Telangana & Andhra Pradesh BIEAP TS AP Intermediate Inter 1st Year Physics Study Material Textbook Solutions Guide PDF Free Download, TS AP Inter 1st Year Physics Blue Print Weightage 2022-2023, Telugu Academy Intermediate 1st Year Physics Textbook Pdf Download, Questions and Answers Solutions in English Medium and Telugu Medium are part of AP Inter 1st Year Study Material Pdf.
Students can also read AP Inter 1st Year Physics Syllabus & AP Inter 1st Year Physics Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through AP Inter 1st Year Physics Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
AP Intermediate 1st Year Physics Study Material Pdf Download | Jr Inter 1st Year Physics Textbook Solutions
AP Inter 1st Year Physics Study Material in English Medium
- Chapter 1 Physical World
- Chapter 2 Units and Measurements
- Chapter 3 Motion in a Straight Line
- Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane
- Chapter 5 Laws of Motion
- Chapter 6 Work, Energy and Power
- Chapter 7 Systems of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Chapter 8 Oscillations
- Chapter 9 Gravitation
- Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Chapter 11 Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Chapter 12 Thermal Properties of Matter
- Chapter 13 Thermodynamics
- Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory
AP Inter 1st Year Physics Study Material in Telugu Medium
- Chapter 1 భౌతిక ప్రపంచం
- Chapter 2 ప్రమాణాలు, కొలత
- Chapter 3 సరళరేఖాత్మక గమనం
- Chapter 4 సమతలంలో చలనం
- Chapter 5 గమన నియమాలు
- Chapter 6 పని, శక్తి, సామర్ధ్యం
- Chapter 7 కణాల వ్యవస్థలు, భ్రమణ గమనం
- Chapter 8 డోలనాలు
- Chapter 9 గురుత్వాకర్షణ
- Chapter 10 ఘనపదార్ధాల యాంత్రిక ధర్మాలు
- Chapter 11 ప్రవాహుల యాంత్రిక ధర్మాలు
- Chapter 12 పదార్ధ ఉష్ణ ధర్మాలు
- Chapter 13 ఉష్ణోగతిక శాస్త్రం
- Chapter 14 అణుచలన సిద్ధాంతం
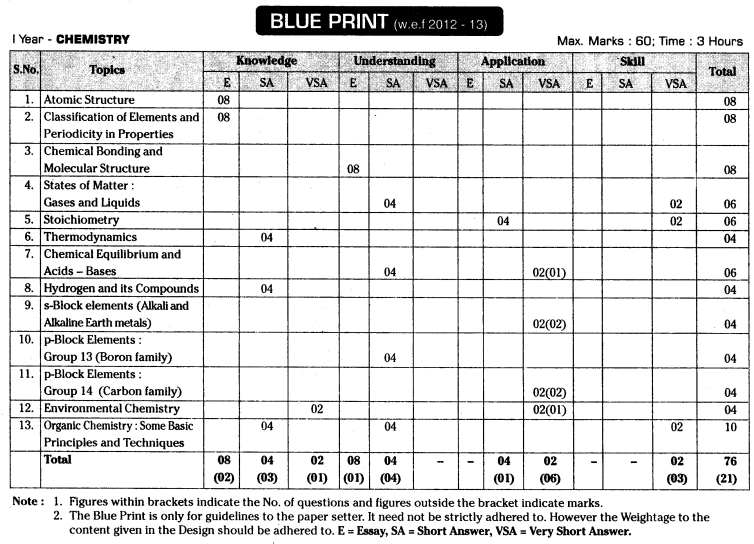
TS AP Inter 1st Year Physics Weightage Blue Print 2022-2023
TS AP Inter 1st Year Physics Weightage 2022-2023 | TS AP Inter 1st Year Physics Blue Print 2022
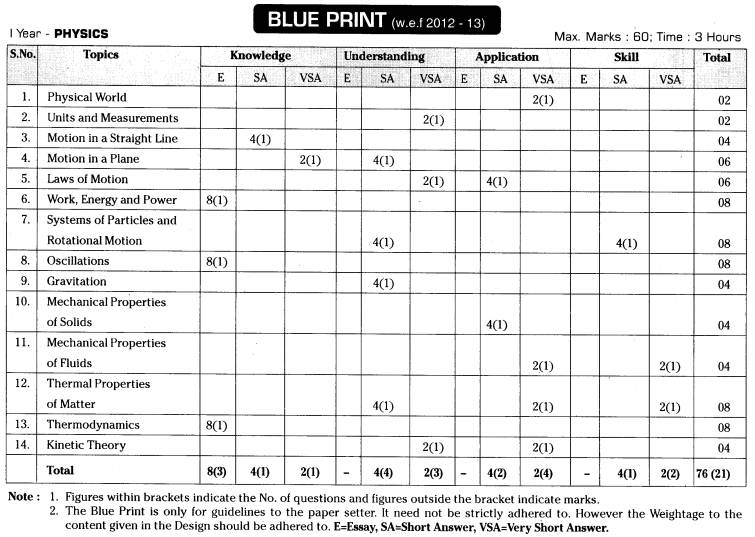
Intermediate 1st Year Physics Syllabus
TS AP Inter 1st Year Physics Syllabus
Chapter 1 Physical World
What is Physics?, Scope and excitement of Physics, Physics, technology, and society, Fundamental forces in nature, Nature of Physical laws.
Chapter 2 Units and Measurements
Introduction, The international system of units, Measurement of length, Measurement of mass, Measurement of time, Accuracy, the precision of instruments, and errors in measurement, Significant figures, Dimensions of physical quantities, Dimensional formulae and dimensional equations, Dimensional analysis and its applications.
Chapter 3 Motion in a Straight Line
Introduction, Position, path length, and displacement, Average velocity and average speed, Instantaneous velocity and speed, Acceleration, Kinematic equations for uniformly accelerated motion, Relative velocity.
Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane
Introduction, Scalars and vectors, Multiplication of vectors by real numbers, Addition and subtraction of vectors, graphical method, Resolution of vectors, Vector addition, analytical method, Motion in a plane, Motion in a plane with constant acceleration, Relative velocity in two dimensions, Projectile motion, Uniform circular motion.
Chapter 5 Laws of Motion
Introduction, Aristotle’s fallacy, The law of inertia, Newton’s first law of motion, Newton’s second law of motion, Newton’s third law of motion, Conservation of momentum, Equilibrium of a particle, Common forces in mechanics, friction, Circular motion, Solving problems in mechanics.
Chapter 6 Work, Energy and Power
Introduction, Notions of work and kinetic energy: The work-energy theorem, Work, Kinetic energy, Work done by a variable force, The work-energy theorem for a variable force, The concept of potential energy, The conservation of mechanical energy, The potential energy of a spring, Various forms of energy: the law of conservation of energy, Power, Collisions.
Chapter 7 System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Introduction, Centre of mass, Centre of Gravity, The motion of centre of mass, Linear momentum of a system of particles, Vector product of two vectors, Angular velocity and its relation with linear velocity, Kinematics of rotational motion about a fixed axis, Torque and angular momentum, Equilibrium of a rigid body, Moment of inertia, Theorems of perpendicular and parallel axes, Dynamics of rotational motion about a fixed axis, Angular momentum in case of rotations about a fixed axis, Rolling motion.
Chapter 8 Oscillations
Introduction, Periodic and oscillatory motions, Simple harmonic motion, Simple harmonic motion and uniform circular motion, Velocity and acceleration in simple harmonic motion, Force law for Simple Harmonic Motion, Energy in simple harmonic motion, Some systems executing Simple Harmonic Motion, Damped simple harmonic motion, Forced oscillations and resonance.
Chapter 9 Gravitation
Introduction, Kepler’s laws, The universal law of gravitation, The gravitational constant, Acceleration due to the gravity of the earth, Acceleration due to gravity below and above the surface of the earth, Gravitational potential energy, Escape speed, Earth satellite, The energy of an orbiting satellite, Geostationary and polar satellites, Weightlessness.
Chapter 10 Mechanical Properties of Solids
Introduction, Elastic behaviour of solids, Stress and strain, Hooke’s law, Stress-strain curve, Elastic moduli, Applications of elastic behaviour of materials.
Chapter 11 Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Introduction, Pressure, Streamline flow, Bernoulli’s principle, Viscosity, Reynolds number, Surface tension.
Chapter 12 Thermal Properties of Matter
Introduction, Temperature and heat, Measurement of temperature, Ideal-gas equation and absolute temperature, Thermal expansion, Specific heat capacity, Calorimetry, Change of state, Heat transfer, Newton’s law of cooling.
Chapter 13 Thermodynamics
Introduction, Thermal equilibrium, Zeroth law of thermodynamics, Heat, internal energy, and work, The first law of thermodynamics, Specific heat capacity, Thermodynamic state variables and equation of State, Thermodynamic processes, Heat engines, Refrigerators and heat pumps, The second law of thermodynamics, Reversible and irreversible processes, Carnot engine, Carnot’s theorem.
Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory
Introduction, Molecular nature of matter, Behaviour of gases, Kinetic theory of an ideal gas, Law of equipartition of energy, Specific heat capacity, Mean free path.
We hope that this Telangana & Andhra Pradesh BIEAP TS AP Intermediate Inter 1st Year Physics Study Material Textbook Solutions Guide PDF Free Download 2022-2023 in English Medium and Telugu Medium helps the student to come out successful with flying colors in this examination. This Jr Inter 1st Year Physics Study Material will help students to gain the right knowledge to tackle any type of questions that can be asked during the exams.




 ద్వారా నిర్వచితమనుకోండి. అప్పుడు \(\stackrel{L t}{x \rightarrow 3}\) f(x) = 5 అని చూపండి.
ద్వారా నిర్వచితమనుకోండి. అప్పుడు \(\stackrel{L t}{x \rightarrow 3}\) f(x) = 5 అని చూపండి.
 , అయితే \(\underset{\mathbf{x} \rightarrow 1+}{\text { Lt }}\) f(x) \(\underset{\mathbf{x} \rightarrow 1-}{\text { Lt }}\) f(x) లను కనుక్కోండి.
, అయితే \(\underset{\mathbf{x} \rightarrow 1+}{\text { Lt }}\) f(x) \(\underset{\mathbf{x} \rightarrow 1-}{\text { Lt }}\) f(x) లను కనుక్కోండి.




























 ద్వారా నిర్వచితమైన ప్రమేయం f, R పై అవిచ్ఛిన్నమా ? [May ‘ 11]
ద్వారా నిర్వచితమైన ప్రమేయం f, R పై అవిచ్ఛిన్నమా ? [May ‘ 11]
 ద్వారా నిర్వచితమైన ప్రమేయం f, 0 పై అవిచ్ఛిన్నామా ? [May ’12]
ద్వారా నిర్వచితమైన ప్రమేయం f, 0 పై అవిచ్ఛిన్నామా ? [May ’12]




 తో నిర్వచితమైతే f అవిచ్ఛిన్నతను చర్చించండి.
తో నిర్వచితమైతే f అవిచ్ఛిన్నతను చర్చించండి.

































































