SCERT AP Board 6th Class Social Solutions 7th Lesson Emergence of Kingdoms and Republics Textbook Questions and Answers.
AP State Syllabus 6th Class Social Studies Solutions 7th Lesson Emergence of Kingdoms and Republics
6th Class Social Studies 7th Lesson Emergence of Kingdoms and Republics Textbook Questions and Answers
Improve Your Learning
Question 1.
What do you mean by Gana? How were they different from the kingdoms ruled by the kings?
Answer:
The term ‘gana’ means people of equal status. Sangha means ‘assembly’. Gana Sangha means an assembly of equal-status people. They cover a small area that was ruled by a superior group among them. These gana sanghas practiced “all are equal” traditions.
A kingdom means a territory and was ruled by a king or queen. In a kingdom, a family which rules for a long, period becomes a dynasty.
Question 2.
Why did the Rajas of Mahajanapadas build forts?
Answer:
- The rajas of Mahajanapadas built forts to protect their capital city.
- Huge walls of wood, brick or stone were built around the cities.
- Forts were probably built because people were afraid of attacks from other kings and needed protection.
- Some rulers wanted to show their wealth and strength by building large, tall, and impressive walls around their cities.
- The land and the people living inside the forts could be controlled more easily by the king.

Question 3.
Can you point out the difference between the way villages are managed today and in the time of Mahajanapadas?
Answer:
Nowadays, regular elections are taking place in villages which promotes democracy in our country. But in earlier times there was a ruler who controlled the village which did not help the democracy, but it helped in the monarch system which went for a long time in our country.
Question 4.
Find out how the craftspersons are; taxed by the government today? Was it the same in the times of Mahajanapadas?
Answer:
Craft persons have to pay taxes at the time of Mahajanapadas. Sometimes they have to work free of charge for the king for one day of every month.
But today if a craft person earns money more than the specified amount by the government they have to pay the tax for the excess amount they earned. There is no chance to work instead of paying tax.
Question 5.
Through what sources do you know about Mahajanapadas?
Answer:
We can know much about those villages and towns from two kinds of sources from archaeological excavations in different places and from the books composed during that period:
Question 6.
Write the agricultural practices that led to an increase in agricultural production in the time of Mahajanapadas.
Answer:
Two major changes were practiced during the Mahajanapadas period.
- Iron ploughshares were used. Heavy, clayey soil could be turned over better than with a wooden ploughshare, so that more grain could be produced.
- People of Mahajanapadas began transplanting paddy. Instead of scattering seeds on the ground, from which plants would sprout, saplings were grown and then planted in the fields. Production developed due to this since many plants survived.

Question 7.
“ The Mahajanapadas developed on the river banks.” Do you agree or not? Justify your answer.
Answer:
All the Mahajanapadas developed on the river banks. I agree with this statement. Archeologists found hundreds of sites in the Ganges valley. As this plain receives very high rainfall, it is very fertile. These rivers bring silt from the Himalayas and flow throughout the year. Transportation is also easy from these places. So Mahajanapadas developed on the river banks. If we observe all the Mahajanapadas, all the janapadas emerged around the river banks of Ganga, Yamuna, Narmada and Godavari.
Question 8.
How do you appreciate the works of craftsmen in the times of Mahajanapadas?
Answer:
During the period of Mahajanapadas, craftsmen played a key role in the development of Mahajanapadas. Availability of iron facilitated craft production also. Blacksmiths made necessary tools for agriculture like ploughshares, sickles, axes, arrows etc., With the use of iron ploughshare productivity improved. Potters made pots for cooking and storing grains. Carpenters made carts and with the help of these carts transportation was made easy. Weavers weaved cloth which was exported to other places and it helped the economy of Mahajanapadas. Potters made special type of pottery known as painted grey ware, which became famous in those days.
In this way craftsmen participated in the development of Mahajanapadas.
Question 9.
What were the taxes collected by the rulers of the Mahajanapadas?
Answer:
The taxes collected by the Mahajanapadas were :
- 1/6th of the total agricultural produce as a tax on crops.
- Craftsmen had to pay taxes in the form of labor.
- Taxes on the sale and purchase of goods and services for trade.
- Taxes on herders in the form of animals or animal products and taxes on hunters and gatherers in the nature of their collection from forests.

Question 10.
How are present-day elections different from the way in which rulers were chosen in Janapadas?
Answer:
Choosing of rulers in ‘janapadas’ – Men were chosen ‘rajas’ by performing big sacrifices. The ‘Ashwamedha was one such ritual that was used to identify a ‘raja’. The ‘raja’ chosen by this sacrifice was considered very powerful.
Electing rulers today – Today, we have a democratic system of government. Each citizen has a right to cast his vote and to form the government through his elected representative.
Question 11.
What is similar in the way crops were grown in the Mahajanapadas and how they are grown today?
Answer:
The crops that were grown in the Mahajanapadas were wheat, barley, peas, and lentils. These crops are grown in the same way as those were grown in the ancient days.
In the time of Mahajanapads, they planted paddy saplings instead of grains.
Even today the same system was followed by the farmers.
Question 12.
How can you appreciate the role of natural resources in the emergence of Magadha as a powerful kingdom?
Answer:
The rivers made the land very fertile and the Grihapatis could irrigate their lands easily. The rivers were also used for transporting goods and armies. Parts of the Magadha were forested. Elephants were captured from there and trained for fighting in the armies. Wood from the forests was used for building fortresses and palaces and chariots. In the southern parts of Magadha, there were iron ore deposits that could be used for making weapons, etc.
All this enabled Magadha to emerge as a very powerful kingdom. The kingdom extended from the northwest part of India to Odisha.
Thus Magadha used the natural wealth of the region to build a powerful kingdom.
Question 13.
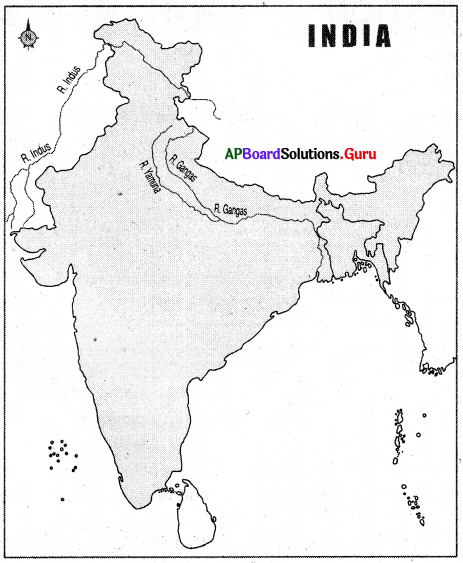
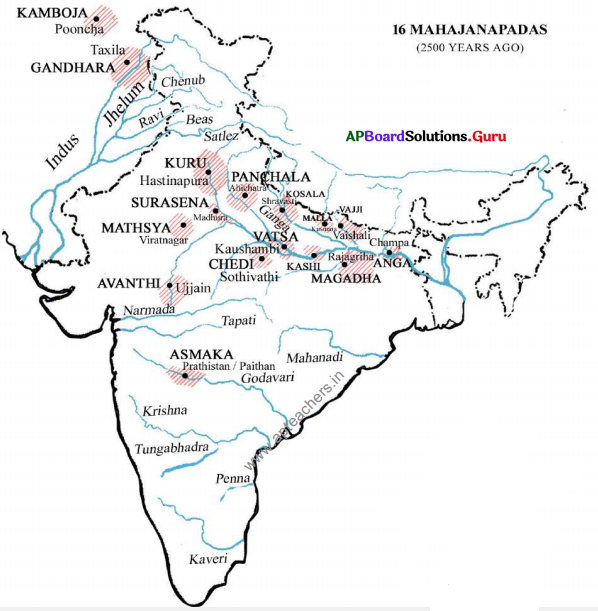
Locate the 16 Mahajanapadas and their capitals in the following India outline map.
Answer:

Question 14.
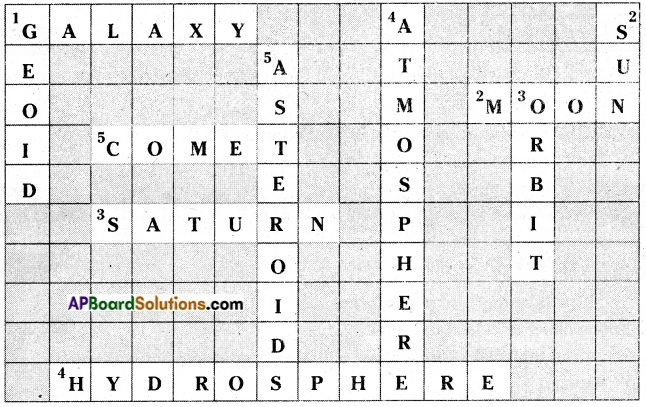
Solve the puzzle with new terms you have learned in this lesson. Take the support of your teacher.

Down ↓
- The mahajanapada located on the extreme eastern side
- This is the capital city of Avanti
- Farmers used this metal to make plough shares.
- The Mahajanapada located on the banks of river Godavari
- The slaves employed at Gahapatis
- Kusinara is the capital of this kingdom
- The capital city of Surasena Cross
Cross →
- The powerful kingdom of Mahajanapadas
- another name for Varanasi
- Kaushambi is the capital of this Mahajanapada
- Mahabharata tells us about the battle among the kings of this mahajanapada
- 1 /6th of farm produce collected as tax from farmers
- These condemned caste systems and the use of yagnas
- Vajji has this type of government.
Answer:


Project Work
Collect the information about 16 Mahajanapadas, and the state, in which they were located. Prepare a table as given below. Refer to India Political map given.
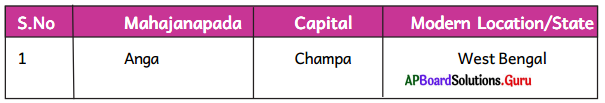
Answer:
| S.No. |
Mahajanapada |
Capital |
Modern Location / State |
| 1. |
Anga |
Champa |
West Bengal |
| 2. |
Magadha |
Girivraja/Rajagriha |
Gaya & Patna / Bihar |
| 3. |
Kasi |
Banaras/Varanasi |
Uttar Pradesh |
| 4. |
Vatsa |
Kausambi |
Around Allahabad / UP |
| 5. |
Kosala |
Shravasti |
Modern Avadh region / Eastern UP |
| 6. |
Surasena |
Mathura |
Western UP region |
| 7. |
Kuru |
Indraprasta |
Meerut & Southeastern Haryana |
| 8. |
Matsya |
Viratnagar |
Around Jaipur |
| 9. |
Chedi |
Sothirati |
Bundelkhand region |
| 10. |
Avanti |
Ujjaini/Mahismati |
Around Malwa MP |
| 11. |
Gandhara |
Taxila |
Rawalpindi/Pakistan |
| 12. |
Kamboja |
Pooncha |
Kashmir & Hindukush |
| 13. |
Asmaka |
Pratisthan / Pothan |
Telangana & Maharashtra |
| 14. |
Vajji |
Vaishali |
Bihar |
| 15. |
Malla |
Kusihara |
Deoria & UP |
| 16. |
Panchala |
Ahichatra/Kampliya |
Western UP |
6th Class Social Studies 7th Lesson Emergence of Kingdoms and Republics InText Questions and Answers
Let’s Do
(Textbook Page No. 75)
Question 1.
Look at the physical map of India and identify the plains through which the rivers Ganga and Yamuna flow
Answer:

Question 2.
Identify the modern cities of India like Delhi, Allahabad, Varanasi, Lucknow and Patna.
Answer:
Question 3.
Do you think this area will be similar to your villages? Give your reasons.
Answer:
I don’t think that our villages are similar to that of Delhi, Allahabad, Varanasi, Lucknow, and Patna. They are well developed from the time of Mahajanapadas itself. Because of high fertility lands and transportation facilities these areas developed from that time. Now they became big cities and Delhi being our national capital. So, we can’t compare our villages to the cities mentioned above.
(Textbook Page No. 77)
Question 4.
The important Janapadas of those times are shown on the map.
Look at the map and fill in the blanks.
1. The …………. Janapada was settled on both the banks of the Yamuna.
2. The Panchala was settled on both the banks of the river …………..
3. The ………….. Janapada was situated on the western side of the Surasena.
4. The ………….. Janapada was on the extreme north.
5. The ………….. Janapada was situated on the banks of the river Godavari.
6. The Gandhara was situated on the banks of the river …………..
Answer:
1) Kuru
2) Ganga
3) Matsya
4) Kambhoja
5) Asmaka
6) Kubha

Think and Respond
(Textbook Page No. 75)
Question 1.
Find out the names of a few Janas (tribes) who initially settled down in the Indo – Gangetic plain,
Answer:
- Magadha dynasty
- Imperial Kanauj
- Mughal Empire
- Maratha Empire are some of the janapadas who initially settled down in the Indo – Gangetic plains.
Question 2.
What do you mean by Janapada? How is it different from Mahajanapadas?
Answer:
People of different tribes settled down to practice agriculture in many parts of the valley. These tribes were called Jana and the place they settled was called Janapada. Many groups of such villages and towns are called Mahajanapadas.
Question 3.
How is paddy grown today? (Textbook Page No. 78)
Answer:
- Land is to be prepared and levelled.
- Planting on time to be done.
- Fertilization to be done.
- Field is to be watered.
- Pests is to be controlled.
- Harvest on time.
- Storing safely.
- Milling efficiently.

Question 4.
Describe the relationship between Grihapatis and Craftsmen of the village. (Textbook Page No. 79)
Answer:
In most villages, there Were craft persons like blacksmiths who made tools necessary for agriculture (like ploughshares, sickles, axes, arrows, etc), potters who made pots for cooking and storing grains, carpenters who made carts, ploughs, furniture etc., and weavers who wove cloth for the villagers.
Probably the Grihapatis gave them grains in return for their products. These craft products were necessary for agriculture, but the Grihapatis may not have had the time or skill to make them.
(Textbook Page No. 80)
Question 5.
The people of the towns would haMe needed grain, milk, meat etc. How do you think they got them if most townspeople were not doing any farming?
Answer:
Even though the townspeople were riot doing, any farming they get milk and meat by purchasing them from nearby villages and shops situated in the town.
Question 6.
Have you ever seen a fort on TV or have you ever been there? Why were there big walls around the fort?
Answer:
I have seen Red fort. I had been to Delhi and I have seen the Red Fort there. There are big walls around the fort. To protect the enemy kings by not entering them into the fort big walls were constructed around the fort.

Question 7.
What were they made of? How do you think the kings managed to get the wealth needed for all this?
Answer:
The Red fort got its name from the stone used to construct it. The entire fort is made up of red sandstone. Maybe it was constructed with the tax amount collected and conquering other kingdoms.
Question 8.
Why did the king of Mahajanapadas need armies?
Answer:
The kings of Mahajanapadas were afraid of attacks from other kings and enemies. They needed protection. So the king of Mahajanapada needed armies.
(Textbook Page No. 81)
Question 9.
In which form the hunter-gatherers paid taxes to their kings?
Answer:
Hunters and gatherers paid taxes to the Raja from what they got from the forest like hides, woods, and honey etc.
Question 10.
- If everyone was forced to give away a part of their earnings as tax, how did it affect their lives?
Answer:
If everyone was forced to give away a part of their earnings, they will lose the earning for that part which was given as tax.
- Why do you think they agreed to pay the taxes? Do you think they benefited in any way from the new arrangements?
Answer:
They will get encouragement, and support from the king – besides protection.
- What is bhaga? Does the government of our times take the produce of farmers in , a similar way?
Answer:
The Grihapatis had to divide their crops into six parts and one part of them is to be given to king as tax. This was called bhaga.
The government of our times does not collect produce from the farmers. The government collects tax from the farmers as per the quantity sold.

(Textbook Page No. 82)
Question 11.
- Why were the kings of Mahajanapadas keen to increase craft production and trade?
Answer:
The kings of Mahajanapadas were k^en to increase craft production and trade because they would get more taxes. The wealth of the kingdom will increase.
- How did the headmen of the villages benefit from the imposition of taxes by the kings?
Answer:
The kings of Mahajanapadas wanted the village headmen to collect the taxes on their behalf. This might have helped the headmen to increase their power in the villages.
(Textbook Page No. 83)
Question 12.
Write a couple of lines on each of the natural resources of Magadha and how it could have been used by the kings.
Answer:
- Magadha kingdom was spread on both sides of the river Ganga. The river made the land fertile and the Grihapatis could irrigate the land easily and produce was high.
- The river was also used for transporting goods and armies.
- Elephants were captured from the forests that spread over in the kingdom and trained for fighting in the wars.
- In southern parts of Magadha, there were iron ore deposits that were used for making weapons etc.
Question 13.
Compare the gana form of government in Vajji with the present-day republic. Who was not allowed to participate in the assembly of Vajji Mahajanapada?
Answer:
Vajji had gana form of government which was nearly equal to the present-day form of government. Gana was ruled by a group of leaders instead of a single ruler. In the present republic type of government, we will elect local loaders and they will discuss our problems in the assemblies through discussion and debate.
Women, slaves and wage earners are not allowed to participate in the assembly of vajji mahajanapadas.

Explore
Question 1.
A famous religious epic tells us about many of these Janapadas. Find out about it. (Textbook Page No. 77)
Answer:
The Mahabharat.
Do you know
Question 1.
Make a list of the Mahajanapadas and the cities which were situated in the Ganges valley. (Textbook Page No. 76)
Answer:
- Kasi – Banaras
- Kosala – Shravasti
- Anga – Champa
- Magadha – Girivraja or Rajagriha
- Vajji or Vriji – Vaishali
- Malya – Kushinagar
- Vatsa – Kausambi
- Kuru – Indraprasta/Hastinapur
- Pachala – Ahichhtra
- Surasena – Mathura

![]()

![]()
![]()