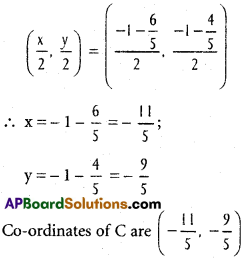
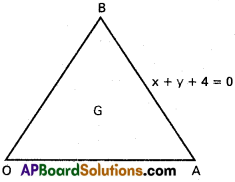
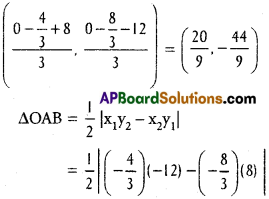
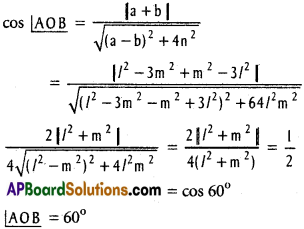
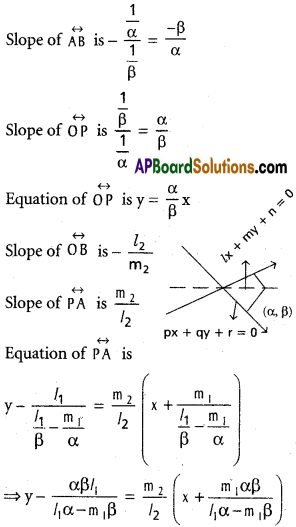
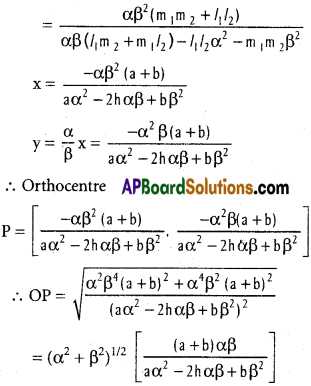
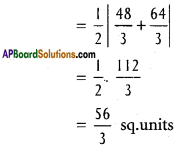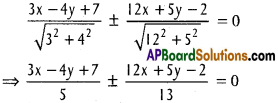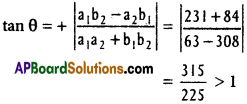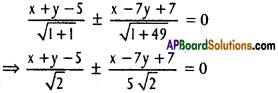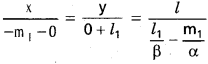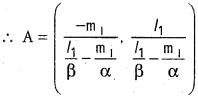Andhra Pradesh AP Board 4th Class Maths Solutions 1st Lesson గుర్తుకు తెచ్చుకుందాం Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 4th Class Maths Solutions Chapter 1 గుర్తుకు తెచ్చుకుందాం
Textbook Page No. 1
1. హర్షిత తన నాయనమ్మ నాగమ్మతో కలిసి బొమ్మల దుకాణానికి వెళ్ళింది. బొమ్మలపై రాసి ఉన్న ధరలను పరిశీలిస్తున్నది. మీరు కూడా వాటి పై ఉన్న ధరలను పరిశీలించండి.

ఈ క్రింది ప్రశ్నలకు సమాధానాలు రాయండి.
ప్రశ్న 1.
మీరెప్పుడైనా బొమ్మల దుకాణానికి వెళ్ళారా?
జవాబు:
అవును, నేను బొమ్మల దుకాణానికి వెళ్ళాను.
ప్రశ్న 2.
బొమ్మల దుకాణంలో మీరేమేమి చూశారు ?
జవాబు:
నేను బొమ్మల దుకాణంలో రకరకాల బొమ్మలను చూశాను.
ప్రశ్న 3.
పటంలో ఎన్ని కారు బొమ్మలు ఉన్నాయి ?
జవాబు:
పటంలో 6 కారు బొమ్మలు ఉన్నాయి.

ప్రశ్న 4.
తెల్ల టెడ్డీ బొమ్మ ధర ఎంత ?
జవాబు:
తెల్ల టెడ్డీ బొమ్మ ధర ₹200.
ప్రశ్న 5.
ఆకుపచ్చ కారు ఎంత ?
జవాబు:
ఆకుపచ్చ కారు ధర ₹150.
అభ్యాసం – 1.0
1. కింది వానికి విస్తరణ రూపం రాయండి.
అ) 8
జవాబు:
ఎనిమిది
ఆ) 20
జవాబు:
ఇరవై
ఇ) 35
జవాబు:
ముప్పై ఐదు
ఈ) 46
జవాబు:
వలభై ఆరు

ఉ) 100
జవాబు:
వంద
ఊ) 101
జవాబు:
నూట ఒకటి
ఋ) 150
జవాబు:
నూట యాభై
బ) 200
జవాబు:
రెండు వందలు
ఎ) 375
జవాబు:
మూడు వందల డెబ్బై ఐదు
ఏ) 425
జవాబు:
నాలుగు వందల ఇరవై ఐదు
ఐ) 802
జవాబు:
ఎనిమిది వందల రెండు
ఒ) 892
జవాబు:
ఎనిమిది వందల తొంభై రెండు
ఓ) 956
జవాబు:
తొమ్మిది వందల యాభై ఆరు
2. క్రింది వానిని సంఖ్యా రూపంలో రాయండి.
అ) ఆరు
జవాబు:
6
ఆ) పద్దెనిమిది
జవాబు:
18

ఇ) యాభై రెండు
జవాబు:
52
ఈ) డెబ్బై ఐదు
జవాబు:
75
ఉ) నాలుగు వందల డెబ్బై.
జవాబు:
470
ఊ) ఆరువందల నాలుగు
జవాబు:
604
ఋ) ఎనిమిది వందల ఒకటి
జవాబు:
801
ఋ) రెండు వందల ఇరవై రెండు
జవాబు:
222
3. కింది సంఖ్యలలోని గీత గీయబడిన అంకెల స్థానం, స్థాన విలువలు రాయండి.

జవాబు:

4. కింది వానికి విస్తరణ రూపం రాయండి.
అ) 56
జవాబు:
50 + 6
ఆ) 62
జవాబు:
60 + 2

ఇ) 83
జవాబు:
80 + 3
ఈ) 87
జవాబు:
80 + 7
ఉ) 95
జవాబు:
90 + 5
ఊ) 110
జవాబు:
100 + 10 + 0
ఋ) 175
జవాబు:
100 + 70 + 5.
బూ) 325
జవాబు:
300 + 20 + 5
ఎ) 1,450
జవాబు:
1000 + 400 + 50+ 0
ఏ) 3752
జవాబు:
3,000 + 700+ 50 + 2

ఐ) 5,927
జవాబు:
5,000 + 900 + 20 + 7
5. కింది వానికి సంక్షిప్త రూపం రాయండి.
అ) 20+5
జవాబు:
25
ఆ) 40 + 7
జవాబు:
47
ఇ) 80 + 2
జవాబు:
82
ఈ) 300 + 20
జవాబు:
320
ఉ) 600 + 40 + 8
జవాబు:
648
ఊ) 900 + 90 +9
జవాబు:
999
ఋ) 3000 + 400 + 20 + 5
జవాబు:
3,425

బూ) 5000 + 20 + 7
జవాబు:
5,027
అభ్యాసం – 1.1
1. కింది వానిని కూడండి.
అ)

జవాబు:

ఆ)

జవాబు:

ఇ)

జవాబు:


ఈ)

జవాబు:

ఉ)

జవాబు:

ఊ)

జవాబు:

2. ఈ క్రింది కూడికలను చేయండి
అ)

జవాబు:

ఆ)

జవాబు:


ఇ)

జవాబు:

ఈ)

జవాబు:

ఉ)

జవాబు:


ఊ)

జవాబు:

3. ఈ కింది ఇవ్వబడిన ఖాళీలలో సరియైన సంఖ్యను రాయండి.
అ) 526 + 326 + 94 = ………………
జవాబు:
526 + 326 + 94 = 946
ఆ) 829 + 408 = …………….. + 829
జవాబు:
829 + 408 = 408 + 829
ఇ) ……………….. + 396 = 396
జవాబు:
0 + 396 = 396
4. ఈ కింది సంఖ్యలను సమీప పదులకు సవరించి రాయండి.
అ) 56
జవాబు:
56కి సమీప పదులలో 60
ఆ) 79
జవాబు:
79కి సమీప పదులలో 80

ఇ) 42
జవాబు:
42కి సమీప పదులలో 40
ఈ) 91
జవాబు:
91కి సమీప పదులలో 90
ఉ) 28
జవాబు:
28కి సమీప పదులలో 30
5. ఈ కింది సంఖ్యలను సమీప వందలకు సవరించి రాయండి.
అ) 235
జవాబు:
235 కి సమీప వందలలో 200
ఆ) 374
జవాబు:
374 కి సమీప వందలలో 400
ఇ) 929
జవాబు:
929 కి సమీప వందలలో 900
ఈ)562
జవాబు:
562 కి సమీప వందలలో 600

ఉ) 810
జవాబు:
810 కి సమీప వందలలో 800
ప్రశ్న 6.
ఒక తోటలో 235 మామిడి, 652 జమ మరియు 120 కొబ్బరి చెట్లు కలవు. తోటలోని మొత్తం చెట్లెన్ని?
జవాబు:
తోటలో మామిడి చెట్లు సంఖ్య = 235
తోటలో జామ చెట్లు సంఖ్య = 652
తోటలో కొబ్బరి చెట్లు సంఖ్య = 120

తోటలో మొత్తం చెట్లు సంఖ్య = 1007
ప్రశ్న 7.
ఒక పాఠశాలలో బాలికల సంఖ్య బాలుర సంఖ్య కన్నా 92 ఎక్కువ. బాలికలు 358 మంది అయిన పాఠశాలలోని మొత్తం విద్యార్థుల సంఖ్య ఎంత ?
జవాబు:
పాఠశాలలో బాలికల సంఖ్య = 358
బాలికల సంఖ్య బాలుర సంఖ్య కన్నా 92 ఎక్కువ
∴ బాలుర సంఖ్య = 358 – 92 = 266
∴ పాఠశాలలోని మొత్తం మొత్తం విద్యార్థుల సంఖ్య = 358 + 266
= 624 మంది
Textbook Page No. 5
ప్రయత్నించండి
కింద ఇవ్వబడిన ఖాళీలలో సరియైన సంఖ్యలను రాయండి.
అ) 5+3 = 3 + _____________
జవాబు:
5+3 = 3 + 5

ఆ) 82 + 40 = __________ + 82
జవాబు:
82 + 40 = 40 + 82
ఇ) _______________ + 596 = 596
జవాబు:
0 + 596 = 596
అభ్యాసం – 1.2
1. ఈ కింది తీసివేతలను చేయండి.
అ)

జవాబు:

ఆ)

జవాబు:


ఇ)

జవాబు:

ఈ)

జవాబు:

ఉ)

జవాబు:

ఊ)

జవాబు:


ఋ)

జవాబు:

బూ)

జవాబు:

2. తీసివేయండి.
అ) 62 నుంచి 59
జవాబు:

ఆ) 92 నుంచి 86.
జవాబు:

ఇ) 536 నుంచి 192
జవాబు:

ఈ) 928 నుంచి 485
జవాబు:


ప్రశ్న 3.
205 మరియు 62 ల బేధం ఎంత ?
జవాబు:
205 మరియు 62 ల బేధం =

ప్రశ్న 4.
653 నుండి ఎంత తీసివేసిన 268 వస్తుంది?
జవాబు:
653 కు268 కి గల బేధము 385

∴ 653 నుండి 268 తీసిన 385 వచ్చును.
ప్రశ్న 5.
246కు ఎంత కలిపిన 859 వస్తుంది ?
జవాబు:
859 మరియు 246 మధ్య బేధము = 613

∴ 246 కు 613 ను కలిపిన 859 వచ్చును.

ప్రశ్న 6.
రెండు సంఖ్యల మొత్తం 453. వాటిలో ఒక సంఖ్య 285 అయిన రెండవ సంఖ్య ఎంత ?
జవాబు:
ఒక సంఖ్య = 285
రెండు సంఖ్యల మొత్తం = 453
453, 285 ల బేధం

∴ రెండవ సంఖ్య 168.
ప్రశ్న 7.
రెండు సంఖ్యల భేదం 568. వాటిలో ఒక సంఖ్య 796 అయిన రెండవ సంఖ్య ఎంత?
జవాబు:
ఒక సంఖ్య 796
రెండు సంఖ్యల భేదం = 568.
∴ రెండవ సంఖ్య = 796 – 568
= 228
అభ్యాసం – 1.3
1. ఈ క్రింది గుణకారాలను చేయండి.
అ)

జవాబు:

ఆ)

జవాబు:

ఇ)

జవాబు:


ఈ)

జవాబు:

ఉ)

జవాబు:

ఊ)

జవాబు:


ఋ)

జవాబు:

2. ఈ కింది లబ్దాలను కనుగొనండి:
అ) 395 × 7 = __________
జవాబు:
2765
ఆ) 402 × 9 = ___________
జవాబు:
3618
ఇ) 534 × 4 = ____________
జవాబు:
2136
ఈ) 826 × 5 = ___________
జవాబు:
4130

ఉ) 498 × 0 = ___________
జవాబు:
0
ఊ) 0 × 35 = ___________
జవాబు:
0
ప్రశ్న 3.
ఒక పెన్ను ₹ 25. అటువంటి 9 పెన్నుల ధర ఎంత?
జవాబు:
ఒక పెన్ను ధర = ₹ 25
9 పెన్నుల ధర = 9 × ₹ 25 = ₹ 225
ప్రశ్న 4.
ఒక మామిడి పండ్ల బుట్ట బరువు 36 కి.గ్రా. అటువంటి 10 మామిడి పండ్ల బుట్టల బరువు ఎంత?
జవాబు:
మామిడి పండ్ల బుట్ట బరువు = 36 కి.గ్రా.
10 మామిడి పండ్ల బుట్టల బరువు
= 10 × 36 కి.గ్రా.
= 360 కి.గ్రా.
ప్రశ్న 5.
ఒక బియ్యం బస్తా బరువు 24 కి.గ్రా. 478 బస్తాల బియ్యం బరువెంత ?
జవాబు:
ఒక బియ్యం బస్తా బరువు = 24 కి.గ్రా.
478 బియ్యం బస్తాల బరువు = 478 × 24
= 11,742 కి.గ్రా.

ప్రశ్న 6.
ఒక సంఖ్య మరియు 5ల లబ్దం ‘0’. ఆ సంఖ్యను కనుక్కోండి.
జవాబు:
5 మరియు ‘0’ల లబ్దం = 5 × 0 = 0
అభ్యాసం – 1.4
1. ఇవి చేయండి :
అ) 6 ÷ 2
జవాబు:

ఆ) 8 ÷ 4
జవాబు:

ఇ) 9 ÷ 3
జవాబు:

ఈ) 24 ÷ 6
జవాబు:


ఉ) 45 ÷ 3
జవాబు:

ఊ) 96 ÷ 4
జవాబు:

ఋ) 224 ÷ 7
జవాబు:

బూ) 845 ÷ 8
జవాబు:

2.
అ) 40 ÷ 4 = ?
జవాబు:


ఆ) 60 ÷ 10 = ?
జవాబు:

ప్రశ్న 3.
90లో ఎన్ని 9లు ఉన్నాయి ?
జవాబు:
90 ÷ 9 = 10 .
∴ 90 లో 9 లు 10 ఉన్నాయి.
4. ఈ కింది భాగహారాల నుంచి భాగ ఫలాలను కనుక్కోండి.
అ) 69 ÷ 3
జవాబు:

∴ భాగఫలం = 23
ఆ) 76 ÷ 4
జవాబు:

∴ భాగఫలం = 19

ఇ) 96 ÷ 2
జవాబు:

∴ భాగఫలం = 48
ఈ) 846 ÷ 3
జవాబు:

∴ భాగఫలం = 282
ఉ) 925 ÷ 5
జవాబు:

∴ భాగఫలం = 185

ప్రశ్న 5.
ఈ క్రింది పట్టికను పూరించండి.

జవాబు:

ప్రశ్న 6.
57 సెం.మీ పొడవు గల రిబ్బనను ఎన్ని 3 సెం.మీ. ముక్కలుగా కత్తిరించవచ్చు ?
జవాబు:
మొత్తం పొడవు గల రిబ్బన్ = 57 సెం.మీ.
ఒక్కొక్క రిబ్బన్ ముక్క పొడవు = 3 సెం.మీ.
కత్తిరించిన ముక్కల సంఖ్య = 57 ÷ 3
= 19 సెం.మీ.
ప్రశ్న 7.
ఒక వ్యక్తి 12 చాక్లెట్లను 4 గురు పిల్లలకు సమానంగా పంచిన, ఒకొక్క పిల్లవాడికి ఎన్నెన్ని చాక్లెట్లు వస్తాయి?
జవాబు:
మొత్తం చాక్లెట్లు = 12
మొత్తం పిల్లల సంఖ్య = 4
ఒక్కొక్క పిల్లవానికి పంచిన చాక్లెట్లు
= 12 ÷ 4
= 3 చాక్లెట్లు

ప్రశ్న 8.
91 రోజులలో వారాలు ఎన్ని ?
జవాబు:
మొత్తం రోజులు = 91
వారంలో రోజుల సంఖ్య = 7
91 రోజులలో ఉన్న వారాల సంఖ్య
= 91 ÷ 7
= 13 వారాలు
అభ్యాసం – 1.5
ప్రశ్న 1.
ఎక్కువ బరువు కలిగిన వస్తువుకు సున్న చుట్టండి.

జవాబు:

ప్రశ్న 2.
ఈ కింది వాహనాలను వాటి బరువులను బట్టి ఆరోహణ క్రమంలో అమర్చండి.
అ) సైకిలు
ఆ) బస్సు
ఇ) మోటారు సైకిల్
ఈ) కారు
జవాబు:
సైకిల్ < మోటార్ సైకిలు < కారు < బస్సు

ప్రశ్న 3.
సరైన కొలత ప్రమాణం (కిలోగ్రాం లేక, గ్రాంలలో) రాయండి.
జవాబు:
బియ్యం బస్తా – కిలోగ్రాం లలో
రబ్బరు – గ్రాంలలో
పుస్తకాల సంచి – కిలోగ్రాంలో
అభ్యాసం – 1.6
ప్రశ్న 1.
ఈ కింది వానిలో ఏవి మీటర్లలో మరియు ఏవి ‘సెంటీమీటర్లలో కొలుస్తారో గుర్తించండి.
అ) మీ తరగతి గది నల్లబల్ల పొడవు
ఆ) పెన్సిలు పొడవు
ఇ) జెండా స్తంభం పొడవు
ఈ)నీ చేతివేలు పొడవు
జవాబు:
అ) మీ తరగతి గది నల్లబల్ల పొడవు – మీటర్లు
ఆ) పెన్సిలు పొడవు – సెంటీమీటర్లు
ఇ) జెండా స్తంభం పొడవు – మీటర్లు
ఈ)నీ చేతివేలు పొడవు – సెంటీమీటర్లు
ప్రశ్న 2.
ఈ కింది పొడవులను ఆరోహణ క్రమంలో అమర్చండి.
a) 8మీ.
b) 10 సెం.మీ.
c) 5మీ.
d) 20 సెం.మీ.
జవాబు:
8 మీ. > 5 మీ. > 20 సెం.మీ. > 10 సెం.మీ.

ప్రశ్న 3.
ఏవైనా మూడు వస్తువులు మీటర్లలో మరియు మూడు వస్తువులు సెంటీ మీటర్లలో కొలిచేవి రాయండి.
జవాబు:
మీటర్లలో
- మంచం
- కిటికీలు
- గ్యాస్ పొయ్యి
సెంటీమీటర్లలో
- దువ్వేన
- పెన్సిల్
- రబ్బరు
అభ్యాసం – 1.7
ప్రశ్న 1.
లీటర్లలో కొలిచే కొన్ని పదార్థాలమ రాయండి.

జవాబు:
పాలు, నీరు మరియు నూనెలను లీటర్లలలో కొలుస్తారు.
ప్రశ్న 2.
ఎక్కువ పరిమాణం గల వస్తువులకు టిక్ పెట్టండి.
మగ్గు ( )
బక్కెట్టు ( )
నీళ్ళసీసా ( )
నీళ్ళ ట్యాంకు ( )
జవాబు:
మగ్గు ( )
బక్కెట్టు ( )
నీళ్ళసీసా ( )
నీళ్ళ ట్యాంకు (✓)

ప్రశ్న 3.
ఈ కింది వాటిని లీటర్లలో సుమారుగా అంచనా వేసి, చెప్పండి.
అ) ఒక రోజుకు ఒక వ్యక్తి త్రాగే నీరు
ఆ) ఒకసారి ఒక వ్యక్తి స్నానానికి కావలసిన నీరు
ఇ) దంతధావనానికి కావలసిన నీరు
ఈ) ఒక మొక్కకు పోయడానికి కావలసిన నీరు
జవాబు:
అ) 5 లీటర్లు
ఆ) 24 లీటర్లు
ఇ) 2 లీటర్లు
ఈ) 7 లీటర్లు
అభ్యాసం – 1.8
1. గడియారాలలో చూపబడిన సమయాన్ని చదివి రాయండి.
అ)

జవాబు:


ఆ)

జవాబు:

ఇ)

జవాబు:

ఈ)

జవాబు:

2. ఈ కింది సమయాలను గడియారాలలో సూచించండి.
అ) 9 : 45
జవాబు:

ఆ) 1 : 15
జవాబు:


ఇ) 6 : 30
జవాబు:

ఈ) 11 : 20
జవాబు:

Textbook Page No. 11
ఇవి చేయండి.
కింది పట్టికను పూర్తిచేయండి.

జవాబు:

అభ్యాసం – 1.9
1. ఈ కింది ఆకారాల పేర్లను కింద ఇవ్వబడిన పెట్టెలలో రాయండి.
అ)

జవాబు:
త్రిభుజం
ఆ)

జవాబు:
చతురస్రం
ఇ)

జవాబు:
దీర్ఘచతురస్రం

ఈ)

జవాబు:
వృతం
ప్రశ్న 2.
ఈ కింది పట్టికను పూరించండి.

జవాబు:

ప్రశ్న 3.
ఈ కింది పట్టికను పూరించండి.

జవాబు:

అభ్యాసం – 1.10
1. ఈ కింది సంఖ్యలకు గణన చిహ్నాలు రాయండి.
అ) 4 = __________
జవాబు:
||||

ఆ) 3 = ___________
జవాబు:
|||
ఇ) 1 = ____________
జవాబు:
|
ఈ) 2 = ____________
జవాబు:
||
2. ఈ కింది గణన చిహ్నాలకు సంఖ్యలు రాయండి.
a) || = ________
జవాబు:
3
b) | = ________
జవాబు:
1
c) || = ________
జవాబు:
2
d) |||| = ________
జవాబు:4
ప్రశ్న 3.
ఈ కింది పట్టికను పూరించండి.


జవాబు:

Textbook Page No. 13
ఇవి చేయండి
సమాన భాగాలుగా విభజించబడిన పటాలను గుర్తించండి.
అ)

జవాబు:
✓
ఆ)

జవాబు:
✗

ఇ)

జవాబు:
✓
అభ్యాసం – 1.11
ప్రశ్న 1.
సమభాగాలుగా విభజించబడిన పటాలను టిక్ (✓) చేయండి.

జవాబు:

ప్రశ్న 2.
ఈ కింది బొమ్మలలో సగ (1/2) భాగాన్ని షేడ్ చేయండి.

జవాబు:


ప్రశ్న 3.
ఈ కింది బొమ్మలలో పావు (1/4) భాగాన్ని షేడ్ చేయండి.

జవాబు:

బహుళైచ్ఛిక ప్రశ్నలు
ప్రశ్న 1.
524 యొక్క సంఖ్యా నామం
A) ఐదువందల ఇరవై నాలుగు
B) ఐదు వందల ఇరవై
C) ఐదు వందల నాలుగు
D) ఏదీకాదు
జవాబు:
A) ఐదువందల ఇరవై నాలుగు
ప్రశ్న 2.
ఏడువందల ఇరవై నాలుగు యొక్క సంఖ్యాగుర్తును కనుగొనుము.
A) 720
B) 724
C) 742
D) 702
జవాబు:
B) 724

ప్రశ్న 3.
352 సంఖ్యలో 3 యొక్క స్థాన విలువ
A) 30
B) 3000
C) 300
D) 3
జవాబు:
C) 300
ప్రశ్న 4.
5000 + 30 + 8 యొక్క సంక్షిప్త రూపం
A) 5038
B) 538
C) 5308
D) ఏదీకాదు
జవాబు:
A) 5038
ప్రశ్న 5.
845ను దగ్గరి వందలకు రాయగా
A) 900
B) 800
C) 850
D) ఏదీకాదు
జవాబు:
B) 800

ప్రశ్న 6.
960 మరియు 456 ల భేదం ?
A) 504
B) 540
C) 489
D) 450
జవాబు:
A) 504
ప్రశ్న 7.
ఒక పెన్సిల్ ఖరీదు – 6 అయితే 27 పెన్సిళ్ళు ధర ఎంత ?
A) 162
B) 621
C) 261
D) ఏదీకాదు
జవాబు:
A) 162
ప్రశ్న 8.
64 లో ఎన్ని 8లు ఉన్నాయి ?
A) 8
B) 16
C) A
D) 6
జవాబు:
A) 8
ప్రశ్న 9.
జెండా స్తంభం యొక్క పొడవును దేనితో కొలుస్తారు?
A) గ్రాముల్లో
B) కిలోగ్రాముల్లో
C) మీటర్లు
D) సెంటీమీటర్లు
జవాబు:
C) మీటర్లు

ప్రశ్న 10.
1 లీటరు = ………….. ml.
A) 10
B) 1000
C) 100
D) ఏదీకాదు
జవాబు:
B) 1000
ప్రశ్న 11.
1 గంట = __________ నిమిషాలు
A) 06
B) 100
C) 10
D) 60
జవాబు:
D) 60
ప్రశ్న 12.
త్రిభుజానికి ఎన్ని శీర్షాలు ఉంటాయి
A) 4
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
జవాబు:
D) 3

![]()

![]()




![]()



![]()



![]()