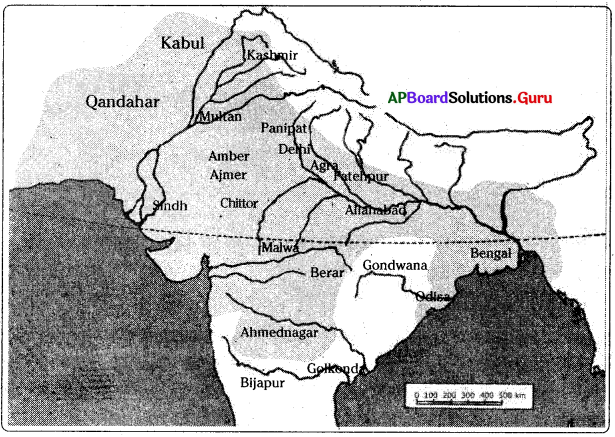
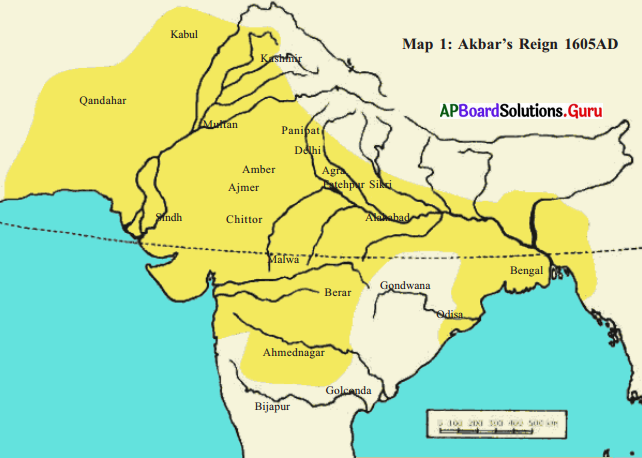
AP State Syllabus 7th Class Social Important Questions 15th Lesson Establishment of the British Empire in India
Question 1.
Study the following information and answer the questions given below.
| Place: The military cantonment at Meerut | – Indian soldiers began firing their guns on English officers. |
| Date: Sunday, May 10, 1857 | – They were not getting salaries on time and they were not treated with respect. |
| – They are not ready to use new rifles because they suspected that the cartridges for these guns were coated with cow and pig fat. | |
| Place: Meerut town Date: Sunday night. Monday, May 10, 11,1857 |
– Revolt spread in Meerut – Police too joined the mobs |
| Place: Delhi, the Lai Quila Date: Monday, May 11, 1857 | – Soldiers entered the Lai Quila – Declared Bahadur Shah Zafar their Badshah – Gave the clear call “Drive out the English and bring back the Mughal rule” |
a) Where and when did the 1857 Revolt start?
Answer:
The 1857 Revolt started on 10th May 1857 at Meerut.
b) What was the immediate cause of the Revolt?
Answer:
The use of guns was coated with cow & pig fat.
c) Who was the last Mughal Emperor?
Answer:
Bahadur Shah Zafar.
d) What was the call of rebels?
Answer:
“Drive out the English and bring back the Mughal rule”.
![]()
Question 2.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Tie royal charter, however, could not prevent other European powers from entering the Eastern markets. By the time the first English ships sailed down the west coast of Africa, round the Cape of Good Hope, and crossed the Indian Ocean, the Portuguese had already established their presence in the western coast of India and had their base in Goa. It was Vasco da Gama, a Portuguese explorer, who had discovered this sea route to India in1498. By the early seventeenth century, the Dutch (Holland) too were exploring the possibilities of trade in the Indian Ocean. Soon the French traders arrived on the scene.
a. What do you think was the sea route to India?
Answer:
Starting from Portugal, they had to sail down the west coast of Africa, round the Cape of Good Hope, across the Indian ocean, and then reach the western coast of India.
b. Who discovered the sea route to India?
Answer:
Vasco da Gama
c. Which European country first established its trade center in India?
Answer:
Portugal
d. Which European country was the last one to establish their trade relationship with India?
Answer:
England
e. Write the order of the European countries that established trade relationships with India?
Answer:
Portugal, Dutch (Holland); France, and England.
Question 3.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
The English East India Company also forced the Nizam of Hyderabad to hand over the coastal Andhra Pradesh districts (Krishna, East Godavari, West Godavari, Srikakulam, Vijayanagaram, Prakasam, Visakhapatnam, and Guntur) between 1765-1768. These were known as the ‘Northern Sarkars’ of the Madras province of the company. In return, the English agreed to maintain an army contingent for the use of the Nizam. In fact, this army was used more to control the Nizam rather than to help him.
a. What did the English East India company force Nizam of Hyderabad to do?
Answer:
To hand over the coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh to them.
b. Which districts were called the ‘Northern Sarkars’?
Answer:
Guntur, Krishna, Prakasam, West Godavari, East Godavari, Visakhapatnam, Srikakulam, and Vijayanagaram are called the Northern Sarkars.
c. Which province did Northern Sarkars belong to?
Answer:
Northern Sarkars belonged to the Madras province of the company.
d. In return how did the English agree to help Nizam?
Answer:
The English agreed to maintain an army contingent for the use of the Nizam.
e. How was the army contingent, supposed to maintain for Nizam used to actually?
Answer:
The army contingent supposed to maintain for Nizam was actually used to control the Nizam.
![]()
Question 4.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
The royal families resisted them because the English would anoint or remove rulers as and when it suited their purposes.
Farmers and landowners resisted them because the English imposed very high taxes on them and collected the taxes very strictly. So they lived in constant fear of failing to pay the taxes and losing their lands as a result.
Tribal people also offered resistance, because of the new rules and laws the English began implementing in their areas. As a result, many tribal people lost their rights over jungles and land.
Many Hindus and Muslims feared that the English would destroy their religions and convert them to Christianity.
a. Why did the royal families resist the English?
Answer:
Because the English anointed or removed rulers as and when it suited their purposes.
b. Why did the landowners and farmers oppose the English?
Answer:
Because the English imposed very high taxes on them and collected the taxes very strictly.
c. Why did the tribal people offer resistance to British rule?
Answer:
Because of the new rules and laws of the English, they began implementing them in their areas.
d. What did the Hindus and the Muslims fear?
Answer:
Many Hindus and Muslims feared that the English would destroy their religions and convert them to Christianity.
e. Why did the farmers and landowners live in constant fear?
Answer:
The farmers and landowners lived in constant fear of failing to pay the taxes and losing their lands as a result.
Question 5.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Place: Delhi, the Lai Quila Date: Monday, May 11, 1857
By daybreak, the sipahis of Meerut had crossed the Yamuna and reached Delhi. They entered the Lai Quila where Badshah Bahadur Shah Zafar of the Mughal dynasty was imprisoned by the English. They declared him their Badshah and persuaded hint to reject the sovereignty of the British. ‘Drive out the English and bring back Mughal rule was the clarion call of the rebels.
a. Why did the Sipahis go to Delhi?
Answer:
To declare Bahadur Shah Zafar as their Badshah.
b. Who was Bahadur Shah Zafar?
Answer:
Bahadur Shah Zafar was the last emperor of the Mughal empire.
c. Who did Sipahis declare as their Badshah?
Answer:
The Sipahis declared Bahadur Shah as their Badshah.
d. What did the Sipahis ask Bahadur Shah to do?
Answer:
The Sipahis persuaded Bahadur Shah to reject the sovereignty of the British.
e. What was the clarion call of the rebels?
Answer:
‘Drive out the English and bring back Mughal rule’ was the clarion call of the Sipahis.
![]()
Question 6.
Picture Reading:
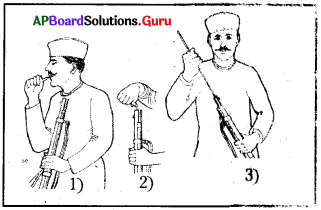
Study the following picture:
- The soldier was supposed to tear open the paper case with his teeth.
- He would pour the gun powder into the rifle.
- He would then ram the bullet wrapped in paper into the rifle.
Now answer the following questions:
a. What does the picture show?
Answer:
How to use the greased cartridges.
b. What does picture no. 1 show?
Answer:
The soldier was supposed to tear open the paper case with his teeth.
c. What does picture no. 2 show?
Answer:
The soldier should pour the gun powder into the rifle.
d. What does picture no. 3 show?
Answer:
The soldier should then ram the bullet wrapped in paper into the rifle.
e. What is the significance of the picture?
Answer:
The use of these greased cartridges was opposed by the Indian soldiers and caused the outbreak of the 1857 revolt.
Question 7.
Study the following table.
| Sections of society | Why they resisted the English in the 1857 revolt? | How Queen victoria addressed their complaints in 1858? |
| The royal families and Indian kings | The English anointed or removed the rulers as and when it suited their purposes. | The Indian kings should rule their own kingdoms without anxiety because the English would not try to dethrone them. |
| Farmers and landowners (common people) |
The English imposed very high taxes on them and collected the taxes very strictly. | The Indians would be included in the government. |
| Zamindars | Because the English confiscated their properties when they were not able to collect the stipulated amount of revenue. | Zamindars were given many concessions and were assured that their property would be protected. |
| Hindus and Muslims | Feared that the English would destroy their religions and convert them to Christianity. | The pundits and maulvis were assured that the British government would not interfere in matters relating to Indian religions and would let the old traditions continue. |
Write a short note on the need for unity to avert foreign invasion.
Now answer the following questions:
a. Why did the royal families revolt against the English in 1857? And how did the Queen address their complaints in 1858?
Answer:
The royal families and the local kings resisted the English in 1857 because they anointed or removed the rulers when it suited their purposes. So In 1858, the queen assured the Indian kings should rule their own kingdom without anxiety because the English would not try to dethrone them.
![]()
b. Why did the farmers and landowners (common people) resist the English in 1857? And how did the Queen address their complaints in 1858?
Answer:
The farmers and the landowners (the common people) resisted the English because the English imposed very high taxes on them and collected the taxes strictly Queen Victoria assured the Indians they would be included in government.
c. Why did the Zamindars fight against the British in 1857? And how did the Queen address their complaint in 1858?
Answer:
Zamindars resisted the English because the English used to confiscate their proper¬: ties when they Were not able to collect the stipulated amount of revenue. But Queen Victoria assured Zamindars were given many concessions and were assured their prop¬erty would be protected.
d. Why did the Hindus and the Muslims fight against the English in 1857? And how did the Queen address their complaint in 1855?
Answer:
The Hindus and Muslims resisted the English because they feared that the English would destroy their religions and convert them to Christianity. But Queen Victoria assured the pundits and maulvis that they would not interfere in matters relating to Indian religions and would let the old traditions continue.
Question 8.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
In 1757 AD, the English defeated Sirajuddaula, the Nawab of Bengal, at a place called Plassey and established their rule over Bengal. The Battle of Plassey is an important event in Indian history. After that, the English started conquering many of the kingdoms of India, big and small.
a. When did the battle of Plassey take place?
Answer:
In 1757 AD.
b. Who did the English defeat in the battle of Plassey?
Answer:
Sirajuddaula.
c. Which battle led to the establishment of British rule in India?
Answer:
Battle of Plassey.
d. Why do you think, ‘the battle of Plassey’ is an important event in the history of India?
Answer:
Because of this battle, the English established their rule in India.
e. Who was Sirajuddaula?
Answer:
The Nawab of Bengal.
![]()
Question 9.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Place: The military cantonment at Meerut, where the British army had camped
Date: Sunday, May 10, 1857
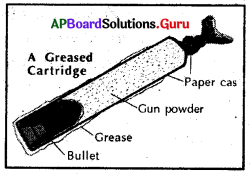
The sun was about to set when the Indian soldiers began firing their guns on their English officers. These Were the same soldiers who had helped the English to conquer the kingdoms of India. They were now fed up with the behavior of the English. They were not getting their salaries on time and they were not treated with respect in the British army. On top of this, the sipahis suspected that the cartridges for their new guns (rifles) were being coated with cow and pig fat to keep them dry. They felt that their religious faith was being violated. Based on this suspicion, a similar uprising had occurred at Barrackpur, near Kolkata in March 1857.
a. Which event was described in the passage?
Answer:
The revolt of 1857.
b. Where did the incident take place?
Answer:
In Meerut.
c. When did the incident take place?
Answer:
On May 10.
d. How were the soldiers fed up with the behavior of the English?
Answer:
- They were not paid their salaries on time.
- They were treated as slaves.
- They felt their religious faiths were being violated when they were asked to use the greased cartridges.
e. Why did the soldiers feel that their faith was being violated?
Answer:
They were asked to use the greased cartridges which were coated with the fat of cows and pigs. So they felt their religious faiths were being violated.
f. What do you think was the immediate cause of the revolt?
Answer:
Use of greased cartridges.
g. Where did the similar uprising as Meerut took place?
Answer:
At Barrackpur, near Calcutta.
![]()
Question 10.
What were the causes that led to the 1857 revolution? (OR)
Explain the causes for the 1857 revolt in detail.
Answer:
There was discontent almost in all spheres of Indian society against the British.
- By waging wars, concluding subsidiary alliances and annexations on the pretext of maladministration, and with the doctrine of lapse of Dalhousie the British annexed Indian kingdoms one after the other. So many royal families such as the Nawab of Avadh, the Maratha Peshwa Nana Sahib, Lakshmi Bai of Jhansi, and Tantia Tope joined the revolt.
- The increased land tax due to frequent changes in the revenue policies affected farmers badly. Due to the economic policies of the British, the people had no employment to earn their livelihood. So the common people and even the landowners took part in the revolt.
- The Hindus and the Muslims of India feared that the English would destroy their religions and convert them into Christianity. The British’s interference into the Indian’s religious matters led to unrest and discontent among the masses and so joined the revolt.
- Indian Sipahis were racially discriminated against. They were paid low salaries and allowances. They were humiliated. Their religious beliefs were violated. So there was a lot of discontent and unrest among the Indian Sipahis.
- On top of that, the Sipahis suspected that the cartridges for their new guns were being coated with the fat of the pig and cow. They felt that their religious faith was being violated. Based on this, uprisings took place at Barrackpur, Meerut and the revolt spread like wildfire.
Question 11.
What are the causes for the failure of the revolt?
Answer:
There were many reasons which caused the failure of the revolt of 1857.
- There were two major weaknesses among the rebels. In every town or religion, different groups of rebels fought separately against the English. They did not fight together. So the English were able to tackle the rebels one by one in each area.
- There was no combined and well-planned effort. So the English were able to tackle the rebels one by one in each area.
- The rebels also faced a shortage of arms. The rebels had to fight with old guns, arrows, spears, and swords.
![]()
Question 12.
Discuss why the idea of the Mughal empire brought the rebelling Indian people together.
Answer:
Hoping that the English would be driven away and the Mughal rule and the earlier political order would be restored, armies of rebels, Sipahis, and rulers from different corners of the country marched-towards Delhi. Though the Mughals were originally foreigners they did not treat the Indians as slaves or second-rated people as the British did. Moreover, they tried to attain harmony between the Hindus and the Muslims. So Mughal emperors continued to be symbolically important. When a rebellion against the British rule broke out in 1857, Bahadur Shah Zafar, the Mughal emperor at that time was seen as the natural leader, when we oppose something you need an alterna¬tive in its place. So when the rebels opposed the British, the immediate alternative that came to their mind was the earlier successful political order i.e., Mughal rule.
Question 13.
While carrying on trade with India why did the English East India company start thinking of establishing its rule over the country?
Answer:
In the areas, the company had acquired the company tried to squeeze revenue from the peasants beyond reasonable limits. When the rulers protested against such practices the English fought against them. They even went to the extent of dethroning kings and anointing successors who would be only too willing to remove any obstacles in the way of their trade. The English gradually began to feel that they could make fuller and freer use of India for trade if they themselves ruled the country. So they began removing the Nawabs and Rajas and started ruling themselves.
Question 14.
In 1857, which soldiers felt their religious faith was being violated, and why?
Answer:
The Sipahis suspected that the cartridges for their new guns were being coated with cow and pig fat to keep them dry. The soldiers were supposed to tear open the paper case with his teeth. The Hindu and Muslim soldiers felt that their religious faiths were. being violated because the cow is a sacred animal for the Hindus and pig is hated by the Muslims. Based on this suspicion the Sipahis revolted against the British.
![]()
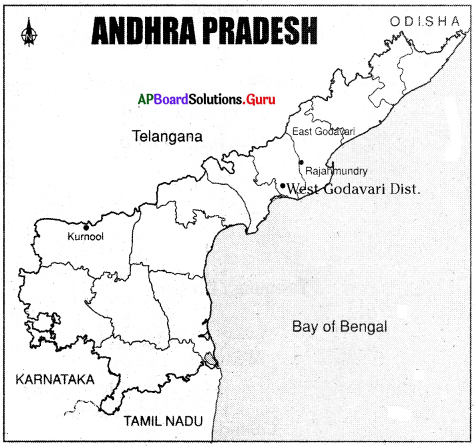
A) Map Reading:
Question 15.
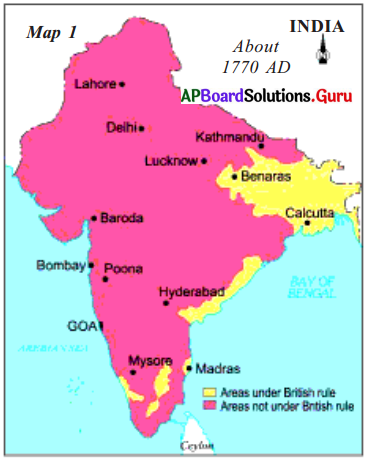
Study the given map.
Now answer the following questions:
a. What does the above map show?
Answer:
The map shows the areas which were under British rule and which were not under British rule.
b. In the above map which shows the areas under British rule?
Answer:
The unshaded part in the above map shows the areas under British rule.
c. According to the above map, which areas were under British rule?
Answer:
A part of Kerala and Madras and a part of Tamilnadu, Coastal Andhra Pradesh, Calcutta, and Bihar were under British rule.
d. According to the above map, which was the main trade centers under the British?
Answer:
Calcutta, Machilipatnam, and Madras.
e. Some part of the present-day Andhra Pradesh was under British rule then. What was that part called in those days?
Answer:
Northern Sarkars.
f. Which part of the western coast was under British control?
Answer:
A part of Kerala.
Question 16.
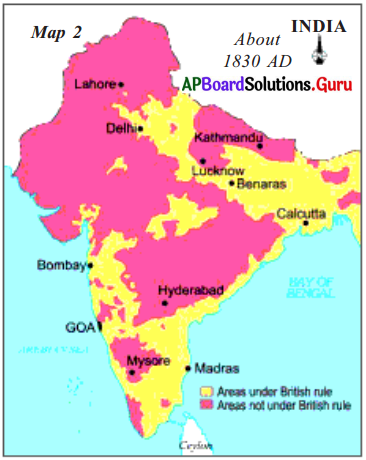
Study the given map:
Now answer the following questions:
a. What does the adjacent map show?
Answer:
The adjacent map shows the areas under British rule in 1830 AD.
b. What does the shaded part show?
Answer:
The shaded part of the map shows the areas which were not under British rule in 1830 AD.
c. What does the unshaded part show?
Answer:
The unshaded part of the map shows the areas which were under British rule in 1830 AD.
d. Which southern kingdoms were still enjoy¬ing independence?
Answer:
Mysore, Hyderabad, and a part of Kerala were, still enjoying the Independence.
e. What Were the main seaports under British control?
Answer:
Calcutta, Machilipatnam, Madras, and Bombay.
f. What do you think was the capital of British Indian territories then?
Answer:
Calcutta.
![]()
Question 17.
Study the given map:
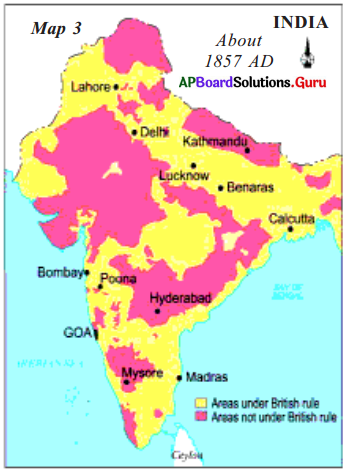
Now answer the following questions:
a. Make a comment about British India in 1857 AD.
Answer:
All the fertile plains, all the productive areas of India almost all the coastal area was under the British rule.
b. What does the above map show?
Answer:
The map shows the area Under British control in 1857.
c. Which seaport was not under British rule?
Answer:
Goa.
d. Which seaport on the west coast was under British rule?
Answer:
Bombay.
e. Which parts of Northern India were not under British control?
Answer:
Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Gujarat were not under British control.
B) Map Pointing:
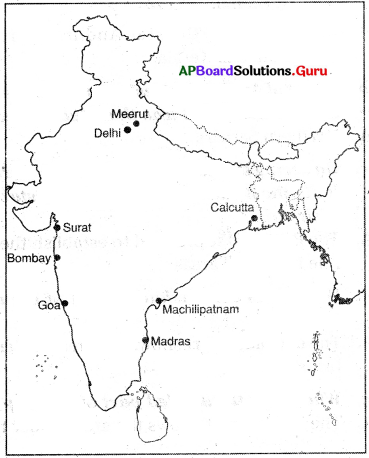
Question 18.
Locate the following places on the map given below.
- Madras
- Bombay
- Calcutta
- Surat
- Machilipatnam
- Goa
- Delhi
- Meerut
Answer:
![]()
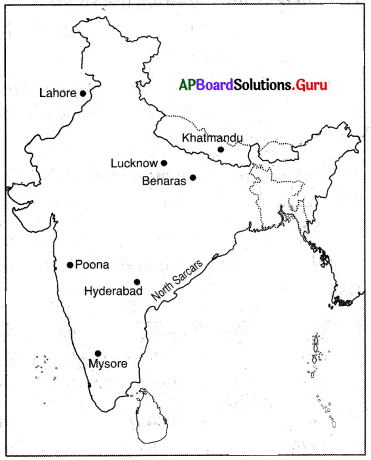
Question 19.
Locate the following places on the map given below:
- Hyderabad
- Mysore
- Poona
- Lahore
- Lucknow
- Benaras
- North Sarcars
- Kathmandu
Answer:
Question 20.
Study the following map.

Now answer the following questions :
a. Which states of present-day India were under British rule then?
Answer:
Bihar, Bengal, Coastal Andhra, parts of Tamilnadu, and Kerala.
b. A part of Andhra Pradesh was under British rule then what was that place called?
Answer:
Northern Sarkars
c. On seeing the above map, in which parts of India the British preferred first to establish their rule?
Answer:
The British first referred to establish their rule in coastal areas.
d. What does the unshaded part of the map show?
Answer:
The unshaded part shows the areas under British rule.
e. What does the shaded part of the map show?
Answer:
The shaded part shows the areas under the rule of the Indian kingdom.
![]()
Question 21.
Study the following map:

Now answer the following questions:
a. What does the shaded part show?
Answer:
The area was not under British rule.
b. What does the unshaded part show?
Answer:
The area was under British rule.
c. Which port city was not under British rule?
Answer:
Goa.
d. What does the map show?
Answer:
The area was under British rule.
e. What do you think was the capital of British India?
Answer:
Calcutta.
![]()
Question 22.
Imagine that you are a villager living at that time when the Mughal Empire lias been declining and the English are beginning to establish their rule (sometime around 1800). Write a first-person account telling your opinions about the Mughals and about the English?
Answer:
I am a common man. I live in a village. My grandfather was an officer in the Mughal court. Our family then was flourished. My grandfather was removed from the service when the British took our area under their control. My father worked as a peasant on our small farm. But now we lost it for we could not pay the tax to the Zamindar. He confiscated our land. With their policy of economic exploitation of India, they destroyed the native cottage industries and handicrafts. They compelled the farmers to sell their agricultural products to them such as cotton at very low rates. Common people and even the landowners who were put to less by their economic policies. We don’t have any employment to earn our livelihood. In one word the English are ruling us as aliens. But the Mughals settled in India. They considered India their own country and took care of all the subjects. They developed agriculture and handicrafts. We used to have a lot of work to do. We were flourished in those days we cannot call the English rulers. Because they don’t have any commitment to the welfare of the people. They are alien businessmen who plundered all our wealth. They tortured every section of Indian society. They interfered in our religion also. They are Christians. They tried to convert us into Christianity.