AP State Syllabus 7th Class Social Important Questions 22nd Lesson Rulers and Buildings
Question 1.
Describe the main features of the ‘trabeate’ or ‘corbelled’ style of architecture.
Answer:
Between the seventh and tenth centuries, architects started adding more rooms, doors, and windows to buildings. Making large rooms with an elaborate superstructure requires more sophisticated skills. Roofs, doors, and windows were still made by placing a horizontal beam across two vertical columns, a style of architecture called trabeate or corbelled style of architecture. Between the eighth and thirteenth centuries, the trabeate style was used in the construction of temples, mosques, tombs, and in buildings attached to large stepped – wells.

Question 2.
What are the two technological and stylistic developments?
Answer:
Two technological and stylistic developments are noticeable from the twelfth century.
- Arcuate style of architecture: The weight of the superstructure above the doors and windows was sometimes carried by arches. The roofs too used this principle and was converted into vaults and domes. This architectural firm is called ‘arcuate’.
- Use of Limestone Cement: Limestone cement was increasingly in the construction of heavy and large structures. This was very high-quality cement, which, when mixed with stone chips hardened into concrete. This made the construction of large structures easier and faster. Arches, domes, and limestone mortar were used extensively in buildings after 1190 A.D.
Question 3.
Describe the plan of the temples of the Chandela dynasty?
Answer:
To begin with, an ornamented gateway led to an entrance and the main hall (mahamandapa) where dances were performed. The image of the chief deity was kept in the main shrine (garbha griha). This was the place for ritual worship where only the king, his immediate family, and priests gathered.
Question 4.
What are the main characteristics of the Vijayanagara style of architecture?
Answer:
Vijayanagara kings wanted their architecture to reflect all the important imperial build¬ing traditions. They followed the architectural styles of Cholas and Pandyas. This included vimanas and the gopurams y/hich were built on a scale and height. The first floor of the gopuram was built of solid granite and the upper floors were built of brick and sunnam. Other distinctive features include mandapas or pavilions and long pillared corridors that often ran around the shrines within the temple complex. They built secular royal buildings modeled on the style and techniques of the sultanate architecture.
Question 5.
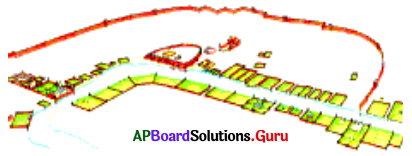
Look at the following picture.
Now answer the following questions:
a. What does the picture show?
Answer:
The riverfront garden city of Agra.
b. Which river is flowing through the city?
Answer:
The Yamuna.
c. Which great monument is shown in the picture?
Answer:
The Taj Mahal.
d. Whose garden palaces are shown in the map?
Answer:
Garden palaces of the nobles.
e. Can you locate the Taj Mahal in the picture?
Answer:
Yes.

Question 6.
Describe the arcuate style of architecture.
Answer:
The weight of the superstructure above the doors and windows was sometimes carried by arches. The roofs too used this principle and were converted into vaults and domes. This architectural firm is called the ‘arcuate’ style of architecture. This style is used from the twelfth century.
Question 7.
How were the tallest – shikhara constructed by using heavy stones?
Answer:
Constructing tall Shikharas was not easy because there were no cranes in those days and the 90 tonne stone for the top of the shikhara was too heavy to lift manually. So the architects built an inclined path to the top of the temple, placed the boulder on rollers, and rolled it all the way to the top. The path started more than four kilometers away so that it would not be too steep. This path was dismantled after the temple was constructed.
Question 8.
Study the following table.
| Style of the architecture | Characteristics | Used in |
| Trabeate (or) corbelled | A roof can be made by placing a horizontal beam across two vertical columns, a style of ‘ architecture is called trabeate or corbelled. | in the construction of temples, mosques and tombs. |
| Arcuate style | The weight of the superstructure above the doors and windows was sometimes carried by arches. The roofs used this principle and was converted into vaults and domes. This architectural form is called arcuate’. | in constructing roofs and domes. |
| Imperial style of the Vijayanagara period. | The Vijayanagara style of architecture had been developed by using the techniques of Chola and Pandya styles. This included Vimanas and Gopurams. Towers on the central shrines were dwarfed. Other distinctive features of this style include mandapas or pavilions and long pillared corridors that often ran around the shrines within the temple complex. | in building Gopurams, Vimanas and Mandapas of the temple. |
Now answer the following questions:
a. Write the characteristic of trabeate style of architecture.
Answer:
A roof can be made by placing a horizontal beam across two vertical columns. This style of architecture is called trabeate or corbelled type of architecture. This style is used in the construction of temples, mosques, and tombs.
b. Write the characteristics of Arcuate style of architecture.
Answer:
The weight of the superstructure above the doors and windows was sometimes carried by arches. The roofs too used this principle and were converted into vaults and domes. This architectural form is called ‘Arcuate’. This is used in constructing roofs and domes of temples and mosques.
c. Write about the imperial style of Vijayanagara period.
Answer:
The Vijayanagara style of architecture had been developed by using the techniques of Chola and Pandyan styles. This included Vimanas and Gopurams. Towers on the central shrines were dwarfed other distinctive features of this style include mandapams or pavilions and long pillared corridors that ran around the shrines with in the temple complex.

Question 9.
Read the following passage.
Temples and mosques were beautifully constructed because they were places of worship. They were also meant to demonstrate the power, wealth and devotion of the patron. Take the example of the Rajarajeshvara temple. An inscription mentions that it was built by King Rajarajadeva for the worship of his god, Rajarajeshvara. Notice how the name of the ruler and the god are very similar. The king took the god’s name because it was auspicious and he wanted to appear like a god. Through the rituals of worship in the temple, one god (Rajarajadeva) honored another (Rajarajeshvara).
Now answer the following questions.
a. Why were the temples and mosques constructed beautifully?
Answer:
Temples and mosques were built beautifully because they were places of worship.
b. What were the beautiful temples and mosques meant to?
Answer:
Temples and mosques were meant to demonstrate the power, wealth and devotion of the patron.
c. Who built the Rajarajesvara temple?
Answer:
The King Rajarajadeva built Rajarajeshvara temple.
d. Why did King Rajaraja take the name of God?
Answer:
King Rajarajadeva took the name of God – Rajarajesvara because it was auspicious and he wanted to appear like a god.
e. Who were the two gods mentioned in the passage?
Answer:
The Lord Rajarajeshvara and the King Rajarajadeva who himself wanted to appear like a god.
Question 10.
Read the following passage :
Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni was a contemporary of Rajendra I. During his campaigns in the subcontinent, he also attacked the temples of defeated kings and looted their wealth and idols. Sultan Mahmud was not a very important ruler at that time. But by destroying temples – especially the one at Somnath – he tried to win credit as a great hero of Islam. In the political culture of the Middle Ages, most rulers displayed their political might and military success by attacking and looting the places of worship of defeated rulers.
Now answer the following questions.
a. Which Chola ruler was the contemporary of Rajendra I?
Answer:
Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni
b. What is called the Subcontinent?
Answer:
India.
c. Why did Mahmud of Ghazni destroy temples?
Answer:
To win credit as a great hero of Islam.
d. What was the prevalent political culture of the middle ages?
Answer:
To display their political might and military success by attacking and looting the places of worship.
e. Who looted the Somanath temple?
Answer:
Mahmud of Ghazni.

Question 11.
Read the following passage:
The city of Vijayanagara was developed by the Rayas to act as the imperial capital of the entire South India. Thus they wanted it to reflect all the important imperial building traditions. They built large temples for Sri Virupaksha, Ramachandra, Krishna, and Vitthala using a style that had been developed by Chola and Pandya emperors% of Tamil Nadu. This included the Vimanas and the Gopurams. The Rayas paid special attention to the Gopurams which were now built on d scale and height as drivers before. It consisted of a first floor usually built of solid granite and a series of upper. floors made of brick and sunnam.
Now answer the following questions.
a. Which city was developed as the imperial capital of the entire South India?
Answer:
Vijayanagara.
b. What were the temples built by Vijayanagara Kings?
Answer:
Sri Virupaksha, Ramachandra, Krishna and Vitthala.
c. Whose style of architecture was used by the Vijayanagara Kings?
Answer:
Chola and Pandya styles of Architecture.
d. Which elements of Chola and Pandyan style of architecture did Vijayanagara kings use in building temples?
Answer:
Vimanas and Gopurams?
e. What, were Gopurams?
Answer:
Gopurams were the towering gateways of the temples.
Question 12.
Read the following passage.
The most impressive remain of Vijayanagara, the Mahanavami Dibba is a very high platform, of 55 feet that is as tall as a five-floor building and 11000 feet in area. Its height was increased at least three times during two hundred years. The sides of the platform were covered with sculptures of various kinds. It did not have a complete building on the top. The platform Was covered by cloth shamiana or pandal sup¬ported by wooden pillars. On this platform, the Vijayanagara kings held their Navaratri Puja and held their Dussera court in which all their subordinate chiefs, nayakas and officers paid their tributes to the Emperor. Ambassadors from Europe and other sultan¬ates also attended the festival.
Now answer the following questions.
a. What was the most impressive remain of the Vijayanagara Kingdom?
Answer:
Mahanavami Dibba.
b. Why was it called ‘dibba’?
Answer:
Because it was built on a high platform of 55 feet.
c. How did Vijayanagara used this dibba for?
Answer:
The Vijayanagara Kings used this dibba for performing Navaratri puja and held Dussera court.
d. Who paid tributes during the Dussera court?
Answer:
Subordinate chiefs, nayakas and officers paid their tributes to the Emperor.
e. What were the sides of the platform covered with?
Answer:
The sides of the platform were covered with sculptures of various kinds.

Question 13.
Read the following passage.
Under the Mughals, architecture became more complex. Mughal emperors were per¬sonally interested in literature, art and architecture. In his autobiography, Babur described his interest in planning and laying out formal gardens, placed within rectangular walled enclosures and divided into four quarters by artificial channels.
These gardens were called chahar baghs, four gardens, because of their symmetrical division into quarters. Beginning with Akbar, some of the most beautiful chahar baghs were constructed by Jahangir and Shah Jahan in Kashmir, Agra, and Delhi.
Now answer the following questions.
a. What were Mughal emperors interested in?
Answer:
The Mughal emperors were interested in literature, art and architecture.
b. What was Babur interested in?
Answer:
Babur was interested in planning and laying out formal gardens.
c. What are Chahar baghs’?
Answer:
Formal gardens are placed within rectangular walled enclosures and divided into four quarters by artificial channels. These gardens were called Chahar bagh, four gardens.
d. Why are chahar baghs called so?
Answer:
These gardens were called Chahar bagh “four gardens, because of their symmetrical division into quarters.
e. Where did Mughal emperors construct Chahar baghs?
Answer:
Chahar bags were constructed in Kashmir, Agra, and Delhi by Akbar, Jahangir, and Kashmir.
Question 14.
Read the following passage.
Qutb Minor is five stories high. The band of inscriptions you see is under its first balcony. The first floor was constructed by Qutbuddin Aybak and the rest by Iltutmish around 1229. Over the years it was damaged by lightning and earthquakes and repaired by later kings.
Now answer the following questions.
a. How tall is Qutub Minor?
Answer:
Qutub Minar is five storeys high.
b. Who started the construction of Qutb Minar?
Answer:
Qutbuddin Aybak.
c. Who completed the construction of Qutb Minar?
Answer:
Iltutmish.
d. When was the construction of Qutub Minar completed?
Answer:
In 1229 A.D.
e. What damaged Qutb Minar?
Answer:
Qutb Minar was damaged by lightning and earthquakes.

Question 15.
Read the following passage.
Muslim Sultans and Badshahs did not claim to be incarnations of god but Persian court chronicles described the Sultan as the “Shadow of God”. An inscription in the Delhi mosque explained that God chose Alauddin as a king because he had the qualities of Moses and Solomon, the great law-givers of the past. The greatest law¬giver and architect was God himself. He created the world out of chaos and introduced order and symmetry.
Now answer the following questions.
a. What was it that described the Sultan as the: “Shadow of God”?
Answer:
The Persian court chronicles.
b. Did the Muslim Sultans and Badshahs claim themselves to be the incarnations of God?
Answer:
No.
c. Why did God choose Allauddin as a king according to the inscription in the Delhi mosque?
Answer:
Because he had the qualities of Moses and Solomon.
d. Who were Moses and Solomon?
Answer:
The great law-givers of the past.
e. Who is actually the greatest lawgiver and architect?
Answer:
God himself.
Question 16.
Read the following passage.
In the early ninth century, when the Pandyan king Shrimara Shrivallabha invaded Sri Lanka and defeated the king, Sena I (831-851), the Buddhist monk and chronicler Dhammakitti noted: “he removed all the valuables … The statue of the Buddha made entirely of gold in the Jewel Palace… and the golden images in the various monasteries – all these he seized. ” The blow to the pride of the Sinhalese ruler had to be avenged and the next Sinhalese ruler, Sena II, ordered his general to invade ‘Madurai, the capital of the Pandyas. The Buddhist chronicler noted that the expedition made a special effort to find and restore the gold statue of the Buddha.
Now answer the following questions.
a. Which Pandyan King invaded Srilanka?
Answer:
Shrimara Shrivallabha.
b. Who did Shrimara Srivallabha defeat?
Answer:
Sena I.
c. Who was Dhamma kitti?
Answer:
A Buddhist monk and chronicler.
d. What are the values to seized by Shrivallabha?
Answer:
The Golden statue of Buddha and the Golden images.
e. How was the golden statue of Buddha recaptured by the Sinhalese?
Answer:
According to Dhammakitti, the expedition led by Sena II made a special effort to find and restore the golden statue of the Buddha.

Question 17.
Read the following passage.
Shah Jahan adapted the river-front garden in the layout of the Taj Mahal, the grand¬est architectural accomplishment of his reign. Here the white marble mausoleum was placed on a terrace by the edge of the river and the garden was to its South. The new city of Shahjahanabad that he constructed in Delhi, the imperial palace commanded the riverfront. Only especially favoured nobles – like his eldest son Dora Shukoh – were given access to the river. All others had to construct their homes in She city away from the River Yamuna.
Now answer the following questions.
a. What did Shah Jahan adapt in the layout of the Taj Mahal?
Answer:
The riverfront gardens.
b. What was the grandest architectural accomplishment of Shah -Jahan’s reign?
Answer:
The Taj Mahal.
c. What is referred to as *White marble mausoleum9 in the above passage?
Answer:
The Taj Mahal.
d. Who constructed the new Shah Jahanabad?
Answer:
Shah Jahan.
e. Who was Dara Shukoh?
Answer:
Shahjahan’s eldest son.
Question 18.
An Inscription in Shah Jahan’s diwan – i – khas in Delhi stated: “If there is Paradise on Earth, It is here, It is here. It is here”, How was this Image created?
Answer:
The ceremonial halls of the public and private audience – diwan – i – khas or diwan – i – aam were carefully planned. These courts were also described as chihil sutun or forty-pillared halls, placed within a large courtyard. Thus the beautiful courtyards, carefully planned halls with different elements of Mughal architecture Shah Jahan’s biwan – i – khas (or) diwan – i – aam were called the paradises on earth.

Question 19.
Look at the picture.
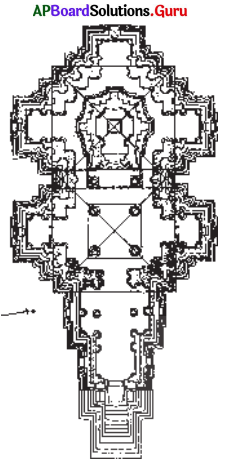
Now answer the following questions.
a. What does the above picture show?
Answer:
The above picture shows the plan of the temple of the Chandala dynasty.
b. How many main parts are there? What are they?
Answer:
There are three main parts in the plan – They are
- ornamented gateway,
- Maha mandapa and
- Garbhagriha.
c. Locate the Mahamandapa on the map.
Answer:

d. Locate the garbhagriha in the map.
Answer:
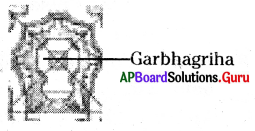
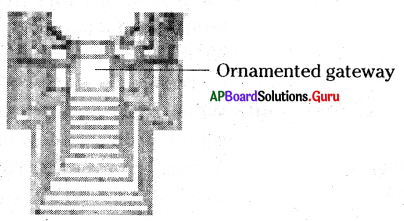
e. Locate the ornamented gateway.
Answer:

Question 20.
Look at the picture.
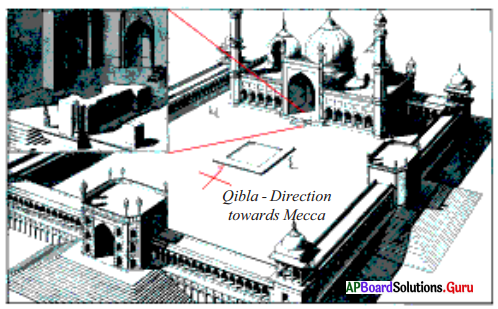
Now answer the following questions.
a. What does the above picture show?
Answer:
The plan of the Jami Masjid.
b. Who built this structure?
Answer:
Shah Jahan.
c. Where was it built?
Answer:
At Shahjahanabad.
d. What was special about this?
Answer:
Qibla was built in direction of Mecca.
e. Which Masjid was shown in the picture?
Answer:
Jami Masjid.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()