – డి / సన్ షైన్ విటమిన్
ii) టోకోఫెరాల్ / విటమిన్ – ఇ / యాంటీ స్టెరిలిటి విటమిన్ / రెటినాల్
iii) థయామిన్ (విటమిన్ B1), తృణధాన్యాలు, నూనె గింజలు, కూరగాయలు, పాలు, మాంసం, చేపలు మరియు గుడ్లు తినాలి.
iv) కూరగాయలు, పండ్లు, చేపలు, మాంసం, మొలకెత్తిన గింజలు, కాడ్ లివర్ ఆయిల్, షార్క్ లివర్ ఆయిల్, పాలు, ఆకుకూరలు, తృణధాన్యాలు, నూనె గింజలు.

ప్రశ్న 4.
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో గాలి ప్రధాన పాత్రను పోషిస్తుందని తెల్పుటకు ప్రీస్టే, చేసిన గంట జాడీ, పుదీనా మొక్క ప్రయోగాన్ని రాయండి.
జవాబు:
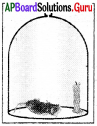
- ఆకుపచ్చని మొక్కల పెరుగుదలలో గాలి ప్రధాన పాత్ర పోషిస్తుందని 1770వ సంవత్సరంలో జోసఫ్ ప్రీస్టే (Priestly) నిర్వహించిన ప్రయోగాల ద్వారా తెలిసింది.
- గాలి చొరబడని గంట జాడీలో వెలుగుతున్న కొవ్వొత్తి త్వరగా ఆరిపోవడాన్ని ప్రిస్టీ (Priestly) గమనించాడు. అదే విధంగా గాలి చొరబడని గంట జాడీలో ఉంచిన ఎలుకకు ఊపిరి ఆడకపోవడాన్ని కూడా గమనించాడు.
- ఈ పరిశీలన ద్వారా వెలిగే కొవ్వొత్తి లేదా ఎలుక లేదా రెండూ కూడా ఏదోవిధంగా గంట జాడీలోని గాలికి నష్టం కలిగించినట్లు నిర్ధారణకు వచ్చాడు.
- కానీ గంట జాడీలో ఒక పుదీనా మొక్కను ఉంచి పరిశీలించినపుడు ఎలుక ప్రాణంతో ఉండడాన్ని, కొవ్వొత్తి వెలుగుతూ ఉండడాన్ని గమనించాడు.
- ప్రిస్టీ (Priestly) ఈ క్రింది నిర్ధారణకు వచ్చాడు.
“జంతువుల శ్వాసక్రియకు, కొవ్వొత్తి వెలగడానికి ఖర్చు అవుతున్న గాలిని మొక్కలు తిరిగి గాలిలోకి ప్రవేశపెడ్తాయి”.
ప్రశ్న 5.
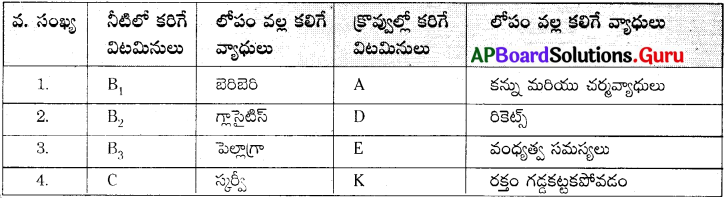
B1, B2, B3, A, C, D, E, K – ఇవి విటమినుల సంకేతాలు. ఇందులో కొన్ని నీటిలో కరుగుతాయి. మరికొన్ని క్రొవ్వులో కరుగుతాయి. వీటిని పై రెండు రకాలుగా విభజించి వీటి లోపం వల్ల కలిగే వ్యాధులను పట్టికలో పొందుపరచండి.
జవాబు:
ప్రశ్న 6.
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ సందర్భంగా క్లోరోప్లాస్లో అనేక సంఘటనలు జరుగుతాయి. వాటిలో కొంతి ఆధారిత చర్యలను నివరించుము.
(లేదా)
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో కాంతి చర్య యొక్క యాంత్రికాన్ని వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
కాంతిచర్య / కాంతి రసాయన చర్య :
1) కాంతి ద్వారా ప్రేరేపించబడి అనేక రసాయన చర్యలు ఒకదాని వెంబడి ఒకటి అతి త్వరగా జరుగుతుంటాయి. కనుక దీనిని కాంతి చర్య లేదా కాంతి రసాయన దశ అంటారు. కాంతి చర్య క్లోరోప్లాలోని గ్రానా థైలకాయిడ్ లో జరుగుతుంది.
2) మొదటి సోపానం :
క్లోరోఫిల్ కాంతిలోని కాంతి ఫోటాన్లను శోషించి క్రియావంతమవుతుంది.
3) రెండవ సోపానం :
(ఫోటోలైసిస్ / హిల్ చర్య) నీటి అణువు H+, OH– అయాన్లుగా విడగొట్టడానికి కాంతి శక్తి – వినియోగించబడుతుంది. దీనిని కాంతి విశ్లేషణ అంటారు. లేదా హిల్ చర్య అంటారు.
H2O → H+ + OH–
4) మూడవ సోపానం :
OH– అయాన్లు ఒకదాని వెంట ఒకటిగా జరిగే అనేక చర్యల పరంపర ద్వారా నీరు (H2O) మరియు NADPH లను ఉత్పత్తి చేస్తుంది. ATP లు NADPH లు అంత్యపదార్థాలుగా ఏర్పడుతాయి. వీటిని శక్తిగ్రాహకాలు అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 7.
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు కాంతి అవసరమని నిరూపించే ప్రయోగానికి కావలసిన పరికరాలు మరియు ప్రయోగ విధానాన్ని వివరించండి.
జవాబు:
బ్లాక్ పేపర్, క్లిప్స్, కుండీలో పెరుగుతున్న మొక్క అయోడిన్, మిథైలేటెడ్, స్పిరిట్, పెట్రెడిష్
ప్రయోగ విధానం :
- కుండీలో పెరుగుతున్న మొక్కలోని పిండి పదార్థం తొలగించడానికి వారం రోజులు చీకటిలో ఉంచాలి. ఒక నల్లని కాగీతం తీసుకొని మీకు నచ్చిన డిజైన్ కత్తిరించండి.
- డిజైను కాగితాన్ని ఆకుకు పైన క్రింద ఉంచి క్లిప్స్ పెట్టాలి. నల్లటి భాగం గుండా కాంతి ఆకుపైన పడకుండా కాగితం ఉండేలా అమర్చాలి.
- అమరికలో ఉన్న మొక్కను సూర్యరశ్మిలో ఉంచండి. కొన్ని గంటల తర్వాత ఆకును వేరుచేసి నీటిలో వేడి చేయండి.
- ఆకును పరీక్ష నాళికలో ఉంచి మిథైలేటెడ్ స్పిరిట్ పోసి, దానిని నీరు ఉన్న బీకరులో ఉంచి వేడి చేయాలి. ఆకు నుండి పత్రహరితం తొలగిన తరువాత దానిని పెట్రిడిలో ఉంచాలి.
- ఆకుపై కొన్ని చుక్కల అయోడిన్ వేయండి. ఎక్కడైతే సూర్యరశ్మి సోకలేదో అక్కడ తెల్లగా, మిగతా భాగం నీలంగా మారింది.
నిర్ధారణ :
ఆకుపై ఎక్కడైతే సూర్యరశ్మి సోకలేదో అక్కడ పిండి పదార్థం ఏర్పడక తెల్లగా ఉంది. ఆకు మిగతా భాగంలో సూర్యరశ్మితో సహా అన్ని కారకాలు ఉండటం వల్ల పిండిపదార్థం ఏర్పడింది. ఆకు నీలంగా మారింది.
ప్రశ్న 8.
కొవ్వులలో కరిగే విటమిన్లేవి ? వాటి లోపం వలన కలిగే వ్యాధులు మరియు వ్యాధి లక్షణాలను గూర్చి రాయండి.
జవాబు:
క్రొవ్వులో కరిగే విటమిన్లు
| విటమిన్ల పేర్లు | వ్యాధి పేరు | వ్యాధి లక్షణాలు |
| విటమిన్ A (రెటినాల్) | రేచీకటి, చత్వారం | రాత్రిపూట సరిగ్గా కనబడకపోవటం, కంటి నుండి నీరు కారటం, నేత్రపటల సమస్యలు, చర్మం పొలుసు బారటం. |
| విటమిన్ D (కాల్సిఫెరాల్) | రికెట్స్ | ఎముకలు సరిగ్గా పెరగకపోవటం, పెళుసు బారడం, దొడ్డికాళ్ళు, ముంజేతి వాపు, దంత సమస్యలు |
| విటమిన్ E (టోకోఫెరాల్) | వంధ్యత్వం | పురుషులలో వంధ్యత్వం, స్త్రీలలో గర్భస్రావం |
| విటమిన్ K (ఫైలోక్వినోన్) | అధిక రక్తస్రావం | రక్తం తొందరగా గడ్డకట్టకపోవటం |

ప్రశ్న 9.
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సెడ్ అవసరము అని నిరూపించుటకు మీ పాఠశాల ప్రయోగశాలలో ఒక ప్రయోగాన్ని నిర్వహించే ఉంటారు. 9వ తరగతి చదువుచున్న రాజు కూడా ఆ ప్రయోగాన్ని నిర్వహించాలనుకుంటున్నాడు. అతనికి గల కొన్ని అనుమానాలను నివృత్తి చేయుము.
i) ప్రయోగానికి ముందు కుండీలో పెరుగుతున్న మొక్కను చీకటి గదిలో సుమారు వారం రోజుల వరకు ఉంచారు కదా! ఎందుకు?
జవాబు:
మొక్కలోని పిండిపదార్థం తొలగించుటకు ప్రయోగానికి ముందు కుండీలో పెరుగుతున్న మొక్కను చీకటి గదిలో సుమారు వారం రోజుల వరకు ఉంచారు.
ii) గాజు జాడీలో KOH గుళికలు ఉంచారు. ఎందుకు?
జవాబు:
కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ ను శోషించుటకు గాజు జాడీలో KOH గుళికలు ఉంచారు.
iii) ఈ ప్రయోగ నిర్వహణకు ఉపయోగించిన పరికరాలు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
పరికరాలు :
కుండీలో పెరుగుచున్న మొక్క, వెడల్పు మూతిగల పారదర్శక గాజుసీసా, చీల్చబడిన రబ్బరు కార్కు.
iv) ఈ ప్రయోగాన్ని ఒక వేళ నీడలో నిర్వహిస్తే ఫలితం ఎలా ఉంటుంది?
జవాబు:
ఈ ప్రయోగాన్ని ఒక వేళ నీడలో నిర్వహిస్తే కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరగదు.
ప్రశ్న 10.
ప్రయోగ పరికరాల అమరికను గమనించి కింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.

1) కొవ్వొత్తి ఎందుకు ఆరిపోయింది?
జవాబు:
క్రొవ్వొత్తి వెలగడానికి అవసరమయిన వాయువు (ఆక్సిజన్) అయిపోవడం వలన క్రొవ్వొత్తి ఆరిపోయింది.
2) ఈ ప్రయోగంలో ఎలుక, కొవ్వొత్తి మధ్య మీరు ఏమైనా సంబంధాన్ని గుర్తించారా?
జవాబు:
ఈ ప్రయోగంలో ఎలుక జీవించడానికి, క్రొవ్వొత్తి వెలగడానికి ఒకే వాయువు (ఆక్సిజన్) అవసరం.
3) ఈ ప్రయోగం నందు ప్రీస్టే పరిశీలనలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ప్రీస్ట్రీ ఈ ప్రయోగం ద్వారా, మొక్కలు వదిలే వాయువు కొవ్వొత్తి వెలగడానికి, జంతువుల మనుగడకు దోహదం చేస్తుందని పరిశీలించాడు.
4) గంట జాడీ నందు పుదీన మొక్కను ఉంచినపుడు కొవ్వొత్తి నిర్విరామంగా వెలుగుతుంది. ఎందుకు?
జవాబు:
గంట జాడీ నందు పుదీనా మొక్క విడుదలచేసే ఆక్సిజన్ వలన క్రొవ్వొత్తి నిర్విరామంగా వెలుగుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 11.
ఈ క్రింది పట్టికను విశ్లేషించి, దిగువనీయబడిన ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానములు వ్రాయుము.
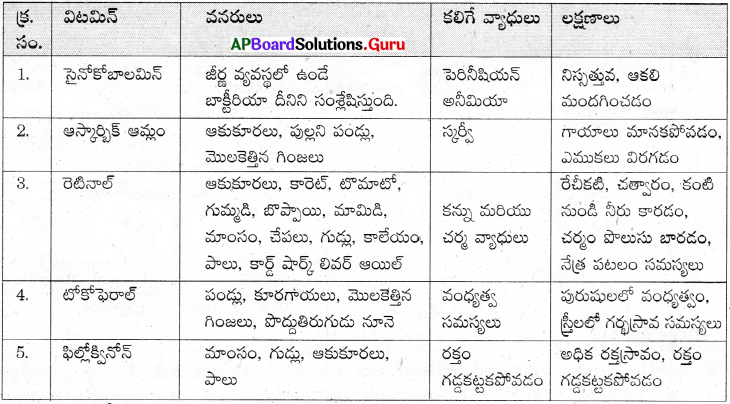
i) పై వాటిలో వంధ్యత్వ నివారణకు ఉపయోగపడే విటమినను గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:
విటమిన్ – ఇ (టోకోఫెరాల్)
ii) చిగుర్ల నుండి రక్తము రావడానికి ఏ విటమిన్ లోపం కారణము?
జవాబు:
విటమిన్ – సి (ఆస్కార్బిక్ ఆమ్లం)
iii) పై వాటిలో కొవ్వులలో కరిగే విటమిన్లు ఏవి?
జవాబు:
రెటినాల్ (ఎ), టోకోఫెరాల్ (ఇ), ఫిల్లోక్వినోన్ (3)
iv) K విటమిన్ లోపం వల్ల కలిగే వ్యాధి యొక్క లక్షణాలేవి?
జవాబు:
అధికరక్తస్రావం, రక్తం గడ్డకట్టకపోవటం.
ప్రశ్న 12.
“ఆకులలో పిండిపదార్థం కలదని” నిరూపించే ప్రయోగ విధానాన్ని, జాగ్రత్తలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
ఉద్దేశ్యం :
ఆకులలో పిండి పదార్థము కలదని నిరూపించుట.
పరికరాలు :
1) బీకరు 2) పరీక్షనాళిక 3) ట్రైపాడ్ స్టాండ్ 4) బున్ సెన్ బర్నర్ 5) ఇనుప వల 6) పెట్రెడిష్ 7) డ్రాపర్ 8) బ్రష్
రసాయనాలు :
1) ఇథనాల్ / మిథలేటెడ్ స్పిరిట్ 2) నీరు 3) ఆకు 4) అయోడిన్ / బెటాడిన్ ద్రావణం
ప్రయోగ విధానము :
- కుండీలో పెరుగుతున్న మొక్క నుండి ఒక ఆకును తీసుకోవాలి.
- పరీక్షనాళికలో మిథలేటెడ్ స్పిరిట్ తీసుకొని అందులో ఆకును ఉంచాలి.
- పరీక్షనాళికను నీరు కలిగిన బీకరులో ఉంచి వేడి చేయడం వలన ఆకులోని పత్రహరితము తొలగించబడి ఆకు పాలిపోయినట్లుగా కనబడుతుంది.
- ఆకును పెట్రెడిష్ లో ముడుతలు పడకుండా వెడల్పుగా పరిచి అయోడిన్ లేదా బెటాడిన్ ద్రావణాన్ని చుక్కలు చుక్కలుగా వేయాలి.
పరిశీలన :
ఆకు నీలి నలుపు రంగులోకి మారుతుంది. దీనిని బట్టి ఆకులలో పిండిపదార్థము కలదని నిరూపించవచ్చు.
జాగ్రత్తలు :
- మెత్తగా పలుచని ఆకులు కలిగిన మొక్కను ఎంపిక చేసుకోవాలి.
- వేడి పరీక్ష నాళిక నుండి ఆకును చేతితో నేరుగా తీయకుండా, బ్రష్ ను ఉపయోగించాలి.
- అయోడిన్ చుక్కలను డ్రాపర్ సహాయంతో మాత్రమే వేయాలి.
ప్రశ్న 13.
జంతువులు వినియోగించుకొంటున్న గాలిని మొక్కలు భర్తీ చేస్తాయని ప్రీస్టే ఎలా నిర్ధారించాడు?
జవాబు:

గాలి చొరబడని గంట జాడీలో వెలుగుతున్న కొవ్వొత్తి త్వరగా ఆరిపోవడాన్ని ప్రీస్టే గమనించాడు. అదేవిధంగా గాలి చొరబడని గంట జాడీలో ఉంచిన ఎలుకకు . ఊపిరాడకపోవడం కూడా గమనించాడు. ఈ పరిశీలన ద్వారా వెలిగే కొవ్వొత్తి, ఎలుక రెండూ కూడా ఏదో విధంగా గంట జాడీలోని గాలికి నష్టం కలిగించినట్లు నిర్ధారణకు వచ్చాడు. కానీ గంట జాడీలో ఒక పుదీనా మొక్కను ఉంచి పరిశీలించినప్పుడు ఎలుక ప్రాణంతో ఉండడాన్నీ, కొవ్వొత్తి వెలుగుతూ ఉండడాన్ని గమనించాడు. జంతువుల శ్వాసక్రియకూ, కొవ్వొత్తి వెలగడానికీ ఖర్చు అవుతున్న గాలిని మొక్కలు గాలిలోకి పంపుతుంటాయని .ఈ ప్రయోగం ద్వారా జోసఫ్ ప్రీస్టే ఊహించాడు.
ప్రశ్న 14.
కాంతి చర్యను వర్ణించండి.
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ ప్రధానంగా రెండు దశలలో జరుగుతుంది. అవి
1. కాంతి చర్య (Light dependent reaction)
2. నిష్కాంతి చర్య (Light independent reaction)
కాంతి చర్య (కాంతి రసాయన దశ) (Light dependent reaction)
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో మొదటి దశ ఇది. ఈ చర్యలో కాంతి ప్రధాన పాత్ర వహిస్తుంది. ఇందులో కాంతి ద్వారా ప్రేరేపించబడిన అనేక రసాయనిక చర్యలు ఒకదాని వెంట ఒకటి అతి త్వరగా జరుగుతుంటాయి. అందువలన ఈ దశను కాంతి రసాయన దశ (Photochemical phase) అంటారు. కాంతిచర్య క్లోరోప్లాస్లోని గ్రానా, థైలకాయిలో జరుగుతుంది. కాంతి చర్య వివిధ సోపానాలలో జరుగుతుంది.
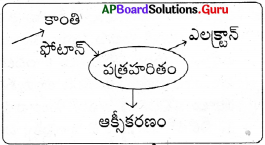
మొదటి సోపానం :
క్లోరోఫిలను కాంతిశక్తికి బహిర్గతం ఎలక్ట్రాన్ చేసినప్పుడు ఫోటాన్లను శోషించి క్రియావంతమవుతుంది.
రెండవ సోపానం :
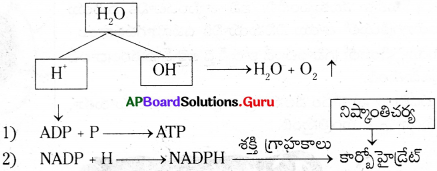
నీటి అణువు హైడ్రోజన్ (H), హైడ్రాక్సిల్ (OH–) అయాన్లుగా విచ్ఛిత్తి చేయడానికి ఈ కాంతిశక్తి వినియోగించబడుతుంది.
H2O → H+ + OH–
ఈ చర్యను నీటి కాంతి విశ్లేషణ (Photolysis) అంటారు. ఫోటో అనగా కాంతి-లైసిస్ అనగా విచ్ఛిత్తి చేయడం అని అర్థం. అంటే కాంతి ద్వారా నీటి అణువు విచ్చిత్తి చెందడం అన్నమాట. దీనిని ‘హిల్’ అనే శాస్త్రవేత్త నిరూపించాడు. అందువల్ల దీనిని ‘హిల్ చర్య’ అని కూడా అంటారు.
మూడవ సోపానం :
అత్యంత చర్యాశీలమైన నీటి అయాన్లు రెండు మార్గాలలో తొందరగా మార్పు చెందుతాయి.
- OH– అయాన్లు ఒకదాని వెంట ఒకటిగా జరిగే అనేక చర్యల పరంపర ద్వారా నీరు (H2O) మరియు ఆక్సిజన్ (O2) ఉత్పత్తి చేస్తుంది.
- నీరు మొక్క లోపల వినియోగించబడుతుంది. కానీ ఆక్సిజన్ మాత్రం వాతావరణంలోకి విడుదలవుతుంది.
- H+ అయాన్ నిష్కాంతి చర్యలో క్రమానుగత చర్యల పరంపరలకు లోనవుతుంది.
- కాంతి చర్యలో అడినోసిస్ ట్రై ఫాస్ఫేట్ (ATP) మరియు నికోటినమైడ్ అడినోసిన్ డై ఫాస్ఫేట్ (NADPH) లు అంత్య పదార్థాలుగా ఏర్పడతాయి. వీటిని శక్తిగ్రాహకాలు (Assimilatory powers) అని కూడా అంటారు.
ప్రశ్న 15.
నిష్కాంతి చర్యలను వర్ణించండి.
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలోని రెండవ దశను నిష్కాంతి చర్య అంటారు. వీటికి కాంతిశక్తితో సంబంధం లేనప్పటికి, కాంతిచర్యలో ఏర్పడిన శక్తి గ్రాహకాలు తప్పని సరిగా కావాలి. ఈ చర్యలన్నీ హరిత రేణువులోని అవర్ణికలో జరుగుతాయి.
1) ఈ చర్యలలో మొదటిగా రిబ్యులోజ్ బై ఫాస్ఫేట్ పదార్థంచే CO2 గ్రహించబడి ఆరు కార్బన్లు గల హెక్సోజ్ చక్కెరగా మారుతుంది.
CO2 + రిబ్యులోజ్ బై ఫాస్ఫేట్ → హెక్సోజ్ చక్కెర
2) నిలకడలేని ఈ హెక్సోజ్ చక్కెర విచ్ఛిన్నం చెంది, మూడు కార్బన్లు గల ఫాస్ఫా గ్లిజరిక్ ఆమ్లం (PGA) గా విడిపోతుంది.
హెక్సోజ్ చక్కెర → 2 PGA
3) ఫాస్ఫాగ్లిజరిక్ ఆమ్ల అణువులు రెండు కలిసి, కొన్ని వరుస మార్పుల తరువాత గ్లూకోజ్ గా మారును.
2 PGA → గ్లూకోజ్
4) ఈ గ్లూకోజ్ వినియోగించబడి, మిగిలినది పిండిపదార్థంగా నిల్వచేయబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 16.
అమీబాలో ఆహార సేకరణ విధానం తెలపండి.
జవాబు:
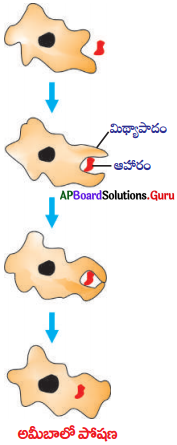
- ఏక కణజీవి అమీబాలో ఆహారం శరీరం ఉపరితలం నుండి సేకరించ బడుతుంది.
- అమీబా ఆహార సేకరణ కొరకు శరీర ఉపరితలం నుండి వేళ్ళవంటి మిథ్యాపాదాలను ఏర్పాటు చేసుకుంటుంది.
- ఈ మిథ్యాపాదాలను ఆహారం చుట్టూ వ్యాపింపజేసి ఆహారపు రిక్తికగా మారుస్తుంది.
- ఆహార రిక్తికలో సంక్లిష్ట ఆహారపదార్థాలు సరళపదార్థాలుగా విడగొట్టబడిన తరువాత కణద్రవ్యంలోకి వ్యాపనం చెందుతాయి.
- జీర్ణం కాని పదార్థం కణం ఉపరితలానికి చేరి అక్కడ నుండి వెలుపలికి పంపబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 17.
బంగారు తీగను వర్ణించండి.
జవాబు:

బంగారు తీగ కాండం సన్నగా పొడవుగా, నారింజ, లేత గులాబి, పసుపు లేదా గోధుమ రంగులో గాని ఉంటుంది. డాడర్ పుష్పాలు బొడిపెల రూపంలో గుంపులు గుంపులుగా ఉంటాయి. పసుపు లేదా తెలుపు రంగులో ఆకర్షక పత్రాలు ఉండే తమ్మెలు గంట ఆకారంలో (సంయుక్త ఆకర్షక పత్రాలు) ఉంటాయి. పత్రాలు సన్నటి పొలుసుల మాదిరిగా క్షీణించి ఉంటాయి.
బంగారు తీగ కాండం తీగలా అతిథేయ మొక్క చుట్టూ మెలికలు తిరిగిన తరువాత పక్కనున్న మరొక కాండాన్ని చుట్టి పెనవేసుకొని పోవడం వలన అతిథేయి మొక్కపై మొత్తం వల మాదిరిగా ఆక్రమించి జాలాకారంగా కస్కుటాలో హాస్టోరియాలు కనబడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 18.
విటమిన్స్ లభ్యత, వాటి లోపం వలన కలిగే వ్యాధులు, లక్షణాలు తెలుపుతూ పట్టిక రూపొందించండి.
జవాబు:
ప్రశ్న 19.
ప్రక్క పటం పరిశీలించి క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
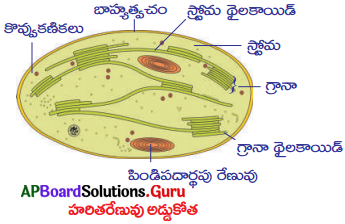
a) ప్రక్క పటంలో చూపించిన కణాంగము ఏ క్రియను నిర్వహిస్తుంది?
b) ఈ కణాంగము ఏ భాగాలలో ఉంటుంది?
c) ఈ కణాంగములోని ప్రధానభాగాలు ఏమిటి?
d) ఈ కణాంగములో సంశ్లేషణ చేయబడు పదార్థం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
a) ఈ కణాంగము పేరు హరితరేణువు. ఇది కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియను నిర్వహిస్తుంది.
b) ఈ కణాంగము మొక్కల ఆకుపచ్చభాగాలైన పత్రము లేతకాండాలలో ఉంటుంది.
c) ఈ కణాంగంలో ప్రధానంగా 1) త్వచం 2) హేమా పిండిపదార్థపు రేణువు 3) గ్రానా అనే భాగాలు ఉంటాయి.
d) ఈ కణాంగంలో గ్లూకోజ్ సంశ్లేషణ చేయబడి తరువాత పిండిపదార్థంగా మారుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 20.
కింది పటం పరిశీలించి క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
a) ఈ పటము ఏ నిర్మాణాన్ని సూచిస్తుంది?
b) పటం మధ్యభాగంలో వలయాకారంగా ఉన్న నిర్మాణం పని ఏమిటి?
c) పటంలో పైన, క్రింద ఉన్న వరుసకణాల పని ఏమిటి?
d) స్తంభాకార స్పంజి కణజాలం మధ్య భేదాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
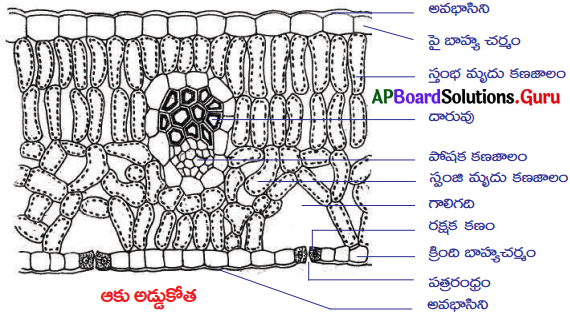
a) పటంలో ఆకు అడ్డుకోత చూపబడింది.
b) పటం మధ్యలో ఉన్న వలయాకార నిర్మాణం నాళికాపుంజం. ఇది రవాణాకు తోడ్పడుతుంది. పై భాగంలో ఉండే దారువు నీటి రవాణాకు, క్రింది భాగంలో ఉండే పోషక కణజాలం ఆహార రవాణాకు తోడ్పడును.
c) పైన, క్రింద ఉన్న వరుస కణాలను బాహ్యచర్మం అంటారు. ఇది రక్షణకు తోడ్పడును.
d) స్తంభాకార కణజాలం దగ్గరగా అమర్చబడి, అధికసంఖ్యలో హరితరేణువులను కలిగి కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు తోడ్పడుతుంది. స్పంజి కణజాలం కణాంతర భాగాలను కలిగి వాయు మార్పిడికి తోడ్పడుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 21.
కింది పటం పరిశీలించి క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.

a) ఈ ప్రయోగం యొక్క ఉద్దేశం ఏమిటి?
b) ఈ ప్రయోగంలో ఉపయోగించిన పరికరాలు ఏమిటి?
c) సీసాలో ఉంచిన రసాయనం ఏమిటి? దాని అవసరం ఏమిటి?
d) ప్రయోగం తరువాత, పత్రం యొక్క ఏ భాగం నీలిరంగుకు మారును?
జవాబు:
a) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు CO2 అవసరమని నిరూపించుట ఈ ప్రయోగ ఉద్దేశం.
b) ఈ ప్రయోగంలో, వెడల్పు మూతిగల సీసా, రబ్బరుబిరడా, కుండీ మొక్క ఉపయోగించారు.
c) సీసాలోపల తీసుకొన్న రసాయనం KOH. ఇది సీసాలోని CO2 ను పీల్చుకొంటుంది.
d) ప్రయోగ అనంతరం సీసా వెలుపలి ఉన్న పత్రభాగం నీలిరంగుగా మారును.
ప్రశ్న 22.
క్రింద ఉన్న ఫ్లోచార్టును గమనించి క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.

a) ఈ ఫ్లోచార్ట్ ఏ జీవక్రియను వివరిస్తుంది?
b) మానవుని జీర్ణవ్యవస్థలో ఆహారం జీర్ణమయ్యే ప్రాంతాలు గుర్తించండి.
c) ఫ్లోచార్టులో ఉదహరించబడిన గ్రంథులు, వాటి జీర్ణరసాలు తెలుపండి.
d) జీర్ణవ్యవస్థలో ఆహారం శోషణ చెందే ప్రాంతము ఏది?
జవాబు:
a) ఈ ఫ్లోచార్టు మానవ జీర్ణవ్యవస్థను, జీర్ణక్రియను వివరిస్తుంది.
b) ఆహారం జీర్ణమయ్యే ప్రాంతాలు, 1) నోరు, 2) జీర్ణాశయం, 3) ఆంత్రమూలం, 4) చిన్న ప్రేగు
c) కాలేయం – పైత్యరసం
క్లోమము – క్లోమరసం
d) జీర్ణమైన ఆహారం చిన్న ప్రేగులో శోషణ చెందుతుంది.
ప్రశ్న 23.
పటాన్ని పరిశీలించి క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు ఇవ్వండి.

a) ఈ ప్రయోగం నిర్వహించిన శాస్త్రవేత్త ఎవరు?
b) ఈ ప్రయోగంలో కొవ్వొత్తి, ఎలుకకు ఉన్న సంబంధం ఏమిటి?
c) ఈ ప్రయోగంలో పుదీనా మొక్కకు బదులు మరొక ఎలుకను ప్రవేశపెడితే ఏం జరుగును?
d) భూమి మీద మొక్కల ప్రాధాన్యత ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
a) ఈ ప్రయోగం నిర్వహించిన శాస్త్రవేత్త జోసఫ్ ప్రీస్టే.
b) ఈ ప్రయోగంలో కొవ్వొత్తి మరియు ఎలుక రెండూ ఆక్సిజనన్ను వినియోగించుకొన్నాయి.
c) పుదీనా మొక్క స్థానంలో మరొక ఎలుకను ప్రవేశపెడితే, ఆక్సిజన్ త్వరగా అయిపోయి ఎలుకలు త్వరగా మరణిస్తాయి. కొవ్వొత్తి త్వరగా ఆరిపోతుంది.
d) భూమి మీద ఉన్న జీవరాశులకు ఆక్సిజన్ను అందించేవి మొక్కలు. ఇవి కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ ద్వారా, జంతువులకు ఆహారాన్ని ఆక్సిజన్ను అందిస్తున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 24.
జీవక్రియల్లో కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరగకపోతే భూగోళంలో కలిగే అనర్దాలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:
1) మొక్కలు కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరపకపోతే మిగతా సజీవులకు ఆహారం లభ్యంకాదు. ఎందుకంటే మిగిలిన జీవులన్నీ ఆహారం కోసం మొక్కల మీద ఆధారపడినాయి.
2) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరుగుటకు కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సెడ్ అవసరం. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరుగకపోతే గాలిలో కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ శాతం పెరుగుతుంది. ఇది జరిగితే భూ ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు పెరిగి భూగోళం వెచ్చబడటానికి కారణమవుతుంది. భూ ఉష్ణోగ్రతలు పెరిగితే ధృవాల వద్ద ఉన్న మంచు కరిగి సముద్ర మట్టాలు పెరుగుతాయి. దీనివలన సముద్ర తీర ప్రాంతాలు మునిగిపోతాయి, అనేకమైన జీవులు చనిపోతాయి.
3) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ గాలిలోనికి ఆమ్లజనిని విడుదల చేస్తుంది. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరుగకపోతే ఆమ్లజని విడుదల కాకపోవడం చేత సజీవులు మరణిస్తాయి.

ప్రశ్న 25.
స్వయంపోషకాలలో పోషణ, సూర్యకాంతి ఉన్నప్పుడు, లేనప్పుడు కూడా జరుగుతుంటుంది కదా! ఈ రెండు సందర్బాలకు తేడాలు ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
మొక్కలు మరియు కొన్ని రకాల బాక్టీరియాలు స్వయంపోషకాలకు ఉదాహరణలు. మొక్కలు సూర్యకాంతి ఉన్నప్పుడు స్వయంగా ఆహారాన్ని తయారు చేసుకుంటాయి. బాక్టీరియా కాంతి లేనప్పుడు స్వయంగా ఆహార పదార్థాలను తయారు చేసుకుంటుంది. ఈ బాక్టీరియాలు అకర్బన శక్తి వనరులను వినియోగించి కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ నుండి కర్బన సమ్మేళనాలను తయారు చేసుకుంటాయి. అందువలన ఈ బాక్టీరియాలను రసాయన స్వయంపోషక జీవులు అంటారు. ఈ ప్రక్రియ ద్వారా బాక్టీరియాలు తమకు కావలసిన ఆహారము లేదా శక్తిని సమకూర్చుకుంటాయి. రసాయన ప్రక్రియ ద్వారా ఆహారమును తయారు చేయడానికి కావలసిన శక్తిని అకర్బన అణువులయిన ఇనుము, గంధకము మరియు మెగ్నీషియంలను ఆక్సీకరణము చేయుట ద్వారా పొందుతాయి.
ఉదా : నత్రజని స్థాపక బాక్టీరియా – నేలయందు ఉండునది.
లావా పదార్థములందుండు ఇనుము ఆక్సీకరణ బాక్టీరియా సముద్ర అడుగుభాగమున వేడి రంధ్రముల యందుండే గంధకము ఆక్సీకరణ బాక్టీరియా.
ప్రశ్న 26.
డాక్టర్ను అడిగి కింది విషయాల గురించి తెలుసుకోండి. చార్టును తయారుచేసి మీ తరగతిలో ప్రదర్శించండి.
ఎ) ఏ పరిస్థితులలో రోగికి గ్లూకోజ్ అవసరమౌతుంది?
బి) ఎప్పటి వరకు గ్లూకోజ్ అందిస్తారు?
సి) గ్లూకోజ్ రోగిని ఎలా కోలుకోనేటట్లు చేస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
ఎ) గ్లూకోజ్ అవసరమయ్యే పరిస్థితులు :
- రోగి బాగా నీరసంగా ఉన్నప్పుడు
- రోగి దీర్ఘకాలంగా వ్యాధితో బాధపడుతూ బలహీనం చెందినపుడు
- డయేరియాతో రోగి నీరసించినపుడు
- ఆపరేషన్ తరువాత రోగి త్వరగా కోలుకోవటానికి, గ్లూకోజ్ ఎక్కిస్తారు.
బి) ఎప్పటి వరకు గ్లూకోజ్ ఎక్కిస్తారు?
1. సాధారణంగా వ్యక్తి యొక్క ఆరోగ్యస్థితి, వ్యాధిని బట్టి డాక్టర్లు ఎక్కించాల్సిన గ్లూకోజు మోతాదును నిర్ణయిస్తారు. కొన్నిసార్లు రోగి కోలుకోనే వరకు గ్లూకోజ్, విరామంతో ఎక్కిస్తుంటారు.
సి) గ్లూకోజ్ రోగిని ఎలా కోలుకొనేటట్లు చేస్తుంది?
1. గ్లూకోజ్ సరళమైన చక్కెర పదార్థం. ఇది నేరుగా రక్తంలోనికి శోషణ చెంది, కణ శ్వాసక్రియలో పాల్గొని, శక్తిని ఇస్తుంది. తక్షణ శక్తి లభించుట వలన రోగి త్వరగా కోలుకుంటాడు. మిగిలిన ఆహార పదార్థాలవలె గ్లూకోజ్ జీర్ణక్రియలోనికి చేరి జీర్ణం కావలసిన అవసరం లేదు. అందుకే నేరుగా రక్తంలోనికి ఎక్కిస్తారు.
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson పోషణ – ఆహార సరఫరా వ్యవస్థ ½ Mark Important Questions and Answers
సరైన గ్రూపును గుర్తించండి
1. ఏ జీవుల సమూహం జాంతవ పోషణను చూపిస్తుంది?
A. శాకాహారులు, మాంసాహారులు, సర్వభక్షకులు
B. స్వయం పోషకాలు, పూతికాహారులు, పరాన్నజీవులు
జవాబు:
సమూహం A
2. ఈ క్రింది ఏ సమూహం, పరపోషణకు సంబంధించినది?
A. స్వయంపోషణ, సహజీవనము, పరాన్న జీవనం
B. పూతికాహార పోషణ, పరాన్న జీవనం, జాంతవ పోషణ
జవాబు:
సమూహం B
3. ఏ జీవుల సమూహం పూతికాహారులు?
A. హుక్ వార్మ్, కస్కుట, లైకెన్
B. శిలీంద్రం, రొట్టె బూజు, పుట్టగొడుగు
జవాబు:
సమూహం B
4. ఏ గ్రూపు జీవులలో జాంతవ పోషణ ఉండదు?
A. అమీబా, పారామీషియం, మానవులు
B. మొక్కలు, కస్కుట, శిలీంధ్రాలు
జవాబు:
సమూహం B
5. ఏ సమూహంలోని కాంతి చర్య సంఘటనలు సరియైన క్రమంలో అమర్చబడినాయి?
A. పత్రహరితం కాంతిని శోషించుట, నీటి కాంతి విశ్లేషణ, స్వాంగీకరణ శక్తి ఏర్పడటం
B. పత్రహరితం కాంతిని శోషించుట, స్వాంగీకరణ శక్తి ఏర్పడటం, నీటి కాంతి విశ్లేషణ
జవాబు:
సమూహం A
6. ఏ సమూహంలోని వ్యాధులకు విటమిన్ లోపంతో సంబంధం లేదు?
A. క్వాషియోర్కర్, మెరాస్మస్, ఊబకాయం
B. అనీమియా, స్కర్వీ, రికెట్స్
జవాబు:
సమూహం A
7. ఏ గ్రూపులోని ఎంజైమ్ లు – కార్బోహైడ్రేట్ల పై పని చేయవు?
A. టయలిన్, అమైలేజ్, సుక్రేజ్
B. లైపేజ్, ట్రిప్సిన్, పెప్పిన్
జవాబు:
సమూహం B
8. ఏ సమూహంలోని విటమిన్ లు రక్తహీనతను కలిగిస్తాయి?
A. పైరిడాక్సిన్, ఫోలిక్ ఆమ్లం, సయానోకోబాలమిన్
B. నియాసిన్, ఆస్కార్బిక్ ఆమ్లం, బయోటిన్
జవాబు:
సమూహం A

9. క్లోమరసంలో ఏ గ్రూపు ఎంజైమ్ లు ఉంటాయి?
A. అమైలేజ్, పెప్సిన్, లైపేజ్
B. అమైలేజ్, ట్రిప్సిన్, లైపేజ్
జవాబు:
సమూహం B
10. ఏ సమూహంలోని విటమిన్స్ కొవ్వులో కరుగుతాయి?
A. విటమిన్ ఎ, విటమిన్ డి, విటమిన్ కె
B. విటమిన్ ఎ, విటమిన్ బి, విటమిన్ సి
జవాబు:
సమూహం A
ఫ్లో చార్టులు
11.
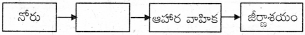
జవాబు:
ఆస్యకుహరం
12.
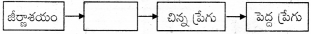
జవాబు:
ఆంత్రమూలం
13.
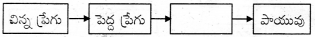
జవాబు:
పురీషనాళం
14.
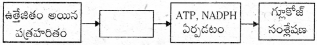
జవాబు:
నీటి అణువు విచ్ఛిన్నం
15.
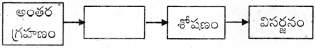
జవాబు:
జీర్ణక్రియ
16.
జవాబు:
నీటిలో కరిగే విటమిన్లు
17.
జవాబు:
మొక్కలు / కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ బాక్టీరియా
18.
జవాబు:
పక్షి / మానవుడు
19.
జవాబు:
పూతికాహార పోషణ
20.
జవాబు:
క్వాషియోర్కర్
విస్తరించుము
21. CO2 – కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
22. H2S – హైడ్రోజన్ సల్ఫైడ్
24. ATP – అడినోసిన్ ట్రై ఫాస్ఫేట్
25. NADP – నికోటినమైడ్ అడినైన్ డై న్యూక్లియోటైడ్ ( విటమిన్లు
26. NADPH – నికోటినమైడ్ అడినైన్ డై న్యూక్లియోటైడ్ హైడ్రోజన్ ఫాస్ఫేట్
27. RUBP – రిబ్యులోజ్ 1, 5 బై ఫాస్ఫేట్
ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి
28. మొక్కల వలె కాంతి శక్తిని ఉపయోగించుకొని తమకు కావలసిన ఆహారాన్ని తామే తయారు చేసుకునే సామర్థ్యం కలిగి ఉండే జీవికి ఒక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ జరిపే బాక్టీరియా / శైవలాలు
29. కస్కుట మొక్క పరాన్నజీవికి ఉదాహరణ. జంతు పరాన్న జీవికి ఉదాహరణను ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
రింగ్ వార్మ్ / జలగ / పేను / జంతువులు
30. పూతికాహార పోషణకు పుట్టగొడుగు ఒక ఉదాహరణ. మరో ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
శిలీంధ్రాలు / రొట్టె బూజు జాంతవ పోషణ
31. జాంతవ పోషణను చూపించే ఏకకణ జీవికి ఒక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
అమీబా / పారామీషియం
32. ట్రిప్సిన్ అనే ఎంజైమ్ ప్రోటీన్ల మీద పనిచేస్తుంది. కొవ్వులపై చర్య జరిపే ఎంజైమ్ కు మరో ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
లైపేజ్
33. క్వాషియోర్కర్, పోషకాహార లోపానికి ఒక ఉదాహరణ. మరో ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
మెరాస్మస్
34. నెమరు వేసే జీవులలో వ్యతిరేక పెరిస్టాలసిస్ కనిపిస్తుంది. మానవులలో దీనిని ఏమని పిలుస్తారు?
జవాబు:
వాంతి చేసుకోవడం
35. రక్తంలో గ్లూకోజ్ స్థాయిలను క్రమబద్ధం చేసే జీర్ణ గ్రంథికి ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
క్లోమం
36. విటమిన్ ‘ఎ’ ని కలిగి ఉన్న పండ్లకు ఒక ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
బొప్పాయి / మామిడి

37. విటమిన్ బి-కాంప్లెక్స్ నీటిలో కరిగే విటమిన్ను ఉదాహరణగా చెప్పుకోవచ్చు. మరో ఉదాహరణ ఇవ్వండి.
జవాబు:
విటమిన్ సి
శాస్త్రవేత్తను గుర్తించండి
38. 1931లో కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు సమీకరణాన్ని ప్రతిపాదించి ఆమోదించారు. పర్పుల్ సల్ఫర్ బ్యాక్టీరియా పై పరిశోధన చేస్తూ కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో కాంతి పాత్ర గురించి కనుగొన్నాడు.
జవాబు:
సి.బి. వాన్ నీల్.
39. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో ఆక్సిజన్, నీటి నుంచి విడుదల అవుతుందని తెలియజేశాడు. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో కాంతి చర్యలను గురించి కనుగొన్నాడు.
జవాబు:
రాబర్ట్ హిల్
40. తాను నిర్వహించిన ప్రయోగాల ద్వారా వాయు వినిమయం జరగడం వలన మొక్కలు వదిలే వాయువు కొవ్వొత్తి వెలగడానికి, జంతువుల మనుగడకు దోహదం చేస్తుందని నిర్ధారించాడు.
జవాబు:
జోసెఫ్ ప్రీస్టే
41. ఆయన డచ్ శాస్త్రవేత్త. నీటి మొక్కలపై జరిపిన ప్రయోగంలో, ప్రకాశవంతమైన సూర్యకాంతి సమక్షంలో నీటిమొక్కల, ఆకుపచ్చ భాగాల చుట్టూ చిన్నపాటి బుడగలు ఏర్పడతాయని చీకటిలో ఉన్నప్పుడు బుడగలు ఏర్పడలేదని తెలియజేశాడు.
జవాబు:
జాన్ ఇంజెన్ హౌజ్
42. ఆయన జర్మన్ వృక్ష శాస్త్రవేత్త. పత్రహరితం మొక్కలలోని కణం అంతా వ్యాపించి ఉండదని గమనించాడు.
జవాబు:
జులియస్ వాన్ సాక్స్
43. అతను జర్మన్ వృక్ష శాస్త్రవేత్త. ఆక్సిజన్ ఉత్తేజిత బాక్టీరియాలపై ప్రకాశవంతమైన ఎరుపు మరియు నీలి కాంతి కిరణాలను ప్రసరింపజేసినపుడు అవి గుంపులుగా ఏర్పడటం గమనించాడు.
జవాబు:
ఎంగల్ మన్
44. ఈ ఇద్దరు శాస్త్రజ్ఞులు ఆకుపచ్చ రంగులో ఉన్న పదార్థాన్ని వెలికితీసి, దానికి పత్రహరితమని పేరు పెట్టారు.
జవాబు:
పెల్లిటియర్ మరియు కావనో
దోషాన్ని గుర్తించి, సరిచేసి రాయండి
45. పరపోషకాలు అనేవి కాంతి శక్తిని ఉపయోగించుకోవడం ద్వారా తమ స్వంత ఆహారాన్ని సంశ్లేషణ చేయగల జీవులు.
జవాబు:
స్వయంపోషకాలు అనేవి కాంతి శక్తిని ఉపయోగించుకోవడం ద్వారా తమ స్వంత ఆహారాన్ని సంశ్లేషణ చేయగల జీవులు.
46. మొక్కలు ఆకుపచ్చ వర్ణద్రవ్యం కెరోటిన్ ని కలిగి ఉంటాయి.
జవాబు:
మొక్కలు ఆకుపచ్చ వర్ణద్రవ్యం పత్రహరితంని కలిగి ఉంటాయి.
47. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో ఒక కార్బోహైడ్రేట్ అణువు ఏర్పడటంతో పాటుగా ఒక నీటి అణువు, ఒక అణువు కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ కూడా ఉత్పన్నమవుతాయి.
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో ఒక కార్బోహైడ్రేట్ అణువు ఏర్పడటంతో పాటుగా ఒక నీటి అణువు, ఒక అణువు ఆక్సిజన్ కూడా ఉత్పన్నమవుతాయి.
48. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో ఆక్సిజన్, కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్ నుంచి విడుదలవుతుంది.
జవాబు:
కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో ఆక్సిజన్, నీరు నుంచి విడుదలవుతుంది.
49. పిండిపదార్థం యొక్క ఉనికిని నీలం ఆకుపచ్చ రంగు ద్వారా గుర్తించవచ్చు.
జవాబు:
పిండిపదార్థం యొక్క ఉనికిని నీలం – నలుపు రంగు ద్వారా గుర్తించవచ్చు.
50. అమీబా తన శైలికల ద్వారా ఆహారాన్ని సేకరిస్తుంది.
జవాబు:
అమీబా తన మిథ్యాపాదాలు ద్వారా ఆహారాన్ని సేకరిస్తుంది.
51. జీరాశయంలో పాక్షికంగా జీర్ణమైన ఆహారాన్ని బోలస్ అంటారు.
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయంలో పాక్షికంగా జీర్ణమైన ఆహారాన్ని క్రైమ్ అంటారు.
52. జీర్ణాశయం చివర ఉండే ఉప జిహ్విక ఆహార పదార్థాన్ని జీర్ణాశయం నుండి చిన్న ప్రేగులోకి వచ్చే విధంగా నియం త్రిస్తాయి.
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయం చివర ఉండే వలయాకార సంవరిణి కండరాలు ఆహార పదార్థాన్ని జీర్ణాశయం నుండి చిన్నప్రేగులోకి వచ్చే విధంగా నియంత్రిస్తాయి.
53. పెప్సిన్ పిండి పదార్థాన్ని డెక్టోజ్ మరియు మాల్టోజ్ చక్కెరలుగా మారుస్తుంది.
జవాబు:
టయలిన్ పిండి పదార్థాన్ని డెక్ట్రోజ్ మరియు మాల్టోజ్ చక్కెరలుగా మారుస్తుంది.

54. బయోటిన్ లోపం వల్ల పిల్లగ్రా వస్తుంది.
జవాబు:
నియాసిన్ లోపం వల్ల పెల్లగ్రా వస్తుంది.
నేను ఎవరు
55. నేనొక విటమిన్ సి. ప్రేగుల్లో ఉండే బాక్టీరియా నన్ను సంశ్లేషణ చేస్తాయి.
జ. బి12 / సయానోకోబాలమిన్
56. నేనొక విటమిన్ లోపం వలన కలిగే వ్యాధిని. ఎముకలు సరిగా పెరగకపోవడం, పెళుసు బారడం, దొడ్డి కాళ్ళు, ముంజేతి వాపు, దంత సమస్యలు వ్యాధి లకణాలు.
జవాబు:
రికెట్స్
57. నేనొక విటమిన్ ని. నేను ఆకుకూరలలో, పుల్లని పండ్లు మరియు మొలకెత్తిన గింజలలో లభిస్తాను. నా రసాయన నామం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ఆస్కార్బిక్ ఆమ్లం
58. నేనొక విటమిన్ ని. క్యారెట్, టమోటా, బొప్పాయి, మామిడి మరియు ఆకుకూరల్లో ఎక్కువగా లభిస్తాను. నా లోపం వల్ల మీ దేహంలో ఏ భాగం ప్రభావితం అవుతుంది?
జవాబు:
కన్ను మరియు చర్మం
59. నేను ఎంజైములు లేని జీర్ణ రసాన్ని మరియు కొవ్వుల మీద పనిచేస్తాను.
జవాబు:
పైత్యరసం
60. నేను జఠర గ్రంథుల నుండి స్రవించబడే ఎంజైమ్ ను మరియు ప్రోటీన్ల మీద పనిచేస్తాను.
జవాబు:
పెప్సిన్
61. నేను కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ ప్రయోగంలో ఉపయోగించే రసాయన పదార్థాన్ని మరియు CO2 ని శోషించుకునే లక్షణం నాకు ఉంది.
జవాబు:
KOH
62. కన్వాల్వులేసి కుటుంబానికి చెందిన, తీగలుగా చుట్టు కుంటూ పెరిగే పత్రరహిత పరాన్నజీవి మొక్కను నేను.
జవాబు:
కస్కుట
63. అధిక కేలరీల ఆహారం తీసుకోవటం వలన కలిగే పోషకాహార లోపాన్ని నేను.
జవాబు:
ఊబకాయం
64. పత్రహరితాన్ని తొలంచడానికి సహాయపడే రసాయన పదార్థాన్ని నేను.
జవాబు:
మిథిలేటెడ్ స్పిరిట్
పోలికను గుర్తించుట
65. స్వయం పోషకాలు : మొక్కలు :: పరపోషకాలు 😕
జవాబు:
జంతువులు నేను ఎవరు?
66. హుక్ వార్మ్ : పరాన్న జీవి :: రైజోపస్ 😕
జవాబు:
పూతికాహారి
67. లాలాజలం : నోరు :: పైత్యరసం 😕
జవాబు:
ఆంత్రమూలం
68. కాంతి చర్యలు 😕 :: నిష్కాంతి చర్యలు : అవర్ణిక
జవాబు:
గ్రానా
69. ఆక్సిజన్ : కాంతి చర్యలు :: ? : నిష్కాంతి చర్యలు
జవాబు:
కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
70. అమైలేజ్ : కార్బోహైడ్రేట్ :: ? : కొవ్వులు
జవాబు:
లైపేజ్
71. కార్బో హైడ్రేట్ : గ్లూకోజ్ :: ప్రోటీన్ 😕
జవాబు:
అమైనో ఆమ్లాలు
72. కాంతి చర్యలు : ? :: నిష్కాంతి చర్యలు : క్రెబ్
జవాబు:
రాబర్ట్ హిల్
73. థయామిన్ : బెరి బెరి :: ? : గ్లోసైటిస్
జవాబు:
రైబోఫ్లేవిన్
74. విటమిన్ K : ఫిల్లోక్వినోన్ :: విటమిన్ E 😕
జవాబు:
టోకోఫెరోల్
జతపరుచుట
75. తప్పుగా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
అంతర గ్రహణం – నోరు
శోషణ – జీర్ణాశయం
మల విసర్జన – పాయువు
జవాబు:
శోషణ – జీర్ణాశయం
76. సరిగ్గా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
ఆహార వాహిక – పెరిస్టాలసిస్
నోరు – చిలకడం
జీర్ణాశయం – మాస్టికేషన్
జవాబు:
ఆహార వాహిక – పెరిస్టాలసిస్

77. తప్పుగా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
కాలేయం – పైత్యరసం
క్లోమం – క్లోమరసం
జీర్ణాశయం – ఆంత్రరసం
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయం – ఆంత్రరసం
78. సరిగ్గా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
క్వాషియోర్కర్ – ప్రోటీన్ లోపం
ప్లోరోసిస్ – విటమిన్ లోపం
ఊబకాయం – కేలరీల లోపం
జవాబు:
క్వాషియోర్కర్ – ప్రోటీన్ లోపం
79. తప్పుగా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
విటమిన్ D – కాల్సిఫెరాల్
విటమిన్ B6 – పైరిడాక్సిన్
విటమిన్ A – టోకోఫెరాల్
జవాబు:
విటమిన్ A – టోకోఫెరాల్
80. సరిగ్గా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
రికెట్స్ – కన్ను
గ్లాసైటిస్ – నాలుక
జెరోఫ్తాల్మియా – చర్మం
జవాబు:
గ్లాసైటిస్ – నాలుక
81. సరిగ్గా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
పాంటాథెనిక్ ఆమ్లం – చిలకడదుంప
ఆస్కార్బిక్ ఆమ్లం – తృణధాన్యాలు
థయమిన్ – నిమ్మ
జవాబు:
పాంటాథెనిక్ ఆమ్లం – చిలకడదుంప
82. సరిగ్గా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
జాన్ ఇంజెన్ హౌజ్ – హైడ్రిల్లా ప్రయోగం
జోసెఫ్ ప్రీస్ట్లీ – అర్ధపత్ర ప్రయోగం
మోల్ – గంటజాడీ ప్రయోగం
జవాబు:
జాన్ ఇంజెన్ హౌజ్ – హైడ్రిల్లా ప్రయోగం
83. సరైన క్రమాన్ని గుర్తించండి.

జవాబు:
సి
84. సరిగ్గా జతచేయబడిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
శాకాహారి – కుక్క
మాంసాహారి – కుందేలు
సర్వభక్షకి – కాకి
జవాబు:
సర్వభక్షకి – కాకి
బొమ్మలపై ప్రశ్నలు
85.

ఈ పటం ఏ విటమిన్ లోపాన్ని సూచిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
విటమిన్ K
86.

ఈ పరీక్ష దేనిని సూచిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
పిండిపదార్థ పరీక్ష
87.
గంట జాడీలో ఎలుకకు ఊపిరి ఆగక పోవడానికి ఏ వాయువు కారణం?
జవాబు:
కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
88.

ఈ ప్రయోగం పేరేమిటి?
జవాబు:
మోల్స్ అర్ధపత్ర ప్రయోగం మోల్
89.
ఈ ప్రయోగంలో గరాటులో ఉంచిన మొక్క, పేరేమిటి?
జవాబు:
హైడ్రిల్లా / ఎలోడియా మొక్కలు
90.
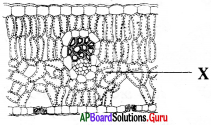
పటంలోని X భాగాన్ని గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:
స్పంజి మృదుకణజాలం :
91. ఈ పటంలో తప్పుగా లేబుల్ గుర్తించిన భాగాన్ని
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయం
92.

ఈ జీవిలో ఏ రకమైన పోషణ కనిపిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
జాంతవ పోషణ
93.

పటంలో చూపిన ‘X’ అనే భాగం పేరేమిటి?
జవాబు:
లాలాజల గ్రంథులు
94.

పటం సహాయంతో మీ శరీరంలో ఉండే అతి పెద్ద జీర్ణగ్రంథి గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:
కాలేయం
95.
ఆకులో ఈ నిర్మాణాలు ఎక్కడ కనపడతాయి?
జవాబు:
క్రింది బాహ్యచర్మం
ఖాళీలను పూరించండి
96. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో వెలువడే వాయువు ………….
జవాబు:
ఆక్సిజన్
97. కిరణజన్య సంయోగ క్రియలో అంతర కారకం ………..
జవాబు:
పత్రహరితం
98. థైలకాయిడ్ దొంతరను ఇలా ………….. అంటారు.
జవాబు:
గ్రాన

99. నీటి అణువు విచ్చిన్నం చెందే ప్రక్రియ …………
జవాబు:
నీటి కాంతి విశ్లేషణ
100. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలోని రెండవ దశ ………….
జవాబు:
నిష్కాంతి దశ
101. ఆహార నాళ ప్రారంభ భాగం ………..
జవాబు:
నోరు
102. అతిపెద్ద జీర్ణగ్రంథి …………
జవాబు:
కాలేయం
103. జీర్ణనాళంలో ఆమ్ల స్థితి కలిగిన భాగం ……….
జవాబు:
జీర్ణాశయం
104. జీర్ణక్రియకు తోడ్పడే రసాయనాలు ……….
జవాబు:
ఎంజైమ్స్
105. జీర్ణవ్యవస్థలో శోషణ జరిగే భాగం ………….
జవాబు:
చిన్న ప్రేగు
10th Class Biology 1st Lesson పోషణ – ఆహార సరఫరా వ్యవస్థ 1 Mark Bits Questions and Answers
1. తప్పుగా ఉన్న జతను గుర్తించండి.
A) హస్టోరియా – కస్కుటా
B) టెస్టోస్టిరాన్ – స్త్రీ బీజకోశము
C) గ్రానం – హరిత రేణువు
D) ఉపజిహ్వక – నోరు
జవాబు:
B) టెస్టోస్టిరాన్ – స్త్రీ బీజకోశము
2. ఫోలిక్ ఆమ్లము లోపం వల్ల కలిగే వ్యాధి
A) రక్త హీనత
B) పెల్లాగ్రా
C) గ్లాసైటిస్
D) రికెట్స్
జవాబు:
A) రక్త హీనత
3. కిరణజన్య సంయోగ క్రియకు సంబంధించి సరైన వాక్యం
A) కాంతిశక్తి ఉష్ణశక్తిగా మారుతుంది
B) కాంతిశక్తి రసాయనిక శక్తిగా మారుతుంది
C) కాంతిశక్తి విద్యుత్ శక్తిగా మారుతుంది
D) ఉష్ణశక్తి రసాయనిక శక్తిగా మారుతుంది
జవాబు:
B) కాంతిశక్తి రసాయనిక శక్తిగా మారుతుంది
4. పిండి పదార్థాన్ని గుర్తించే పరీక్షలో అయోడిను బదులుగా ఈ క్రింది పదార్థాన్ని కూడా వాడవచ్చు …….
A) బెటాడిన్
B) బ్రోమిన్
C) క్లోరిన్
D) బెంజీన్
జవాబు:
A) బెటాడిన్
5. క్రింది సమీకరణంలో లోపించినది రాయండి.
CO2 + 2H2O → CH2O + …….. + O2
A) CO2
B) H2O
C) C6H12O6
D) 6SO2
జవాబు:
B) H2O
6. ఈ క్రింది విటమిన్ లోపం వల్ల గ్లాసైటిస్ అనే వ్యాధి కల్గుతుంది.
A) B1
B) B2
C) B3
D) B6
జవాబు:
B) B2
7. అయోడిన్ పరీక్ష ద్వారా కింది ఏ పదార్థాల ఉనికిని తెలుసుకోవచ్చు?
A) కొవ్వులు
B) మాంసకృత్తులు
C) విటమిన్లు
D) పిండి పదార్థాలు
జవాబు:
D) పిండి పదార్థాలు

8. ఈ క్రింది వానిలో సరైన జతకానిది ………….
A) ప్రోటీన్లు – అమైనో ఆమ్లాలు
B) కార్బోహైడ్రేట్స్ – గ్లూకోజ్
C) క్రొవ్వులు – పిండిపదార్థం
D) గ్లూకోజ్ – పిండిపదార్థం
జవాబు:
C) క్రొవ్వులు – పిండిపదార్థం
9. క్రింది వ్యాఖ్యలను చూడండి.
ఎ) క్వాషియోర్కర్ వ్యాధి ప్రోటీన్ల లోపం వల్ల కలుగుతుంది.
బి) మెరాస్మస్ వ్యాధి కేవలం కేలరీల లోపం వల్ల వస్తుంది.
A) ఎ, బి రెండూ సత్యాలు
B) ఎ సత్యము, బి అసత్యము
C)ఎ అసత్యము, బి సత్యము
D) ఎ, బి రెండూ అసత్యాలే
జవాబు:
B) ఎ సత్యము, బి అసత్యము
10. మొక్కను చీకటి గదిలో ఉంచితే ……… జరగదు.
A) శ్వాసక్రియ
B) ప్రత్యుత్పత్తి
C) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ
D) నీటి రవాణా
జవాబు:
C) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ
11. ఒక వ్యక్తి అజీర్తితో బాధపడటం లేదంటే ఈ విధంగా విశ్లేషించవచ్చు
A) సమతుల ఆహారాన్ని తీసుకోవడం లేదు
B) ఆహారాన్ని తొందరగా తినడం
C) ఆహారాన్ని బాగా నమిలి తినడం
D) తిన్న వెంటనే వ్యాయామం చేయడం
జవాబు:
C) ఆహారాన్ని బాగా నమిలి తినడం
12. ఈ కణాంగం పేరు
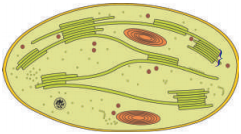
A) త్వచము
B) మైటోకాండ్రియా
C) హరితరేణువు
D) ఏదీకాదు
జవాబు:
C) హరితరేణువు
13. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియ అంత్య పదార్థము
A) గ్లూకోజ్
B) ఆక్సిజన్
C) నీరు
D) అన్ని
జవాబు:
A) గ్లూకోజ్
14. క్రింది వానిలో పరాన్న జీవనము జరిపేది
A) కస్కుట
B) ఈస్ట్
C) పుట్టగొడుగు
D) చేప
జవాబు:
A) కస్కుట
15. మీ ఆహారంలో విటమిన్ ‘A’ లోపించినట్లైతే వచ్చే’ వ్యాధిలో లక్షణాలు ఉండవచ్చు?
A) తక్కువ కాంతిలో చూడలేకపోవుట
B) ఆకలి లేకపోవడం
C) వెలుతురు చూడలేకపోవడం
D) నీటి విరేచనాలు
జవాబు:
A) తక్కువ కాంతిలో చూడలేకపోవుట

16. ఎండలో పెరిగే మొక్కలను నీడలో ఉంచితే ఏమౌతుంది?
A) మొక్క చనిపోతుంది
B) బాగా పెరుగుతుంది
C) పొట్టిగా మారుతుంది
D) పైవేవి కాదు
జవాబు:
D) పైవేవి కాదు
17. ప్రోటీన్ల లోపం వలన కలిగే వ్యాధి
A) క్వాషియార్కర్
B) మెగాస్మస్
C) స్థూలకాయత్వం
D) అనీమియా
జవాబు:
A) క్వాషియార్కర్
18. అతిథేయి మొక్కలోనికి చొచ్చుకొని పోయి ఆహారాన్ని గ్రహించడానికి కస్కుటా మొక్కలలో గల ప్రత్యేక నిర్మాణాలు
A) డాడర్
B) హాస్టోరియా
C) లెగ్యూమ్ వేర్లు
D) వాయుగత వేర్లు
జవాబు:
B) హాస్టోరియా
19. ఈ క్రింది వానిలో సరయిన దానిని గుర్తించండి.
a. థయమిన్ (B1) ( ) 1. స్కర్వీ
b. సిట్రికామ్లం (C) ( ) 2. రేచీకటి
c. రెటినాల్ (A) ( ) 3. బెరిబెరి
A) (a – 3), (b – 1), (c – 2)
B) (a – 1), (b – 2), (c – 3)
C) (a – 2), (b – 3), (c – 1)
D) (a – 3), (c – 1), (b – 2)
జవాబు:
A) (a – 3), (b – 1), (c – 2)
20. భిన్నమైన దానిని గుర్తించుము.
A) కార్బోహైడ్రేట్లు
B) కొవ్వులు
C) ప్రోటీన్స్
D) పైరిత్రాయిడ్స్
జవాబు:
D) పైరిత్రాయిడ్స్
21. కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియకు అవసరమైన ముఖ్య కారకాలు
A) కాంతి, కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్, పత్రహరితం, ఉష్ణోగ్రత
B) కాంతి, నీరు, పత్రహరితం, ఉష్ణోగ్రత
C) కాంతి, ఉష్ణోగ్రత, పత్రహరితం, కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
D) కాంతి, నీరు, పత్రహరితం, కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
జవాబు:
D) కాంతి, నీరు, పత్రహరితం, కార్బన్ డై ఆక్సైడ్
22. క్రింది వానిలో ఎంజైమ్ లేని జీర్ణరసం
A) పైత్యరసం
B) జఠరరసం
C) క్లోమరసం
D) లాలాజలం
జవాబు:
A) పైత్యరసం
23. క్రింది వాటిలో పరాన్న జీవి మొక్క
A) కస్కుట
B) మందార
C) కాకర
D) మల్లె
జవాబు:
A) కస్కుట
24. పెప్సిన్ : ప్రోటీన్లు : : లైపేజ్ : …………
A) కార్బోహైడ్రేట్లు
B) కొవ్వులు
C) విటమిన్లు
D) సుక్రోజ్
జవాబు:
B) కొవ్వులు
25. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → + 6H2O + శక్తి
A) 6CO2
B) C6H12O6
C) 6O2
D) 12CO2
జవాబు:
A) 6CO2
26. క్రింది వాక్యాలను సరిచూడండి.
1. పత్రహరితం రక్తంలోని హీమోగ్లోబిన్ అనే వర్ణకంను పోలి ఉంటుంది.
2. హీమోగ్లోబిన్లో ఐరన్ ఉంటే, పత్రహరితంలో మెగ్నీషియం ఉంటుంది.
A) 1 సరియైనది, 2 తప్పు
B) 1 తప్పు, 2 సరియైనది
C) 1, 2 రెండూ సరియైనవి
D) 1, 2 రెండూ తప్పు
జవాబు:
C) 1, 2 రెండూ సరియైనవి
27. ఈ క్రింది వాక్యాలను పరిశీలించండి.
i) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో గ్లూకోజ్, నీరు మరియు ఆక్సీజన్లు అంత్య పదార్థాలుగా ఏర్పడతాయి.
ii) కిరణజన్య సంయోగక్రియలో నీటి అణువు విచ్ఛిత్తి చెందటం ఒక ముఖ్యమైన సంఘటన.
A) (i) – సత్యము, (ii) – సత్యము
B) (i) – అసత్యము, (ii) అసత్యము
C) (i) – సత్యము, (ii) – అసత్యము
D) (i) – అసత్యము, (ii) – సత్యము
జవాబు:
A) (i) – సత్యము, (ii) – సత్యము

28. నేనొక విటమినను. నేను పప్పుధాన్యాలు, గింజలు, కూరగాయలు, కాలేయము, పాలు, మూత్రపిండాలు మొదలగువానిలో లభిస్తాను. నా లోపం వల్ల మీకు నాడీ సంబంధ సమస్యలు కలుగుతాయి. నేనెవరిని?
A) థయమిన్
B) పైరిడాక్సిన్
C) పాంటోథెనిక్ ఆమ్లం
D) బయోటిన్
జవాబు:
D) బయోటిన్
29. కింది వానిలో టీకాల ద్వారా నివారించలేని వ్యాధి
A) పోలియో
B) హెపటైటిస్
C) మలేరియా
D) కోరింతదగ్గు
జవాబు:
C) మలేరియా
30. సరికాని జత ఏది?
A) విటమిన్ A – రెటినాల్
B) విటమిన్ D – కాల్సిఫెరాల్
C) విటమిన్ K – టోకోఫెరాల్
D) విటమిన్ C – ఆస్కార్బిక్ ఆమ్లం
జవాబు:
C) విటమిన్ K – టోకోఫెరాల్
31. క్రింది వాటిని జతపరుచుము.
| జాబితా – A | జాబితా – B |
| i) పెప్సిన్ | a) పిండి పదార్థాలు |
| ii) అమైలేజ్ | b) ప్రోటీన్లు |
| iii) లైపేజ్ | c) క్రొవ్వులు |
A) (i) – (b), (ii) – (a), (iii) – (c)
B) (i) – (a), (ii) – (b), (iii) – (c)
C) (i) – (c), (ii) – (b), (iii) – (a)
D) (i) – (a), (ii) – (c), (iii) – (b)
జవాబు:
A) (i) – (b), (ii) – (a), (iii) – (c)
32. ప్రయోగశాలలో ద్రావణాల్లో ఆక్సిజన్ ఉందో, లేదో తెలుసుకోవడం కోసం ఉపయోగించే కారకం
A) KOH ద్రావణం
B) జానస్ గ్రీన్ B
C) అయోడిన్ ద్రావణం
D) మిథిలీన్ బ్లూ
జవాబు:
B) జానస్ గ్రీన్ B
33. క్రింది వానిలో సరియైన జత కానిది?
A) పైత్యరసం – కాలేయం
B) ట్రిప్సిన్ – క్లోమం
C) పెప్సిన్ – చిన్నప్రేగు
D) టయలిన్ – లాలాజల గ్రంథులు
జవాబు:
C) పెప్సిన్ – చిన్నప్రేగు
34. ఆకులోని హరిత పదార్థమును తొలగించడానికి చేసే ప్రయోగంలో ఉపయోగించే రసాయనము
A) మిథిలేటెడ్ స్పిరిట్
B) KOH ద్రావణము
C) అయొడిన్ ద్రావణం
D) అసిటిక్ ఆమ్లము
జవాబు:
A) మిథిలేటెడ్ స్పిరిట్

35. ‘E’ విటమిను ఇలా కూడా పిలుస్తారు.
A) ఫైలోక్వినోన్
B) కాల్సిఫెరాల్
C) ఆస్కార్బిక్ ఆమ్లం
D) టోకోఫెరాల్
జవాబు:
D) టోకోఫెరాల్
మీకు తెలుసా?
* కణం పగిలినప్పుడు అందులోని క్లోరోప్లాస్ట్ కూడా ముక్కలైపోతుంది. అటువంటప్పుడు కిరణజన్యసంయోగ క్రియలోని వివిధ సోపానాలను అధ్యయనం చేయడానికి అవసరమైన క్లోరోప్లాన్లను వేరుచేయలేము. కాని 1954 తరువాత డేనియల్ ఆర్నాన్ మొక్క కణంలో నుండి కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ నిర్వహణకు తోడ్పడే క్లోరోప్లాస్టు వేరుచేయగలిగాడు.
పునశ్చరణ
I.
| శాస్త్రవేత్త | అంశము |
| 1. సి.బి. వాన్ నీల్ | కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ సమీకరణం |
| 2. వాన్ హెల్మాంట్ | మొక్కల బరువు పెరుగుదలలో నీటిపాత్ర |
| 3. జోసఫ్ ప్రీస్టే | కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో గాలి ప్రాధాన్యత, ఆక్సిజన్ ఆవిష్కరణ |
| 4. లేవోయిజర్ | ఆక్సిజన్ కు నామకరణం |
| 5. ఇంజన్ హౌజ్ | కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియలో కాంతి ప్రాధాన్యత |
| 6. ఎంగల్మన్ | కిరణజన్యసంయోగక్రియ కనుగొనే స్థానం |
| 7. పెల్లిటియర్, కావనో | పత్రహరిత కషాయం |
| 8. జూలియస్ వాన్సక్స్ | పత్రహరిత పరిశీలన |
| 9. డేనియల్ ఆర్నాన్ | హరితరేణువును కణం నుండి వేరుచేయుట |
II.
| ఆహారపదార్థం | ఎంజైమ్స్ | అంత్య ఉత్పన్నం |
| 1. పిండిపదార్థం | అమైలేజ్, రెనిన్ (లాలాజలం) | చక్కెరలు, గ్లూకోజు |
| 2. ప్రోటీన్లు | పెప్సిన్ (జఠరరసం)
ట్రిప్సిన్ (క్లోమరసం)
పెప్టిడేజెస్ (ఆంత్రరసం) | ఎమైనో ఆమ్లాలు |
| 3. కొవ్వులు | పైత్యరసం (కాలేయం)
లైపేజ్ (క్లోమరసం) | కొవ్వు ఆమ్లాలు, గ్లిజరాల్ |
![]()
![]()