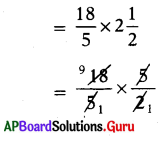
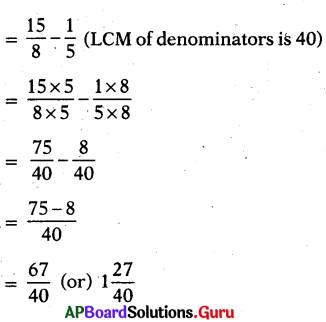
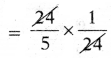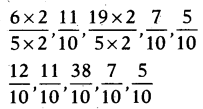SCERT AP Board 7th Class Hindi Study Material 12th Lesson कोंडापल्ली की यात्रा Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Hindi 12th Lesson Questions and Answers कोंडापल्ली की यात्रा
7th Class Hindi 12th Lesson कोंडापल्ली की यात्रा Textbook Questions and Answers
सोचिए-बोलिए
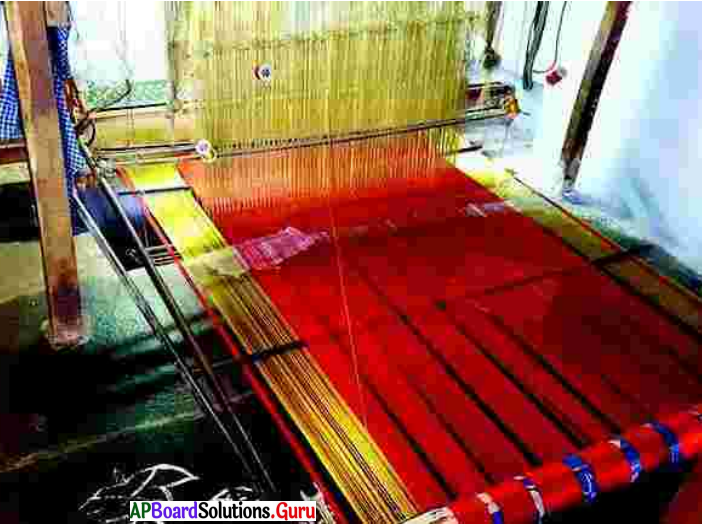

प्रश्न 1.
इस चित्र में आपको क्या – क्या दिखाई दे रहे हैं? (ఈ చిత్రంలో మీకు ఏమేమి కన్పించుచున్నవి?)
उत्तर:
इस चित्र में एक हथकरघा, आदमी, कपडे, पंखा आदि दिखाई दे रहे हैं। )
(ఈ చిత్రంలో ఒక చేతి మగ్గం, మనిషి, బట్టలు, ఫ్యాన్ మొదలుగునవి కనిపించుచున్నవి.)

प्रश्न 2.
कपड़े बनानेवाले को क्या कहते हैं? (బట్టలు తయారు చేయు వానిని ఏమందురు??)
उत्तर:
कपडे बनानेवाले को जुलाहा कहते हैं। (బట్టలు తయారు చేయువానిని పద్మసాలీలు అంటారు.)
कोडापल्ली की यात्रा (కొండపల్లి యాత్ర)
आँध्रप्रदेश के कृष्णा जिले में एक गाँव है। इसका नाम कोंडापल्ली है। यह विजयवाडा से 24 कि.मी. की दूरी पर है। यह प्रांत हाथ से बनी लकड़ी के खिलौनों के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। इन्हें देखने के लिए दूर – दूर से लोग आते हैं। एक दिन पाठशाला के कुछ छात्र अपने अध्यापक के साथ रविवार को कोंडापल्ली की यात्रा पर गये। वहाँ पर एक पुराना किला है। इस किले को 14 वीं शताब्दी के राजाओं ने बनाया। इसे देखकर बच्चे बहुत खुश हुए। उसके बाद वहाँ के खिलौने देखने गए।
अध्यापक और छात्रों को देखकर स्थानीय खिलौने बनानेवाले कारीगरों ने उनका स्वागत किया। आंध्रप्रदेश में लोग संक्रांति और दशहरा के पर्व दिनों में ‘गोलू’ यानी, ‘बोम्मल कोलुवु’ रखते हैं। ये खिलौने आसपास के ‘तेल्ला पोणिकी’ नामक नरम लकड़ी से बनाये जाते हैं। इन्हें प्राकृतिक रंगों से रंगा जाता है।
यहाँ कई प्रकार के खिलौने बनते हैं। इन खिलौनों में दशावतार, ताड़ का पेड़, बैलगाड़ी, गीतोपदेश, पालकी, वर-वधु, नर्तकी, हाथी का हौदा, ग्रामीण वातावरण के खिलौने प्रसिद्ध हैं।
आजकल ये हस्तकलाएँ धीरे – धीरे लुप्त होती जा रही हैं। आंध्र प्रदेश सरकार ‘लेपाक्षी’ नामक बिक्री केंद्रों द्वारा इन्हें बेचती है। इससे कारीगरों को आजीविका और प्रोत्साहन मिलता है।
సారాంశము
ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని కృష్ణాజిల్లాలో ఒక గ్రామము కలదు. దీని పేరు కొండపల్లి. ఇది విజయవాడ నుండి 24 కి.మీ దూరాన కలదు. ఈ ప్రదేశము చేతితో చేయు కొయ్య ఆటబొమ్మలకు ప్రసిద్ధి. వీటిని చూచుటకు దూర-దూర ప్రాంతాల నుండి ప్రజలు వచ్చెదరు. ఒకరోజు పాఠశాలకు చెందిన కొంతమంది విద్యార్థులు తమ ఉపాధ్యాయునితో ఆదివారము నాడు కొండపల్లి యాత్రకు వెళ్ళిరి. అక్కడ ఒక పాత కోట ఉన్నది. ఈ కోటను 14వ శతాబ్దమునకు చెందిన రాజులు కట్టించిరి. దీనిని చూసి పిల్లలు చాలా సంతోషించిరి.. ఆ తర్వాత అక్కడి ఆట బొమ్మలను చూచుటకు వెళ్ళిరి.
ఉపాధ్యాయులు మరియు విద్యార్థులను చూసి స్థానిక ఆటబొమ్మలను తయారు చేయు పనివాళ్ళు వారికి స్వాగతం పలికిరి. ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లో ప్రజలు సంక్రాంతి మరియు దసరా పండుగ రోజుల్లో ‘గోలూ” అనగా “బొమ్మల కొలువు” ను ఏర్పాటు చేయుదురు. ఈ బొమ్మలను గ్రామ సమీపంలోని “తెల్ల పొణికి” అను మెత్తని కర్ర నుండి తయారుచేస్తారు. వీటిని ప్రాకృతిక (సహజ) రంగులతో రంగులు వేస్తారు.
ఇక్కడ ఎన్నో రకముల ఆటబొమ్మలు తయారు చేస్తారు. ఈ బొమ్మలలో దశావతారములు, తాటిచెట్లు, ఎద్దుల బండ్లు, గీతోపదేశము, పల్లకీ, వరుడు వధువు, నర్తకీ, ఏనుగు అంబారీ, గ్రామీణ వాతావరణపు ఆట వస్తువులు ముఖ్యమైనవి.
ఈ రోజుల్లో ఈ చేతికళలు (హస్తకళలు) అడుగంటి పోతున్నాయి. ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ ప్రభుత్వము లేపాక్షి అను పేరు గలిగిన విక్రయ కేంద్రాల ద్వారా వీటిని అమ్ముతున్నది. అందువలన బొమ్మలను తయారు చేయు చేతి కళాకారులకు జీవితాంతము జీవనోపాధి మరియు ప్రోత్సాహము లభించుచున్నది.
Summary
There is a village in Krishna district of Andhra Pradesh. Its name is Kondapalli. It is 24 km away from Vijayawada. This place is famous for hand-made wooden toys. People from distant places come to see these toys. One day some students of a school went on an excursion on Sunday accompanied by their teacher. An old fort is located there. Kings who belonged to 14th century built this fort. The children were elated on seeing this. Later, they went to see the locally made toys.
The crafts persons who make the toys welcomed the teacher and the students. In Andhra Pradesh, the people arrange ‘Bommala Koluvu’ (Display of Toys) called ‘Golu’. They make toys with the softwood of “Tella poniki’ available near the village. They use natural colours for the toys.
Different kinds of toys are made here. The toys describing dasavataras, palmyra trees, bullock carts, Gitopadesa, pallak, bride and groom, narthak, a howdah on an elephant’s back, village’s serene atmosphere are important among them.
Nowadays the handicrafts are losing their lustre. The government of Andhra Pradesh is selling these toys through ‘Lepakshi’ centre. Therefore the crafts persons who make the toys are able to earn their living and get encouragement throughout their life.
Intext Questions & Answers
प्रश्न 1.
अपने गाँव की हस्तकलाओं के बारे में आप क्या जानते हैं? (మీ గ్రామపు హస్త కళలను గురించి మీకు ఏమి తెలియును?)
उत्तर:
मेरा गाँव कोंडपल्ली है। हमारा गाँव हाथ से बनी लकडी के खिलौनों के लिए प्रसिद्ध है। हमारे गाँव में खिलौने बनाकर इन्हें प्राकृतिक रंगों से रंगा जाता है।
(మా గ్రామము కొండపల్లి. మా గ్రామము చేతితో తయారు చేయబడిన చెక్క బొమ్మలకు ప్రసిద్ది. మా గ్రామంలో బొమ్మలను తయారుచేసి వాటికి ప్రాకృతిక రంగులు అద్దెదరు.)
Improve Your Learning
सुनिए-बोलिए
प्रश्न 1.
आंध्रप्रदेश की हस्त कलाओं के बारे में बताइए। (ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని హస్తకళల గురించి తెలపండి.)
उत्तर:
कलमकारी आँध्रप्रदेश में प्रचलित कला है। इसमें सब्ज़ियों के रंगों से र्धामिक चित्र बनाये जाते हैं। इसकी जड़ें आँध्र के श्रीकालहस्ति और मचिलीपट्टनम से हैं। बोब्बिलि में वीणा तैयार की जाती है। आँध्रा में हैंडलमू हस्तकला भी है। चीराला, गद्वाल, मंगलगिरि, उप्पाडा, आदि इसके लिए प्रसिद्ध है।
(కలంకారీ ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని ప్రసిద్ధి చెందిన ఒక చిత్రించే కళ. వెదురుతో చేసిన కలంతో సహజమైన రంగులను ఉపయోగించి ధార్మిక చిత్రాలు చిత్రిస్తారు. వీటి మూలాలు శ్రీకాళహస్తి మరియు మచిలీపట్నంలో ఉన్నాయి. బొబ్బిలిలో వీణ తయారు చేయబడుతుంది. ఆంధ్రలో చేనేత హస్తకళ కూడా ఉంది. చీరాల, గద్వాల్, మంగళగిరి, ఉప్పాడ మొదలైనవి వీటికి ప్రసిద్ది.)

प्रश्न 2.
कोंडापल्ली किले का निर्माण किस शताब्दी में हुआ? (కొండపల్లి కోట నిర్మాణము ఏ శతాబ్దములో జరిగినది?)
उत्तर:
कोंडपल्ली किले का निर्माण 14 वीं शताब्दी में हुआ।
(కొండపల్లి కోట నిర్మాణము 14వ శతాబ్దములో జరిగినది.)
प्रश्न 3.
गोलू किसे कहते हैं? (‘గోలూ’ అని దేనిని అంటారు?)
उत्तर:
आंध्रप्रदेश में लोग संक्रांति और दशहरा के पर्व दिनों में बोम्मल कोलुवु रखते हैं। इस बोम्मल कोलुवु को ही ‘गोलु’ कहते हैं।
(ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లో సంక్రాంతి మరియు దసరా పండుగ రోజుల్లో బొమ్మల కొలువు ఉంటుంది. ఈ బొమ్మల కొలువునే “గోలూ” అని అంటారు).
पढ़िए
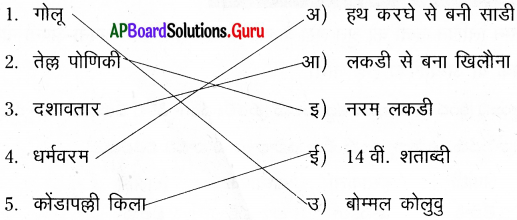
अ) जोड़ी बनाइए।
| 1. गोलू | उ) बोम्मल कोलुवु |
| 2. तेल्ल पोणिकी | इ) नरम लकडी |
| 3. दशावतार | अ) हथ करघे से बनी साडी |
| 4. धर्मवरम। | आ) लकडी से बना खिलौना |
| 5. कोंडापल्ली किला | ई) 14 वीं. शताब्दी |
आ) पाठ में वाक्यों के सही क्रम को पहचानकर क्रम संख्या कोष्ठक में लिखिए।
1. आजकल ये हस्तकलाएँ लुप्त होती जा रही हैं। [ 4 ]
2. तेलुगु में गोलू को बोम्मला कोलुवु कहते हैं। [ 3 ]
3. इस किले का निर्माण 14 वीं शताब्दी में हुआ। [ 1 ]
4. इससे कारीगरों को आजीविका मिल रही है। [ 5 ]
5. उसके बाद कोंडापल्ली के खिलौने देखने गए। [ 2 ]
इ) सही वर्तनी वाले शब्दों पर गोला “O” बनाइए।

ई) नीचे दिए गए वाक्यों में चित्रों से संबंधित शब्दों पर गोला “O” बनाइए।

उत्तर:

लिखिए
अ) नीचे दिये गये प्रश्नों के उत्तर छोटे – छोटे वाक्यों में लिखिए।
క్రింది ఇవ్వబడిన ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానములు చిన్న – చిన్న వాక్యములలో వ్రాయండి.
1. कोंडापल्ली विजयवाड़ा से कितने किलोमीटर की दूरी पर है? (కొండపల్లి, విజయవాడ నుండి ఎన్ని కిలోమీటర్ల దూరాన ఉన్నది?)
उत्तर:
कोंडपल्ली विजयवाडा से 24 किलोमीटर की दूरी पर है।
(కొండపల్లి, విజయవాడ నుండి 24 కి.మీ. దూరాన కలదు.)

2. कोंडापल्ली में खिलौने बनानेवालों को सरकार किस तरह प्रोत्साहन दे रही है? (కొండపల్లిలో బొమ్మలు తయారు చేయువారిని ప్రభుత్వము ఏ విధముగా ప్రోత్సహించుచున్నది?)
उत्तर:
कोंडपल्ली में खिलौने बनानेवालों के खिलौनों को आंध्रप्रदेश सरकार खरीदकर उन्हें लेपाक्षी बिक्री केंद्रों में बेचती हैं। इससे कारीगरों को आजीविका और प्रोत्साहन मिलते हैं।
(కొండపల్లిలో బొమ్మలు తయారు చేయువాని బొమ్మలను ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ ప్రభుత్వం కొని వాటిని లేపాక్షి విక్రయ కేంద్రంలో అమ్ముతుంది. దీనితో – కార్మికులకు ఉపాధి మరియు ప్రోత్సాహం లభిస్తాయి.)
आ) नीचे दिये गये प्रश्न का उत्तर पाँच – छह वाक्यों में लिखिए।
క్రింది ఇవ్వబడిన ప్రశ్నకు సమాధానము 5 -6 వాక్యములలో వ్రాయండి.
1. “कोंडापल्ली की यात्रा” पाठ का सारांश अपने शब्दों में लिखिए। (‘కొండపల్లి యాత్ర’ పాఠ్య సారాంశము మీ మాటల్లో వ్రాయండి.)
उत्तर:
कोंडापल्ली की यात्रा पाठ में हस्तकलाओं के बारे में वर्णन है। कोंडापल्ली आँध्रप्रदेश का प्रसिद्ध हस्तकला केंद्र है। यहाँ बने अनेक तरह के लकड़ी के खिलौनों में कारीगरों का कौशल दिखाई देता है। संक्रांति पर्व के दिन गोलू रखा जाता है। हमें हस्तकलाओं को प्रोत्साहन देना चाहिए।
(కొండపల్లి యాత్ర అను ఈ పాఠంలో హస్తకళలను గురించి వర్ణించడమైనది. కొండపల్లి ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని ప్రముఖ హస్తకళా క్షేత్ర కేంద్రము. ఇక్కడ తయారుచేసిన అనేక రకాల చెక్కబొమ్మల తయారీలో పనివారి నైపుణ్యము కన్పించును. సంక్రాంతి పండుగ రోజున “గోలూ” అనగా బొమ్మల కొలువు వుంచబడుతుంది.)
इ) उचित शब्दों से खाली जगह भरिए।
1. कोंडापल्ली ……. जिले में है। (कृष्णा/ कड़पा)
उत्तर:
कृष्णा
2. कोंडापल्ली …….. के लिए मशहूर है। (चित्रकला/ खिलौनों)
उत्तर:
खिलौनों
3. गोलू …….. त्यौहार के दिनों में रखा जाता है। (संक्रांति/ उगादी)
उत्तर:
संक्रांति
4. खिलौने …. रंगों से रंगे जाते हैं। (प्राकृतिक/ कृत्रिम)
उत्तर:
प्राकृतिक
5. कोंडापल्ली देखने …. के दिन गए। (सोमवार रविवार)
उत्तर:
रविवार

ई) संकेतों के आधार पर वाक्य बनाइए।

उत्तर:
1. कोंडापल्ली कृष्णा जिले में हैं।
2. कोंडपल्ली में एक पुरातन किला है।
3. हाथी का हौदा ग्रामीण वातावरण का खिलौना है।
4. लेपाक्षी एक बिक्री केंद्र है।
5. खिलौने तेल्लापोणिकी नामक नरम लकडी से बनाये जाते हैं।
उ) वर्ण विच्छेद कीजिए।
1. खिलौना : ख् + इ + ल् + औ + न् + आ
2. कोंडापल्ली : ………………….
उत्तर:
क् + ओं + ड् + आ + प् + अ + ल् + ल् + ई
3. संक्रांति : ……………………..
उत्तर:
स + अं + क् + र् + आ + त् + ई
4. गोलू : …………………….
उत्तर:
ग + ओ + ल् + ऊ
5. प्रसिद्ध
उत्तर:
प + र् + अ + स् + इ + द् + ध् + अ
भाषांश
अ) वर्ग पहेली से पाठ में आये शब्दों को ढूंढकर लिखिए।
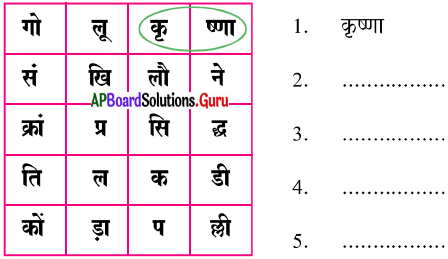
उत्तर:
1. कृष्णा
2. गोलू
3. संक्रांति
4. कोंडापल्ली
5. खिलौने
6. लकडी
7. प्रसिद्ध

आ) पर्यायवाची शब्द लिखिए।
1. हाथ – कर, हस्त
2. पाठशाला – ……………
उत्तर:
विद्यालय, स्कूल
3. छात्र – ……………
उत्तर:
विद्यार्थी, शिक्षार्थी
4. दर्शन – ……………
उत्तर:
देखना, वीक्षण
5. कारीगर – ……………
उत्तर:
कर्मचारी, काम करनेवाले
इ) विलोम शब्द लिखिए।
1. शहर × गाँव
2. प्रसिद्ध × अप्रसिद्ध
3. बेचना × खरीदना
4. खुश × नखुश
5. पास × दूर
सृजनात्मकता
अ) किसी एक यात्रा का वर्णन अपने शब्दों में कीजिए।
(ఏదేని యాత్ర గురించి మీ మాటల్లో వర్ణించండి.)
उत्तर:
हम सभी अपनी गर्मी की छुट्टियाँ बिताने के लिए किसी न किसी पर्यटक स्थल पर अवश्य जाते हैं। मैं भी अपनी गर्मी की छुट्टियाँ बिताने के लिए पर्वतीय प्रदेश शिमला गया था। मैं गर्मी के मौसम में भी ठंडक का आनंद ले सकूँ। मैं और मेरा परिवार शाम की बस से शिमला गये और पहाडों में बना रास्ता हमें डरा रहा था। हमने रास्ते में घर का बना खाना खाया, गाने गाए और प्राकृतिक सौंदर्य का आनंद लिया। हम रात के नौ बजे शिमला पहुंचे जहाँ हमने थोडा सा विश्राम कर माल रोड घूमा जिसकी शोभा रात के समय में दो गुनी हो जाती है।
अगले दिन हम सब तैयार होकर जाखू मंदिर में हनुमान जी के दर्शन करने गए और नीचे उतरकर रीज में गए। इस समय तक हल्की – हल्की बारिश होने लगी । जिसने ठंडे मौसम को और अधिक ठंडा कर दिया था। हम उस दिन शाम को कुफरी के लिए निकल गए जहाँ पर बर्फ पड रही थी। अगले दिन हम ने स्वींग का आंनद लिया, चिडियाघर देखा और बर्फ में खूब खेले। हमारा वहाँ इतना मन लगा कि हमने वहीं दो दिन व्यतीत किये। उसके बाद हम शिमला वापिस आए और वहाँ की संस्कृति और संग्रहालय देखा। अगले दिन हम वापिस घर के लिए निकले और हमारे दिल में यात्रा की यादें थी। वह मेरी आज तक की सब से बेहतरीन यात्रा थी।
आ) परियोजना कार्य :
मिट्टी या कागज़ से खिलौनों को बनाकर कक्षा में दिखाइए।
(మట్టితో లేదా కాగితముతో ఆటబొమ్మలను తయారుచేసి తరగతిలో చూపించండి.)
उत्तर:
छात्र गतिविधि

इ) अनुवाद कीजिए।
1. बच्चों को खिलौने पसंद हैं।
उत्तर:
बच्चों को खिलौने पसंद हैं। పిల్లలకు ఆటబొమ్మలు ఇష్టము.
2. वीणा लकड़ी से बनाई जाती है।
उत्तर:
वीणा लकड़ी से बनाई जाती है। వీణను కొయ్యతో తయారు చేస్తారు.
3. दिल्ली देश की राजधानी है।
उत्तर:
दिल्ली देश की राजधानी है। ఢిల్లీ దేశ రాజధాని.
4. बेंगलूरु सुंदर नगर है।
उत्तर:
बेंगलूरू सुंदर नगर है। బెంగళూరు సుందర నగరం.
5. हिंदी सरल भाषा है।
उत्तर:
हिंदी सरल भाषा है। హిందీ సరళమైన భాష.
व्याकरणांश

क्रिया विशेषण
रेखांकित शब्द क्रिया की विशेषता बताते हैं। क्रिया की विशेषता बतानेवाले शब्दों को क्रिया – विशेषण कहते हैं।
(గీత గీయబడిన పదములు క్రియ యొక్క విశేషతను తెలియజేయుచున్నవి. వీటిని క్రియా విశేషణములు అందురు.)
उदा : धीरे – धीरे, तेज, सुंदर, प्रतिदिन, खूब आदि।
अ) नीचे दिये गये वाक्यों में क्रिया – विशेषण शब्द को पहचानकर लिखिए।
1. दीपा धीरे – धीरे खाती है।
उत्तर:
धीरे – धीरे
2. परसों मैं दिल्ली जाऊँगा।
उत्तर:
परसों
3. नदी निरंतर बहती है।
उत्तर:
निरंतर
4. तुम जल्दी आओ।
उत्तर:
जल्दी
5. रमा वहाँ बैठी है।
उत्तर:
वहाँ
अध्यापकों के लिए सूचना :
लकडी से बने खिलौनों के लिए प्रसिद्ध अन्य प्रदेशों के बारे में कक्षा में चर्चा कीजिए।
(Sradogss తయారుచేసే ఆట బొమ్మల కోసం ప్రసిద్ది చెందిన ఇతర ప్రదేశాలను గురించి తరగతి గదిలో చర్చించండి.)
उत्तर:
लकडी से बने खिलौनों के लिए प्रमुख अन्य प्रदेशों में एक है एटिकोप्पाका। आंध्रप्रदेश के एटिकोप्पाका खिलौने विख्यात हैं। लकडी के पारंपरिक एटिकोप्पाका खिलौने बनाने की कला,जो लक्कपिडतलु नाम से प्रचलित हैं | करीब 400 साल से अधिक पुरानी है। लकडी से बने खिलौनों के लिए और एक प्रसिद्ध स्थान है धर्मनगरी। वारणासी को ही धर्म नगरी कहते हैं।
मध्यप्रदेश में ग्वालियर तथा इंदौर, केरल में तैनीचेरी व कोझीकोडे, उत्तर प्रदेश में मधुरा व आग्रा राजस्थान में जयपुर, तमिलनाडु में पनरुपति, कुड्डालेरु और तन्जौर प्रांतों में भी खिलौने तैयार किये जाते हैं। उदयपुर भी एक प्रसिद्ध लकडी के खिलौनों का केंद्र है। राजस्थान में गलियाकोट लकडी के खिलौनों के लिए प्रसिद्ध शहर है। आंध्रप्रदेश के बोब्बिली में भी वीणा के साथ – साथ खिलौनों की तैयारी की जाती है।
पाठ का सारांश
कोंडापल्ली की यात्रा पाठ में हस्तकलाओं के बारे में वर्णन है। कोंडापल्ली आँध्रप्रदेश का प्रसिद्ध हस्तकला केंद्र है। यहाँ बने अनेक तरह के लकड़ी के खिलौनों में कारीगरों का कौशल दिखाई देता है। संक्रांति पर्व के दिन गोलू रखा जाता है। हमें हस्तकलाओं को प्रोत्साहन देना चाहिए।
పాఠ్య సారాంశం
కొండపల్లి యాత్ర అను ఈ పాఠంలో హస్తకళలను గురించి వర్ణించడమైనది. కొండపల్లి, ఆంధ్రప్రదేశ్ లోని ప్రముఖ హస్తకళా క్షేత్ర కేంద్రము. ఇక్కడ తయారుచేసిన అనేక రకాల చెక్కబొమ్మల తయారీలో పనివారి నైపుణ్యము కన్పించును. సంక్రాంతి పండుగ రోజున “గోలూ” అనగా బొమ్మల కొలువు వుంచబడుతుంది.
Summary
The handicrafts are described in this lesson named ‘Excursion to Kondapalli’. Kondapalli is famous centre for handicrafts in Andhra Pradesh. The expertize of the craftspersons is found in making of different toys that are made here. On the occasion of Sankranthi day, Bommala Koluvu (Display of Toys) called ‘Golu’ is arranged in Andhra Pradesh. We should encourage the handicrafts.
व्याकरणांश (వ్యాకరణాంశాలు)
लिंग बदलिए (లింగములను మార్చండి)
बच्चा – बच्ची
स्त्री – पुरुष
नर – मादा
बेटा – बेटी
नर – नारी
लडका – लडकी
आदमी – औरत
बूढ़ा – बूढ़ी
स्त्री – पुरुष
माँ – बाप
माता – पिता
दादा – दादी
बाल – बाला
ग्वाला – ग्वालिन
चाचा – चाची
पडोसी – पडोसिन
बालक – बालिका
बलवान – बलवती

वचन बदलिए (వచనములను మార్చండి)
गाँव – गाँव
करघा – करघे
साडी – साडियाँ
खिलौना – खिलौने
कला – कलाएँ
लकडी – लकड़ियाँ
लोग – लोग
छात्र – छात्र
यात्रा – यात्राएँ
किला – किले
शताब्दी – शताब्दियाँ
राजा – राजा
लोग – लोग
कारीगर – कारीगर
पर्व – पर्व
बच्चा – बच्चे
विलोम शब्द (వ్యతిరేక పదములు)
प्रसिद्ध × अप्रसिद्ध
गाँव × शहर
पुराना × नया
खुश × नखुश
बनाना × बिगाडना
नरम × कडा
प्राकृतिक × कृत्रिम/अप्राकृतिक
यहाँ × वहाँ
बेचना × खरीदना
शब्दार्थ (అర్థాలు) (Meanings)
लोग = जनता, ప్రజలు, the people
नज़दीक = पास, దగ్గర, near
अध्यापक = शिक्षक, ఉపాధ్యాయుడు, a teacher
रविवार = इतवार,ఆదివారం, Sunday
बिक्री = विक्रय, అమ్మకము, sale
आजीविका = रोजगार, జీవనోపాధి, livelihood
किला = दुर्ग, కోట, fort
स्वागत = रिसेप्शन अभिनंदन, ఆహ్వానము, welcome
पर्व = त्यौहार, పండుగ, festival

श्रुत लेख : శ్రుతలేఖనము : Dictation
अध्यापक या अध्यापिका निम्न लिखित शब्दों को श्रुत लेख के रूप में लिखवायें। छात्र अपनी-अपनी नोट पुस्तकों में लिखेंगे। अध्यापक या अध्यापिका इन्हें जाँचे।
ఉపాధ్యాయుడు లేదా ఉపాధ్యాయిని క్రింద వ్రాయబడిన శబ్దములను శ్రుతలేఖనంగా డిక్లేట్ చేయును. విద్యార్థులు వారి వారి నోట్ పుస్తకాలలో వ్రాసెదరు. ఉపాధ్యాయుడు లేదా ఉపాధ్యాయిని వాటిని దిద్దెదరు.


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()