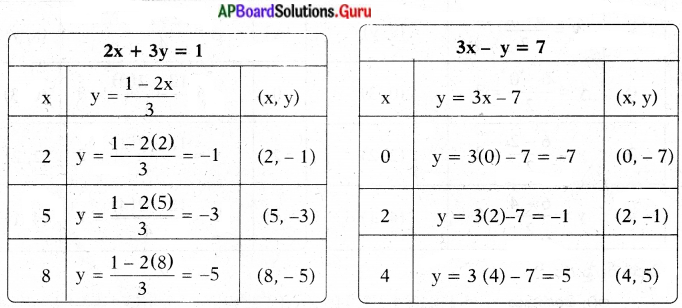
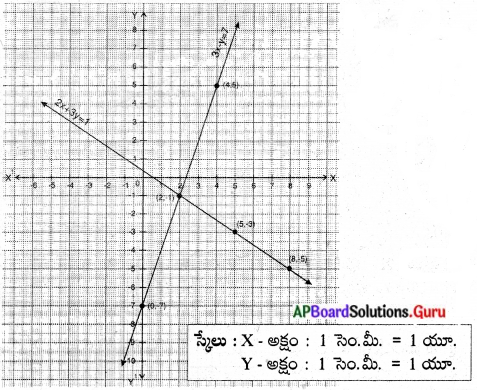
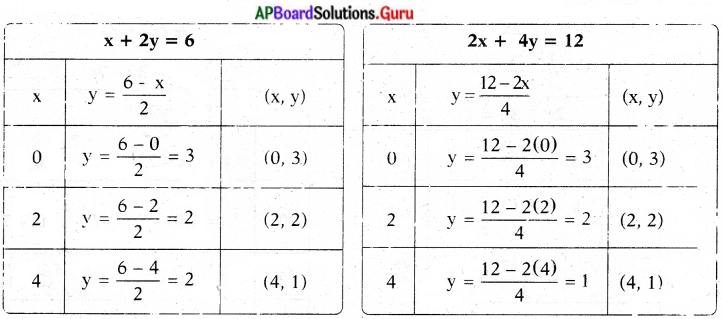
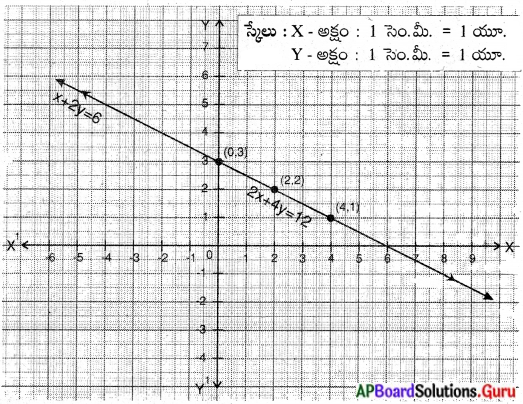
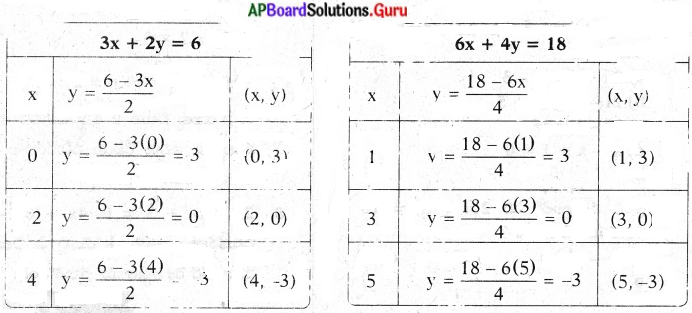
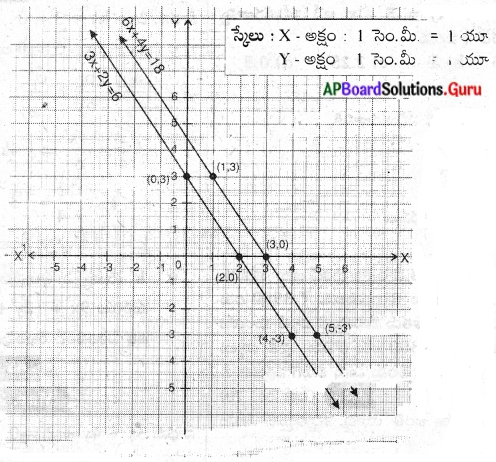
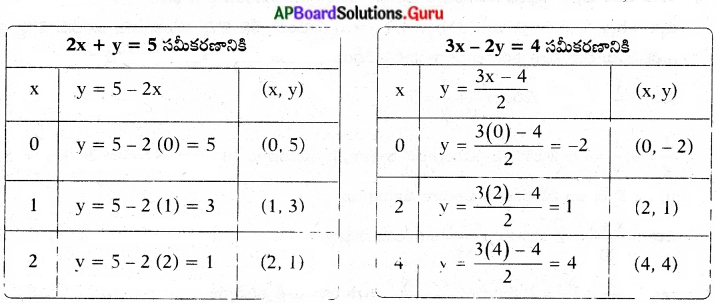
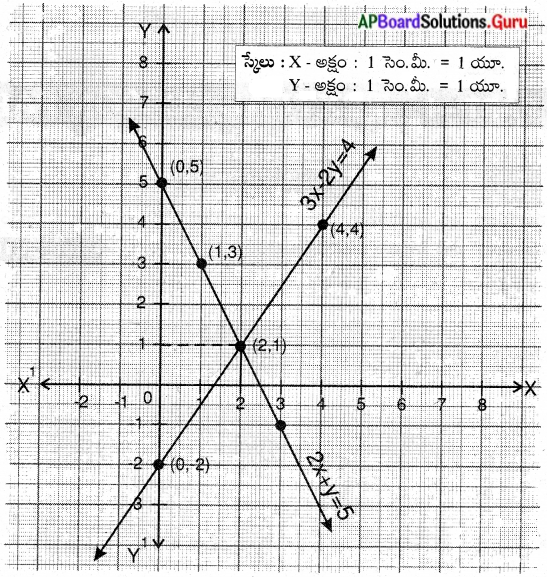
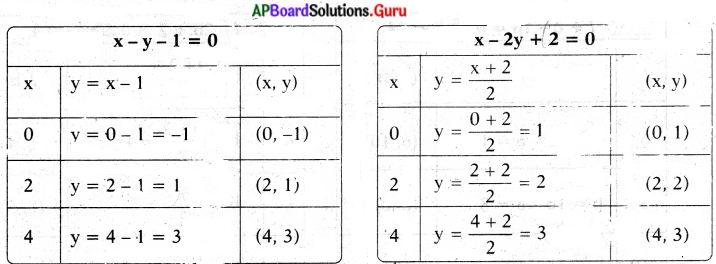
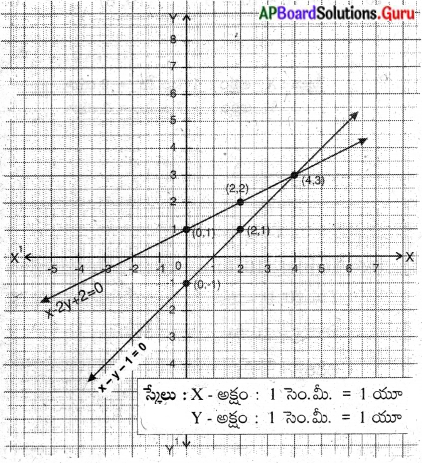
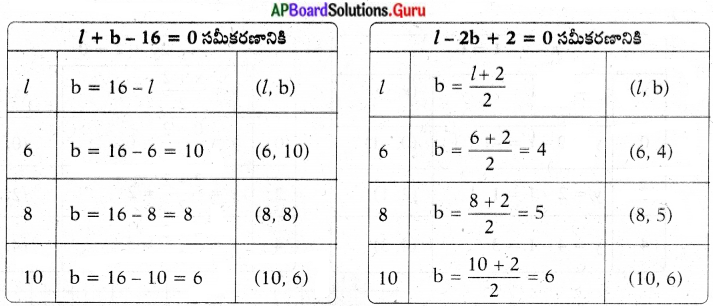
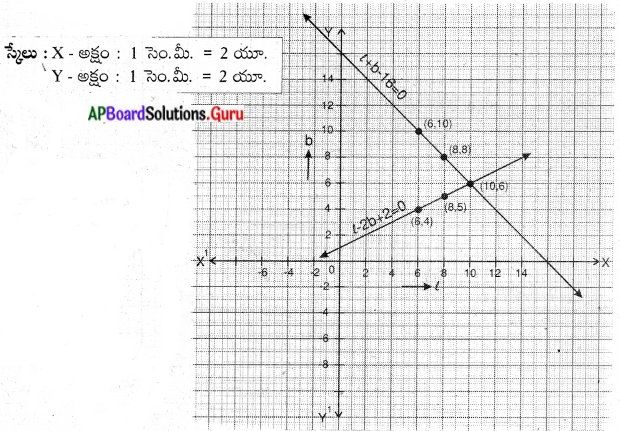
These AP 7th Class English Important Questions 2nd Lesson The Turning Point will help students prepare well for the exams.
AP Board 7th Class English Unit 2 Important Questions and Answers The Turning Point
Reading Comprehension (Seen)
1. Read the following passage carefully.
I was in class V when the Second World War, the largest conflict in human history, was at its peak- Because of the war all the resources were scarce and the prices were not affordable. So, 1 had to take up my first job as a newspaper boy My task was to pick up a bundle of Tamil Newspapers and to deliver them to some local offices, some tea stalls, and occasionally a few homes. Before I set out to distribute, I used to sit on the bench there at the station, open the bundle, and carefully pluck out a copy of the daily newspaper Dinamani. The first page always caught my attention as it was usually filled with photos of fighter aircraft and stories of the Second World War. The German air force called Luftwaffe was sending hundreds of planes and bombers to attack the city and the British Royal Air Force had to deploy their full air force to defend their motherland. The stories would be about brave pilots from both the sides, and how they manoeuvred their aircraft and bombers. As a young boy I used to love the stories of the pilots and their planes. I was curious about planes. I wanted to be a pilot myself. (The Turning Point)
Now, answer the following questions.
1. What was the class that Kalam was in at the time of the Second World War?
Answers:
In class V
2. What made the resources scarce?
Answers:
The Second World War
3. What was his first job?
Answers:
He worked as a newspaper boy.
4. What was the news that was published on the first page of the newspaper?
Answers:
The photos of fighter aircrafts and stories of the Second World War
5. What made the speaker want to become a pilot?
Answer:
The stories of the pilots and their planes in the Second World War
![]()
2. Read the following passage carefully.
My curiosity grew in science because of a very special teacher when I was a ten-year-old boy in Class V. This was indeed a life-changing event. My science teacher’s name was Shri Siva Subramania Iyer. One day the topic of discussion in our class of sixty-five was ‘how birds fly? He drew a sketch of a bird with a tail, wings, feathers, and head on the board and explained how a bird flew. He explained how a bird could lift elf, fly and change direction by using its wings and the tail. He asked us whether we understood.
We gave a gloomy reply – no. Mr. Iyer did not get upset. That evening he took all of us to the seashore. The sunset, waves, cool breeze, and the chirping of birds all together made it a very pleasant atmosphere. He asked all of us to notice how the birds make a formation in a group and fly. He also told us to notice the shape of the formation made by the birds while flew. He drew our attention towards how they flap their wings to fly higher and how they use the tail to propel directions. Mr. Iyer also made us notice how the bird is powered to fly by itself. In 15 minutes, all the students cheerfully shouted “yes sir, we now understand how birds fly on their own.” (The Turning Point)
Now, answer the following questions.
1. What was the speaker curious for?
Answer:
Science
2. What was the topic of discussion in the class?
Answer:
How birds fly
3. What did the teacher explain?
Answer:
The flight or flying of the bird
4. What did the teacher do to make his students understand the topic well?
Answer:
He took his students to the seashore and showed them how the birds really fly.
5. How was the atmosphere at the seashore?
Answer:
It was very pleasant.
3. Read the following passage carefully.
The flight principle got imprinted in my mind and I decided that in the future I will study subjects related to flight. However, as a little boy I needed guidance to pursue this field. I asked my teacher Mr. Iyer to guide and tell me how to pursue my interest. He told me to study and explore the field of aviation science and aeroplanes.
Whatever I had learnt that day changed my life. 1 was inspired to have an aim. Later I realized how important it was to study Physics. I chose Physics. I opted for Aeronautical Engineering at the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Then, I became an Aeronautical Engineer and a space technologist. Mr. Iyer’s class had transformed my life which led me to make a profession out of my passion. Aeronautics, or the science of flight, was special to me. My career began in this field. (The Turning Point)
Now, answer the following questions.
1. What was imprinted in the speaker’s mind?
Answer:
The flight principle
2. What decision did the speaker take to do in future?
Answer:
He wanted to study subjects related to flight.
3. Who guided the speaker to pursue his interest?
Answer:
Mr. Siva Subramania Iyer, his science teacher
4. What did the speaker study at IIT, Madras?
Answer:
Aeronautical Engineering
5. How did the speaker start his career?
Answer:
He started his career as an aeronautical scientist.
![]()
4. Read the following lines carefully.
This is my prayer to thee, My Lord – strike, strike at the root of penury in my heart.
Give me the strength lightly to bear my joys and sorrows.
Give me the strength to make my love fruitful in service.
Give me the strength never to disown the poor or bend my knees before insolent might.
Give me the strength to raise my mind high above daily trifles.
And give me the strength to surrender my strength to thy will with love. (Give Me Strength)
Now, answer the following questions.
1. Who is praying to whom?
Answer:
The post is playing to God
2. What does the poet pray for?
Answer:
For strength to bear his joys end sorrows
3. What does the poet want the Lord to strike?
Answer:
The root of penury in his hear
4. Who are not to be disowned?
Answer:
The poor
5. What is ‘thy will’ according to the poet?
Answer:
To serve human beings
Reading Comprehension (Unseen)
1. Read the following passage carefully.
Up the river Hudson in North America are the Catskill mountains. They are not so high as the Himalayas in India. In a certain village at the foot of these mountains there lived long ago a man called Rip Van Winkle. He was simple and good natured. A very kind neighbour and a great favourite of all the good wives in the neighbourhood. The women took his side and put the blame on Dam Van Winkle. .
The children of the village too would shout with joy whenever they saw him. He made play things for them. He told them fairy tales. So they liked him.
Now, answer the following questions.
a) Why did children like Rip Van Winkle?
Answer:
Rip Van Winkle used to make play things for children. He told them fairy tales. So children liked Rip Van Winkle very much.
b) What kind of man was Rip Van Winkle?
Answer:
Rip Van Winkle was simple and good natured. He was a very kind neighbour and a great favourite of all the women and children in the village.
Choose the correct answer from the choices given.
c) Where are the Catskill mountains?
i) In South America
ii) In Africa
iii) In North America
Answer:
iii) In North America
d) Where did Rip Van Winkle live?
i) On the top of Catskill mountains
ii) In a village at the foot of the Catskill mountains
iii) In a city in North America
Answer:
ii) In a village at the foot of the Catskill mountains
e) Who liked Rip Van Winkle very much?
i) All the wives in the neighbourhood
ii) All the husbands in the neighbourhood
iii)All the friends in the village
Answer:
i) All the wives in the neighbourhood
![]()
2. Read the following passage carefully.
In the American War of Independence, a Corporal and a party of soldiers were ordered to raise a heavy beam for a battery that was being repaired. There were too few men for the work, but the Corporal, full of his dignity did nothing but stand by and shout orders, presently an officer, not in uniform rode up. “Hallo,” he said to Corporal, ‘why don’t you lend your men a hand to get that beam up?” “Don’t you know that I am a Corporal ?” was the reply, “Are you ?” said the officer, who then got down from his horse and joined the men. He worked till the sweat streamed down his face. When the beam had been raised and put to its place, he turned to the Corporal and bade him a low bow, “Good day Mr. Corporal. Next time when you have too few men for this kind of work, send for the Commander in Chief and I shall be happy to help you again.”
It was George Washington himself.
Now, answer the following questions.
a) Why did the officer get down from the horse?
Answer:
The officer got down from his horse to help the men in their work.
b) Who was the person that helped the men and the Corporal?
Answer:
The person that helped the man and the Corporal was none other than the President of America, George Washington.
Choose the correct answer from the choices given.
c) What was to be raised?
i) A battery
ii) A cannon
iii) A beam
Answer:
iii) A beam
d) Who was the person that was having dignity?
i) The Corporal
ii) The Soldier
iii) The President
Answer:
i) The Corporal
e) What did the Corporal have?
i) Very few men
ii) Many ment
iii) A lot of soldiers
Answer:
i) Very few men
Interpretation Of Non-Verbal Information
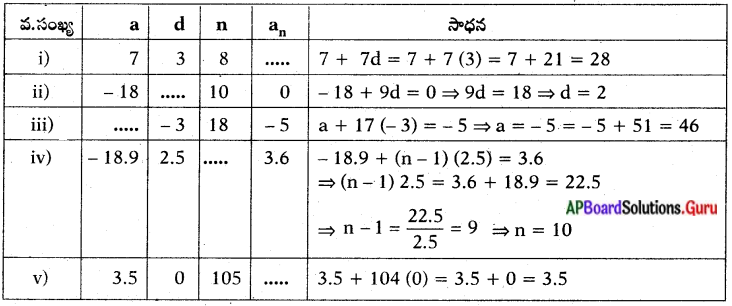
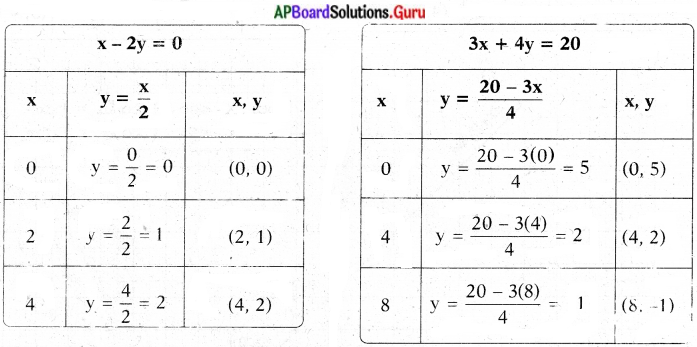
1. In the table given below the data is given about different age groups in different employment sectors.
Read the table and answer the following questions :
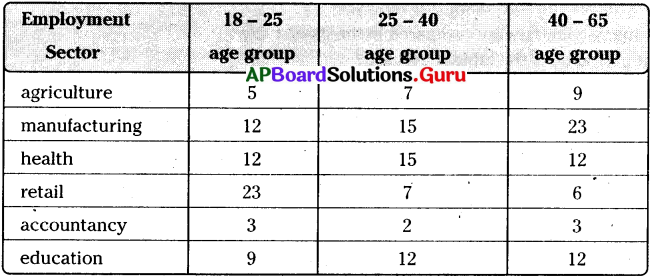
Now answer the following questions.
a) What does the above table show?
b) In which sector are very small member of people working?
c) In which sector are maximum number of people working?
d) In which sector are maximum number of young people working?
e) In which sector are maximum number of old people working?
Answer:
a) The above table shows people of different age groups working under different employment sectors.
b) In accountancy very small number of people are working.
c) In manufacturing sector maximum number of people are working.
d) In retail sector maximum number of young people are working.
e) In manufacturing sector maximum number of old people are working.
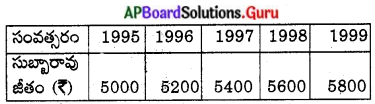
2. Study the table given below and observe the changing patterns of unemployment in some advanced countries.
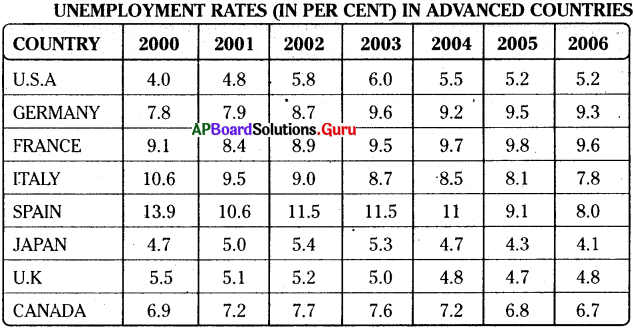
Now answer the following questions.
a) How many countries are compared in the given table?
b) What period does the table represent?
c) Which country has the least unemployment rate in 2005?
d) Which country has a decrease of nearly 6% in unemployment rate between 2000 and 2006?
e) In the case of every country we can notice that (Choose the correct answer.)
i) The unemployment rate is steadily increasing.
ii) The unemployment rate is steadily decreasing.
iii) The unemployment rate is fluctuating, i.e. sometimes it rises and sometimes it falls.
f) Which year recorded the highest unemployment rate for many countries?
g) Which country recorded the least fluctuations in the unemployment rate?
Answer:
a) Eight countries are compared in the given table.
b) The table represents the period 2000 – 2006.
c) Japan has the least unemployment rate in 2005.
d) Spain has a decrease of nearly 6% in unemployment rate between 2000 and 2006.
e) iii
f) 2003
g) Germany
Vocabulary
Synonyms
Choose the words with similar meanings (synonyms) from the list given to the words underlined.


Answer:
a) a) hand over, b) sometimes
b) a) strike, b) place
c) a) benefit, b) presence
d) a) refreshing, b) observe
e) a) driven, b) joyfully
f) a) direct, b) curiosity
Antonyms
Write the opposites (antonyms) for the underlined words.
a) Because of the war all the resources were scarce (a) and the prices were not affordable (b).
b) Before I set out to distribute (a), I used to sit on the bench there at the station, open (b) the bundle and carefully pluck out a copy of the daily newspaper Dinamani.
c) The stories would be about brave (a) pilots from both the sides, and how they maneuvered their aircraft and bombers. As a young (b) boy, I used to love the stories of the pilots and their planes.
d) My curiosity (a) grew in science because of a very special (b) teacher when I was a ten-year-old boy in class V.
e) The sunset (a), waves, cool breeze, and the chirping of birds all together made it a very pleasant (b) atmosphere.
f) Mr. Iyer also made us notice how the bird is powered (a) to fly by itself. In 15 minutes, all the students cheerfully (b) shouted, “Yes sir, we now understand how birds fly on their own.”
Answer:
a) a) abundant / plentiful, b) unaffordable
b) a) collect, b) close
c) a) timid, b) old
d) a) disinterest, b) ordinary
e) a) sunrise, b) unpleasant
0 a) exhausted, b) sorrowfully
Right Forms of the Words
Fill in the blanks with the right form of the words given in the brackets.
a) I was in class V when the Second World War, the ____ (a) (larger / largest) conflict in human history, was at its peak. Because of the war all the resources were ____ (b) (scarce / scarcity) and the prices were not affordable.
b) The German air force called Luftwaffe was ____ (a) (sending / send) hundreds of planes and bombers to attack the city and the British Royal Air Force had to ____ (b) (deploy / deployment) their full air force to defend their motherland.
c) As a young boy, I used to ____ (a) (love / lover) the stories of the pilots and their planes. I was ____ (b) (curiosity / curious) about planes.
d) My ____ (a) (curious / curiosity) grew in science because of a very ____ (b) (special / speciality) teacher when I was a ten-year-old boy in class V.
e) The sunset, waves, cool breeze and the chirping of birds all together made it a very ____ (a) (pleasant / pleasantly) atmosphere. He asked all of us to notice how the birds make a ____ (b) (formed / formation) in a group and fly.
f) Mr. Iyer’s class had ____ (a) (transformation / transformed) my life which ____ (b) (led / leader) me to make a profession out of my passion.
Answer:
a) a) largest, b) scarce
b) a) sending, b) deploy
c) a) love, b) curious
d) a) curiosity, b) special
e) a) pleasant, b) formation
f) a) transformed, b) led
![]()
Spelling Test
Type – 1 : Vowel Clusters
Complete the following words using “ae, ai, au, ea, ee, ei, eo, eu, ia, ie, io, oa, oo, ou, ua, ue or ui”.
a) The first page always c _ _ ght my attent _ _ n as it was usually filled with the photos of fighter aircrafts and stories of the Second World War.
b) As a y _ _ ng boy, I used to love the stories of the piiots and their planes. I was cur _ _ us about planes.
c) My curiosity grew in science bee _ _ se of a very special t _ _ cher when 1 was a ten-year-old boy in class V.
d) He asked us whether we underst _ _ d. We gave a gl _ _ my reply – no.
e) The sunset, waves, c _ _ i breeze and the chirping of birds all together made it a very pi _ _ sant atmosphere.
f) Whatever I had l _ _ rnt that day changed my life. I was Inspired to have an _ _ m.
Answer:
a) caught, attention
b) young, curious
c) because, teacher
d) understood, gloomy
e) cool, pleasant
f) learnt, aim
Type – 2 : Suffixes
Complete the following words with the suitable suffixes given in the brackets.
a) The first page always caught my attent ___ (ion / ian) as it was usual ___ (liy / ly) filled with the photos of figher aircrafts and stories of the Second World War.
b) My curio ___ (city / sity) grew in science because of a very special teach ___ (er / or) when 1 was a ten-year-old boy in class V.
c) He explained how a bird could lift itself, fly and change direct ___ (ion/ian) by using its wings and the tail. He asked us whether we understood. We gave a gloom ___ (y / ey) reply – no.
d) He drew our attention towards how they flap their wings to fly high ___ (est /er) and how they use the tail to propel direct ___ (ions / ians).
e) I opted for aero ___ (nautic / nautical) engineering at the Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Then, I became a space techolog ___ (yist / ist).
Answer:
a) attention, usually
b) curiosity, teacher
c) direction, gloomy
d) higher, directions
e) aeronautical, technologist
Type – 3 . Wronalv Spelt Words
Identify the wrongly spelt word and write its correct spelling in the space provided.
a) canflict, seashore, direction, realize
Answer:
conflict
b) resorce, discussion, chirp, career
Answer:
resource
c) important, field, plesant, deliver
Answer:
pleasant
d) technology, interest, ocassionally explain
Answer:
occasionally
e) caught, discuss, skech, flight
Answer:
sketch
Classification of Words
Arrange the following words under the correct headings.
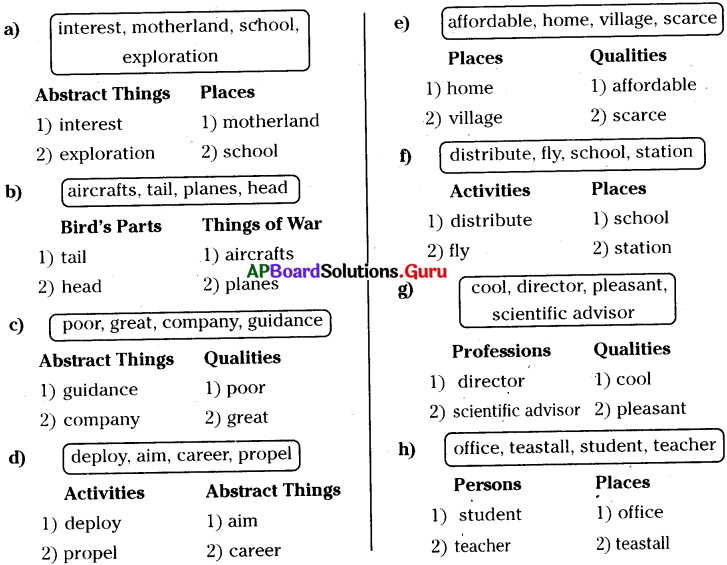
Choice of the Words
Fill in the blanks choosing the suitable words from those given in the box.

Answer:
a) 1) set out, 2) carefully
b) 1) explained, 2) direction
c) 1) attention, 2) propel
d) 1) pursue, 2) explore
Compound Adjectives
1. Fill in the blanks to complete the given paragraph using the compound adjectives given in the box.
long-sleeved high-heeled open-mouthed sweet-looking well-dressed odd-looking part-time
Mrs. Das has a __(1)__ job in a clothes shop. Yesterday, an __(2)__ woman walked into the shop. She was wearing __(3)__ shoes. A __(4)__ dog was with her. “I want a __(5)__ shirt for my dog, please,” she said. “For your dog?” asked Mrs.Das, __(6)__ in surprise. “Yes,” replied the woman. “I want him to be __(7)__ for my next party.”
Answer:
1) part-time,
2) odd-looking,
3) high-heeled,
4) sweet-looking,
5) long-sleeved,
6) open-mouthed,
7) well-dressed.
2. Match the following words in Set – A with Set – B to make compound adjectives and write them in the space given.
| Set – A | Set – B | Compound Adjective |
| 1. cold | A) lasting | cold-blooded |
| 2. four | B) blooded | four-day |
| 3. well | C) day | well-read |
| 4. five | D) read | five-star |
| 5. long | E) star | long-lasting |
Grammar
I. Edit the following passage correcting the underlined parts.
1. Tigers lives (a) in different parts of Asia and Siberia. The tiger or (b) the lion are the biggest animals in the cat family. An (c) male tiger is about 10 feet long. Their (d) coat is yellow and black.
Answer:
a) live, b) and, c) A, d) Its
2. Around the earth there was (a) atmosphere who (b) is like a rind round the (c) fruit. It is made up of oxygen, nitrogen, water vapour or (d) a number of other gases.
Answer:
a) is, b) which, c) a, d) and
3. In a village there lived a boy and his mother. There (a) are (b) very poor. The boy collected wood in (c) the forest and sold it. He cuts (d) down small trees also.
Answer:
a) They, b) were, c) from, d) cut
4. The Banyan tree is possibly a (a) biggest and friendliest of all our trees. We did (b) not see many banyan trees in our cities nowadays. This (c) trees require plenty of space for (d) spread themselves.
Answer:
a) the, d) do, c) These, d) to
![]()
II. Complete the passage choosing the right words from those given below. Each blank is numbered and for each blank four choices are given. Choose the correct answer and write (A), (B), (Q) or (P) in the blanks.
1. Every Sunday Daniel and his family ____(1) to the beach. They live far ____(2) the beach. ____(3) once a week the family gets into the car and Daniel’s father for hours ____(4) they reach the beach.
1) A) goes B) went C) go D) going
2) A) away B) from C) to D) of
3) A) And B) But C) Or D) Yet
4) A) till B) to C) until D) up to
Answer:
1) C 2) B 3) B 4) C
2. Mahatma Gandhi freed India from ____(1) British Empire. He did not ____(2) the British ____(3) guns ____(4) he loved all people.
1) A) a B) an C) the D) some
2) A) fight B)fought C) fighted D) fighting
3) A) from B) by C) with D) ou
4) A) so B) because C) why D) for
A. 1) C 2) A 3) C 4) B
3. Of all ____(1) creatures, butterflies are perhaps ____(2) most beautiful. Thev have such briehtlv ____(3) wings. If vou look at the wings ____(4) a magnifying glass, you will see that they are covered by tiny scales.
1) A) fly B) flying C) flew D) flown
2) A) a B) an C) the D) some
3) A) colour B) colours C) coloured D) colouring
4) A) from B) in C) into D)through
Answer:
1) B 2) C 3) C 4) D
4. Atmosphere makes ____(1) earth a planet of life. It ____(2) us with the air to breathe, protects ____(3) from dangerous solar ravs ____(4) saves us from the extremes of heat and cold.
1) A) a B) an C) the D) that
2) A) supply B) supplies C) supplied D) supplying
3) A) we B) us C) our D) ours
4) A) but B) and C) or D) yet
Answer:
1) C 2) B 3) B 4) B
III. Write the past forms of the words given below.

Answer:
1) belonged
2) grew
3) explained
4) directed
5) understood
6) made
7) shouted
8) decided
9) told
10) opted
IV. Fill in the blanks with past form of the verb given in brackets.
1) He _____ (go) home very late last night.
2) I _____ (meet) her two years ago.
3) They _____ (buy) a new flat last month.
4) Columbus _____ (discover) America.
5) The teacher _____ (appreciate) the students.
Answer:
- went
- met
- bought
- discovered
- appreciated
![]()
V. Fill in the blanks with suitable adverbs of time given iii the box.
1) She has _____ finished training.
2) Have you _____ been to Agra?
3) I have lived in Guntur _____ 2015.
4) He has loved in Chennai _____ a long time.
5) Subhash hasn’t arrived _____ .
6) What time does the film start? It has _____ started.
Answer:
- just
- ever
- since
- for
- yet
- already
Creative Writing
1. In Kalam’s autobiography “The Turning Point”, you have learnt that Kalam worked as a newspaper boy while he was studying in class V. You know that those were the days of the Second World War. Kalam used to sit on the bench there at the station and read the stories of war. Kalam was very enthusiastic about those stories. One day he read the war story of the previous day. Then, he distributed the daily newspaper and went to school. That evening, he started to write a diary.
Imagine that you were Kalam and attempt a diary entry.
Answer:
Friday, 10th September 2021
7:30 p.m.
Dear Diary,
In the morning, the photos I saw are really magnificent. They are the photos of war between Britain and Germany. How attractive they are ! The first page of the daily newspaper Dinamani is totally filled with the photos of fighter aircrafts and stories of the Second World War. The German Air Force is sending hundreds of planes and bombers to attack the city and the British Royal Air Force is deploying their full force to defend their motherland. 1 like those stories of brave pilots from both the sides, and how they manoeuvre their aircrafts and bombers. I love the stories of the pilots and their planes. I am really curious about planes. I love the profession of a pilot. I too shall become a pilot myself. I shall operate the planes. But my family is a poor one where nobody is a literate. What can I do ? Yes, I shall take the guidance from our teachers. That’s all for now! I’m really tired and I am going to sleep.
Kalam
2. In the lesson The Turning Point’ you have learnt that the science teacher Mr. Siva Subramania Iyer took the students of class V to the seashore and taught them how birds fly on their own. The flight priniciple got imprinted in Kalam’s mind and he decided that in the future he would study subjects related to flight. He met Mr. Iyer to seek his guidance.
Now, write a possible conversation between Mr. Iyer and Kalam on the above context.
Answer:
Kalam : Good morning, Sir!
Mr. Iyer : Good morning. What brings you here, Kalam?
Kalam : Sir, yesterday you taught us how birds fly. I now understand how they fly on their own.
Mr. Iyer : Very good.
Kalam : Sir, the flight principle got imprinted in my mind and so I decided
Mr. Iyer : Why do you hesitate, boy? You can express your feelings with me freely.
Kalam : I decided that in the future I will study subjects related to flight.
Mr. Iyer : Oh, very nice to hear.
Kalam : Sir, I need your guidance to pursue my interest.
Mr. Iyer : Certainly, I’ll guide you. If you work hard, you’ll achieve your aim.
Kalam : Thank you very much, sir.
3. Use the following information and write a bio-sketch of Dr. Kalam.
Dr. Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalam
Birth : 15th October 1931 at Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu
Died on : 27th July 2015
Parents : Ashiamma (mother), Jainulabdeen (father)
Education : Schooling at Rameswaram
Childhood friends : Ramanadha Sastry, Aravindan and Sivaprakasan
Alma Matter : St. Joseph’s College, Tiruchirapalli
Madras Institute of Technology
Profession : Professor, author, aerospace scientist
Presidency : 11th President of India on 25th July 2002
Achievements : Evolution of ISRO’s launch vehicle programme, operationalisation of AGNI, PRITHVI missiles
Literary pursuits : Four of his books
– Wings of Fire
– India 2020 – A Vision for the New Millennium
– My Journey
– Ignited Minds
Honours : Honorary doctorate from 30 universities
Awards : Padma Bhushan (1981)
Padma Vibhushan (1990)
Bharat Ratna (1997)
Answer:
Dr. Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalarn
Abdul Kalam was the 11th President of India. He was born on 15th October 1931 at Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu. His mother was Ashiamma and father Jainulabdeen. He did his schooling at Rameswaram. His childhood friends are Ramanadha Sastry, Aravindan and Sivaprakasan.
He studied at St. Joseph’s College in Tiruchirapalli and completed his professional course at Madras Institute of Technology. He stepped into the shoes of many professions such as a professor, author, and an aerospace scientist.
He was elected as 11th President of India on 25th July 2002. He played a key role in the evolution of ISRO’s launch vehicle programme and in the operationalisation of AGNI, PRITHVI missiles.
The four important literary pursuits of Kalam are Wings of Fire, India 2020 – A Vision for the New Millennium, My Journey and Ignited Minds. He was honoured with a honorary doctorate from 30 universities. He got awards like Padma Bhushan in 1981 and Padma Vibhushan in 1990. He also got the most prestigious award Bharat Ratna in 1997. He passed away on 27th July 2015.
![]()
4. Write a letter to your father requesting him to allow you to go on an educational tour with your Mends.
Answer:
| 12-25, Ashok Nagar Mangalagiri. 15 June, 20xx My dear father I am very happy to inform you that our school is arranging an educational tour to visit Mysore and surrounding places. We will visit Brundavan gardens, some industries and educational institutes there. It is a two day programme. Our school teachers will also accompany us. All our friends are going on the trip. I am also interested to go on the tour for which 1 require Rs. 3,000/- for expenses. Hence, I request you to kindly allow me to go on the tour along with my friends and teachers and send the amount as early as possible. 1 am waiting for your reply. Convey my profound regards to Mummy and best wishes to my brother and sister. With love Address on the Envelope : |
5. Write a story using the following hints :
Hints : A crow – find a peice of meat – take the piece of meat fly – about to eat – a cunning fox – sees piece of meat – wants to take it – fox says – crow has a sweet voice – to sing a song – vexed with his repeated requests – put the piece of meat – under his leg says – that he has already read the story – get away from there.
Answer:
One day a crow found a piece of meat somewhere. The crow took the piece of the meat in its beak and flew off to a tree nearby. As it was about to eat the meat, a cunning fox came there. The fox saw the piece of the meat. Somehow he wanted to take it away from the crow. Then the fox said that the crow had a sweet voice. He asked the crow to sing a song for him. He repeatedly requested the crow for a song. Having been vexed with his repeated requests, the crow put the piece of the meat under his claw and asked the fox to get away from there. He told the fox that he had already read the story of stupid crow and cunning fox.
![]()
6. Write a story using the following hints.
Hints : An old farmer – five sons – lazy and selfish – quarrelled one another – old man worried about – his good words – sons did not care – asked servants – bring a bundle of sticks – sons asked to break – but none – bundle loosened – single stick – broken easily – sons understood – unity is strength.
Answer:
The Farmer and His Five Sons
Once there was an old farmer. He had five sons. The sons were lazy and selfish. They always quarrelled with one another. The old man was worried about his sons’ future. He tried to mend their behaviour by saying a few good words. But the sons did not care arid they did not change their ways. So, the old man wanted to teach his sons a lesson and he asked his servants to bring a bundle of sticks. He called his sons and asked them to break the bundle one after another. But they could not break the bundle as it was not an easy task. Then the old man loosened the bundle and gave them a stick each. They could break the sticks easily. Thus the old man tried to make them understand the value of unity like a bundle of sticks. The sons understood the value of unity and they started to believe that unity is strength.
Moral: Unity is strength.