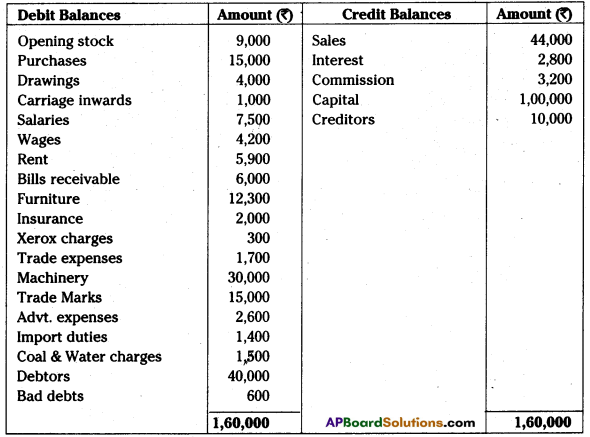
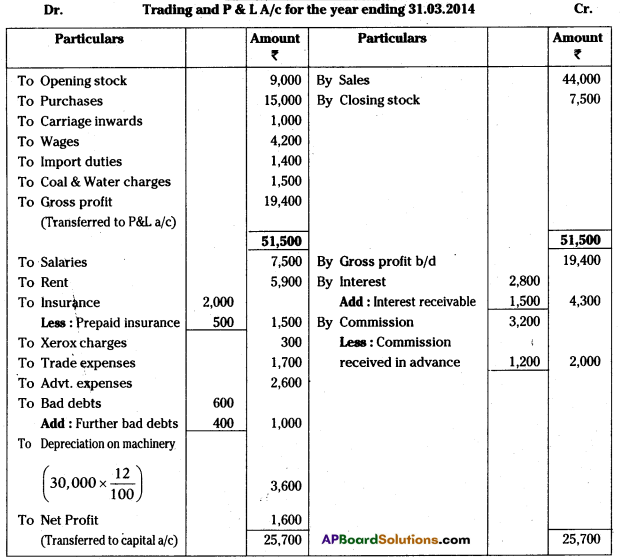
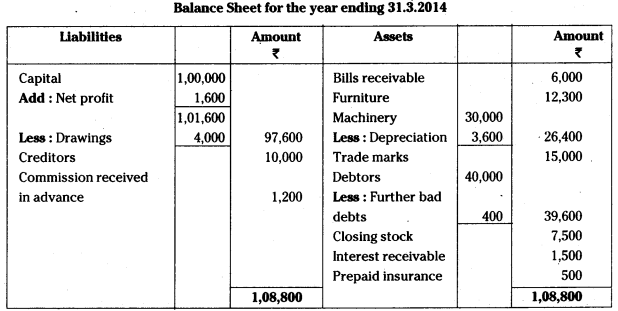
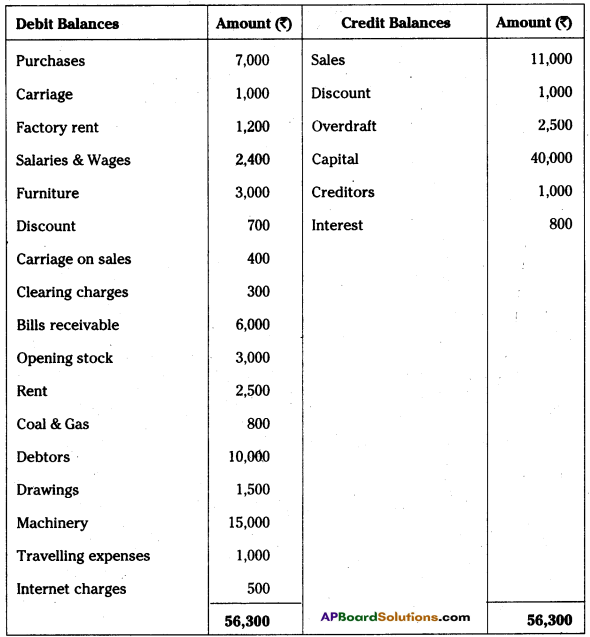
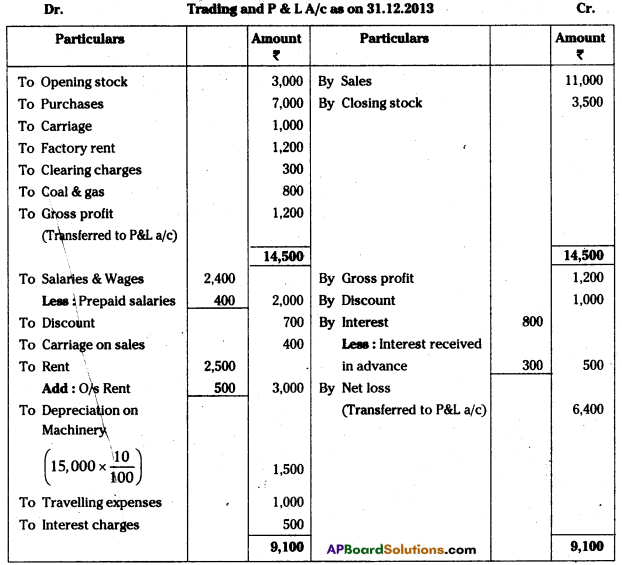
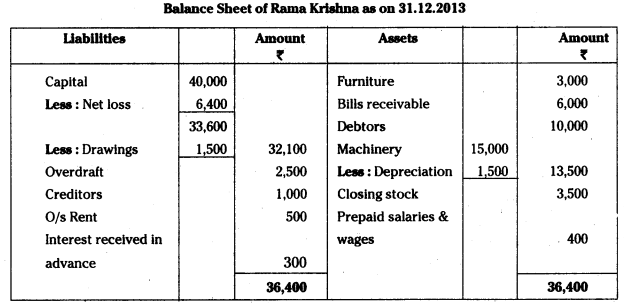
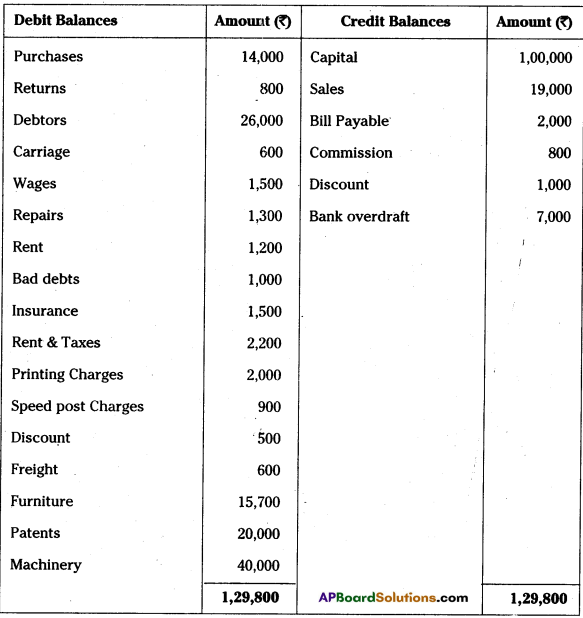
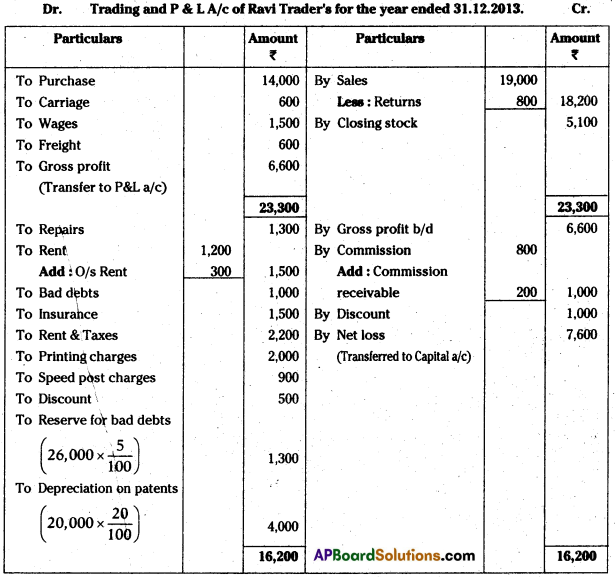
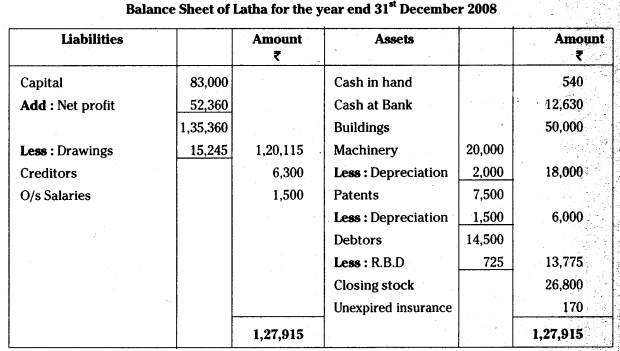
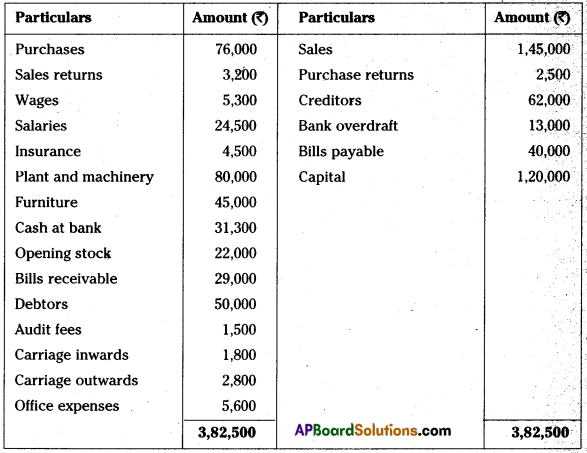
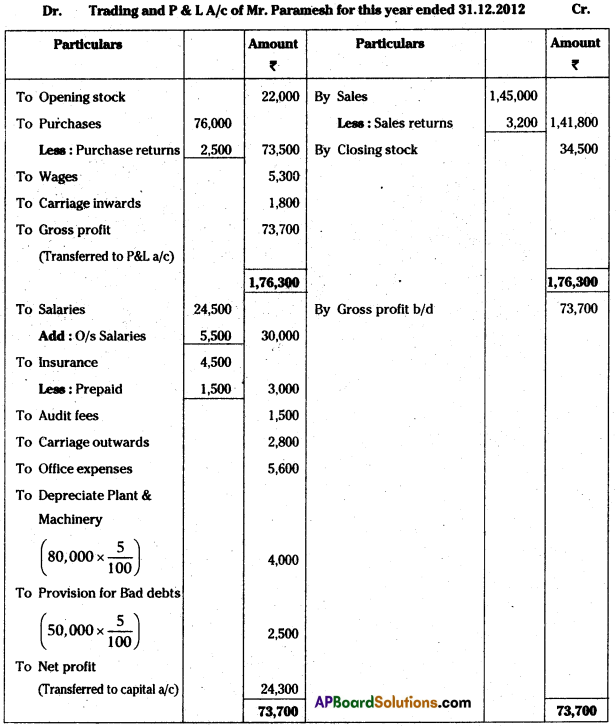
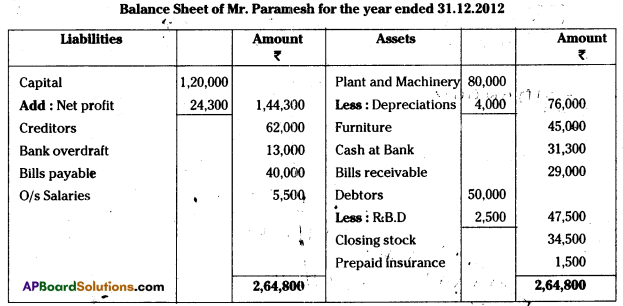
AP State Board Syllabus AP SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions Chapter 10 Natural Resources.
AP State Syllabus SSC 10th Class Biology Important Questions 10th Lesson Our Environment
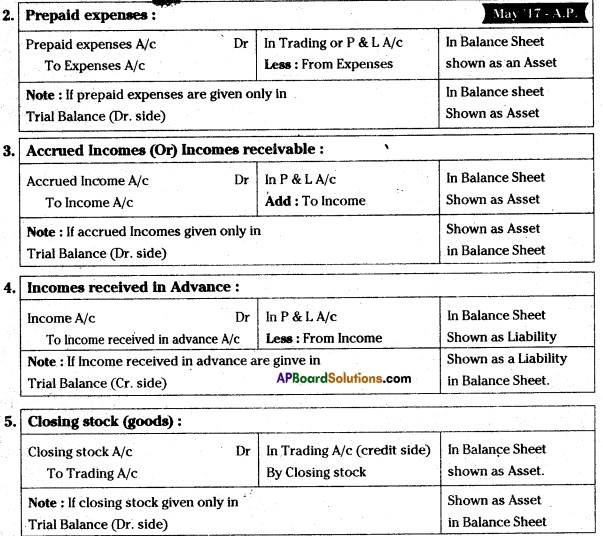
10th Class Biology 10th Lesson Natural Resources 1 Mark Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Recently a new programme was launched in our state known as “Vanam – Manain”. Prepare any two slogans to promote the programme.
Answer:
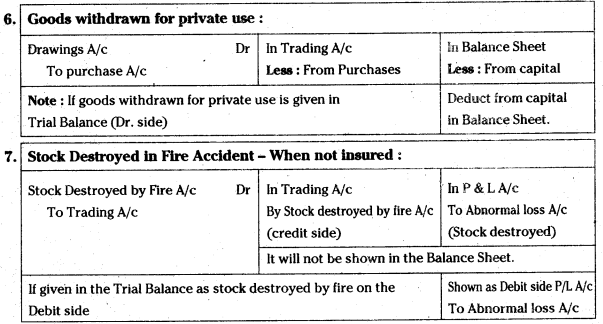
a) Save forest, forest will save you.
b) Grow the plants and get the fresh air.
Question 2.
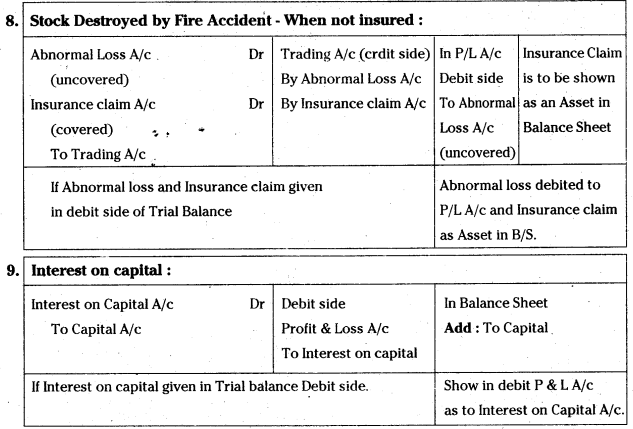
Suggest any two practices suitable to farmers with less water resources.
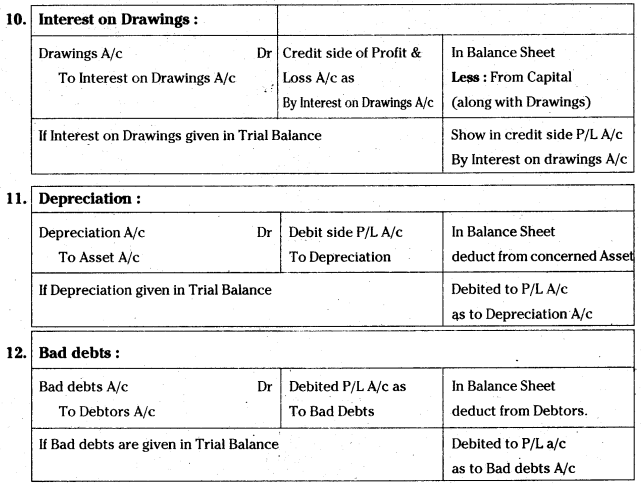
Answer:
- Construction of percolation tanks (or) Soak pits
- Irrigation techniques like drip irrigation and usage of sprinklers.

Question 3.
Why should we conserve forests? Give two reasons.
Answer:
a) Forests serve as lungs for the world. They purify the air and protect the earth from greenhouse effect and global warming,
b) Forests are rich habitats for plants
Question 4.
Ravi observed  symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.
symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.
Answer:
The symbol on the plastic bottle indicates that the bottle is made from recycled plastic and after its use it can be recycled.
Question 5.
Write any two suggestions for the conservation of biodiversity at your village.
Answer:
- Protecting and preserving the natural habitats of birds and animals.
- Replace the wood products with alternative sources.
- Using Recycled products and following the 4’R Principle in day to day life.
Question 6.
Suggest any two activities to check soil erosion in your school.
Answer:
- Observe the school ground after the rain.
- Conduct a field project on soil erosion.
Question 7.
To create awareness on “Water conservation” in your locality, what slogan you will suggest?
Prepare two slogans on ‘Save Water’ propaganda.
Answer:
“Don’t Waste Water”.
“Save every drop”.
“Water is life”.
Question 8.
The symbol  is there on the item you bought. What it instructs? (OR)
is there on the item you bought. What it instructs? (OR)
What does the given logo indicate? What does it mean?

Answer:
It is the Recycle logo. It indicates that the item we bought is prepared from recycled materials or the item can be recycled after use.

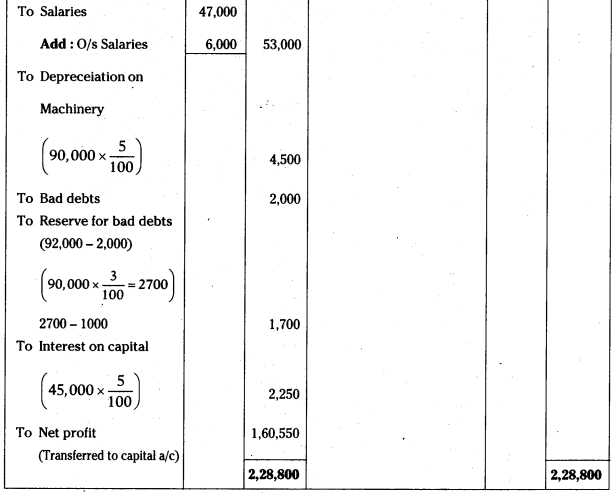
Question 9.
What happens if the forest area decreases rapidly?
Answer:
If the forest area decreases
- It destroys wildlife habitat.
- It increases soil erosion.
- It releases green house gases into the atmosphere contributing to global warming.
- It also harms people who relay on forest for their survival, hunting and gathering, harvesting forest products or using timber and firewood.
Question 10.
Write two activities which you are performing to save electricity.
(OR)
Write any two measures vou take in your home to reduce the consumption of electricity.
Answer:
- We can reduce the consumption of electricity by putting off the fans and lights when there is no need.
- We can use LED (Lighting Emitting Device) bulbs to save electricity.
- To shut down laptops and computers when they are not in use.
Question 11.
Prepare two slogans on protecting non-renewable resources.
Answer:
- Use Biofuel – Reduce Fossil Fuel.
- Use alternative resources – Save the environment.
Question 12.
Write two examples for non-renewable resources.
Answer:
Examples for non-renewable resources are coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Question 13.
What is sustainable development? Is it needful for us?
Answer:
When we use the environment In ways that ensure we have resources for the future, It Is called sustainable development. It Is needed because development and conservation can coexist In harmony.

Question 14.
What are examples for natural resources?
Answer:
Examples for natural resources are water, soil, forests, flora, fauna, etc.
Question 15.
What are percolation tanks?
Answer:
Percolation tanks are normally earthen dams with masonry structures where water may overflow.
Question 16.
What are Kharif crops?
Answer:
Crops grown In the rainy season are termed as Kharif crops, e.g: Paddy, maize, millet and cotton crops.
Question 17.
What are Rabi crops?
Answer:
The crops that are grown only in winter season are generally called Rabi crops, e.g.: Wheat, Gram and Mustard.
Question 18.
What is the average fall of ground water level in Andhra Pradesh state during the period of 1998 – 2002?
Answer:
The average fall of ground water level In Andhra Pradesh state during the period of 1998 – 2002 Is 3 meters.
Question 19.
Which agency in villages of Warangal district helped in recharging wells that were being dried up?
Answer:
Centre for water solidarity (Secundrabad, T.S.) helped In recharging wells that were drying up In the villages.
Question 20.
Give examples for micro irrigation techniques.
Answer:
Drip irrigation, sprinklers are the examples for micro irrigation techniques.

Question 21.
Mow did the boundaries between the villages were fixed in ancient times?
Answer:
In ancient times village boundaries were decided upon a water shed (Land between water sources usually of two rivers or streams) basis fixed at the common point of the drainage system In between two villages by the expert farmers In the village.
Question 22.
Expand ICRISAT.
Answer:
International Crop Research Institute for Semi-Arid Tropics.
Question 23.
What is the other name for Sri Rama Sagar Project?
Answer:
Sri Rama Sagar Project also known as the Pochampadu project on the Godavari river,
Question 24.
What is the use qf planting Gliricidia on field bunds?
Answer:
Planting Gliricidia on field bunds help In strengthen them and make the soli nitrogen-rich.
Question 25.
What is the micro irrigation system that can reduce water consumption by 70%?
Answer:
Drip irrigation can reduce water consumption by 70%.
Question 26.
Who predicted that by 2025, 1.8 billion people will be living in countries or regions with absolute water scarcity ?
Answer:
The Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) of the united nations has predicted that by 2025, 1.8 billion people will be living in countries or regions with absolute water scarcity.
Question 27.
What happens if we use resources wisely?
Answer:
If resources are used wisely and efficiently they will last much longer. Through conservation people can reduce waste and manage natural resources wisely.

Question 28.
Give an example of country where restrictions on water usage were imposed.
Answer:
In Australia restrictions were imposed on activities like, watering lawns by using sprinkler systems, washing vehicles, using house pipes to clean paved areas, and refilling swimming pools.
Question 29.
Why are the natural resources used up quickly?
Answer:
The population of human beings has grown enormously in the past two centuries. Billions of people use up resources quickly as they eat food, build houses, produce goods and burn fuel for transportation and electricity.
Question 30.
What happens if we damage a forest resource?
Answer:
Harm to animals that may be forced to find new habitats. If we damage a forest resource indiscriminately the depletion of resources occur and we may have to face problem for water and timber in future.
Question 31.
What are the results of deforestation?
Answer:
Deforestation destroys wild life habitats and increases soil erosion and also releases green house gases into atmosphere, contributing to global warming.
Question 32.
How the people in China and Mexico recycle paper? (OR)
Give an example of recycling paper by the people. What is the use of recycling paper?
Answer:
People in China and Mexico reuse much of their waste paper, including writing paper, wrapping paper and card board.
Question 33.
How the soil is important for us ? How the soil is importane for us?
Answer:
Soil is vital to food production and also important to plants that grow in the wild.
Question 34.
What are the reasons for depletion of nutrients in soil?
Answer:
Poor farming methods, such as repeatedly planting the same type of crop in the same place cause depletion of nutrients in the soil.

Question 35.
What is biodiversity?
Answer:
Biodiversity is the variety of living things that populate the Earth.
Question 36.
How are people speeding up the loss of biodiversity?
Answer:
Through hunting, pollution, habitat destruction, people are speeding up the loss of biodiversity.
Question 37.
How many plant species are being used by us for medicines world wide?
Answer:
We use between 50,000 to 70,000 plant species for medicines world wide.
Question 38.
What is selective harvesting?
Answer:
The practice or removing individual plants or small groups of plants leaving other plants standing to anchor the soil is called selective harvesting.
Question 39.
How are fossil fuels produced?
Answer:
The fuels that are produced from the remains of ancient plants and animals are called fossil fuels. They include coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Question 40.
What are the alternate sources of energy?
Answer:
The alternate sources of energy are sun, wind and water.
Question 41.
What are the other products made from petroleum?
Answer:
Plastic, synthetic, rubber, fabrics like nylon, medicines, cosmetics, waxes, cleaning products, medical devices, etc., are the other products made from petroleum.
Question 42.
Which plant’s seeds are used for the production of bio-fuel?
Answer:
Seeds from the Jatropa Curcas plant are used for the production of bio-fuel.

Question 43.
How does the mining method, Mountain Top Removal mining (MTR) devastate the environment?
Answer:
The mining method Mountain Top Removal mining devastate the environment. They destroy soil, plants and animal habitats.
Question 44.
In which country car manufacturers recycle many raw materials used in making automobiles?
Answer:
In Japan car manufacturers recycle many raw materials used in making automobiles.
Question 45.
In which country nearly one third of the iron produced comes from recycled automobiles?
A. In the United States, nearly one-third of the iron produced comes from recycled automobiles.
Question 46.
What does the Indian tradition teach us?
Answer:
The Indian tradition teaches us that all forms of life – human, animal and plant are so closely inter linked that disturbance of one gives rise to imbalance in the other.
Question 47.
Expand IUCN.
Answer:
IUCN stands for International Union for the Conservation of Nature.
Question 48.
How is IUCN planning to protect wild life and habitats?
Answer:
IUCN monitors the status of endangered wild life, threatened national parks and preserves.
Question 49.
What are the four R’s to save the environment?
Answer:
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover are the four R’s to save the environment.
Question 50.
How did Amritha Devi and her daughters protest against the king’s order?
Answer:
- Amritha Devi and her daughters, followed by villagers, who clung to trees in the forest surrounding their village and laid down their lives to save them.
- They protested against the king’s order to collect wood for the construction of his palace.

Question 51.
Write a method of soil conservation.
Answer:
One soil conservating method is called contour strip cropping. Several crops such as corn, wheat and clover are planted to alternating strips across a slope or across the path of the prevailing wind.
Question 52.
What is the rate of extinction by the estimation of the scientists?
Answer:
- Scientists estimate that the current rate of extinction is 1,000 times the natural rate through hunting, pollution, habitat destruction.
- Based on various estimates of the number of species on Earth, we could be losing anywhere from 200 to 1,00,000 species each year.
Question 53.
What is the need to protect biodiversity?
Answer:
We need to protect biodiversity to ensure plentiful and varied food sources. Biodiversity is important for more than just food because many plant species are being used for medicines.
Question 54.
Mention two ways in which water harvesting can be undertaken?
Answer:
The two ways by which water harvesting can be undertaken are
- Capturing run off water from, rooftops.
- Capturing run off water from local catchments.
Question 55.
On the basis of the issues raised in the chapter management of natural resources, what changes you in corporate in your lifestyle in a move towards a sustainable use of our resources?
Answer:
I would incorporate the maximum of four R’s i.e., reduce, recycle, reuse and recover in my lifestyle in a move towards a sustainable use of our resources.
10th Class Biology 10th Lesson Natural Resources 2 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Rahul remarked that different human activities are responsible for global warming.
What might be the reasons for his statement?
Answer:
- Deforestation.
- Industrialisation and urbanization.
- Conversion of agriculture lands into residential areas.
- Home appliances like A/C, refrigerators, vehicle pollution.
- Population explosion.

Question 2.
What steps do you take to improve natural resources?
Answer:
- Motivate the people to conserve water.
- Try to avoid wastage of water whenever possible.
- Plantation in the vacant lands.
- Educating the farmer regarding proper utilization of water for irrigation.
- Encourage the people to recycle the water wherever possible.
Question 3.
Proper utilisation of natural resources is the way to show gratitude to our nation.
Can you support this statement? Give your argument.
Answer:
- Natural resources of a nation influence its economical and social development.
- Natural resources are freely available in nature and help in many activities and development of people.
- The generation of natural resources take a lot of time.
- They disappear by indiscriminate usage.
- So proper utilization of natural resources is the way to show gratitude to our nation.
Question 4.
The humans are utilising natural resources indiscriminately. These resources are decreasing more rapidly. Guess what will be the consequences in future?
Answer:
Indiscriminate usage of natural resources causes the following consequences.
- Reduction in rainfall
- Drought will occur.
- Atmospheric temperature becomes increase.
- The rare species become extinct.
Question 5.
Write any four slogans on the conservation of natural resources.
Answer:
Slogans:
- Waste water today – live in desert tomorrow
- Practice eco-friendly methods.
- Use natural resources judiciously.
- Save nature – Save future.
Question 6.
There is an increase in the atmospheric temperature year by year. If it continues, guess and write what would be the consequences?
Answer:
If the temperature on earth increases, the consequences would be as follows.
a) All the glaciers and the frozen ice in the polar region start melting leading to rise in the sea water levels.
b) It results in the submergence of low lying coastal areas throughout the world. Millions of people of those areas would lost their homes.
c) Changes in rainfall patterns take place and it result in the occurance of droughts and decrease in crop production.
d) Global warming results in climate change which cause the breakout of climatic sensitive diseases like Malaria, Dengue, Diarrhoea, etc.

Question 7.
There is water scarcity in Ravi’s village during summer. He wants to conduct a rally to create awareness regarding conservation of water. Write any four slogans required to conduct this rally.
Answer:
- Water is life.
- Save water – Save a life.
- Today’s rain water is tomorrow’s life saver.
- No matter your occupation, water conservation is your obligation.
Question 8.
What steps you take to conserve the biofuels in your daily life?
Answer:
- Development and usage of alternative energy resources in place of bio-fuels.
- Minimise the usage of bio-fuels whenever possible.
- Use public transport, ride by bicycle and walking regularly.
- Use and purchase energy efficient appliances to save bio-fuels.
Question 9.
Why do we use fossil fuels judiciously?
Answer:
- Fossil fuels were produced from the remains of ancient plants and animals.
- They include coal, petroleum (oil) and natural gas.
- We need to use fossil fuels judiciously because they are non – renewable resources.
- We need to conserve fossil fuels so we don’t run out of them.
- The pollution caused by them when burnt, to limit our fossil fuel use.
- Future generations may not get these resources.
- Balance in the nature will be disturbed.
- Electricity production will be stopped.
- Vehicles running with fossil fuels become useless.
Question 10.
Write two suggestions to create awareness on groundwater conservation.
Answer:
- We need to adapt different methods to Improve the quality and increase the quantity of groundwater.
- We should dig water harvesting pits for every house.
- We should clean the silt, mud fill in tanks and ponds.
- We should prohibit the establishment of borewells for extraction of groundwater for agricultural and Industrial use.
- These measures will improve quality and quantity of groundwater.

Question 11.
What is the importance of 4R’s in achieving the goal of “Swachh Bharat”?
Answer:
- Reduce the production of garbage.
- Reuse the garbage for the production of manure and electricity.
- Recycle the garbage by separating It as dry and wet garbage.
- Recover the plants.
Question 12.
Suggest four measures to conserve fossil fuels.
Answer:
Measures to conserve fossil fuels:
- Usage of alternatives to fossil fuel.
- Minimise the usage of fossil fuel.
- Walk, ride by bicycle and use public transportation whenever possible.
- Purchase energy efficient appliances.
- Turn off light and other electronics when you are not using them.
Question 13.
The indiscriminate digging of Borewells may result in what type of consequences in future?
Answer:
- Due to over drilling of borewells and pulling out water by electric motors, the ground water level Is decreasing day by day.
- It Is goes on without recharging, ground water becomes scarce.
- It shows impact on agriculture and the productivity will decrease.
- Fluorine levels In ground water will increase.
- Sometimes, saline water may intrude Into the interior places of land and water becomes unfit for consumption.
- Farmers have to drill the bore wells to more depths which Increase the losses for them.
Question 14.
Ramaiah made broad bed furrow around his field under employment guarantee scheme. Guess the reasons for if. If all the farmers of your village work together, will their water scarcity meet?
Answer:
The reason for Ramaiah making broad bed furrow around his field was, it is useful to conserve soil and water, fertilizer application weeding operations. It also conserves rain water.
The farmers are over coming the water scarcity by sharing water available in the village. They formed groups of farmer including large and small ones who would use the same water resource. Farmers were also motivated to use irrigation techniques like drip irrigation.

Question 15.
What are renewable sources and non-renewable resources?
Answer:
Renewable resources: Resources that can be replaced after they are used are called renewable resources.
Ex: Air, water and soil.
Non-renewable resources: Some other resources, cannot be replaced at all: Once they are used up they are gone forever and are called non renewable resources.
Ex: Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas (fossil fuels).
Question 16.
How do people waste natural resources?
Answer:
- People often waste natural resources.
- Animals are over hunted, forests are cleared, exposing land to wind and water damage.
- Fertile soil is exhausted and lost to erosion because of poor farming practices.
- Fuel supplies are depleted.
- Water and air are polluted.
- Water resources is indiscriminately used for crop growth.
Question 17.
How do people use the forest resources differently?
Answer:
- The need to conserve resources often conflicts with other needs.
- For some people, a forest area may be a good place to put a farm.
- A timber company may want to harvest the area’s trees for construction materials.
- A business company may want to build a factory or a shopping mall on the land.
Question 18.
What are die effects of deforestation?
Answer:
- Deforestation destroys wild life habitats and increases soil erosion.
- It also releases green house gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming,
- Deforestation accounts for 15 per cent of the world’s green house gas emissions.
- Deforestation also harms the people who rely on forests for their survival, hunting and gathering, harvesting forest products, or using the timber for firewood.

Question 19.
In your opinion What are the causes for soil erosion?
Answer:
- Soil erosion is caused by poor farming methods such as repeatedly planting the same type of crop in the same place.
- These methods deplete nutrients in the soil.
- Soil erosion Is also caused by water and wind currents.
- When farmers plough up and down hills, soil erosion occurs.
- Overgrazing by cattle also causes soil erosion.
- Natural floods causes the extensive damage to the top layer of the soil.
Question 20.
What is Biodiversity? Explain.
(OR)
What is the importance of biodiversity?
Answer:
- Biodiversity is the variety of living things that populate the earth.
- The products and benefits we get from nature rely on biodiversity.
- We need to protect biodiversity to ensure plentiful and varied food sources.
- Biodiversity is important for more than just food. For instance we use between 50,000 to 70,000 plant species for medicines world wide.
Question 21.
How can we use the fossil fuels carefully?
Answer:
We can use the fossil fuels carefully by taking the following measures.
- Turn off lights and other electronics when we are not using them.
- Purchase energy-efficient appliances.
- Walk, ride a bicycle, if the distance is less.
- Use public transportation whenever possible.
- It is better to prefer public transport system like bus or train, instead of travel in personal vehicles.

Question 22.
Why the prices of aluminium and iron are expensive?
Answer:
Earth’s supply of raw material resources is in danger. Many mineral deposits that have been located and mapped have been depleted. As the ores for minerals like aluminium and iron become harder to find and extract, their prices go up.
This makes tools and machinery more expensive to purchase and operate.
Question 23.
What are the effects of mining?
Answer:
- Many mining methods such as Mountain Top Removal mining (MTR) devastate the environment.
- They destroy soil, plants and animal habitats.
- Many mining methods also pollute water and air, as toxic chemicals leak into the surrounding ecosystem.
Question 24.
What did Smt. Indira Gandhi said, while launching the world conservation strategy in India on 6th March 1980?
Answer:
“The interest in conservation is not a sentimental one but the discovery of a truth well known to our ancient stages. The Indian tradition teaches us that all forms of life- human, animal and plant – are so closely inter-linked that disturbance in one gives rise to imbalance in the other” said by Smt. Indira Gandhi.
Question 25.
What are the steps taken by the government to conserve resources?
Answer:
- Government enacts laws defining how land should be used and which areas should be set aside as parks and wild life preserves.
- The government enforces laws designed to protect the environment from pollution, such as requiring factories to install pollution control devices and also provide incentives for conserving resources.
Question 26.
What is the necessity of sustainable management of natural resources? Out of the two methods reuse and recycle which one would you suggest to practice and why?
Answer:
- Sustainable management of natural resources is necessary to Increase the over all life of natural resources specially non renewable resources and also to control the environmental pollution.
- Both reuse and recycle are the good choice.
- Reuse: If we reuse something then the cost of recycle will be saved.
- Recycle: It is not necessary that each and everything can be reused, so after getting recycled the life of the resource will be enhanced.

Question 27.
“Burning fossil fuels is a cause of global warming”. Justify this statement?
Answer:
- Fossil fuels are composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and sulphur.
- When these are burnt they produce CO2, H2O, Oxides of Nitrogen and Sulphur.
- Incomplete combustion of fossil fuels produces green house gases such as CO2,
- If huge amount of fossil fuels are burnt, It would produce high amount of CO2 resulting intense global warming.
Question 28.
Can you suggest some changes in your school which would make it environment friendly?
Answer:
The changes that would make my school environment friendly are
- Save energy by turning off lights that we are not using.
- I will suggest to buy recycled paper for decoration and other purposes.
- Use writing paper on both the sides.
- Growing trees and plants all around the play ground.

Question 29.
What is the necessity of replenishment of forest? State four reasons.
Answer:
The replenishment of forest is necessary because of the following reasons.
- It is used to conserve soil.
- It provides shelter to wild animals.
- It reduces atmospheric pollution.
- It controls flood and increases frequency of rainfall.
10th Class Biology 10th Lesson Natural Resources 4 Marks Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Forest is renewable resource. But, each year, the Earth loses about 36 million acres of forest. In this type of situation, what suggestions do you give to save forests from turning into non-renewable resources ?
Answer:
- Forests are the lungs of the world. So I will suggest the following measures to save forests from turning into non-renewable resources.
- Sustainable forestry practices for ensuing resources into the future.
- Low impact logging practices, harvesting with natural regeneration in mind. Prevention of removing all the high value trees or all the largest trees from the forests. Recycling methods should be adopted.
- Replace wood products with alternative sources.
- Preventing forest fires.
- Implementing methods like agro forestry, social forestry crop rotation, green plantation, etc. are essential.
Question 2.
What are four R’s? Explain how they help to conserve the environment?
(OR)
Write about the 4 ‘R’s needed for the protection and conservation of environment.
Answer:
By pursuing the maximum of four R’s i.e., Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover, we can save the environment in an effective way.
- Reduce : It means to use less, I would save electricity by switching off unnecessary lights and fans, prefer walking or cycling than using a vechicle, turn off the engine of car at red light, repair leaky taps and would not waste food.
- Recycle: It means to collect used things like plastic, paper, galss and metal items and recycle these materials to make required things instead of synthesising or extracting fresh plastic, paper, glass or metal.
- Reuse: It refers to use things again and again. For example instead of throwing away used envelops, they can be used by pasting new labels.
- Recover: We should implement ‘recover’ to prevent environmental threat. For example when we cut trees to construct industries or roads for transportation, it is important to grow trees in another areas.

Question 3.
What steps you would like to follow on your part to conserve bio-diversity?
Answer:
- Biodiversity is the variety of living things that populate the earth.
- To conserve biodiversity we should avoid hunting.
- Sustainable forest conservation methods should be followed.
- I will actively participate Vana Mahosthavam programmes.
- I will educate and encourage people and make them participate in conservation programmes.
- Create awareness programmes in and around school.
- Writing slogans and also make some posters about conservation of biodiversity
- Judicious use of electricity wherever possible.
- Finding out of various alternative sources of energy.
- Plant the saplings in the habitat.
- Encouraging of social forestry.
Question 4.
Observe the pie diagram showing water resources available in our state for agriculture and answer the given questions.
 A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?
A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?
B) What are the consequences of excess utilization of underground water?
C) Which water resource should be utilized for agriculture?
D) What are the alternative ways to increase the underground water resources?
Answer:
A) Ground water.
B) Underground water table will be depleted and scarcity of drinking water will arise.
C)
- Tanks should be constructed to harvest with rain water.
- Projects should be constructed across the rivers to store water that can be utilized for agriculture.
D)
- Construction of rain water storage structures on large scale.
- Constructing soaking or percolation pits.
- Contour field bunding.
- Recharge of wells by building dykes or barriers in the nalla.
- Plantation in waste lands.
- Adapting micro irrigation techniques.
(Any two points you can write)

Question 5.
Forests are renewable resource. Write four sentences supporting this.
(OR)
“Forest is a renewable resource”. Do you agree? Justify.
Answer:
- Forests are rich habitat for plants and animals. Forests serve as lungs for the world and a bed of nutrients for new fife to prosper.
- Forest’s pure air protects the earth from green house effect by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and converts it into oxygen.
- Many fruits, medicines, dyes, sandle wood and bamboo is obtained from forest by local people.
- Forest provide employment to large number of people and also help in generating revenue.
Question 6.
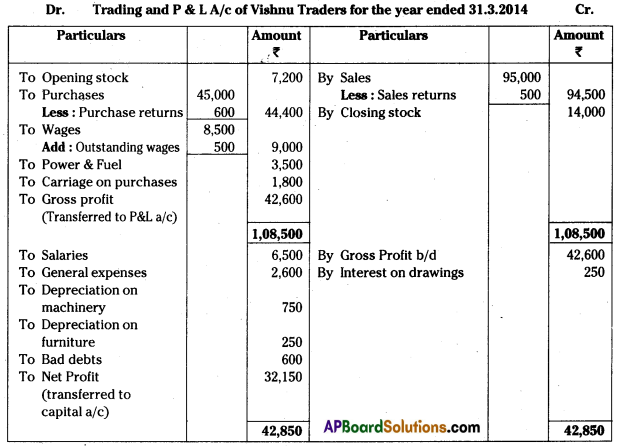
Observe the above table and answer the following questions.
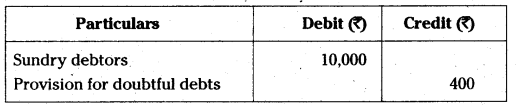
| Village | Type of Farmer | Income per acre on Crops |
| Paddy | Cotton | Mirchi | Maize |
| A | Small | 7,500 | 9,300 | 5,200 | 5,000 |
| Large | 26,700 | 38,000 | 16,700 | 12,900 |
| B | Small | 7,200 | 8,750 | 4,900 | 5,100 |
| Large | 32,900 | 42,000 | 18,400 | 13,700′ |
1. Which crop is most suitable to cultivate for small farmer in both the villages?
Answer:
Cotton, paddy
2. If you are a large farmer, which crop do you select to cultivate?
Answer:
Cotton, paddy, mirchi
3. What similarities you have identified in village A and village B?
Answer:
Small and large fanners cultivated same type of crop in both villages. Large farmer gets more income per acre on crops than small farmer in both the villages.
4. Which is the lowest income crop ?
Answer:
Mirchi.
5. Is there any relationship between production of crops and income ? How ?
Answer:
Commercial crops are good for income. Income may or may not related to production of crop. It depends upon demand of the market.

Question 7.
Read the given information and answer the following questions.
A survey was conducted in two villages, Vanaparthy and Vaddicherla of Warangal district in Telangana State. The first with no scarcity and the second with scarce groundwater. Well census was carried out in the villages in order to get a complete picture of well irrigation and its status as well as availability of water. There are no alternative sources of supply as against wells in Vaddicherla, where there is an existing tank that has been converted into a percolation tank, so that the water situation is much better in Vanaparthy.
i) Why did they conduct survey?
Answer:
A compartive study on available water resources irigation method in the Vaddicharla and Wanaparthi of Warangal Dist of Telangana State.
ii) What are irrigation resources in Telangana State?
Answer:
Lakes, wells, canals and ground water etc…,
iii) In which village, do you suggest drip irrigation?
Answer:
Vaddicherla.
iv) Why the water situation is much better in Vanaparthy village compared to Vaddicherla?
Answer:
Existing tank has been converted into a percolation tank.
Question 8.
Observe the Pie diagram and answer the following questions.
 i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
Answer:
Coal, natural gas, oils are fossil fuels.
ii) Why wastes should be considered as primary energy source in future?
Answer:
The fossil fuels may be exhausted in future. So we may be considered that wastes are primary alternative energy resources.
iii) Why can’t we depend on fossil fuels forever?
Answer:
We can’t depend on fossil fuels forever because fossil fuels are non-renewable resources.
iv) What are the alternatives for fossil fuels?
Answer:
Solar energy, wind energy, tide energy, nuclear energy, energy from waste materials.

Question 9.
Explain the importance and implementation of community based interventions and farmer based interventions for water management.
Answer:
Community based interventions:
- For water harvesting, there is an urgent need to construct earthen and masonry dams. They help us to store rain water during rainy seasons. They are help in increasing the ground water table.
- Construction of percolation pits and field bunding are very helpful in the harvesting every rain drop.
- Open dry wells near nalla canal were recharged by building dykes or barriers in the nalla and maintaining the run – off rain water. The ground water is recharged by these community based interventions.
Farmer based interventions: - Broad Bed Furrow (BBF) land form and contour planting methods are very useful to conserve soil, water and fertilizer application and weeding operations.
- Planting Gliricidia, a leguminous plant adapted to grow in dry areas on field bunds to strengthen them and make the soil nitrogen rich.
- Farmers were encouraged to use water resource jointly and irrigate land using micro irrigation methods like sprinklers and drip irrigation.
Question 10.
Explain the farmer based and community based interventions to conserve soil and water resources.
Answer:
| Water Management | Collected information |
| Farmer based water management | 1. Farmer based water management implemented individual fields were Broad Bed Furrow (BBF) land form and Contour Planting to conserve in situ soil and water. 2. Use of tropiculator for planting, fertilizer application and weeding operations. Planting Gliricidia on field bunds to strengthen bunds conserve rain water and supply nitrogen rich organic matter for in situ application to crops. 3. Farmers will obtain 250 kg more pigeon pea and 50 kg more maize per hectare using broad bed furrows and micro irrigation techniques. |
| Community based water management | 1. Fourteen water storage structures (one earthen and 13 masonry dams) with water storage capacity of 300 to 2000 m3 were to be constructed in Kothapally village of Rangareddy district. 2. More than 250 rain harvesting structures such as checkdams mini percolation pits, sunken pits and gully plugs were erected in watershed throughout the topo – sequence. 3. Farmers were encouraged for water sharing methods. They formed groups of farmers including large and small ones who would use the same water resource. 4. Farmers have to motivated to use irrigation techni- quies like drip irrigation, sprinklers, etc. 5. Construction of soak pits will help to tap rain water optimally should carry out as community effort. |

Question 11.
“The humans who were developed by using the natural resources, today has become the reason for destroying them”. Explain analytically.
Answer:
“The humans who were developed by using the natural resources, today has become the reason for destroying them” – This statement is absolutely true.
- Primitive man lived in forests and hills. He used the natural resources for his livelyhood. He worshipped nature and used them wisely for his development.
- After his development, he becomes greedy and using the natural resources indiscriminately and held responsible for their destruction.
- To meet the needs of growing population, industrialization, urbanization, and huge constructive activities, man utilised natural resources Indiscriminately. At the same time, he did not planned for their revival.
- But now he realised the importance of natural resources and taken up steps for their conservation. The concept of “Sustainable development” is being implemented in natural resource management.
- He focussed on development of alternatives for fossil fuels, conservation of water and soil at community level and farmer based interventions.
- Now he is so keen on conserving forests, wild life and biodiversity.
- He is so cautious in minimising the utilization of natural resources by following 4’R principle in the day to day life [R – Reduce, R – Reuse, R – Recycle, R – Recover]
- Now, he is adopting micro-irrigation methods like sprinklers and drip Irrigation to minimise the water usage in low water available areas.
- He is very interested in following eco-friendly techniques, natural farming methods, using biofertilizers, vermicompost and natural pest control methods in place of toxic chemical pesticides.
Question 12.
The wells and tanks in your village become dry. Ground water levels decreased. Assume the causes for this. Will there be no water scarcity if all the farmers of your village work collectively?
Answer:
Causes for decreasing ground water levels:
- Varying monsoon behaviour in recent years, there is a pressure on ground water utilization.
- Indiscriminate tapping of ground water in our village by too much drilling and construction of deep tube wells and bore wells have resulted in over exploitation and depletion of ground water resources.
- There will be no water scarcity if all the farmers of our village work collectively. Farmers in our village were encouraged to use water resource jointly and irrigate land using micro irrigation techniques. By using micro irrigation techniques farmers in our village obtained more crop yield. Farmers in our village follow the micro irrigation method i.e. drip irrigation and can reduce water consumption by 70% in our village.
Question 13.
Whom do you meet to collect the information of the methods of farmer based, community based water management? Prepare information table to note down your observation.
Answer:
I will meet officials of International Crop Research Institute for Semi – Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) located at Hyderabad to collect information of the methods of farmer based and community based water management.
I also collect information from Central Research Institute for Dry Land Agriculture (CRIDA), National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA), District Water Management Agency (DWMA) and M Venkatarangaiah Foundation (MVF) and NGO.
The information I gathered from these institutions is summarised below.
Information table:
For Information table See Q.No. 10 in 4 Marks.

Question 14.
Think that there is much scarcity of water for drinking and cultivation in your village. What advice do you give to prevent this?
(OR)
How do you overcome the problem of water scarcity in your village?
Answer:
- Motivate the people to conserve water.
- I will educate the people to avoid wastage of water whenever possible.
- Construction of recharge pits in the house, school and in the open areas to increase the underground water level.
- Planting trees wherever possible in the village particularly in the vacant lands.
- Educate the farmers about the micro irrigation system like drip irrigation, sprin¬klers, etc.
- Encourage the farmers to form groups to share available water among themselves.
- Construction of percolation tanks in the low lying areas of the village.
Question 15.
What type of fossil fuels are used in your house? What measures do you take to conserve them?
Answer:
Fossil fuels are sources of energy for cooking, heating and burning in our households. Petrol and diesel are being used in our house for transport and running generators and water pumps.
Measures to be taken to conserve fossil fuels in my house :
- I will put the food material to be cooked on the stove only after arranging all the things which are necessary for cooking.
- By using pressure cookers 20% gas on rice and 41.5% on meat would be saved when compared to Other cooking means.
- We must reduce the flame as soon as the boiling process starts in a pressure cooker. This process saves nearly 35% of fuel.
- I will soak the food material before cooking. It saves 22% of fuel.
- I will cook food in broad and low depth vessel.
- I will keep lid on the cooking vessel. If not, it takes more time to cook.
- For short distances to travel I will go by walk to save fuel for longer distance. I use public transport.
- Encourage people to use solar water heater and solar cooker.

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
 Based on the above information write an essay analysing the following aspects:
Based on the above information write an essay analysing the following aspects:![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
 Answer:
Answer:![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
 Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How?
Who decides the sex of the baby – mother or father? How? (OR)
(OR)


 i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross.
i) Write phenotypic ratio of monohybrid cross. All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation.
All pea plants are yellow in F1 generation on self pollination in F1 generation. In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones.
In F2 generation, we can observe that 75% are yellow seed producing pea plants and 25% are green ones. Answer:
Answer: a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child.
a) Draw a probable diagram showing transfer of chromosomes from parents to give birth to male child. b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ?
b) Who determines the sex of the baby? How can you say ? i) What does the flow – chart represent?
i) What does the flow – chart represent?





























 Answer:
Answer: Write a caption on the above cartoon in the contest of forest. (Textbook Page No. 50)
Write a caption on the above cartoon in the contest of forest. (Textbook Page No. 50) symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals.
symbol on the plastic water bottle purchased by him. What does this symbol indicate? and animals. A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture?
A) Which water resource is using more for agriculture? i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram.
i) Identify the fossil fuels from the above diagram. Answer:
Answer: