AP State Syllabus 7th Class Social Important Questions 16th Lesson Making of Laws in the State Assembly
Question 1.
Expand M.L.A. and M.L.C.
Answer:
MLA – stands for Member of Legislative Assembly
MLC – stands for Member of Legislative Council.

Question 2.
The results of an assembly election in a state having 300 seats are shown in the table below.
Study the table and answer the following questions.
| Political party |
Number of Candidates Elected |
| Party A |
115 |
| Party B |
80 |
| Party C |
65 |
| Party D |
40 |
| Total |
300 |
a) What is the minimum number of elected candidates required for a political party to form government in this state?
Answer:
Minimum 151 elected candidates are required.
b) Based on the election result which party has a better chance of forming the government? Why do you think so?
Answer:
Generally, no party has a chance to form the government because no one has more than 150 seats.
c) Give two different alternatives for the political parties that can form a coalition government in this state?
Party A – 72
Party B – 82
Party C – 66
Others – 30
Answer:
To form the coalition.
First step – party A + B + C = 115 + 80 + 65 = 260
Second step = A + B + D = 115 + 80 + 40 = 235

Question 3.
After an election, different political parties got seats as shown below:
Answer the following questions based on the above information.
a) How many seats are needed for getting a majority to form the government in the state?
Answer:
To form the government in any state a political party should have more than 50% of the total seats. So in this state, more than 125 seats are needed.
b) Which one emerged as the single largest party?
Answer:
Party B emerged as the single largest party.
c) If you were the Governor, which party would you call first to form the government?
Answer:
If I am a governor, I would call party B to form the government and say to them to show their majority in a given time.
d) Can the single largest party form the government here? If not, what can be the alternatives to form the government?
Answer:
The coalition government is the alternative form.
Question 4.
What is called manifestos?
Answer:
In elections, political parties play a major role. All political parties and candidates come out with election manifestos. These manifestos are descriptions of programs that they intend to the local context.

Question 5.
Make a list of active political parties in your area and in your state along with their symbols.
Answer:
| Political Party |
Symbol |
| Congress (I) |
Palm (Hastam) |
| Telugu Desam Party |
Cycle |
| Bharatiya Janata party |
Lotus flower |
| YSR Congress Party |
Fan |
| Communist Party of India |
Sickle and Hammer |
| CPI (M) |
Sickle |
| Janasena |
Glass Tumbler |
Question 6.
How do the assemblies make laws?
Answer:
Before a law is passed, the proposed law is called a ‘Bill’. After being passed by both the chambers and approval of the Governor it becomes a law and it is called an ‘Act’ of the state legislature.
Procedure:
The minister who brings the Bill will describe in detail the reason for the new law in the Assembly. There will be a lot of discussions and sometimes opposition from differ¬ent MLAs. There could be suggestions to improve the provisions in the Bill. A small committee is set up to discuss these suggestions. Then it will be placed before the Assembly for voting. If more than half the members of the Vidhan Sabha accept the bill it will be passed and taken to Vidhan Parishad. If the Vidhana Parishad passes it, then it will be sent to the Governor for approval. After his approval the Bill will be called an Act and published in the gazette.

Question 7.
What is the difference between the role of a ruling party MLA and an opposition Party M.L.A.?
Answer:
A ruling party MLA should be constructive in making laws. He must use his discretion to vote for legitimate laws and oppose the Illegitimate ones. He should be in a position to answer the questions of the opposition MLAs who ask about what steps have the government taken on a certain issue.
On the other hand, the opposition M.L.A. should prevent the Government from making illegitimate laws. He should check the government to make laws to favor one section of society. He should offer the government constructive suggestions. He should not unnecessarily criticize the government. He should not play politics over an important issue.
Question 8.
What do you know about Legislative Council? How is it composed?
Answer:
Legislative Council
Earlier we said Andhra Pradesh has two houses. The second house is called Legis-lative Council and was created in 2007. It is a permanent house. Members of this house are elected for 6 years, known MLAs. To contest in this house person should be above 30 years of age. It consists of 50 members.
Composition:
- 17 members (1/3) are elected by the MLAs.
- 17 members (1/3) are elected by the members who were elected to Local Bodies like panchayats and municipalities.
- 3 or 4 members (1/12) from Graduates
- 3 or 4 members (1/12) from Teachers.
- 8 members (1/6) are nominated by the Governor.
In order to make any law in the state now, it has to get the approval of both the houses.
Question 9.
Why is the system of reservation for weaker sections necessary in Assemblies? How are the constituencies reserved for the weaker sections in the Vidhan Sabha of Andhra Pradesh?
Answer:
System of Reservation
It has been observed that it is very difficult for weaker sections of the population, like the Dalits or Adivasis to fight and win elections. As such very few of them get elected to the assemblies. In order to ensure that they are adequately represented in the Assemblies, the Indian Constitution reserves certain constituencies for the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
Reserved Constituencies in Andhra Pradesh State Legislative Assembly:
Total Number of Constituencies: 175
Constituencies Reserved for SCs: 29
Constituencies Reserved for STs: 07

Question 10.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Bill for a ban on public smoking passed
March 27: The Andhra Pradesh State Legislative Assembly on Wednesday passed a bill providing for the prohibition of smoking in places of public work or public use and in public service, vehicles. It also provides for eviction and levying of fines ranging from Rs. 100 to Rs. 1,000 on those who contravene the provisions.
Some of the concerns expressed by the opposition members include implementation of the ban on the sale of cigarettes within 100 meters of educational institutions, sale to those below 18 years, and prohibition of advertisement of cigarettes. Others spoke of the effect it would have on the livelihood of tobacco farmers and pan shop owners. The Minister allayed their apprehensions.
The Minister said the legislation was necessary for a view of the harmful effects of smoking on the health of people and in pursuance of the Supreme Court directions are given on November 2, 2001. Those contravening Sections 5,6 and 10 relating to the ban on smoking in public places and public service vehicles and display of no smoking board, would be punishable with a fine which may extend to Rs. 100 and for the second or subsequent offense with a fine of Rs. 200 which may extend to Rs. 500.
a. Newspapers are often written with the assumption that they are read by adults. So let us first find out the word meanings – eviction, allayed, apprehension, pursuance, implementation, and contravening.
Answer:
Meanings:
eviction = forcing somebody to leave a house or land especially When you have the legal right to do so
allayed = to make some feeling less strong
apprehension = worry or fear that something unpleasant may happen
pursuance = In order to do something
Implementation = Carrying out, making something that has been officially decided to start or happen
contravening = to do something that is not allowed by a law or a rule
b. In the context of the above news items fill in the following.
i) A ……………….. was passed to prohibit smoking in public places (bill, custom, law, rule)
Answer:
bill
ii) Prohibition of smoking does not include ………………. . (place of work, public vehicles, private gardens, bus stand)
Answer:
Private Gardens
iii) The legislation was in order to …………………. the directions from Supreme Court. (silence, punish, follow, dismiss).
Answer:
follow
iv) The bill was passed in the …………….. . (Supreme Court, Ministry, Collectorate, Assembly)
Answer:
Assembly
v) Does the newspaper article suggest that everyone had same opinion about the bill?
Answer:
No. some spoke of the effect it would have on the livelihood of tobacco farmers and pan shop owners.
vi) What are the provisions for punishment mentioned in the newspaper?
Answer:
The contravening sections 5, 6, and 10 of the Supreme Court directions relating to the ban on smoking in public places and public service vehicles are the provisions for punishment.

Question 11.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Bill: Before a law is passed, the proposed law is called a ‘Bill’. After being passed by both the chambers and after the approval of the Governor, it becomes a law and is called an ‘Act’ of the state legislature.
a. What is called a bill?
Answer:
Before the law is passed, the proposed law bill is called a Bill.
b. Who pays the bills?
Answer:
Both the chambers of the legislature.
c. Who will approve the bill?
Answer:
The Governor.
d. What is called an Act?
Answer:
After the approval of the Governor, the Bill is called an Act.
e. What is the difference between a Bill and Act?
Answer:
Before a law is passed, the proposed law is called a Bill. After being passed by both chambers and approved by the Governor it becomes a law and is called an Act.
Question 12.
Study the following table.
| Political Party |
No. of Candidates Elected |
| Political Party – A |
102 |
| Political Party – B |
67 |
| Political Party – C |
04 |
| Political Party – D |
02 |
| Political Party – E |
00 |
| Political Party – F |
00 |
| Political party – G |
00 |
| Political Party – H |
00 |
| Political Party -1 |
00 |
| Political Party – J |
00 |
| Total |
175 |
Now answer the following questions.
a. Which party has got the majority?
Answer:
Party A
b. Which Party has won the second largest number of Candidates?
Answer:
Party B
c. Member of which party is elected as the Chief Minister?
Answer:
Party A
d. Which party is called the opposition party?
Answer:
Party B
e. Members of which party are selected as the Cabinet?
Answer:
Party A

Question 13.
Study the following table.
| Political Party |
No. of Candidates Elected |
| Political Party – P |
82 |
| Political Party – Q |
60 |
| Political Party – R |
14 |
| Political Party – S |
11 |
| Political Party – T |
04 |
| Political Party – U |
03 |
| Political party – V |
01 |
| Total |
175 |
Now answer the following questions.
a. What does the above table show?
Answer:
Political parties which compete in the elections and the number of seats they got in the elections. .
b. Which party has the right to form the government?
Answer:
Political party – P
c. Which party is considered as the opposition party?
Answer:
Political Party – Q
d. Member of which party becomes the Chief Minister?
Answer:
Political Party – P
Question 14.
Study the following table.
| Political Party |
No. of Candidates Elected |
| Political Party – Abed |
91 |
| Political Party – Mnop |
42 |
| Political Part – Wxyz |
32 |
| Political Party – Stuv |
10 |
| Total |
175 |
Now answer the following questions.
a. How many total seats are there in the Assembly?
Answer:
175.
b. What is the Optimum majority the party needs to form the government?
Answer:
88 (More than half of the seats).
c. Can any party form the Government on its own?
Answer:
Abed parties can form the government.
d. If Abed got 71, and Mnop got 62, what can be the possible alternatives to form the government?
Answer:
Parties Abed and Mnop together can form the government or parties Abed and Wxyz together can form the government or parties, Mnop and Wxyz together can form the government or parties Mnop and Wxyz and Stuv together can form the Government.
e. What type of Government is possible in this context?
Answer:
The Coalition government is possible in this context.

Question 15.
Read the passage and answer the following questions.
There are 175 constituencies in the state. The number of constituencies in a state will depend upon its population. A constituency in Andhra Pradesh has about 1,70,000 voters. You may remember that all men and women of 18 years of age or above have the right to vote. They have to get their names registered as voters in the area where they live. All voters of one constituency will vote to elect one member for the Assembly.
a. Which state has 175 Constituencies?
Answer:
Andhra Pradesh.
b. What do the number of constituencies in a state depend upon?
Answer:
The number of constituencies in a state will depend upon its population.
c. How many voters do a constituency in Andhra Pradesh consist of?
Answer:
A constituency in Andhra Pradesh consists of about 1,70,000 voters.
d. Who has the right to vote?
Answer:
All men and women of 18 years of age or above have the right to vote.
e. Who will elect the member of the Assembly?
Answer:
All voters of one constituency will vote to elect one number for the Assembly.
Question 16.
Read the passage and answer the following questions.
We see that political party A got the 102 seconds largest number of candidates i.e., a number of seats is considered to have got a majority. If any law has to be made they can easily get it passed as more than half the members will support it. The majority members will elect one member among themselves as their leader. He or she will be made the Chief Minister of the state by the Governor. The Chief Minister will select from among party MLAs to be ministers. Together they will be called the Cabinet (or ministry). In popular terms, the Cabinet is also called the ‘Government’. The Cabinet is responsible for the implementation of the laws, for preparing and passing new laws and welfare schemes in the Assembly.
a. Which party is considered to have got the majority?
Answer:
The party which has more than half the number of seats is considered to have got a majority.
b. Who will be made the chief minister?
Answer:
The leader of the majority party.
c. Who is called the Cabinet?
Answer:
The Chief Minister and his ministers together are called the cabinet.
d. Who nominates the Chief Minister?
Answer:
The governor nominates the Chief Minister.
e. What are the duties of the Cabinet?
Answer:
The Cabinet is responsible for the implementation of laws, for implementing development plans, and for preparing and passing new laws and welfare schemes in the assembly.
f. What is called the Cabinet?
Answer:
Ministers selected by the Chief Minister from the MLAs together called the Cabinet.

Question 17.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
This is the most important body for making the laws for the state. The Government of Andhra Pradesh which is responsible for implementing these laws and also formulating policies for the welfare of the state is largely composed of members of the Assembly. Our state Assembly has 175 members (MLAs) who are elected by the people just as panchayat members are elected.
a. What is the most important body for making the laws for the state?
Answer:
Legislative Assembly.
b. Which is responsible for implementing the laws?
Answer:
The State Government.
c. Who formulate the policies for the welfare of the state?
Answer:
The State Government.
d. How many members are there in our Assembly?
Answer:
175
e. Who elected the M.L.As?
Answer:
The people of state directly.
Question 18.
Read the following passage and answer the questions.
Usually, elections to the state legislative assembly are held once every five years.
Persons aspiring to become MLAs contest these elections. Various political parties field their candidates. There are also individuals who contest elections and do not belong to any political party. They are known as “Independents”. To contest elections a person should be a citizen of India and should have completed twenty-five years of age.
a. What is the term of the Legislative Assembly?
Answer:
Five years.
b. Who contest the elections?
Answer:
Persons aspiring to become M.L.As
c. Who are called independent?
Answer:
The individuals who contest elections and who do not belong to any party are called independents.
d. What are the eligible conditions for contesting elections?
Answer:
a) He should be a citizen of India.
b) He should have completed 25 years of age.
e. What is the minimum age to complete by a person to be elected as an MLA?
Answer:
25 years.

Question 19.
Some people feel that elections require spending huge amounts of money which is possible only for very rich people. Do you agree with this?
Answer:
Yes, I agree with this. Many parties which promised clean, free, and fair politics and which are assured to be uncorrupted were not able to get at least 5% of the total votes polled. Voting has today become a trade and ‘vote’ a tradable commodity. The contestants offer the most rewarding inducements to voters. People have been lured to caste their votes for mere a packet of liquor and a couple of hundred rupees. Sometimes the voters are lured with valuable rewards of Gold ornaments. Hence contesting elections re¬quires spending huge amounts of money.
Question 20.
If only rich people are able to contest elections how will it affect the decisions taken in the assembly?
Answer:
If only rich people are able to contest elections. They will generate economic distortions in the public sector by diverting public investment into capital projects where bribes and kickbacks are more plentiful They tend to be corruptive and lower the quality of the Government services and infrastructure and increases budgetary pressure on Government. The rich enter politics mainly to amass and enhance their wealth.
Question 21.
Many people feel that similar reservation of seats for women too should be ensured. What do you feel?
Answer:
India is the World’s largest democracy in the world. Even after 60 years of Independence and in spite of 15 general elections women still have a very low representation in parliament. Women comprise half of the population in India. They constitute 340 million voters out of the total electorate of 710 million in 2009. Still, they constitute a lowly 9% of the total strength of the Loksabha. The Indian constitution guarantees Gender equality in Articles 325 and 326. Patriarchal society, male domination in social and political life, violence in the form of dowry, domestic violence, and female infanticide, all these oppressive measures against women make the reservation for women in legislative Assemblies necessary. Women’s interests can never be completed by a group of men. That is why women need reservations.

Question 22.
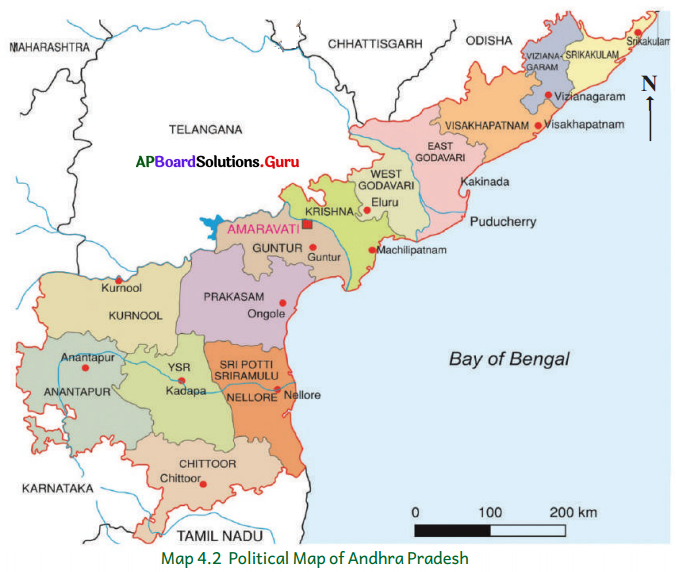
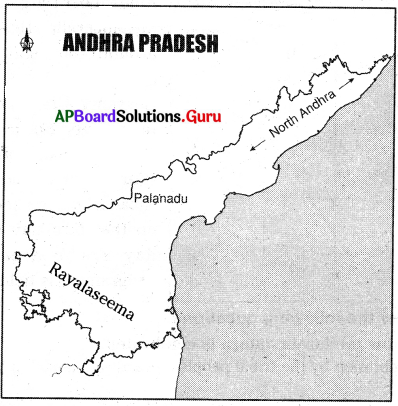
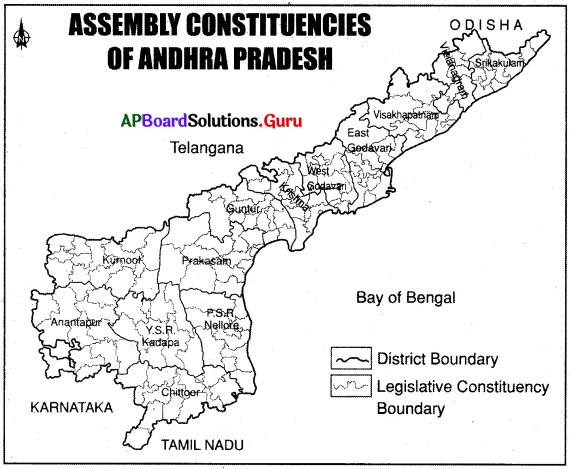
Study the following map:
Now answer the following questions.
a. What does the map show?
Answer:
The map shows the Assembly constituencies of Andhra Pradesh.
b. How many constituencies are there in our state?
Answer:
There are 175 constituencies in our state.
c. Which district has the highest number of constituencies?
Answer:
East Godavari district has the highest number of constituencies.
d. Which district has the lowest number of constituencies?
Answer:
Vijayanagaram district has the lowest number of constituencies.
e. How many constituencies are there in each region?
Answer:
Coastal region: 123 ; Rayalaseema: 52
Question 23.
If you were to contest elections from your district, prepare an election Manifesto- your promises to the constituency people.
Answer:
If I am elected, I promise you, the people of my constituency, that I will
a) do my level best to increase the old age monthly pension from Rs. 200 to 500.
b) make arrangements, to supply drinking water to the neck and corner of my constituency.
c) Provide free education to all from KG to PG.
d) Provide a free power supply to agriculture connections. I will make arrangements to provide a continuous 8 hours supply of power to the agricultural connections.
e) Try to implement Rajiv Arogyasri efficiently to give medical aid to the poor and the needy.

Question 24.
What do you feel about voting for money or caste or out of fear? To what extent will those candidates be interested in formulating good laws and carrying out welfare programs?
Answer:
Voting has become a trade and the ‘vote’ a highly tradable commodity. Very often elections are reduced to show where those constituents who offer the most rewarding inducements and rewards to voters emerge victorious but not on merit. Such political leaders are only engaged in usurping political power and monetary benefits rather than serving the people of India and developing the nation. So I hate voting for money or caste or out of fear. It is embarrassing that billions of dollars are being spent on electing leaders who do nothing more than amassing wealth for themselves after getting elected. Such candidates will not be interested in formulating good laws and carrying out welfare programs.
Question 25.
Suppose you are a member of the Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly. Which issue will you raise for the making of law and why? Explain with example.
Answer:
If I were a member of the Andhra Pradesh Legislative Assembly, I would raise the groundwater level issues in my constituency. Because almost in all the delta area, the corn is being grown as a second crop in the rabi season which needs a lot of water. The crop needs at least 5 spells of watering. It causes a decrease in groundwater level to a great extent. There has been an increase in the number of bore wells. Because of the decrease in groundwater level the bore wells can not pump out the water. So the people have to walk a long distance to fetch water.
Hence I would like to raise the groundwater level issue in the Assembly and ask the government to take proper steps to increase the groundwater level.
Question 26.
What are the malpractices committed by the contestants to persuade the voters?
Answer:
The candidates may seek to influence the voters by offering money and other goods. Sometimes they may try to persuade them to vote for them because they belong to a particular caste or community. Sometimes they may also threaten the voters to vote for them only. These are the malpractices committed by the contestants to influence the voters.

Question 27.
Why do you think voting has to be kept a secret?
Answer:
We should exercise our franchise through a secret ballot system, i.e. we keep it a secret to whom we voted for. If it were not kept a secret, the poor and weak people might be attacked by the bullies, who got defeated in the election. Then it could not be a free and fair election. People have to vote in fear. Then the democracy will be meaningless. Only the people with money and muscle power will be elected.
Question 28.
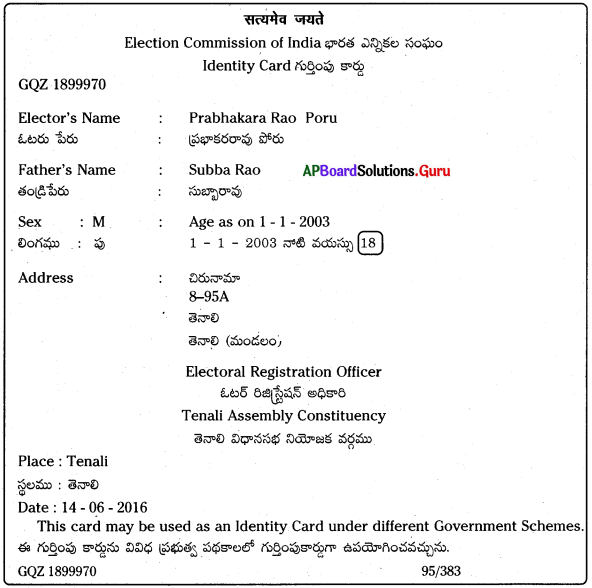
Examine the photo identity card of your parents and try to prepare an imaginary identity card for yourself with all the details.
Answer:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()