SCERT AP 9th Class Biology Study Material Pdf Download 5th Lesson జీవులలో వైవిధ్యం Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 9th Class Biology 5th Lesson Questions and Answers జీవులలో వైవిధ్యం
9th Class Biology 5th Lesson జీవులలో వైవిధ్యం Textbook Questions and Answers
అభ్యసనాన్ని మెరుగుపరుచుకోండి
ప్రశ్న 1.
జీవులలో ఉండే తేడాలు వైవిధ్యానికి ఏ విధంగా ఆస్కారం కల్పిస్తాయి? వివరించండి. (AS 1)
జవాబు:
- ఒకే జాతి జీవుల మధ్య ఉండే తేడాలను వైవిధ్యం అంటారు.
- వేరువేరు జాతుల మధ్య ఉన్న వైవిధ్యం కంటే, ఒక జాతి జీవుల మధ్య వైవిధ్యం తక్కువగా ఉంటుంది.
- ఒక జీవి చూపించే ప్రత్యేక లక్షణాలే జీవులు చూపించే వైవిధ్యానికి ఆధారంగా నిలుస్తాయి.
- నిత్య జీవితంలో మన చుట్టూ అనేక రకాలయిన మొక్కలను, జంతువులను చూస్తాము.
- మనము కొండ ప్రాంతాలు మరియు అటవీ ప్రాంతాలకు వెళ్ళినపుడు మనము రకరకాల మొక్కలను, జంతువులను గమనిస్తాం.
- నిజం చెప్పాలంటే ప్రపంచంలోని ప్రతిభాగము దానికే పరిమితమైన ప్రత్యేక రకమైన జీవులను కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
- అందువలన జీవులలో ఉండే తేడాలు వైవిధ్యానికి ఆస్కారం కల్పిస్తున్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 2.
శాస్త్రవేత్తలు దేని ఆధారంగా మొదటగా వర్గీకరణ ప్రారంభించారు? (AS 1)
జవాబు:
- జీవులు వాటి శరీర నిర్మాణం ఆధారంగా వర్గీకరించబడ్డాయి.
- జీవుల మధ్య ఉన్న పోలికలు, విభేదాలను అనుసరించి జీవులు వర్గీకరించబడ్డాయి.
- చరకుడు, సుశ్రుతుడు మొక్కలను వాటి ఔషధ గుణములను అనుసరించి వర్గీకరించారు.
- పరాశర మహర్షి పుష్ప నిర్మాణం ఆధారంగా మొక్కలను వర్గీకరించాడు.
- అరిస్టాటిల్ జంతువులను అవి నివసించే ప్రదేశం అనగా భూమి, నీరు మరియు గాలి ఆధారంగా వర్గీకరించాడు.
ప్రశ్న 3.
ఏకదళ బీజాలు ద్విదళ బీజాల కంటే ఎలా భిన్నంగా ఉంటాయి? (AS 1)
జవాబు:
| ఏకదళ బీజాలు | ద్విదళ బీజాలు |
| 1. మొక్కల గింజలలో ఒకే దళం కలిగి ఉంటాయి. | 1. మొక్కల గింజలలో రెండు దళాలు కలిగి ఉంటాయి. |
| 2. సమాంతర ఈనెల వ్యాపనం కలిగి ఉంటాయి. | 2. జాలాకార వ్యాపనం కలిగి ఉంటాయి. |
| 3. గుబురు వేరు వ్యవస్థను కలిగి ఉంటాయి. | 3. ప్రధాన వేరు వ్యవస్థను కలిగి ఉంటాయి. |
| 4. ఏకదళ బీజాలకు ఉదాహరణలు వరి, గోధుమ మొదలైనవి. | 4. ద్విదళ బీజాలకు ఉదాహరణ వేప, మామిడి మొదలైనవి. |
ప్రశ్న 4.
విట్టేకర్ ప్రకారం క్రింది జీవులు ఏ రాజ్యానికి చెందుతాయి? (AS 1)

జవాబు:
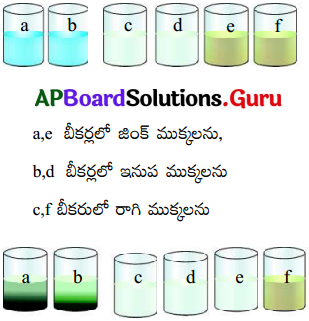
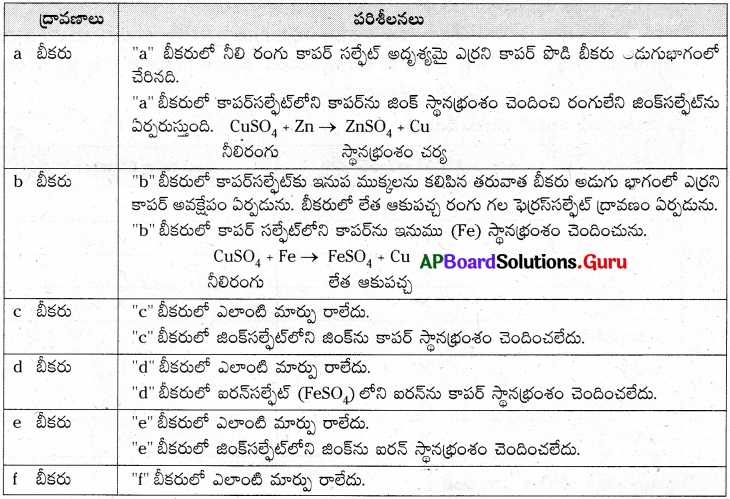
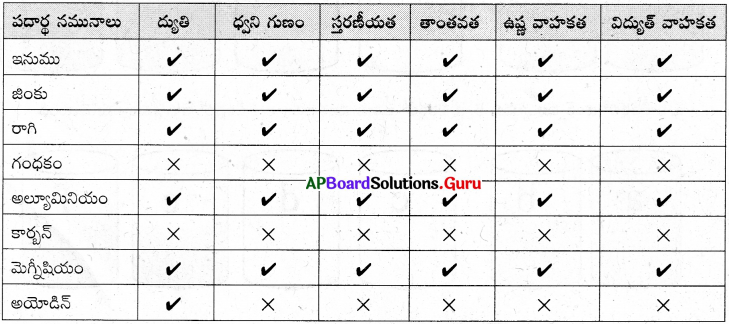
ప్రశ్న 5.
నేను ఏ విభాగానికి చెందుతాను? (AS 1)
ఎ) నా శరీరంలో రంధ్రాలున్నాయి, నేను నీటిలో నివసిస్తాను. నాకు వెన్నెముక లేదు.
జవాబు:
ఫొరిఫెర
బి) నేను కీటకాన్ని. నాకు అతుకుల కాళ్ళున్నాయి.
జవాబు:
ఆల్డోపొడ
సి) నేను సముద్రంలో నివసించే జీవిని, చర్మంపై ముళ్ళు ఉండి, అనుపార్శ్వ సౌష్టవం కలిగి ఉంటాను.
జవాబు:
ఇఖైనోడర్మేట

ప్రశ్న 6.
చేపలు, ఉభయచరాలు, పక్షులలో మీరు గమనించిన సాధారణ లక్షణాలను రాయండి. (AS 1)
జవాబు:
- చేపలు, ఉభయచరాలు, పక్షులు అన్నీ సకశేరుకాలు.
- ఇవి అన్నీ వెన్నెముక కలిగిన జీవులు.
- చేపలు, ఉభయచరాలు, పక్షులు అన్నీ అండజనకాలు.
ప్రశ్న 7.
వర్గీకరణ అవసరం గురించి తెలుసుకోవడానికి నీవు ఏ ఏ ప్రశ్నలు అడుగుతావు? (AS 2)
జవాబు:
ప్రశ్నలు :
i) వర్గీకరణ యొక్క అవసరం ఏమిటి?
ii) వర్గీకరణను ఎవరు, ఎప్పుడు చేశారు?
iii) వర్గీకరణ వలన ఉపయోగం ఏమిటి?
iv) వర్గీకరణలో నూతనముగా వచ్చిన మార్పులు ఏమిటి?
v) వర్గీకరణ అన్ని జీవులకు వర్తిస్తుందా?
ప్రశ్న 8.
స్లెడు తయారు చేసేటప్పుడు నీవు తీసుకున్న జాగ్రత్తలేమిటి? (AS 3)
జవాబు:
స్లెడును తయారుచేసేటప్పుడు తీసుకోవలసిన జాగ్రత్తలు :
- పరిచ్ఛేదాలను పలుచగా కత్తిరించాలి.
- పరిచ్ఛేదాలను వా గ్లాస్ ఉన్న నీటిలో ఉంచాలి.
- పలుచటి పరిచ్చేదాలను మాత్రమే గాజు పలకపై ఉంచాలి.
- పరిచ్ఛేదం ఆరిపోకుండా దానిపై గ్లిజరిన్ చుక్క వేయాలి.
- భాగాలు స్పష్టంగా కనిపించటానికి అవసరమైన రంజకాన్ని ఉపయోగించాలి.
- గాజు పలక పై ఉన్న పరిచ్ఛేదం ఎక్కువ కాలం ఉంచుటకు కవర్ స్లితో మూసి ఉంచాలి.
- గాజు పలకపై కవర్ స్లిప్ ను ఉంచునపుడు గాలిబుడగలు లేకుండా చూడాలి.
- అధికంగా ఉన్న నీటిని లేక గ్లిజరిన్ లేక వర్ణద్రవ్యాన్ని అద్దుడు, కాగితంతో తొలగించాలి.
ప్రశ్న 9.
ఒక రోజు కవిత పెసలు, గోధుమలు, మొక్కజొన్న, బఠాని మరియు చింతగింజలను నీటిలో నానవేసింది. అవి నీటిలో నానిన తరువాత నెమ్మదిగా పగలగొడితే అవి రెండు బద్ధలుగా విడిపోయాయి. ఇవి ద్విదళ బీజాలు. కొన్ని విడిపోలేదు. ఇవి ఏకదళ బీజాలు. కవిత పట్టికను ఎలా నింపిందో ఆలోచించండి. మీరూ ప్రయత్నించండి. (AS 4)
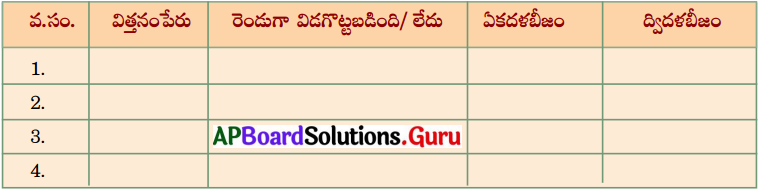
జవాబు:
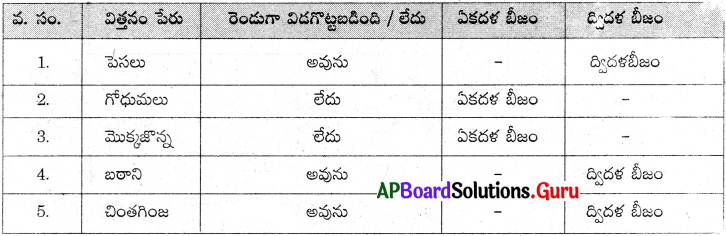
ప్రశ్న 10.
గ్రంథాలయం లేదా అంతర్జాలం నుండి సమాచారం సేకరించి ప్లాటిపస్ మరియు ఎకిడ్నాలను క్షీరదాలను మరియు సరీసృపాలను అనుసంధానం చేసే జీవిగా ఎలా చెప్పవచ్చో వివరించండి. (AS 4)
జవాబు:
- ఎకిడ్నా మరియు ప్లాటిపస్లు రెండూ మెనోట్రీమ్ గ్రూపునకు చెందిన జీవులు,
- ఈ రెండు కూడా అండజనక క్షీరదాలు. అయినప్పటికీ ఇవి సరీసృపాలు లేదా పక్షులు కావు.
- గుడ్లను పొదుగుతాయి. రెండూ పిల్లలకు పాలు ఇస్తాయి.
- ఇవి రెండూ ఆస్ట్రేలియా మరియు టాస్మేనియాలో కనిపిస్తాయి.
- ప్లాటిపస్ ముఖ్య లక్షణాలు మరియు అసాధారణ లక్షణాలు-బాతుకు ఉన్న ముక్కు వంటి నిర్మాణం దీనికి ఉండటం, క్షీరద లక్షణమైన దంతములు లేకపోవటం.
- స్పైనీ ఏంట్ ఈటర్ అయిన ఎకిడ్నాకు కూడా దంతములు లేవు. నాలుక ఆహారం తీసుకోవడానికి ఉపయోగపడుతుంది.
- గుడ్ల నుండి బయటకు వచ్చిన ఎకిడ్నా మరియు ప్లాటిపస్ పిల్లలు బొరియలలో నివసిస్తాయి. కానీ సరీసృపాలు కాదు. ప్రజనన సమయంలో ఎకిడ్నా ప్రాథమికమైన సంచిని అభివృద్ధి చేసుకుంటుంది.
- రెండు జీవులకూ గుంటలు చేయడానికి పదునైన గోళ్ళు కలవు.
- ప్లాటిపస్ మరియు ఎకిడ్నా నీటిని ఇష్టపడతాయి. ప్లాటిపస్ నీటిలో ఆహారం వేటాడుతుంది.
- ఎకిడ్నా నీటిలో ఉండుట ద్వారా తన శరీర ఉష్ణోగ్రతను క్రమబద్దీకరణ చేస్తుంది.
ప్రశ్న 11.
అనిమేలియా రాజ్యాన్ని వాటి లక్షణాల ఆధారంగా ఒక ఫ్లో చార్టు తయారుచేయండి. (AS 5)
జవాబు:
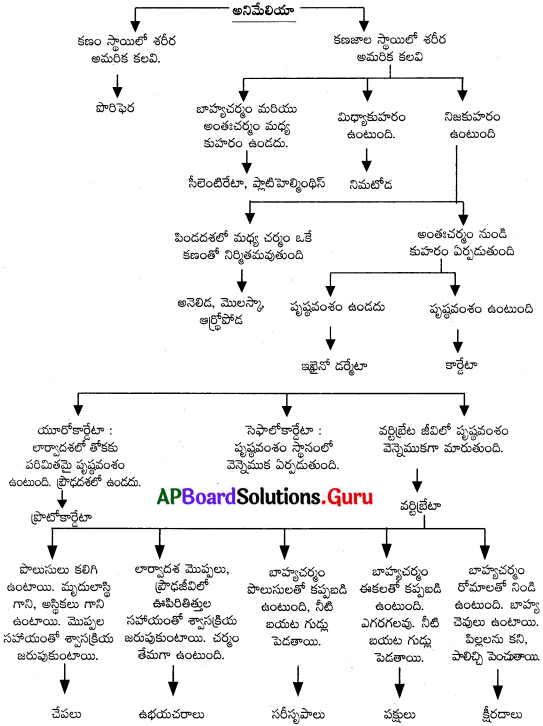
ప్రశ్న 12.
వెన్నెముక గల జీవులను ఉపరితరగతులుగా విభజిస్తూ ఫ్లోచార్ట్ తయారు చేయండి. (AS 5)
జవాబు:
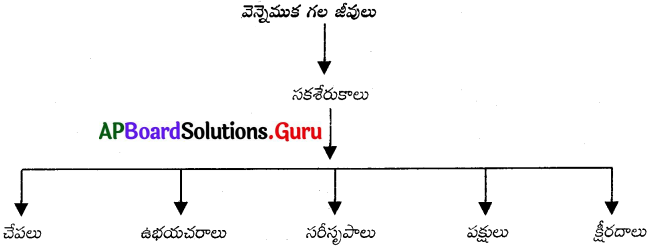
ప్రశ్న 13.
శాస్త్రవేత్తలు వర్గీకరణపై చేసిన పరిశోధనలను నీవు ఏ విధంగా ప్రశంసిస్తావు? (AS 6)
జవాబు:
- శాస్త్రవేత్తలు చేసిన వర్గీకరణముల వలన వైవిధ్యము కలిగిన జీవుల అధ్యయనం సులభమయ్యింది.
- వివిధ మొక్కలు మరియు జంతువుల మధ్య గల సంబంధాలను వర్గీకరణ ద్వారా అవగాహన చేసుకోవచ్చు.
- జీవులు సరళస్థితి నుండి సంక్లిష్ట స్థితి వరకు జరిగిన పరిణామము వర్గీకరణ ద్వారా మనకు అవగాహన కలుగుతుంది.

ప్రశ్న 14.
‘గబ్బిలం పక్షి కాదు క్షీరదం’ అని సుజాత చెప్పింది. మీరు ఆమె మాటలను ఏ విధంగా సమర్థిస్తారు? (AS 7)
జవాబు:
- గబ్బిలం పక్షి కాదు క్షీరదం అని సుజాత చెప్పిన మాటను సమర్థిస్తాను.
- ఇతర క్షీరదాలవలె మానవునితో సహా గబ్బిలానికి శరీరం మీద వెంట్రుకలు లేదా రోమములు కలవు.
- గబ్బిలం ఉష్ణరక్త జంతువు.
- పుట్టిన గబ్బిలం పాలకోసం తల్లిపాల మీద ఆధారపడుతుంది.
- గబ్బిలములు క్షీరదములలో గల ఏకైక ఎగిరే క్షీరదము.
9th Class Biology 5th Lesson జీవులలో వైవిధ్యం Textbook InText Questions and Answers
9th Class Biology Textbook Page No. 63
ప్రశ్న 1.
వృక్షరాజ్యాన్ని వాటి లక్షణాల ఆధారంగా ఒక ఫ్లోచార్ట్ తయారు చేయండి. పేజి నెం. 63
జవాబు:
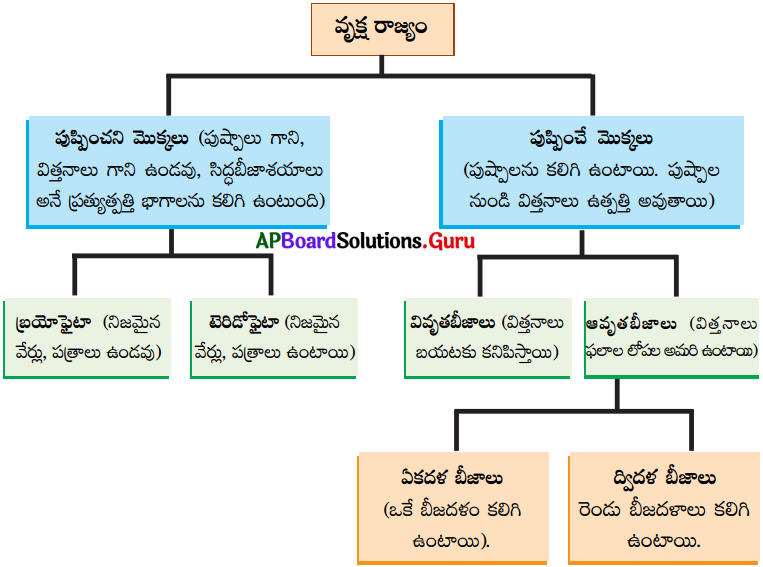
ప్రశ్న 2.
మీ తరగతిలో నలుగురు లేదా ఐదుగురు విద్యార్థులు ఒక జట్టుగా ఏర్పడి పాఠశాల గ్రంథాలయం లేదా అంతర్జాలం నుండి ఏవైనా 20 మొక్కలు, 20 జంతువుల శాస్త్రీయ నామాలతో జాబితా రూపొందించండి. (పేజి నెం. 71)
జవాబు:
మొక్కల శాస్త్రీయ నామములు :
| మొక్క పేరు | శాస్త్రీయ నామం |
| 1. మామిడి | మాంగి ఫెరా ఇండికా |
| 2. కొబ్బరి | కాకస్ న్యూసిఫెర |
| 3. తాటి | బొరాసస్ ప్లాజెల్లి ఫెర్ |
| 4. గరిక గడ్డి | సైనోడాన్ డాక్టలాన్ |
| 5. వరి | ఒరైజా సటైవా |
| 6. అరటి | మ్యూసా పారడైసికా |
| 7. మర్రి | ఫైకస్ బెంగాలెన్సిస్ |
| 8. పెద్ద ఉసిరి | ఎంబ్లికా అఫిసినాలిస్ |
| 9. తోటకూర | అమరాంతస్ గాంజిటికస్ |
| 10. తులసి | ఆసిమమ్ సాంక్టమ్ |
| 11. టేకు | టెక్టోనా గ్రాండిస్ |
| 12. కనకాంబరము | క్రొసాండ్ర ఇన్ఫండిబులిఫార్మిస్ |
| 13. వంకాయ | సొలానమ్ మెలాంజినా |
| 14. సపోట | ఎక్రస్ జపోట |
| 15. గడ్డి చామంతి | ట్రెడాక్స్ ప్రొకంబెన్స్ |
| 16. ధనియాలు (కొత్తిమీర) | కొరియాండ్రమ్ సటైవమ్ |
| 17. జామ | సిడియమ్ గ్వజావ |
| 18. గులాబి | రోజా గ్రాండిప్లోరా |
| 19. చింత | టామరిండస్ ఇండికా |
| 20. మందార | హైబిస్కస్ రోజా – సైనెన్సిస్ |
| 21. బెండ | అబెలియాస్మస్ ఎస్కూలెంటస్ |
| 22. జీడిమామిడి | అనకార్డియం ఆక్సిడెంటాలిస్ |
| 23. పైనాపిల్ | అనాన స్క్వామోజస్ |
| 24. ఆవాలు | బ్రాసికా జెన్షియా |
| 25. క్యా బేజి | బ్రాసికా ఒలరేసియా రకం కాపిటేట |
| 26. తేయాకు | కెమెల్లియా సైనన్సిస్ |
| 27. నారింజ | సిట్రస్ సైనన్సిస్ |
| 28. పసుపు | కుర్కుమా లోంగా |
| 29. ఉమ్మెత్త | దతురా మెటల్ |
| 30. వెదురు | డెండ్రోకాలమస్ కలోస్ట్రాఖియస్ |
| 31. మిరప | కాప్సికమ్ ఫ్రూటి సెన్స్ |

జంతువుల శాస్త్రీయ నామములు :
| జంతువు పేరు | శాస్త్రీయ నామం |
| 1. కాకి | కార్పస్ స్పెండెన్స్ |
| 2. పిచ్చుక | పాస్సర్ డొమెస్టికస్ |
| 3. కప్ప | రానాటైగ్రీనా |
| 4. కుక్క | కేనిస్ ఫెమిలియారీస్ |
| 5. పిల్లి | ఫెలిస్ డొమెస్టికస్ |
| 6. చింపాంజి | ఎంత్రోపిథికస్ ట్రైగ్లో డైట్స్ |
| 7. కోడి | గాలస్ డొమెస్టికస్ |
| 8. పావురము | కొలంబియ లివియ |
| 9. గేదే | బుబాలస్ బుబాలిస్ |
| 10. తేనెటీగ | ఎపిస్ ఇండికా |
| 11. వానపాము | ఫెరిటీమా పోస్తుమా |
| 12. బొద్దింక | పెరిప్లానేటా అమెరికానా |
| 13. జలగ | హిరుడినేరియా గ్రాన్యులోస |
| 14. రొయ్య | పాలియమాన్ మాక్మో సోనీ |
| 15. ఈగ | మస్కా సెబ్యులోం |
| 16. నత్త | పైలాగ్లోబోసా |
| 17. గుడ్లగూబ | బుబోబుబో |
| 18. తాచుపాము | నాజనాజ |
| 19. గుర్రము | ఈక్వస్ కబాలస్ |
| 20. రామచిలుక | సిట్టిక్యుల క్రామెరి |
| 21. చీమ | హైమినోప్టెరస్ ఫార్మిసిడి |
| 22. గాడిద | ఇక్వియస్ అసినస్ |
| 23. కంగారు | మాక్రోఫస్ మాక్రోపాజిడే |
| 24. కుందేలు | రొడెంటియా రాటస్ |
| 25. ఏనుగు | ప్రోబోసిడియా ఎలిఫెండిడే |
| 26. జిరాఫీ | రాఫాకామిలో పారాలిస్ |
| 27. పంది | ఆడియో డక్టలా సుయిడే |
| 28. నీటి గుర్రం | ఇప్పోకాంపస్ సిగ్నాంథిగే |
| 29. నెమలి | పావో క్రిస్టేటస్ |
9th Class Biology 5th Lesson జీవులలో వైవిధ్యం Textbook Activities (కృత్యములు)
కృత్యం – 1
ప్రశ్న 1.
మొక్కలలో ఆకుల పరిశీలన :
మొక్కలలో ఆకుల పరిశీలన. వివిధ రకాల మొక్కల ఆకులను సేకరించి వాటిని పరిశీలించి పట్టికను పూరించండి.
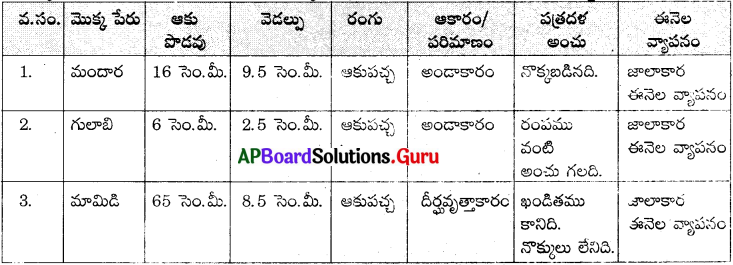
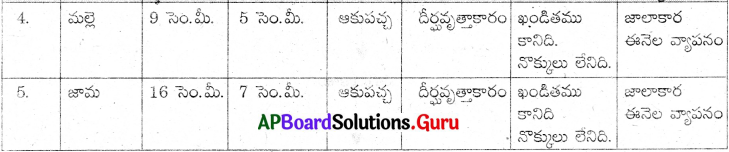
ఎ) పైన పరిశీలించిన ఆకులలో ఏ రెండు ఆకులైనా ఒకే విధంగా ఉన్నాయా? (ఆకారం, పరిమాణం, రంగులో)
జవాబు:
ఏ రెండు ఆకులూ పరిమాణంలోను, ఆకారంలోను ఒకే విధముగా లేవు.
బి) సేకరించిన ఆకులలో మీరు గుర్తించిన ముఖ్యమైన భేదాలను రాయండి. ఏ రెండు లక్షణాలలో ఎక్కువగా భేదాలు చూపుతున్నాయో గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:

i) కొన్ని ఆకుల ఆకారం అండాకారంగాను, మరికొన్ని ఆకుల ఆకారం దీర్ఘవృత్తాకారంగాను ఉంది.
ii) పత్రపు అంచులు కొన్నిటికి నొక్కబడి, కొన్ని రంపము అంచుగలవిగా మరికొన్ని నొక్కులు లేనివిగా ఉన్నాయి.
iii) ఆకుల పొడవు, వెడల్పులలో ఆకులు అన్నీ వివిధ కొలతలలో ఉన్నాయి.
కృత్యం – 2
ప్రశ్న 2.
మొక్కల పరిశీలన :
మీ పరిసరాలలో గల 5 రకాల మొక్కలు వాటి పుష్పాలతో సేకరించి వాటి బాహ్య లక్షణాలను జాగ్రత్తగా పరిశీలించండి. పరిశీలించిన అంశాలను పట్టికలో నమోదు చేయండి.
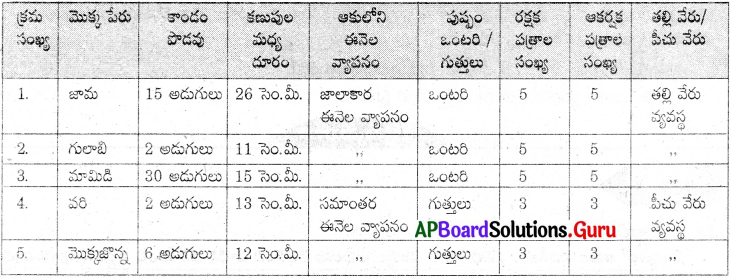
1. ఏయే లక్షణాలలో ఎక్కువ తేడాలు ఉండటం గమనించారు?
జవాబు:
కాండం పొడవు, కణుపుల మధ్య దూరం, ఆకుల, ఈనెల వ్యాపనంలో మరియు వేరు వ్యవస్థలలో తేడాలు ఉన్నాయి.
2. అతి తక్కువ భేదం చూపుతున్న లక్షణమేది?
జవాబు:
పుష్పం నందు అతి తక్కువ భేదం చూపుతున్నవి – పుష్పాలు గుత్తులుగా రావడం అనేది.
3. మీకు వాటిలో ఏమైనా పోలికలు కనిపించాయా? కనిపిస్తే అవి ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
ఈనెల వ్యాపనంలోను, రక్షక ఆకర్షక పత్రాల సంఖ్యలోను వేరువ్యవస్థలోను పోలికలు ఉన్నాయి.
4. పీచు వేర్లు కలిగిన మొక్కలలో పుష్పాలు గుంపులుగా ఉన్నాయా? లేక వేరే విధంగా ఉన్నాయా?
జవాబు:
గుంపులుగా ఉంటాయి.
5. పై పట్టికలో పేర్కొన్న లక్షణాలు కాకుండా ఇంకేమైనా కొత్త లక్షణాలను మీరు పరిశీలించారా ? వాటిని నమోదు చేయండి.
జవాబు:
గులాబి చెట్లకు ముళ్ళుంటాయి.
6. పట్టికలో పేర్కొన్న లక్షణాలు ప్రాతిపదికగా పరిశీలిస్తే ఏ రెండు మొక్కలైనా ఒకేలా ఉన్నాయా?
జవాబు:
లేవు.
7. వేరు వేరు మొక్కలలో ఒకే రకమైన లక్షణాలు పరిశీలించినట్లయితే వాటిని పేర్కొనండి.
జవాబు:
వరి, మొక్కజొన్న నందు సమాంతర వ్యాపనం, పీచు వేరు వ్యవస్థ ఉన్నాయి. మామిడి, గులాబి, జామనందు తల్లివేరు వ్యవస్థ, జాలాకార ఈనెల వ్యాపనం ఉన్నాయి.
8. మీరు సేకరించిన మొక్కలలో ఏ రెండు మొక్కలలో అయినా ఎక్కువ లక్షణాలు ఒకే రకంగా ఉన్నాయా? అవి ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
జామ, గులాబినందు ఎక్కువ లక్షణాలు ఒకే విధంగా ఉన్నాయి.

కృత్యం – 3
ప్రశ్న 3.
విత్తనాలను పరిశీలిద్దాం :
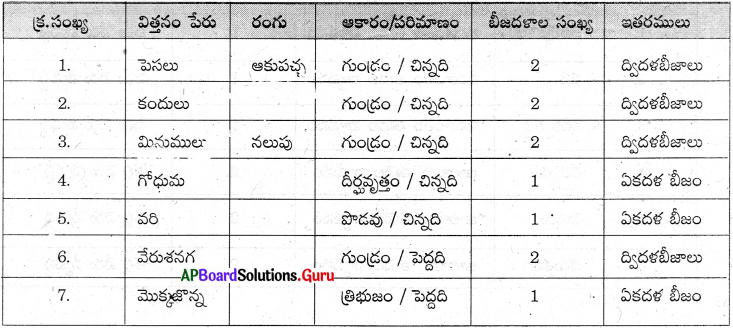
వివిధ రకముల విత్తనములందు గల బీజదళాల సంఖ్యను నీవు ఏ విధముగా పరిశీలిస్తావు? నీ యొక్క పరిశీలనలను పట్టికయందు నమోదు చేయుము.
జవాబు:
విత్తనమునందు గల బీజదళాల సంఖ్యను పరిశీలించు విధము :
- పెసలు, కందులు, మినుములు, గోధుమ, వరి, వేరుశనగ, మొక్కజొన్న విత్తనములను సేకరించి వాటిని ఒక రోజు నీటిలో నానబెట్టాలి.
- వీటిలో మొక్కజొన్న విత్తనాన్ని తీసుకొని చేతివేళ్ళతో నొక్కాలి.
- మొక్కజొన్న విత్తనము నుండి తెల్లని నిర్మాణం బయటకు వస్తుంది.
- తెల్లని నిర్మాణమును పిండం లేదా పిల్లమొక్క అంటారు.
- పిండం కాకుండా మన చేతిలో మిగిలిన భాగంలో ఉన్న విత్తనం పైభాగంలో ఒకే బీజదళం ఉంటుంది.
- ఇదే విధంగా మిగిలిన అన్ని విత్తనాలనూ నొక్కి పరిశీలించాలి.
- భూతద్దం ద్వారా పరిశీలించిన అంశాలను పట్టికలో నమోదుచేయాలి.
కృత్యం – 4
ప్రశ్న 4.
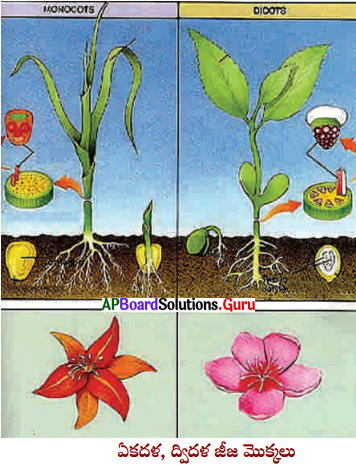
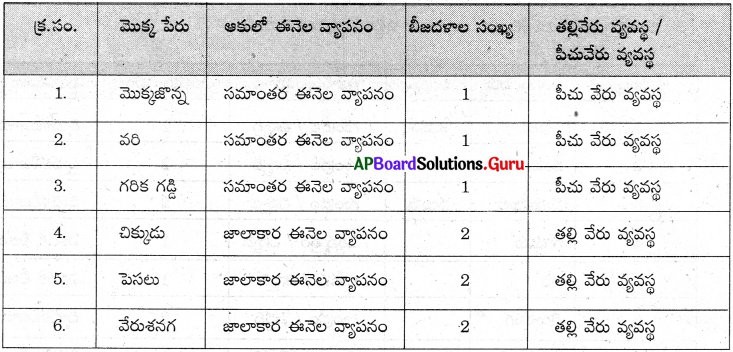
ఏకదళ, ద్విదళ బీజ మొక్కల లక్షణాలను పరిశీలిద్దాం :
ఏకదళ, ద్విదళ బీజ మొక్కలను సేకరించి వాటి లక్షణాలను పరిశీలించి పట్టికను పూరించండి.
జవాబు:
కృత్యం – 5
ప్రశ్న 5.
కీటకాల బాహ్య లక్షణాలను పరిశీలిద్దాం.
మీ పరిసరాలలోని ఈగ, దోమ, చీమ, పేడ పురుగు, సీతాకోక చిలుక మాత్, బొద్దింక మొదలైన కీటకాలను పరిశీలించి పట్టికను పూర్తిచేయండి. ప్రశ్నలకు జవాబులు రాయండి.
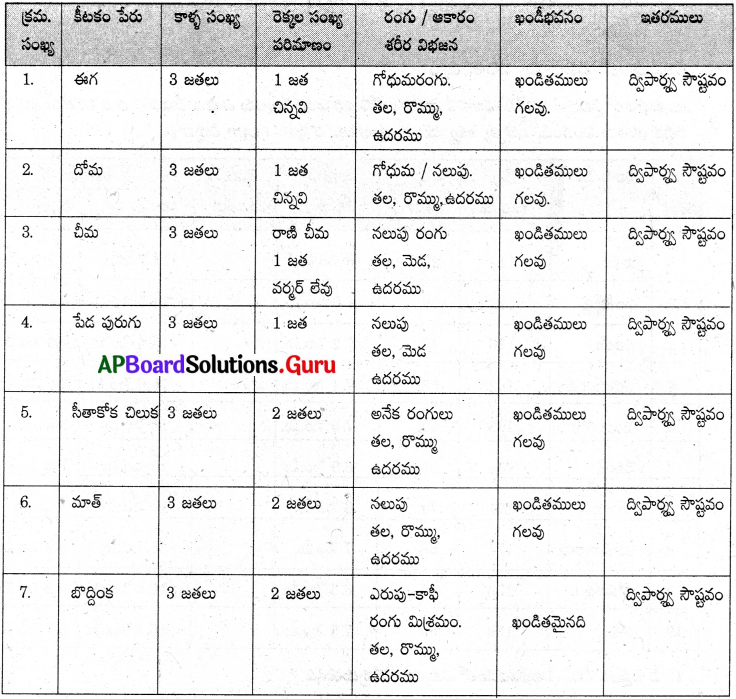
1. అన్ని కీటకాలు ఒకే ఆకారం, పరిమాణం కలిగి ఉన్నాయా?
జవాబు:
కీటకాలు అన్నీ ఒకే ఆకారం, పరిమాణం కలిగి ఉండలేదు.
2. కాళ్ళను పరిశీలిస్తే వాటిలో కనిపించే తేడాలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
కొన్ని కీటకాలకు కీళ్ళు కలిగిన కాళ్ళు ఉన్నాయి. ఒక్కొక్క కీటకము కాళ్ళనందు అతుకులు ఉన్నాయి.
3. రెక్కలను పరిశీలిస్తే వాటిలో కనిపించే తేడాలేమిటి?
జవాబు:
రెక్కలు పెద్దవిగాను, చిన్నవిగాను ఉన్నాయి. కొన్నింటిలో 1 జత రెక్కలు ఉంటే కొన్నింటిలో – (సీతాకోకచిలుక, మాత్, బొద్దింక) రెండు జతల రెక్కలు ఉన్నాయి. రెక్కలు వివిధ రంగులలో ఉన్నాయి.
4. రెక్కల సంఖ్యకి, కాళ్ళ సంఖ్యకి మధ్య ఏమైనా సంబంధం ఉందా?
జవాబు:
కాళ్ళ సంఖ్య స్థిరంగా ఉంటే అనగా 6 కాళ్ళు ఉంటే, రెక్కలు తక్కువ సంఖ్యలో ఉన్నాయి.
5. ఏ రెండు కీటకాల లక్షణాలు ఒకేలా ఉన్నాయా? ‘అవును’ అయితే వాటిని మీ తరగతిలో ప్రదర్శించండి. ‘లేదు’ అయితే తేడాలను మీ నోట్బుక్ లో రాయండి.
జవాబు:
ఏ రెండు కీటకాల లక్షణాలు ఒకే విధంగా లేవు. సీతాకోకచిలుక, బొద్దింక కాళ్ళ సంఖ్యలోను, రెక్కలసంఖ్యలోను ఒకేవిధంగా ఉన్నప్పటికి ఆకారంలోను, రంగులోను తేడాను చూపిస్తున్నాయి.
కృత్యం – 6
ప్రశ్న 6.
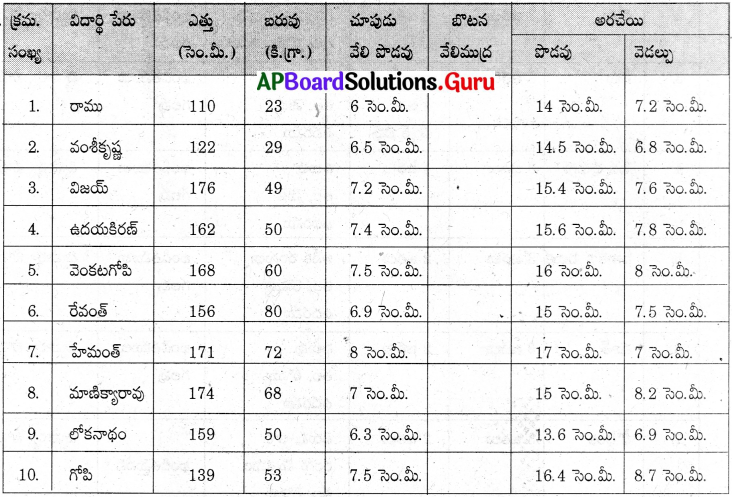
మానవులలో వైవిధ్యాన్ని పరిశీలిద్దాం :
జంతువులలో వైవిధ్యం పరిశీలించడానికి పాఠశాలలోని పదిమంది పిల్లలను ఎంపిక చేసుకొని వారి వివరములను క్రింది పట్టిక యందు నింపండి. ఒక్కొక్క జట్టు యందు నలుగురు చొప్పున జట్లుగా ఏర్పడాలి.
జవాబు:
1. ఏ లక్షణం వీరిని విభజించడంలో ఎక్కువగా తోడ్పడుతుంది?
జవాబు:
‘ఎత్తు’ లక్షణం ద్వారా వీరిని విభజించవచ్చు.
2. ఏ లక్షణం గ్రూపులలో ఒక్కరికి మాత్రమే వర్తిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
బొటన వేలిముద్ర
3. మీ తరగతిలో ఏ ఇద్దరు విద్యార్థులకైనా ఒకే విధమైన లక్షణాలు ఉన్నాయా?
జవాబు:
లేవు
4. మీ పట్టికను ఇతరులతో పోల్చి వివిధ పట్టికలలో ఉన్న అంశాల మధ్య తేడాలను నమోదు చేయండి.
జవాబు:
విద్యార్థి కృత్యము.

కృత్యం – 7
ప్రశ్న 7.
రెండు వేరు వేరు మొక్కలలో వైవిధ్యాన్ని పరిశీలిద్దాం.
రెండు వేరు వేరు వేప మొక్కలలోని వైవిధ్యంను పరిశీలించి కింది పట్టికను పూర్తి చేయంది.
సమాన పరిమాణాలలో ఉన్న రెండు వేప మొక్కలను ఎంపిక చేసుకొని వాటి లక్షణాలను పట్టికలో పూరించాలి.
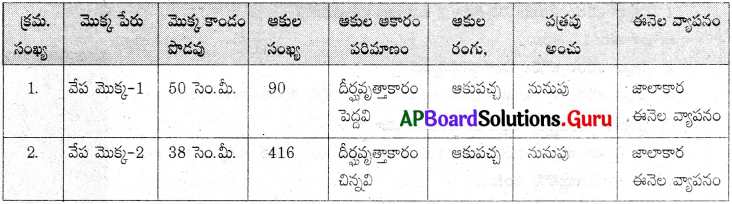
1. ఒకే రకమైన రెండు వేపమొక్కలలో ఏ ఏ తేడాలను నీవు గమనించావు?
జవాబు:
పొడవులో తేడా, ఆకుల సంఖ్యలో తేడా గలవు.
2. అలాంటి తేడాలు వాటిలో ఉండడానికి కారణాలు ఏమై ఉండవచ్చునని ఊహిస్తున్నావు?
జవాబు:
ఒక్కొక్క మొక్క దాని లక్షణాలు ప్రత్యేకంగా ఉంటాయి. మొక్క వయసు కూడా లక్షణాలలో తేడా ఉండడానికి కారణమవుతుంది.
కృత్యం – 8
ప్రశ్న 8.
వివిధ రకాల నాచు మొక్కలను పరిశీలిద్దాం.
నాచు మొక్క (మాస్)ను సేకరించి దానిని భూతద్దంతో గాని సంయుక్త సూక్ష్మదర్శినితో గాని పరిశీలించండి. బొమ్మ గీసి నాచు మొక్కల లక్షణములు రాయండి.
జవాబు:
- గోడలపైన, ఇటుకల మీద వానాకాలంలో పెరిగే ‘పచ్చని నిర్మాణాలను సేకరించాలి.
- వాటి నుండి కొంతభాగం ఒక స్లెడ్ పైన తీసుకొని సంయుక్త సూక్ష్మదర్శినితో పరిశీలించాలి.

పరిశీలనలు :
- నాచు మొక్క సైడ్ నందు కనిపించే పువ్వుల మాదిరి నిర్మాణాలను సిద్ధబీజాలు అంటారు.
- సిద్ధ బీజాలలో చాలా తక్కువ పరిమాణంలో ఆహారపదార్థాలు నిల్వ ఉంటాయి.
- సిద్ధబీజాలు సిద్ధబీజాశయము నుండి ఉత్పత్తి అవుతాయి.
ప్రయోగశాల కృత్యములు
ప్రశ్న 1.
ప్రయోగశాల నుండి హైడ్రాస్లెడ్ ను సేకరించి మైక్రోస్కోపులో పరిశీలించండి. బొమ్మను గీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించి పరిశీనలను రాయండి.
జవాబు:

పరిశీలనలు :
1. హైడ్రా శరీరం ఏకకణ నిర్మితమా ? బహుకణ నిర్మితమా?
జవాబు:
బహుకణ నిర్మితము.
2. హైడ్రా శరీరం లోపల ఎలా కనిపిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
హైడ్రా శరీరం లోపల ఖాళీ ప్రదేశం కనిపిస్తుంది. దానిని శరీరకుహరం అంటారు.
3. హైడ్రాలో ఇంకేమైనా లక్షణాలు కనిపించాయా?
జవాబు:
1) హైడ్రా జీవుల అపముఖము వైపు ఒక సన్నని కాడ చివర ఉన్న ఆధారముతో అంటిపెట్టుకొని ఉంటుంది.
2) స్వేచ్ఛగా ఉండే ముఖభాగము హైపోస్టోమ్ మీద అమరి ఉంటుంది.
3) హైపోస్టోమ్ చుట్టూ 6-10 స్పర్శకాలు ఉంటాయి.
4) కాడ ప్రక్కభాగమున నోరు లేదా స్పర్శకాలతో కూడిన ప్రరోహము ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 2.
బద్దెపురుగు స్పెసిమన్ ను పరిశీలించి బొమ్మగీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించండి. పరిశీలనలు రాయండి.
జవాబు:

పరిశీలనలు:
1. జీవి శరీరం ఎలా కనిపిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
జీవి శరీరం చదునుగా ఉండి, రిబ్బన్ వలె ఉంటుంది. వీటిని ప్లాటీహెల్మింథిస్ లేదా చదును పురుగు అంటారు.
2. జీవి శరీరంలో ఏదైనా ఖాళీ ప్రదేశం కనిపించినదా?
జవాబు:
ఖాళీ ప్రదేశం లేదు. నిజ శరీరకుహరం ఏర్పడలేదు.
3. దాని తల మరియు తోక ఎలా ఉంది?
జవాబు:
తలభాగము చిన్నదిగా గుండుసూదంత పరిమాణంలో ఉంటుంది. తోక కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
ప్రశ్న 3.
నులిపురుగు స్పెసిమన్ ను పరిశీలించండి. గమనించిన అంశాలను నోటు పుస్తకంలో రాయంది. దాని బొమ్మ గీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:

పరిశీలనలు :
1. జీవి శరీరం బద్దెపురుగు (ప్లాటీ హెల్మింథిస్) ను పోలి ఉందా?
జవాబు:
జీవి శరీరం బద్దెపురుగును పోలియుండలేదు. శరీరం గుండ్రంగా ఉంది.
2. బద్దెపురుగు మరియు నులిపురుగులలో ఏమి తేడాలు గమనించారు?
జవాబు:
బద్దెపురుగు చదునుగా, శరీరకుహరం లేకుండా ఉంటుంది. నులిపురుగు గుండ్రంగా మిథ్యాకుహరం కలిగి ఉంటుంది.
3. స్పెసిమన్ లో దాని తల మరియు తోక ఎలా కన్పిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
తల మరియు తోకలు చిన్నవిగా ఉండి మొనదేలి ఉంటాయి.

ప్రశ్న 4.
వానపాము స్పెసిమను పరిశీలించండి. మీరు గమనించిన అంశాలు నోటుపుస్తకంలో రాయండి. దాని బొమ్మ గీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:

పరిశీలనలు :
1. వానపాము ఎలా కదులుతుంది?
జవాబు:
వర్తులాకార మరియు నిలువు కండరాల ఏకాంతర సంకోచ, సడలికల వల్ల కదులుతుంది.
2. దాని రంగు ఎలా ఉంది? శరీరంలో వలయాలు ఉన్నాయా?
జవాబు:
ముదురు గోధుమ వర్ణంలో ఉంది. శరీరంలో వలయాలు ఉన్నాయి.
3. శరీర రంగులో, శరీర భాగాల్లో ఏమి తేడా గమనించారు?
జవాబు:
శరీర పైభాగము ముదురు గోధుమ రంగులో ఉంటుంది. శరీర అడుగుభాగము లేత గోధుమ రంగులో ఉంటుంది. శరీర భాగమునందు ఖండితములు 14 నుండి 17 వరకు ఉన్నాయి. చర్మం మందంగా ఉంది. అక్కడ చర్మం శ్లేష్మంను స్రవించి గట్టిపడుతుంది. శరీరమంతా వలయాకార ఖండితాలు ఉన్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 5.
బొద్దింక స్పెసిమన్ పరిశీలించండి. మీరు గమనించిన అంశాలు నోటు పుస్తకంలో రాయండి. దాని బొమ్మ గీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:

పరిశీలనలు :
1. బొద్దింక చర్మం ఎలా కనిపిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
బొద్దింక చర్మం గట్టిదైన అవభాసినితో ఆవరించబడి ఉంది.
2. వాటి చర్మంపై ఏదయినా గట్టిపొరను గమనించారా?
జవాబు:
గట్టి పొరను గమనించాము. దానిని అవభాసిని అంటారు.
3. బొద్దింక కాళ్ళను గమనించండి. అవి ఎలా కన్పిస్తున్నాయో చెప్పండి.
జవాబు:
బొద్దింకలో 3 జతల కాళ్ళున్నాయి. అవి కీళ్ళు కలిగిన కాళ్ళు.
4. బొద్దింక శరీరాన్ని ఎన్ని భాగాలుగా విభజించవచ్చు?
జవాబు:
బొద్దింక శరీరాన్ని మూడు భాగాలుగా విభజించవచ్చు. అవి : తల, రొమ్ము , ఉదర భాగం.
5. బొద్దింక మాదిరిగా కీళ్ళు కలిగిన కాళ్ళు ఉండే మరికొన్ని కీటకాల జాబితా రాయండి.
జవాబు:
సీతాకోక చిలుక, దోమ, ఈగ, గొల్లభామ, చీమ మొదలైనవి.
ప్రశ్న 6.
నత్త స్పెసిమనను పరిశీలించి గమనించిన అంశాలను నోటుపుస్తకంలో రాయండి. దాని బొమ్మ గీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:

పరిశీలనలు :
1. నత్త బాహ్య స్వరూపం ఎలా కన్పిస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
నత్త బాహ్య స్వరూపం మెత్తగా ఉండి గట్టి కర్పరంతో ఉంటుంది.
2. నత్తను కాసేపు కదలకుండా ఉంచండి. అది కదలికను ఎక్కడ నుంది మొదలు పెట్టింది? ఆ భాగం ఏమిటి?
జవాబు:
పాదము నుండి కదలికను మొదలుపెట్టింది.
3. నత్త శరీరం గట్టిగా ఉందా? మెత్తగా ఉందా?
జవాబు:
నత్త శరీరం గట్టిగా ఉంది.
4. నత్త శరీరంలో ఏవైనా స్పర్శకాలు వంటి నిర్మాణాలు గుర్తించారా?
జవాబు:
నత్త శరీరంలో స్పర్శకాలు వంటి నిర్మాణాలు ఉన్నాయి.
ప్రశ్న 7.
సముద్ర నక్షత్రం స్పెసిమను పరిశీలించండి. మీరు గమనించిన అంశాలను నోటు పుస్తకంలో రాయండి. దాని బొమ్మ గీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:

పరిశీలనలు:
1. సముద్ర నక్షత్రం శరీరం చర్మంపై ఏమి గమనించారు?
జవాబు:
సముద్ర నక్షత్రం శరీరం చర్మంపై ముళ్ళు ఉన్నాయి.
2. వాటికి చేతుల వంటి నిర్మాణాలు ఏమైనా ఉన్నాయా? అవి ఎలా ఉన్నాయి?
జవాబు:
జీవి శరీరం పంచభాగ వ్యాసార్ధ సౌష్టవము కలిగి ఐదు చేతుల వంటి నిర్మాణాలు ఉన్నాయి.
3. శరీరం మధ్యలో ఏదైనా రంధ్రాన్ని గమనించారా?
జవాబు:
సముద్ర నక్షత్రం మధ్య భాగంలో చిన్న రంధ్రము ఉన్నది. అది దాని యొక్క నోరు.

ప్రశ్న 8.
పాఠశాల ప్రయోగశాల నుండి చేప స్పెసిమన్ ను పరిశీలించండి. మీరు గమనించిన అంశాలు నోటుపుస్తకంలో రాయండి. దాని బొమ్మ గీచి, భాగాలు గుర్తించండి.
జవాబు:
పరిశీలనలు :
1. చేప యొక్క చర్మం గమనించి ఎలా ఉందో చెప్పంది.
జవాబు:
చేప చర్మం తేమగా, జిగటగా పొలుసులతో నిండియున్నది.

2. పొలుసులు లేని భాగాలను చేపలో గుర్తించి రాయండి.
జవాబు:
తలభాగము, ఉదరభాగము నందు పొలుసులు ఉండవు.
3. చేప యొక్క నోటిని తెరచి చేప నోటిలో ఏముందో చెప్పంది.
జవాబు:
చేప నోటిలో దంతాలు అమరి ఉన్నాయి. నాలుక ఉన్నది.
4. చేప యొక్క చెవి భాగాన్ని తెరచి అక్కడ ఏమి చూసారో చెప్పండి.
జవాబు:
చేప యొక్క చెవిభాగాన్ని తెరచి చూస్తే అక్కడ ఎర్రగా దువ్వెన మాదిరిగా ఉన్న మొప్పలు ఉన్నాయి.
5. చేపను కోసి దాని గుండెను పరిశీలించండి.
జవాబు:
చేప గుండె ఎరుపురంగులో చిన్నగా ఉన్నది.
6. చేప హృదయంలో ఎన్ని గదులున్నాయో తెల్పండి.
జవాబు:
చేప హృదయంలో రెండు గదులున్నాయి.


![]()




![]()




![]()